Eastern Gorilla
Gorilla berengei
The largest primate in the world!
Advertisement
Eastern Gorilla Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Primates
- Family
- Hominidae
- Genus
- Gorilla
- Scientific Name
- Gorilla berengei
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Eastern Gorilla Conservation Status
Eastern Gorilla Facts
- Main Prey
- Leaves, Seeds, Herbs
- Habitat
- Tropical forest and jungles in mountainous regions
- Predators
- Human, Leopard
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 1
View all of the Eastern Gorilla images!
“The Eastern Gorilla is known as the largest living primate”
The Eastern gorilla is one of two species of gorilla and is the largest primate on earth. It is often observed that the eastern gorilla, which is most commonly found in jungles on mountain tops, is well equipped to survive in the wild. Instead of searching for new habitats in a changing and hotter climate, the mountain gorilla, a subspecies of eastern gorilla, has become more resilient and has evolved to tolerate high climate variability and has learned to live with less water.
The eastern gorilla is much closer to humans than first thought – sharing over 98% of their DNA with us, and can perform tasks like peeling fruits by hand and cradling their babies – much like humans. Even though gorillas are portrayed to be angry and vicious in literature and movies, they actually just want to hang out in peace with their families, eat good food, and watch their children play – much like us.

Incredible Eastern Gorilla Facts!
- Male eastern gorillas that are above 12 years of age experience a change of fur color on their backs – changing from black to grey, thus giving them the name “silverbacks.”
- Much like humans, the eastern gorillas have five fingers on each hand and five toes on each foot.
- Their nose prints can be used to identify each eastern gorilla, much like the fingerprints of humans. Each gorilla’s noseprint is unique and no two of them can ever be the same.
- Eastern gorillas have 32 teeth and relatively small ears.
- Eastern gorillas are very intelligent and use about 25 different vocalizations to communicate with each other.
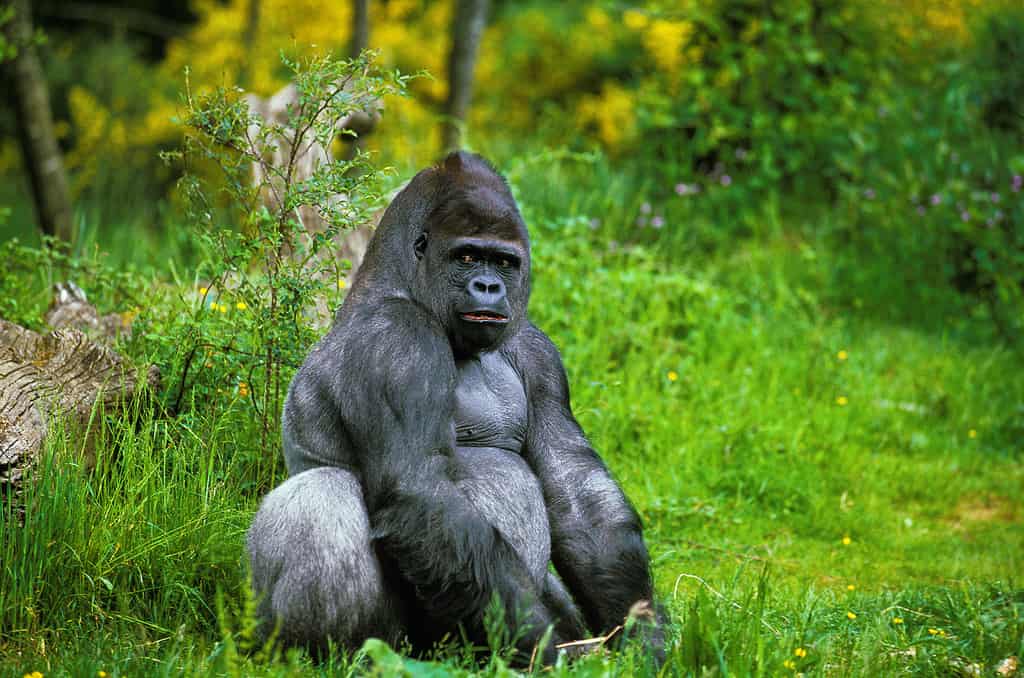

Each gorilla’s noseprint is unique – just as human fingerprints are unique to the individual.
©slowmotiongli/Shutterstock.com
Scientific Name
Eastern gorillas are great apes and carry the scientific name, Gorilla beringei. The word “gorilla” was coined by Hanno the Navigator, a Carthaginian explorer of the fifth century BC, known for his exploration of the west coast of Africa. He called the hairy, savage people he met, “gorillae,” and it is believed that he may have actually encountered gorillas. Even though it is unclear whether the expedition members encountered gorillas, Hanno’s term seemed like a good name for the animal when they were discovered by colonialists later.
The male members of the eastern gorilla families – are known as “silverbacks,” because the hair on the backs of males over 12 changes from dark to silver.
Species
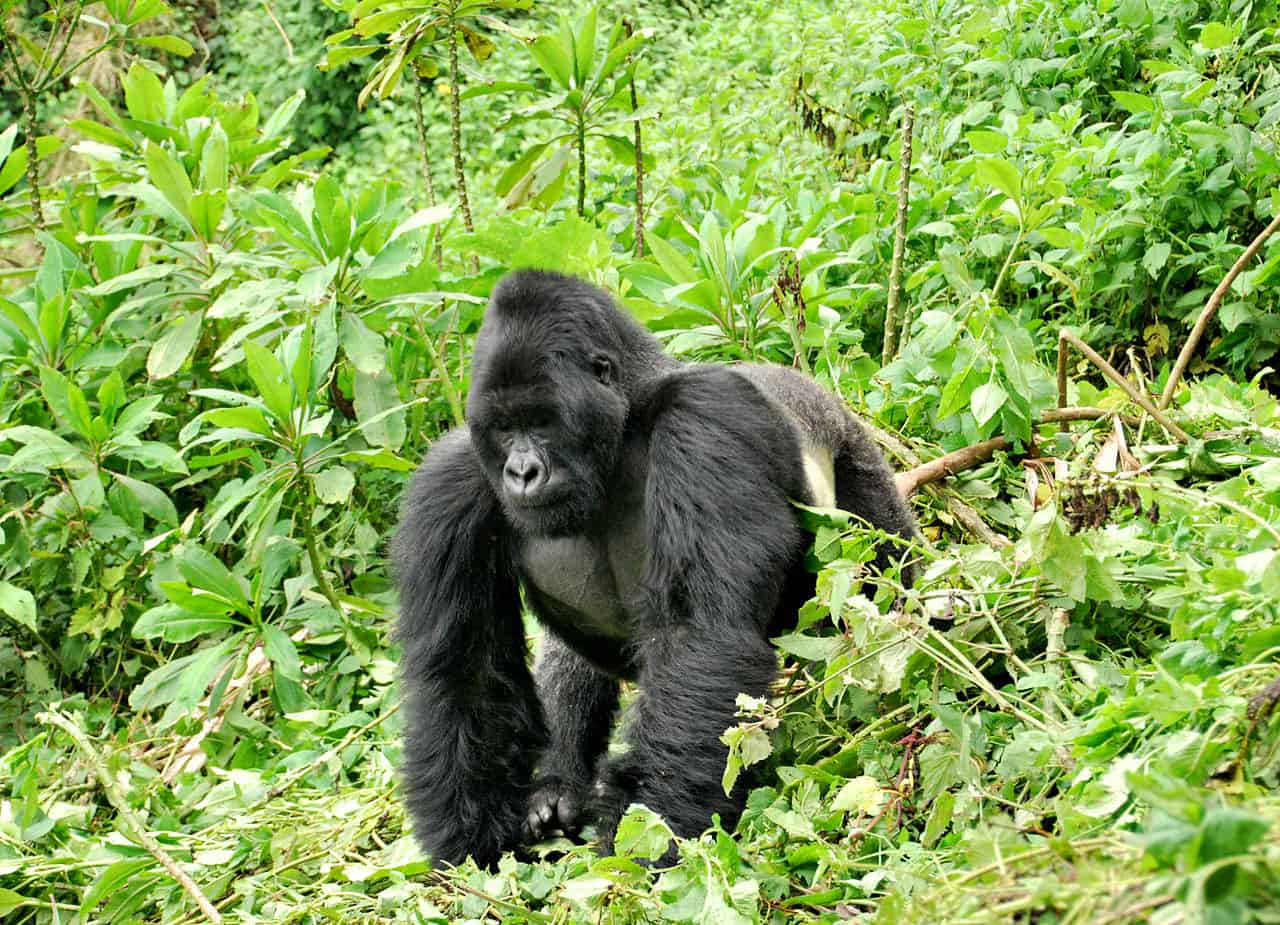

Eastern gorillas are darker in color and larger than Western gorillas.
©Carine06 from UK / CC BY-SA 2.0 – License
Gorilla is the genus that is commonly used to refer to two species of great apes that are divided further into four total subspecies. They are similar in appearance, with the Eastern gorillas being larger and darker in color than their Western counterparts.
Eastern Gorilla (Gorilla beringei)
- Eastern Lowland Gorilla (Gorilla beringei graueri)
- Mountain Gorilla (Gorilla beringei beringei)
Western Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla)
- Western Lowland Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla gorilla)
- Cross River Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla diehli)
Evolution
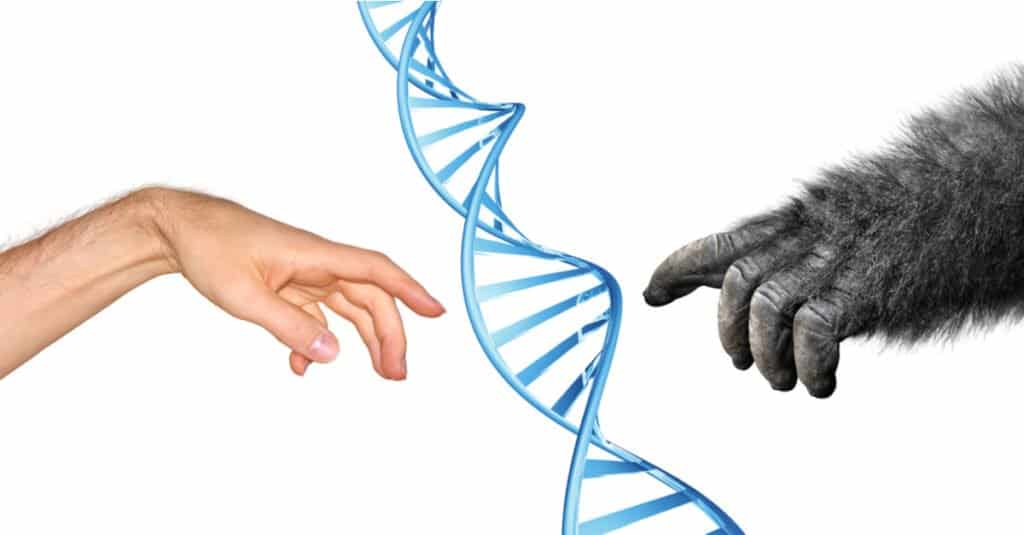

Human gene sequences differ from gorilla sequences by only 1.6%.
©David Carillet/Shutterstock.com
Although not much is known about the evolution of gorillas, they are closely related to humans and chimpanzees. They all diverged from a common ancestor about 7 million years ago. Human gene sequences differ from gorilla sequences by only 1.6% on average.
Gorillas were previously thought to be a single species with three subspecies (western lowland, eastern lowland, and mountain gorillas), but it is now agreed that there are two main species, the western gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) and the eastern gorilla (Gorilla beringei), and they each have two subspecies. Western and eastern gorillas split into two groups around 77,700 years ago.
Appearance and Behavior
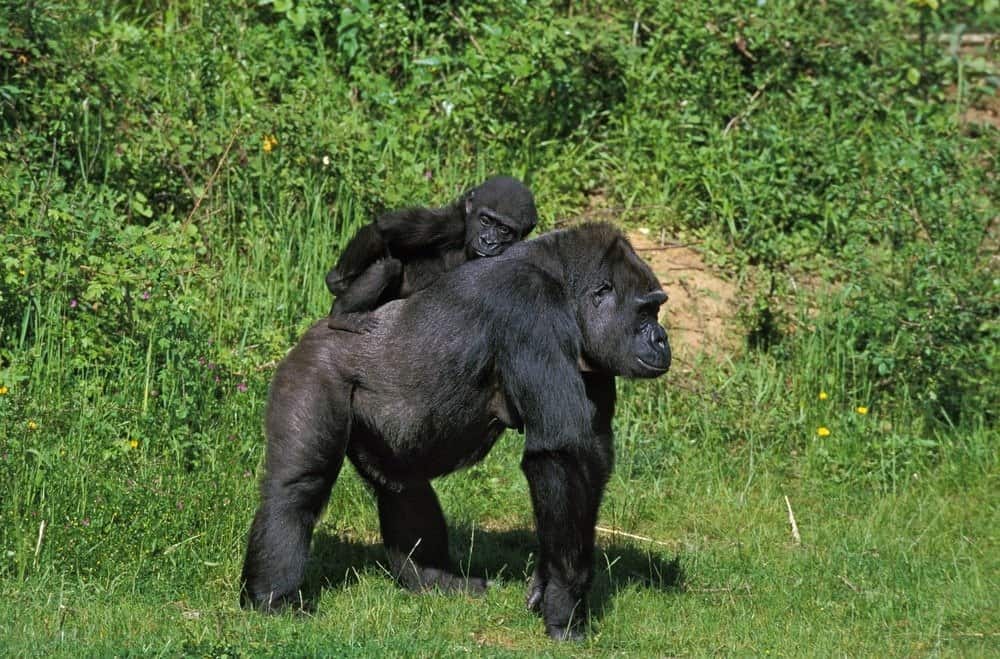

Eastern Gorillas are the largest primates in the world.
©slowmotiongli/Shutterstock.com
Eastern gorillas have strong, powerful bodies that are covered with blackish hair everywhere except the face, hands, and feet. They have long, strong, arms and broad, mostly hairless chests. Male gorillas’ back hair changes from dark to silver after age 12, earning them the status of “silverback.” Alpha silverbacks are the leaders of their family group and mate with the females and protect their territory.
The male eastern gorillas are, on average, about 1.7 meters in height (which is about the same height as the average person). However, they can also go up to 1.9 meters in some cases. Meanwhile, the female Eastern gorillas are usually only 1.5 meters tall.
Weight-wise, the male eastern gorillas usually swing between 300-440 lbs., while the females are usually about 195-220 lbs.
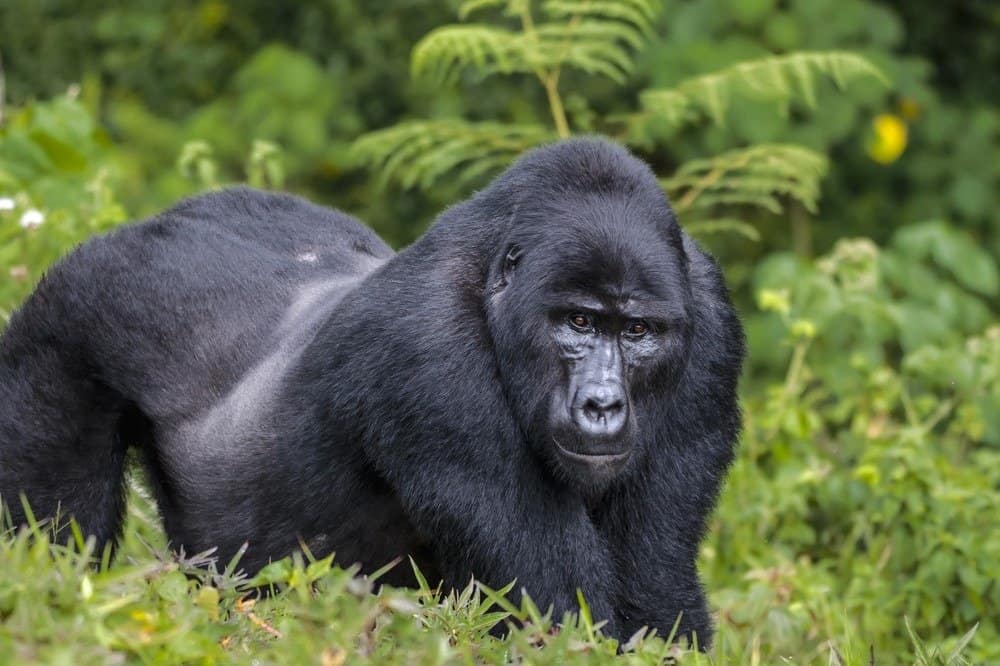

Silverback males lead the gorilla family groups.
©Krasnova Ekaterina/Shutterstock.com
Eastern gorillas live in groups led by a silverback male, together with females and their offspring. Groups are often interconnected, comprising 35 to 50 members each.
These gorillas are known to spend about 40% of their day relaxing and the other 30% doing food-related activities. The remaining day is usually spent roaming around. They are known to rest and sleep in nests that are built on trees or sometimes on the ground.
Most eastern gorillas are peaceful. However, some males are aggressive to assert their dominance.
Habitat
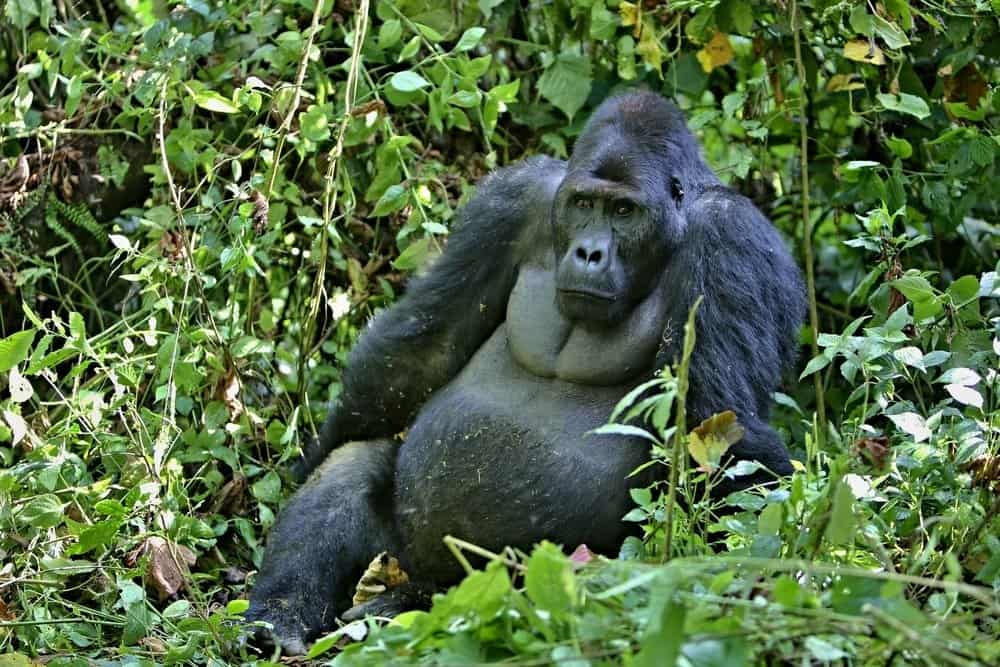

Eastern Gorillas reside in tropical forests in Africa.
©PhotocechCZ/Shutterstock.com
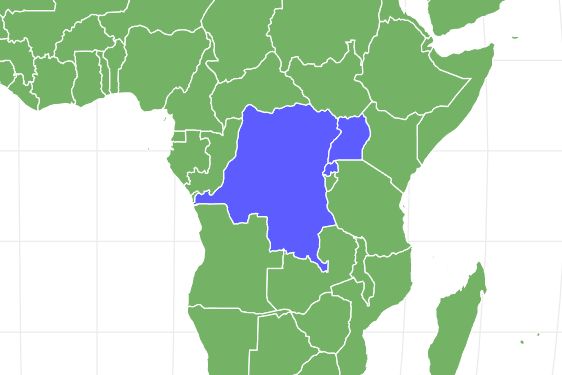
The Eastern gorillas can be found in a variety of regions. Where they are found depends upon the subspecies. The two subspecies are found in different areas – ranging from Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The eastern lowland gorilla or the Grauer’s gorilla is often found in the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Meanwhile, the eastern mountain gorilla is further divided into groups that are distributed across regions.
Some of them live in Virunga mountains at about 1500 to 400 meters altitude above sea level while the others can often be located in Bwindi national park in Uganda, where they usually live in steep mountains – between altitudes of 1100 to 2400 meters. Some other places that the eastern lowland gorillas reside in include the areas between the Tanganyika and Edward lakes and the Lualaba River.
Since much of the Eastern Gorillas’ life involves running or climbing, their impressive muscles give them strength along their upper body and down their arms. With fingers and thumbs like humans, they can easily collect food from high and low places.
Diet

Eastern gorillas are primarily herbivores, sourcing their nutrients from the vegetation in their natural habitat. However, the diet can vary from where they are located and how much altitude they live.
The gorillas that are mostly found in the Bwindi area usually eat fruits. Otherwise, in other locations, the eastern gorillas can also feed on flowers, tree bark, and in some cases, even small invertebrates. Their diet also includes wild berries, fungi, and wood.
Predators & Threats
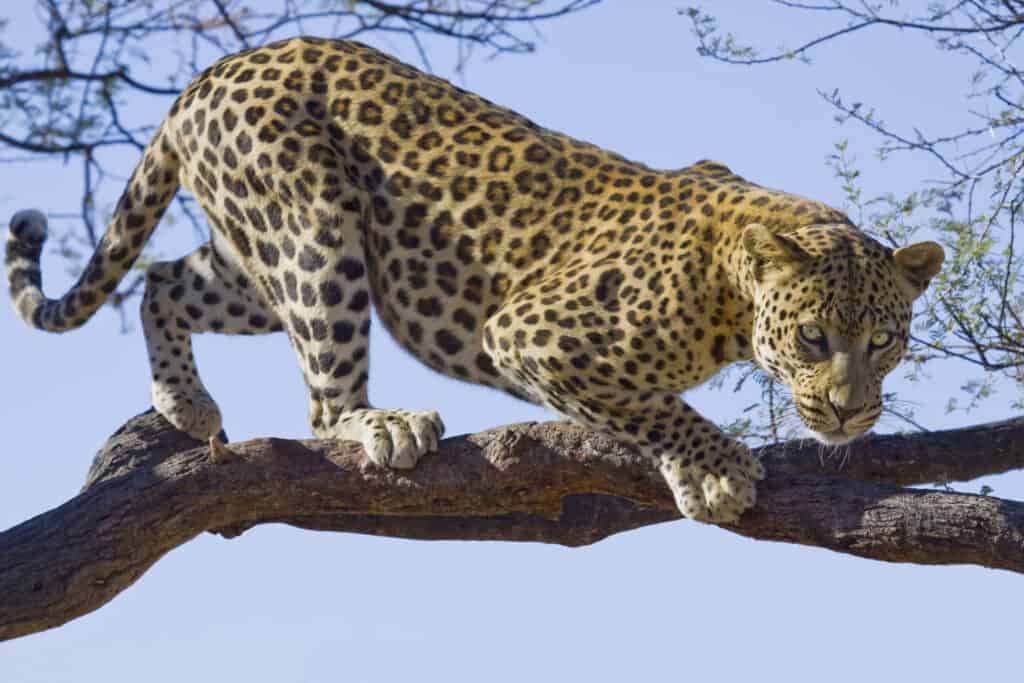

Wild African leopard looking down from a branch of a tree
©iStock.com/lightstock
The main threats to the eastern gorillas are habitat degeneration, poaching, and violence in the areas that they reside in. It has been observed that many of these gorillas have died due to fires in their habitats. Leopards and the odd crocodiles are believed to be the major predators of the eastern gorillas. Meanwhile, the health threats to the eastern gorillas include microfilaria, Simian Immunodeficiency Virus, and Malaria.
The IUCN has declared the Eastern gorilla to be endangered and it is said that the population of these apes is consistently on a decline. The eastern mountain gorilla is at a higher risk of extinction. Sources suggest that as of now, only 300 mature eastern mountain gorillas are left. Meanwhile, the overall number of Eastern gorillas in the world is suspected to be less than 5,000.
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
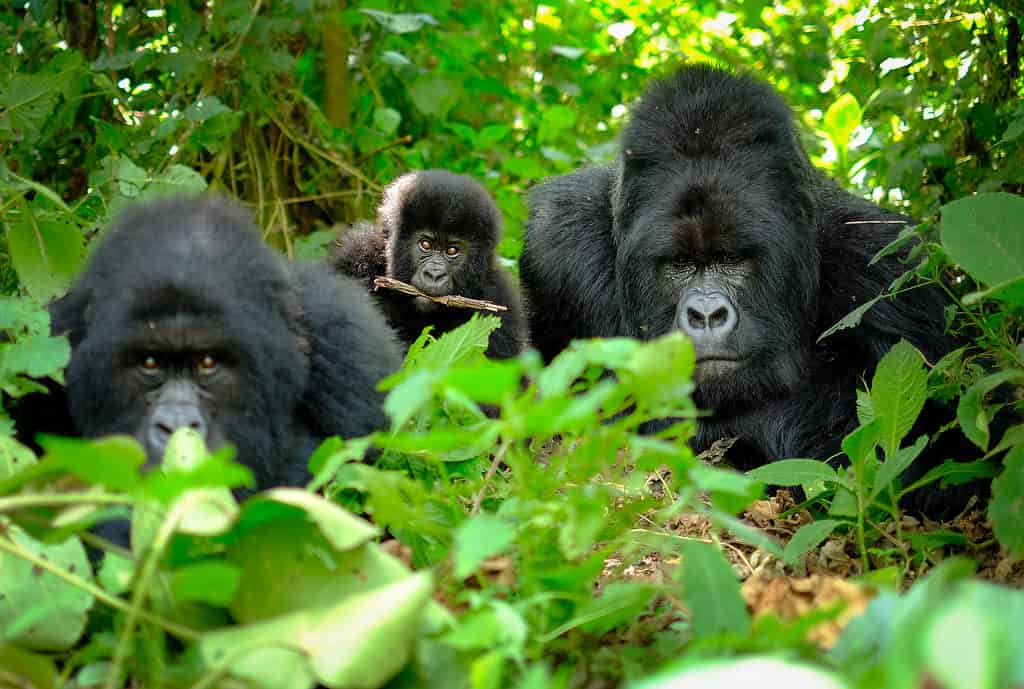

Gorillas live and raise babies in large family groups.
©Marian Galovic/Shutterstock.com
The Eastern gorillas have a polygynous reproduction system which means that the dominant male of each group mates with all the females in the clan. These gorillas are known to mate all year. Once conceived, the gestation period in the eastern gorillas typically lasts about 8.5 months, after which the female gives birth to a single baby. Females give birth only once every three to four years because of the long gestational periods as well as the parental process.
Immediately after birth, the baby is dependent on the parents – especially the mother who carries it around until it is ready to crawl by the time it is about nine weeks old. Their dependency lasts for the first four years, during which time the mother will nurse them as their primary source of food. Even when the baby no longer requires its mother’s milk, it will learn and play each day until it can take care of itself.
Breeding may begin as early as 15 years old, though the lifespan of an eastern gorilla is usually 35 to 40 years. In captivity, these primates may live up to 50 years of age.
Population
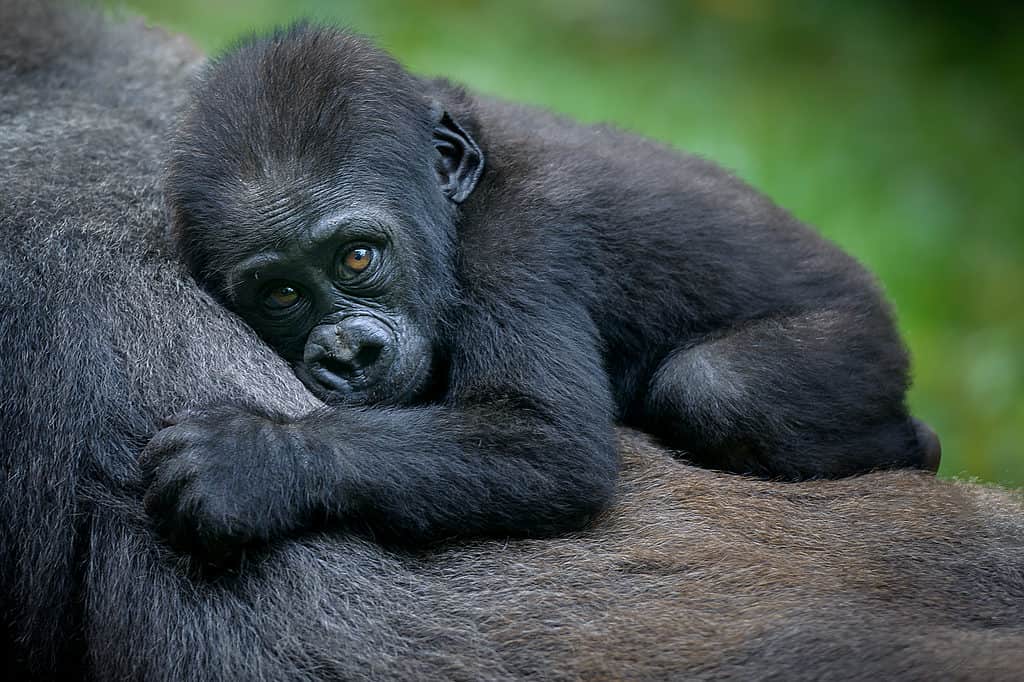

Eastern lowland gorillas have lost all but 13% of their habitat.
©Asaf Weizman/Shutterstock.com
Currently, eastern gorillas are endangered, and the eastern gorilla population has been consistently decreasing over the past few years. During the 1990s, the population of these gorillas was estimated to be about 17,000. However, a recent report showed that the population has now fallen to less than 5000 and close to 4,000 around the globe.
It has also been observed that the eastern lowland gorillas now reside in only 13 percent of areas where they used to be found formerly. However, the eastern mountain gorilla is at a higher risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts

Tourism is raising awareness of the plight of
©Wirestock Creators/Shutterstock.com
Several projects have been initiated to conserve this endangered creature. One such project is the Walikale Gorilla and Forest Conservation Project which began in 2001 after the eastern gorilla population started declining. They have been working on preserving the natural habitat for the gorillas to thrive in so that habitat degeneration does not become a common cause for their decrease.
Other projects have been encouraging to initiate better tourism for the mountain gorillas so that funds can be raised to protect them. However, the public must be cautious to not be around the animal while being sick since any risk to the already endangered species should and must be avoided.
In the Zoo
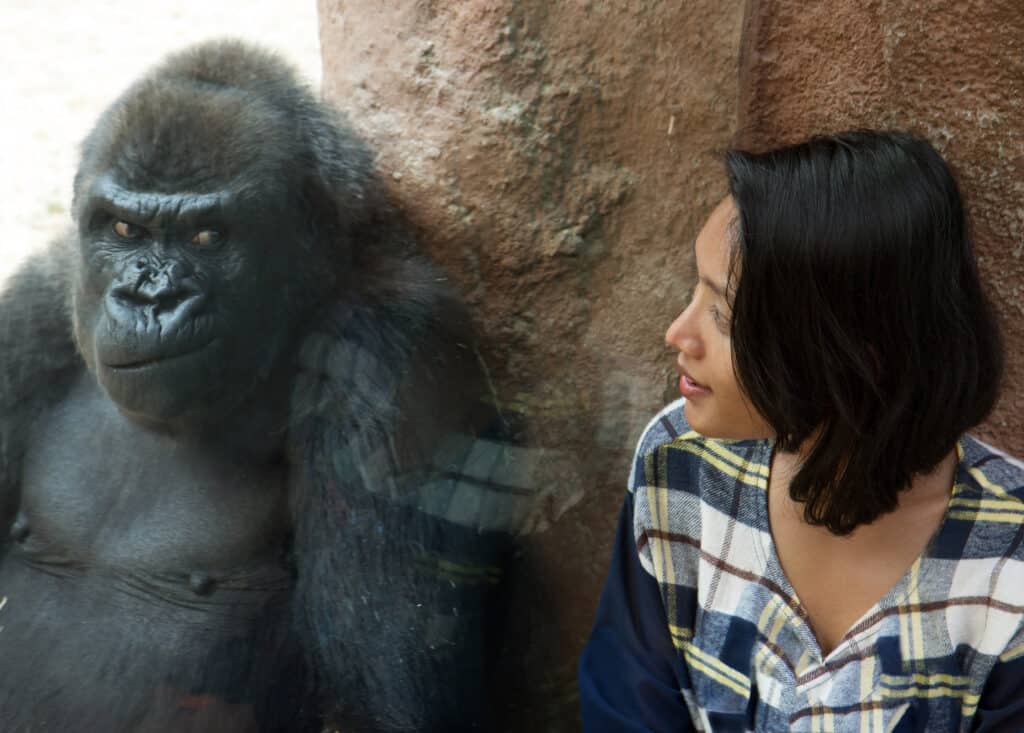

Most gorillas in zoos are male silverbacks.
©Milkovasa/Shutterstock.com
Reports suggest that the Antwerp Zoo in Belgium happens to be the only zoo that has a female eastern gorilla. However, the eastern mountain gorillas are not known to be kept in zoos within the United States at this time.
View all 117 animals that start with EEastern Gorilla FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are eastern gorilla carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
The eastern gorillas are usually herbivores in nature. Their diet usually includes fruits, bark, wood, flowers, and leaves. However, the diet also depends on where they are located and sometimes these gorillas also feed on tiny invertebrates.
Where does the eastern gorilla live?
The eastern gorillas can be found in a vast variety of places. They are found in different areas ranging from Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
What's the difference between an eastern gorilla and a western gorilla?
The Western gorilla is mostly found in areas ranging from Cameroon to the Republic of Congo while the eastern gorilla is found in Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The western gorillas are usually smaller and have a brownish-grey coat while the eastern gorillas have black fur and are much larger in shape and size.
How many eastern gorillas are left?
The conservation status of the eastern gorillas is endangered and there are only less than 5000 eastern gorillas left around the globe now as compared to the 10,000 in the 1990s.
How much does an eastern lowland gorilla weigh?
A typical male eastern gorilla weighs about 145-205 kg while a female eastern gorilla usually weighs about 90-100 kg.
What does the eastern gorilla eat?
The eastern gorilla usually eats fruits, flowers, leaves, barks, wood, and sometimes even tiny invertebrates.
Is the eastern gorilla endangered?
Yes. The IUCN classified the eastern gorilla as an endangered species in 2016, due to illegal poaching.
How fast is an Eastern Gorilla?
An Eastern Gorilla can travel at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals
- Animalia, Available here: http://animalia.bio/eastern-gorilla
- Gorillas-World, Available here: https://www.gorillas-world.com/eastern-gorilla/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eastern_gorilla
- World Wildlife Fund, Available here: https://wwf.panda.org/knowledge_hub/endangered_species/great_apes/gorillas/eastern_lowland_gorilla/