Horseshoe Crab
Horseshoe crabs are older than the dinosaurs and outlived them!
Advertisement
Horseshoe Crab Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Horseshoe Crab Conservation Status
Horseshoe Crab Facts
- Prey
- Worms, algae, small invertebrates, detritus
- Group Behavior
- Largely solitary
- Fun Fact
- Horseshoe crabs are older than the dinosaurs and outlived them!
- Estimated Population Size
- 2.3 to 4.5 million just on the Atlantic coast
- Biggest Threat
- Pollution, over-harvesting, habitat destruction
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Their horseshoe-shaped shell
- Other Name(s)
- helmet crab, horsefoot, saucepan, king crab
- Gestation Period
- Two weeks
- Habitat
- Shallow water off the coast, beaches
- Predators
- Shorebirds who eat the eggs, sea turtles, fish
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 90,000
- Type
- Arthropod
- Common Name
- Horseshoe Crab
- Number Of Species
- 4
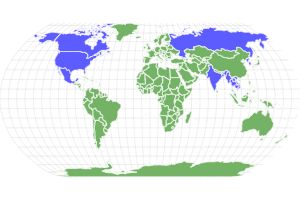
- Location
- Worldwide
- Slogan
- Changed little in over 500 million years!
View all of the Horseshoe Crab images!
Characterized by its big protective shell, the horseshoe crab is a great example of a living fossil.
One of the oldest animals on earth, horseshoe crabs have been roaming the seas for hundreds of millions of years. Indeed, they have had to adapt to continents forming and reforming and have survived Ice Ages and whatever it was that made the dinosaurs and so many other species go extinct. When humans arrived they discovered that horseshoe crabs could be used as food and as bait to catch other kinds of food, and now they are used for medical research.
Five Incredible Horseshoe Crab Facts!
Some fascinating facts about the horseshoe crab include:
- These animal are arthropods, which means it’s related to spiders.
- They’re not crabs. They’re not even crustaceans.
- They evolved about 255 million years ago, and some consider them living fossils.
- The blood of Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda contains tetrodotoxin, a deadly poison that attacks the nervous system.
- Speaking of blood, the blood of these animals is sapphire blue when exposed to oxygen.
Horseshoe Crab Classification and Scientific name
These animals belong to the Limulidae family as well as the suborder Xiphosurida and the order Xiphosura. There are four genera: Carcinoscorpius; Limulus; Mesolimulus, which is extinct, and Tachypleus. There are four living species in these genera. They are:
- Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda
- Limulus polyphemus
- Tachypleus gigas
- Tachypleus tridentatus
The name Lumulidae is modern Latin for “a little askance,” because it used to be thought the animal had only one eye. Xiphosurida is from the Greek words for sword, “xiphos” and the Greek word for tail, “oura.” Carcinoscorpius means “crab scorpion,” with Carcino coming from the Greek word “karkinos,” a crab, and “scorpius” from the Latin word “scorpius,” which borrowed from the Greek word “skorpios.” Rotundicauda means “round tail” These names were inspired by the look of the animal. The “meso” in mesolimulus is Greek for “middle.” Tachypleus comes from the Greek words “tachys,” which means “rapid” and “pleustikos,” which means “sailing” or “swimming.”
Horseshoe Crab Species
The four horseshoe crab are Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda, which is the mangrove horseshoe crab. This crab is found in southern Asia. Limulus polyphemus is the Atlantic horseshoe crab and it lives along the east coast of the United States and Mexico. Tachypleus gigas is the Indo-Pacific horseshoe crab, and it is also found in southern and southeastern Asia. Tachypleus tridentatus is the tri-spine horseshoe crab, and it lives in southeast Asia and East Asia.
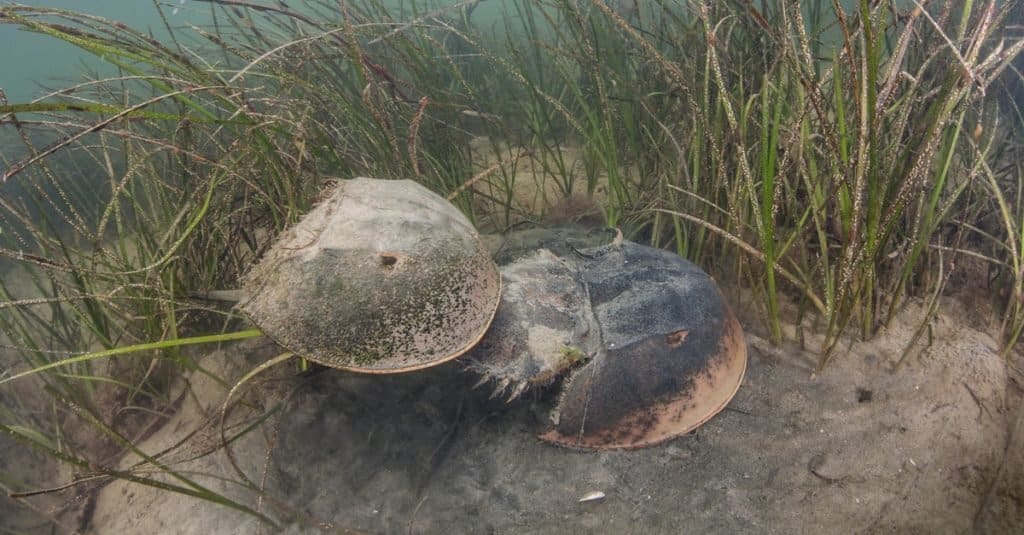
Horseshoe Crab Appearance
The animal’s appearance is unmistakable. The soft parts of its body are completely covered with a tough, horseshoe-shaped carapace. The body has three parts to it. The prosoma can be thought of as the head, then there’s a middle part called the opisthosoma and the tail, or telson. The tail, which is long and stiff, looks menacing, but it’s there to act as a rudder when the horseshoe crab swims and to help turn it upright if it’s turned over.
The females of all species are larger than the males. The male mangrove horseshoe crab is about 12 inches long, but the female of the tri-spine horseshoe crab can be 31.25 inches long and weigh as much as 9 pounds.
The animal has many eyes. It has eyes on and even under its head, and there are even eyes under its tail. This may be why they are sometimes found swimming upside down.
If the animal is flipped upside down, a person will be able to see its book gills, which it uses to breathe underwater. These gills get their name because they look like the pages of a book.
Though they lack teeth, they can still eat shellfish whose shells aren’t too thick. This is because they have a mouth that’s filled with bristles found in the middle of their five pairs of legs. They use their legs to move their food to their mouth, then chew it by walking.
Because their carapace is rigid, the animal needs to molt to grow. They molt frequently during their first year and can molt as many as 18 times before they are of reproductive age, which is about nine. Since females are bigger, they molt more times than males. When the male molts for the last time, he develops claspers that look like boxing gloves. This helps him hold on to the female during the spawning season.

©Ethan Daniels/Shutterstock.com
Horseshoe Crab Distribution, Population, and Habitat
All species like shallow water with muddy or sandy bottoms. There are at least millions of these animals in the oceans of the world, though in some places their numbers are declining. The mangrove and tri-spine horseshoe crabs can be found in salt or brackish water around southeast Asia and north into China and Hong Kong. The Atlantic horseshoe crab is found along North America’s Atlantic coastline and in the Gulf of Mexico. The Indo-Pacific horseshoe crab is found on the coasts of the South China Sea down to the Bay of Bengal.
Horseshoe Crab Predators and Prey
These animals eat small fish, bivalves, and other invertebrates. They also eat algae. Predators on young and adult horseshoe crabs include sea turtles, but the greatest contribution they make to the food cycle is their eggs. Horseshoe crabs come to the beach to lay eggs at the same time many shorebirds are migrating. Horseshoe crab eggs are their main source of protein. Fish such as eels, perches, and flounders also eat the eggs and the newly hatched animals. “Real” crabs also indulge in the bounty of eggs.
These animals also has its share of symbionts, since at one point it will no longer molt. Clams scuds, marine worms, algae, barnacles, oysters, starfish, and other creatures live on and in the horseshoe crab’s shell.
For a complete analysis of what horseshoe crabs eat, make sure to read ‘What Do Horseshoe Crabs Eat? The Main Foods in their Diet.‘
Horseshoe Crab Reproduction and Lifespan
These animals can live as long as 20 years, and some biologists believe the animal can live as long as 30 years. Its spawning is one of the most amazing spectacles in nature. They spawn in the spring at high tide during the new or full moon. Males get to the beach first and wait for the females. When a female arrives, a male attaches himself to the back of her shell with his claspers. There may be half a dozen males clinging or attempting to cling to her.
The female carries between 60,000 to 120,000 eggs that she lays about 4000 at a time during high tide. As she lays the eggs, the male fertilizes them. They hatch after about two weeks if the birds and other animals haven’t gorged on them. In places where farming of the horseshoe crab takes place, eggs can be artificially inseminated.
Horseshoe Crab in Fishing and Cooking
These animals do not have much meat on them, but the meat is considered a delicacy by some who are willing to pay a good price for it. In Thailand, they’re part of a dish called yam khai maeng da. People in Asia also eat the eggs. However, it is crucial to find an edible horseshoe crab, for eating one that has tetrodotoxin can be fatal. Horseshoe crabs are also used as bait for eels, conch, and whelks.
Horseshoe Crab Population
There are millions of Atlantic species, even as its status is near threatened. Half a million are used every year for research and at least a million are used for bait. But the tri-spine species is endangered, and there’s not enough data on the other two species.
View all 104 animals that start with HHorseshoe Crab FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Can you eat horseshoe crab?
The horseshoe crab is edible, but some people may consider it unappetizing or even toxic.
Where do horseshoe crabs live?
The horseshoe crabs live near the coasts of the Eastern United States, India, and East Asia. They come up on the beach every year for the breeding season.
What is horseshoe crab blood used for?
The blood of the horseshoe crab has the ability to coagulate or clump up in the presence of bacterial toxins. In human hands, this helps to ensure that vaccines and other medicine are free of dangerous chemicals. To harvest the blood, the animal is caught, drained a little, and then released back into the water. This method has a mortality rate as high as 30% though.
How many eyes does a horseshoe crab have?
The horseshoe crab has a total of 10 eyes. This includes a pair of true compound eyes near the head, a pair of eyes around the middle that can sense ultraviolet light, and a bunch of other basic photoreceptors along the tail. It actually has relatively poor eyesight during the day, but this is more than compensated with its enhanced night vision.
Can a horseshoe crab hurt you?
Horseshoe crabs are fairly harmless creatures that primarily rely on their hard shell for defense. The sharp tail is not an aggressive instrument. Instead, it serves the purpose of flipping the creature over when it is turned upside down. New Jersey actually started a campaign to inform beachgoers that they should flip over a stuck horseshoe crab.
Are Horseshoe Crabs herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Horseshoe Crabs are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Horseshoe Crabs belong to?
Horseshoe Crabs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Horseshoe Crabs belong to?
Horseshoe Crabs belong to the class Malacostraca.
What phylum to Horseshoe Crabs belong to?
Horseshoe Crabs belong to the phylum Arthropoda.
What family do Horseshoe Crabs belong to?
Horseshoe Crabs belong to the family Limulidae.
What order do Horseshoe Crabs belong to?
Horseshoe Crabs belong to the order Xiphosurida.
What type of covering do Horseshoe Crabs have?
Horseshoe Crabs are covered in Shells.
What are some predators of Horseshoe Crabs?
Predators of Horseshoe Crabs include sharks, alligators, sea turtles, and seabirds.
How many babies do Horseshoe Crabs have?
The average number of babies a Horseshoe Crab has is 90,000.
What is an interesting fact about Horseshoe Crabs?
Horseshoe Crabs have changed little in over 500 million years!
What is a distinguishing feature of the Horseshoe Crab?
Horseshoe Crabs have a hard, horseshoe-shaped shell.
How many species of Horseshoe Crab are there?
There are 4 species of Horseshoe Crab.
What is the biggest threat to the Horseshoe Crab?
The biggest threat to the Horseshoe Crab is habitat destruction.
How many Horseshoe Crabs are left in the world?
The population size of the Horseshoe Crab is unknown.
How do Horseshoe Crabs have babies?
Horseshoe Crabs lay eggs.
Can a horseshoe crab kill you?
A horseshoe crab doesn’t bite or sting, but the blood of the mangrove horseshoe crab can contain a deadly poison.
Why is the horseshoe crab's blood important to humans
The blood of the Atlantic horseshoe crab is used to create Limulus amebocyte lysate, or LAL which helps scientists find bacterial toxins in medicines. The price of LAL is about $15,000 a quart, but the price may be high indeed for the horseshoe crab. About 10 to 30 percent of the animals don’t survive having their blood drawn.
Are horseshoe crabs killed for their blood?
Horseshoe crabs are not intentionally killed for their blood. After blood is drawn, they are supposed to be returned to the wild. Because so many of the animals die anyway, there is some consideration of farming or culturing horseshoe crabs. Horseshoe crabs can be kept in captivity, so farming is an option.
Are horseshoe crabs edible?
Another of the horseshoe crab facts: Some horseshoe crabs are edible, but others contain a potentially deadly toxin.
What do horseshoe crabs eat?
Horseshoe crabs eat worms, bivalves with thin shells, insect and fish larvae, and fish small enough to handle.
What is horseshoe crab blood used for?
Substances in horseshoe crab blood are used to make sure that medicines are safe.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/covid-vaccine-needs-horseshoe-crab-blood?loggedin=true
- Promega Connections, Available here: https://www.promegaconnections.com/evaluating-the-costs-of-endotoxin-testing/
- Animal Diversity Web, Available here: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Limulus_polyphemus/#conservation_status
- The Horseshoe Crab, Available here: https://horseshoecrab.org/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Horseshoe_crab
- EPA, Available here: https://www.epa.gov/ocean-acidification/understanding-science-ocean-and-coastal-acidification