Tetra
Paracheirodon Axelrodi
Native to the freshwater streams of South America!
Advertisement
Tetra Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Characiformes
- Family
- Characidae
- Genus
- Paracheirodon
- Scientific Name
- Paracheirodon Axelrodi
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Tetra Conservation Status
Tetra Facts
- Main Prey
- Algae, Brine Shrimp, Plankton
- Optimum pH Level
- 5.5-7.5
- Habitat
- Clearwater streams of South America
- Predators
- Fish, Eels, Crustaceans
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Favorite Food
- Algae
- Common Name
- Tetra
- Average Clutch Size
- 130
- Slogan
- Native to the freshwater streams of South America!
Tetra is a general name for tropical freshwater fish of the Characidae family.
They are popular because they are peaceful species that can live with many other types of aquarium features. Aquarium enthusiasts also love them because they are easy to maintain, particularly the ember tetra. They come in many bright colors, like yellow, cardinal, and bright greens and blues.

Five Tetra Facts
1. Tetras are among the world’s most popular aquarium fish.
2. Rummy-nose tetras love to shoal.
3. Tetras tend to act livelier when they are in bigger groups.
4. The ember tetra, discovered in 1987, was named after explorer Heiko Bleher’s mother.
5. Glow tetras, also called GloFish tetras, are genetically modified and can reach six inches long.
Classification and Scientific Name
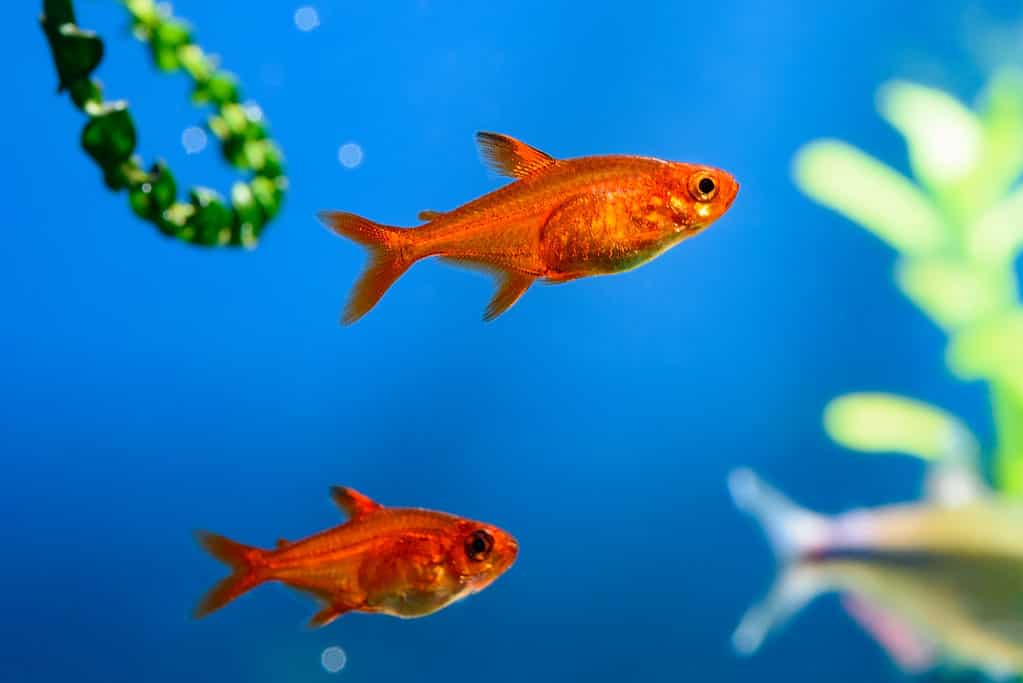

Ember tetras are omnivores, and they are micro-predators that feed on other small invertebrates.
©nektofadeev/Shutterstock.com
All tetras are members of the Chcaraciformes order and the Characidae family. The scientific name of the neon tetra, probably the best known of these aquarium fish, is Paracheirodon innesi. Scientific names of some of the other tetras are yellow tetra, Hyphessobrycon bifasciatus; rummy-nose tetra, Hemigrammus rhodostomus; cardinal tetra, Paracheirodon axelrodi; ember tetra, Hyphessobrycon amandae; and glow tetra, Hemigrammus erythrozonus.
Origins
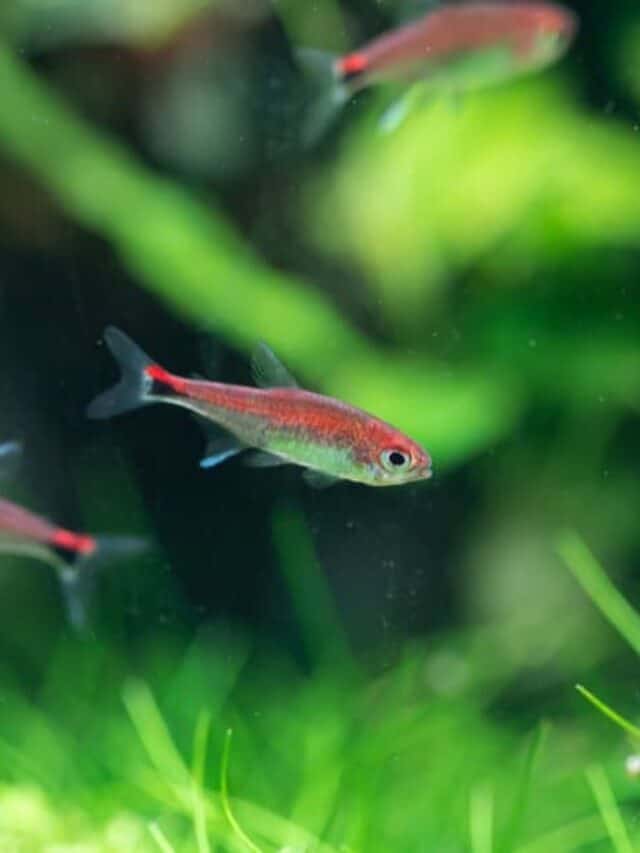

The small yet vibrant ruby tetra fares best in small groups of its own species.
©chonlasub woravichan/Shutterstock.com
Tetra is a descriptive word used to refer to numerous species of small, freshwater characiform fish. These fish are native to Africa, Central America, and South America and belong to the Characidae family, as well as the two former subfamilies Alestidae (or African tetras) and Lebiasinidae. The Characidae family is characterized by a small adipose fin located between the dorsal and caudal fins. Tetra fish such as the neon tetra (Paracheirodon innesi) are popular amongst aquarium hobbyists due to their vivid colors and low-maintenance care requirements. The word “Tetra” is derived from the Greek term “Tetragonopterus” which means “square-finned”.
Many different types of fish are commonly referred to as tetras, even though they may not be related to each other. Tetras are native to South and Central America, Africa, and the Amazon Basin, except for the blind cave tetra that was found in Mexico. Each species of tetra has its own unique range and distribution, but some species may inhabit the same areas. They usually live in regions rich with vegetation and shaded areas.
Species
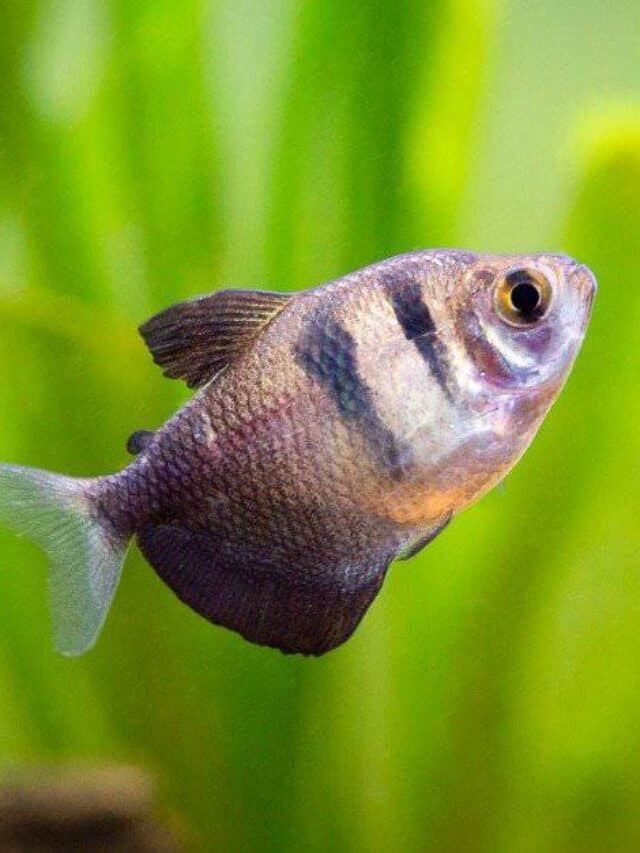

The black skirt tetra gets its name from its black, skirt-like fin.
©iStock.com/Juan Carlos Juarez Jaramillo
More than 150 species of fish considered tetras live worldwide. Although there are many different species, less than 20 are commonly found in aquariums worldwide. Most pet stores sell neon tetras at a low price as they are plentiful. Other popular tetra species among hobbyist fishkeepers include black, cardinal, rainbow, blue, flame, rummy-nose, emperor, and bloodfin tetras. The most popular tetras also have a low price in pet stores, making them affordable.
Appearance
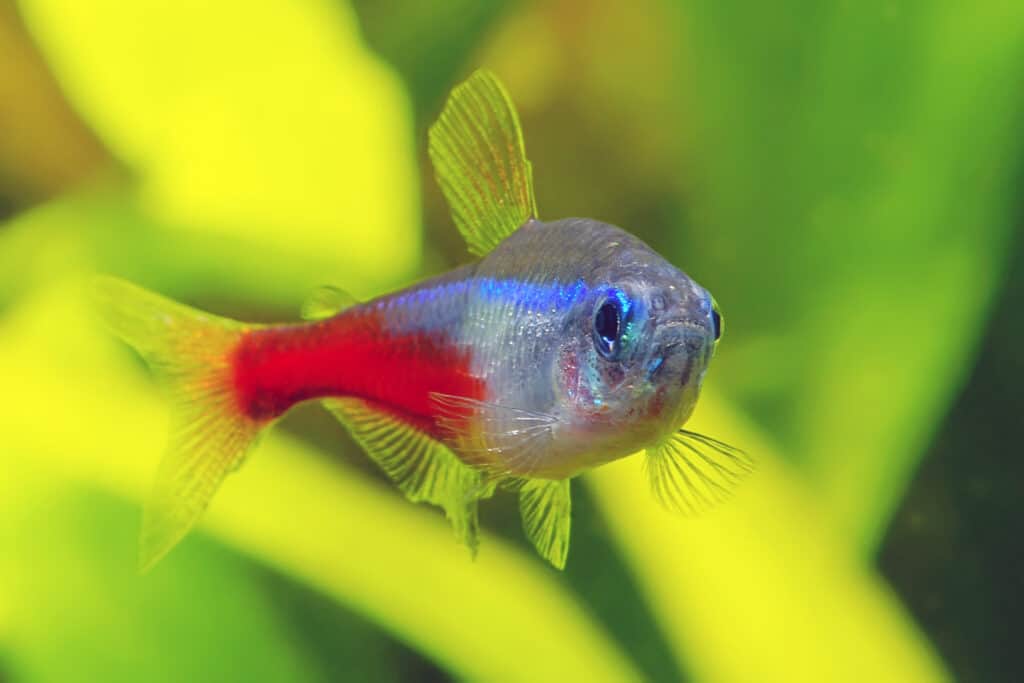

The neon tetra gets its coloration from guanine crystals found inside their cells that reflect off of light.
©Grigorev Mikhail/Shutterstock.com
Tetras are small fish, generally ranging in length from one to four inches. The one exception is the genetically engineered glow tetra, which can grow up to six inches in size. Tetras have a small adipose fin between their dorsal and caudal fins, distinguishing them from other fish. You’ll find a few differences between male and female tetras. Males are usually thinner, while females are more rounded and tend to be larger. Colors are varied, ranging from silver and yellow to deep black.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
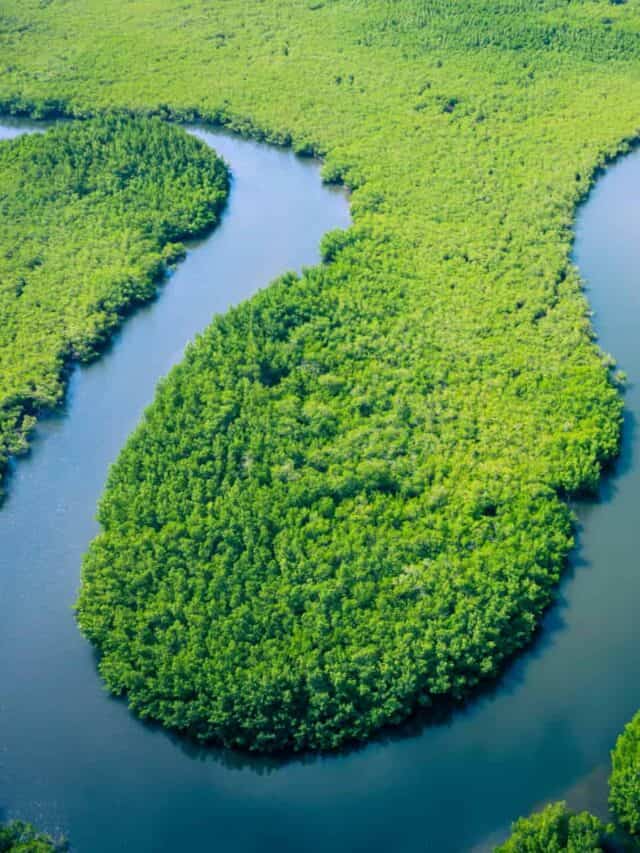

Many types of tetra fish live in the Amazon River Basin.
©Curioso.Photography/Shutterstock.com
Tetras are found around the world, although they are concentrated in the previously mentioned areas. They are primarily found in the freshwater rivers and lakes of the Amazon Basin. Most species generally have stable populations, although some have shown declines, while the numbers of the rest remain unknown.
According to the IUCN Redlist of endangered species, the tetra is considered least concern.
Predators and Prey
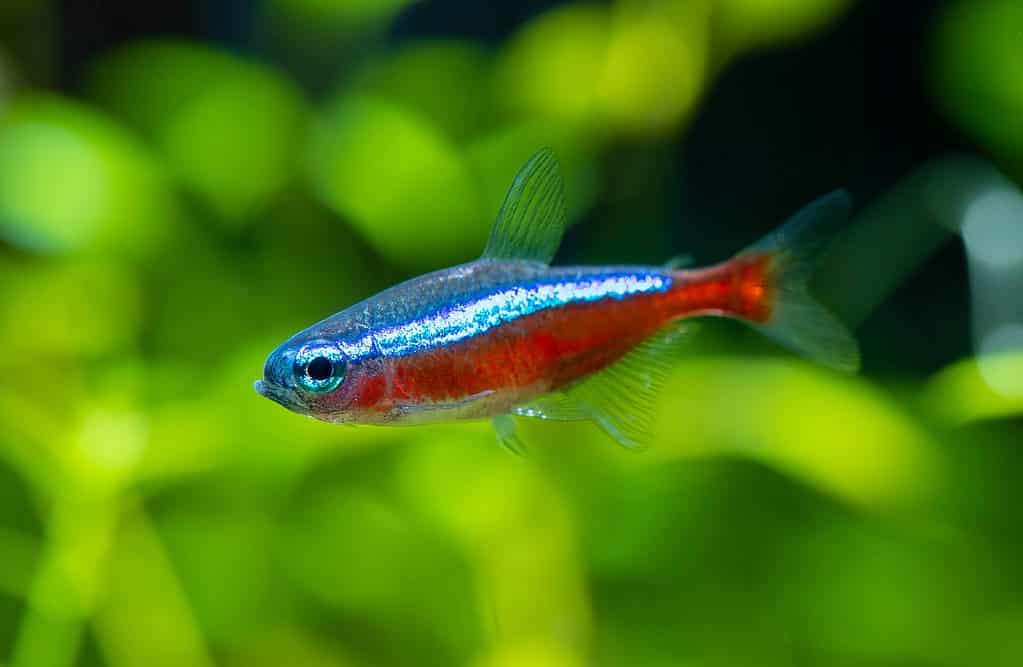

Because tetra fish are so tiny, they have many predators.
©NattapolStudiO/Shutterstock.com
As tetras are small fish, many different predators hunt them. Larger fish, eels, crustaceans, and some invertebrates all feed on tetra. Because of their colorful bodies, predators can easily see tetras. When tetras feel they are in danger, they’ll often try to find somewhere to hide or swim to darker waters where they won’t be as visible.
In the wild and the aquarium, tetras eat almost anything because they are omnivores. The diets of wild and captive tetras are similar, with the exception that captive tetras eat manufactured food like flakes, pellets, frozen brine shrimp, etc. In the wild, they have access to a wide variety of foods. Among the favorite prey are common water fleas called daphnia, mosquito larvae, brine shrimp, bloodworms, and small fish eggs. In aquariums, tetras eat twice daily, consuming as much food as possible in about two minutes.
Reproduction and Lifespan
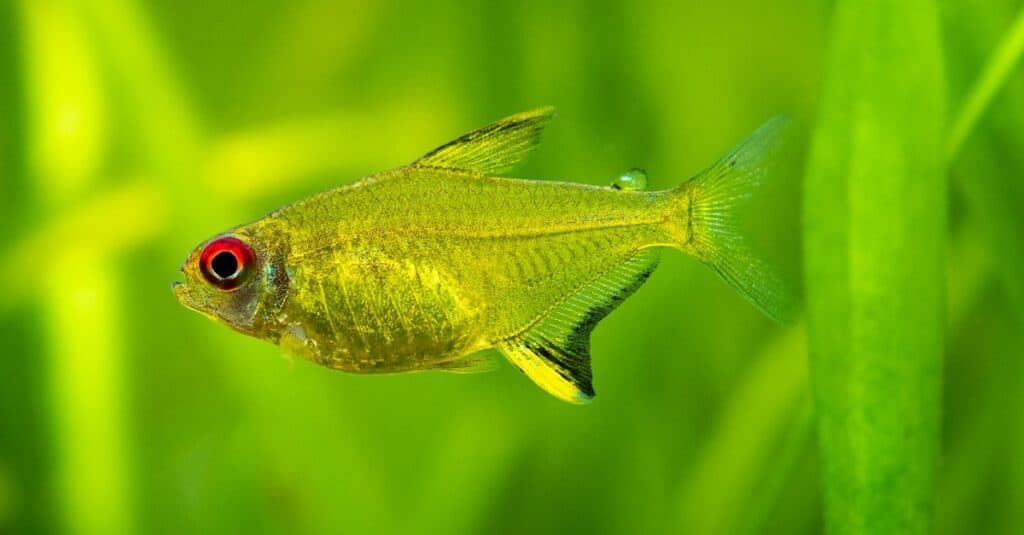

Lemon tetras are known for their neon yellow coloration and mild translucency.
©iStock.com/Juan Carlos Juarez Jaramillo
The lifespan of tetras is between eight to 10 years in the wild but considerably shorter in captivity. For example, neon tetras only live an average of five years. Tetras don’t live as long in captivity because of stress and boredom. Loneliness is also a factor as these fish do best when living in a school of other tetras.
Although most tetras are easy to care for, breeding them in captivity can sometimes be difficult because it’s hard to distinguish males from females. Even though they do not form monogamous pairs, tetras will not necessarily spawn with any other tetra they see and may reject their potential mate. The male tries to attract the female by dancing around her. If she likes him, she will take him to the spawning site. The number of eggs laid can range from 50 to 1,000, depending on the species. Tetras grow slowly. After hatching, it can take neon tetras two months to reach one-quarter inch in length. However, emperor tetras grow quickly as juveniles only take six months to become adults. Eggs take at least 48 hours to hatch.
Fishing and Cooking
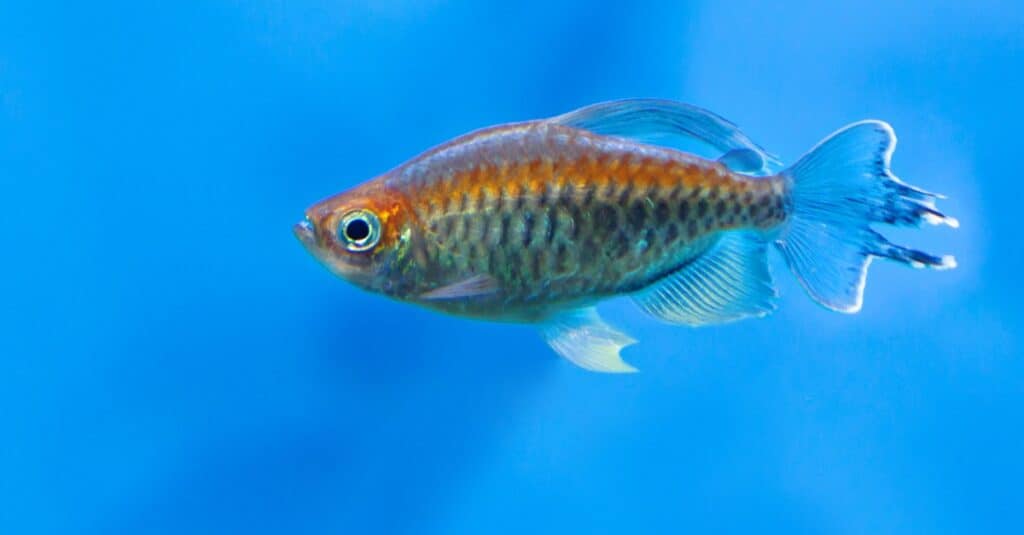

The Congo tetra is one of the larger varieties of tetra fish at around 3 inches long.
©iStock.com/User10095428_393
Generally, fishing for tetras only occurs to bring these fish into captivity to help populate home aquariums. Like most other aquarium fish, tetras are edible, but you probably wouldn’t want to do so. First off, their small size doesn’t produce much protein, but more importantly, you can run into digestive problems when consuming aquarium fish not explicitly raised for food.
Tetra Population
The exact number of tetras in the world is unknown, primarily because many of these fish live in remote regions and dark waters.
99 Types of Tetra Fish
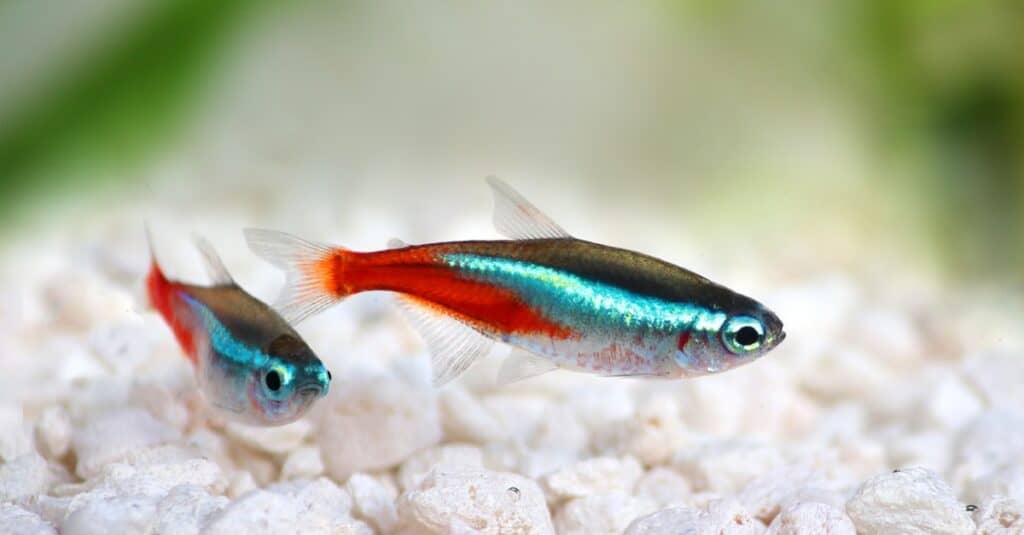

Neon tetras are one of the most vibrant tetra species.
©iStock.com/Mirko_Rosenau
- Adonis Tetra – Lepidarchus adonis
- African Moon Tetra – Bathyaethiops caudomaculatus
- African Red-Eyed Tetra – Arnoldichthys spilopterus
- Arowana Tetra – Gnathocharax steindachneri
- Black Chin Tetra – Piabucus melanostoma
- Black Darter Tetra – Poecilocharax weitzmani
- Black Emperor Tetra – Nemotobrycon palmeri
- Black Line Tetra – Hyphessobrycon scholzei
- Black Neon Tetra – Hyphessobrycon herbertaxelrodi
- Black Phantom Tetra – Hyphessobrycon megalopterus
- Black Widow Tetra – Gymnocorymbus ternetzi
- Blackline Tail Tetra – Moenkhausia costae
- Bleeding Blue Tetra – Hyphessobrycon margitae
- Bleeding Heart Tetra – Hyphessobrycon erythrostingma
- Bloodfin Tetra – Aphyocharax anisitsi
- Blue Eyed Congo Tetra – henacogrammus aurantiacus
- Blue Purple Emperor Tetra – Inpaichthys kerri
- Blue Spot African Tetra – Brycinus poptae
- Blueberry Tetra – Hyphessobrycon wadai
- Brittanichthys Axelrodi Tetra – Brittanichthys Axelrodi
- Broken Line Tetra – Hemigrammus ulreyi
- Bucktooth Tetra – Exodon paradoxus
- Buenos Aires Tetra – Hyphessobrycon anisitsi
- Cardinal Tetra – Paracheirodon axelrodi
- Cochus Blue Tetra – Boehlkea fredcochui
- Coffee Bean Tetra – Hyphessobrycon takasei
- Columbian Redfin Tetra – Hyphessobrycon columbianus
- Congo Tetra – Phenacogrammus interruptus
- Copei Tetra – Moenkhausia copei
- Costello Tetra – Hemigrammus hyanuary
- Dawn Tetra – Aphyocharax paraguayensis
- Diamond Tetra – Moenkhausia pittieri
- Domino Tetra – Neolebias powelli
- Eilyos Tetra – Hyphessobrycon eilyos
- Ember Tetra – Hyphessobrycon amandae
- Emperor Tetra – Mematobrycon palmeri
- Exclamation Mark Tetra – Bryconella pallidifrons
- Fire Ant Tetra – Hyphessobrycon myrmex
- Fire Green Tetra – Aphyocharax rahbuni
- Flag Tetra – Hyphessobrycon heterorhabdus
- Flame Tetra – Hyphessobrycon flammeus
- Flameback Bleedig Heart Tetra – Hyphessobrycon pyrrhonotus
- Frankei Terta – Hyphessobrycon frankei
- Glass Bloodfin Tetra – Prionobrana filigera
- Glowlight Tetra – Hemigramus erythrozonus
- Gold Shoulder Rosy Tetra – Hyphessobrycon paepkei
- Golden Mascara Tetra – Cyphocharax multilineautus
- Golden Tetra – Hyphessobrycon moniliger
- Green Neon Tetra – Paracheirodon simulans
- Head and Taillight Tetra – Hemigrammus ocelifer
- Hummingbird Tetra – Trochilocharax ornatus
- Imperial Tetra – Hyphessobrycon nigricinctus
- Infernal Tetra – Hemigrammus/Hyphessobrycon Infernalis
- Jellybean Tetra – Ladigesia rolofii
- Kitty Tetra – Hyphessobrycon loweae
- Kogal Blue Eyed Tetra – Moenkhausia sp.
- Lemon Tetra – Hyphessobrycon pulchripinnis
- Lipstick Tetra – Moenkhausia cosmops
- Long Finned Tetra – Brycinus longipinnis
- Loreto Tetra – Hyphessobrycon loretoensis
- Mexican Tetra – Astyanax mexicanus
- Montags Tetra – Hyphessobrycon montagi
- More Code Tetra – Hemigrammus sp ‘morese code’
- Mountain Crystal Tetra – Proteocheirodon pi, leptagoniates pi
- Nego Dagua Tetra – Hyphessobrycon negodagua
- Neon Tetra – Paracheirodon innesi
- Ornate Tetra – Hyphessobrycon bentosi
- Penguin Tetra – Thayeria boehlkei
- Phoenix Tetra – Hemigrammus filamentosus
- Pink Lemon Tetra – Hyphessobrycon itaparicensis
- Pretty Tetra – Hemigrammus ulcher
- Racoon Tetra – Hyphessobrycon procyon
- Rainbow Copella Tetra – Copella vilmae
- Rainbow Tetra – Nematobrycon lacortei
- Red Base Tetra – Hemigrammus stictus
- Red Devil Tetra – Hyphessobrycon piranga
- Red Eye Tetra – Moenkhausia sanctaefilomenae
- Red Laser Tetra – Hemigrammus coeruleus
- Red Line Lizard Tetra – Iguanodectes geisleri
- Red Line Tetra – Hyphessobrycon amapaensis
- Red Phantom Tetra – Hyphessobrycon sweglesi
- Red Tail Hemiodus Tetra – Hemiodus gracilis
- Redfin Congo Tetra – Micralestes occidentalis
- Redfin Penguin Tetra – Thayeria sp.
- Reed Tetra – Hyphessobrycon elachys
- Rosy Tetra – Hyphessobrycon rosaceus
- Ruby Tetra – Axelrodia riesei
- Rummy Nose Tetra – Hemigrammus rhodostomus
- Sailfin Tetra – Crenuchus spilurus
- Serpae Tetra – Hyphessobrycon eques
- Silvertip Tetra – Hasemania nana
- Six Stripes Tetra – Hexastichos
- Splash Tetra – Copella arnoldi
- Steel Blue Tetra – Hyphessobrycon weitzmanorum
- Toucan Tetra – Tucanoichthys tucano
- White Skirt Tetra – Gymnocorymbus ternetzi
- X-Ray Tetra – Pristella maxillaris
- Xingu Black eon Tetra – Moenkhausia heikoi
- Yellow Tailed Congo Tetra – Alestopetersius caudalis
Tetra FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Tetras herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Tetras are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Tetras belong to?
Tetras belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Tetras belong to?
Tetras belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Tetras belong to?
Tetras belong to the class Actinopterygii.
What family do Tetras belong to?
Tetras belong to the family Characidae.
What order do Tetras belong to?
Tetras belong to the order Characiformes.
What genus do Tetras belong to?
Tetras belong to the genus Paracheirodon.
What type of covering do Tetras have?
Tetras are covered in Scales.
In what type of habitat do Tetras live?
Tetras live in clearwater streams in South America.
What is the main prey for Tetras?
Tetras prey on algae, brine shrimp, and plankton.
What are some predators of Tetras?
Predators of Tetras include fish, eels, and crustaceans.
What is the average clutch size of a Tetra?
Tetras typically lay 130 eggs.
What is an interesting fact about Tetras?
Tetras are native to the freshwater streams of South America!
What is the scientific name for the Tetra?
The scientific name for the Tetra is Paracheirodon Axelrodi.
What is the lifespan of a Tetra?
Tetras can live for 2 to 5 years.
What is the optimal pH for a Tetra?
The optimal pH for a Tetra is between 5.5 and 7.5.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals