Ghost Catfish
Kryptopterus vitreolus
You can see its heart beating
Advertisement
Ghost Catfish Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Silurormes
- Family
- Siluridae
- Genus
- Kryptopterus
- Scientific Name
- Kryptopterus vitreolus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Ghost Catfish Conservation Status
Ghost Catfish Facts
- Prey
- Larvae, worms
- Group Behavior
- School
- Fun Fact
- You can see its heart beating
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Translucent body
- Other Name(s)
- Glass catfish, X-ray fish
- Optimum pH Level
- 6.0 - 8.0
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Type
- Siluriformes
- Common Name
- Ghost Catfish
View all of the Ghost Catfish images!
Due to its translucent color a ghost catfish is sometimes called a glass catfish, a phantom catfish or even an X-ray fish.
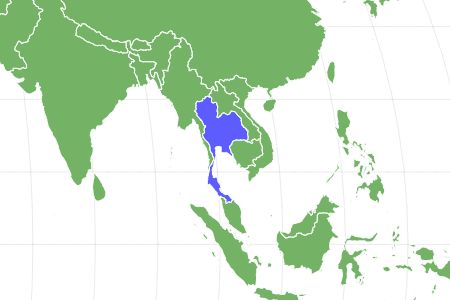
At its largest size, this fish is 2.5 inches long. The ghost catfish is native to inland streams in Thailand and is a popular addition to many freshwater aquariums.
3 Ghost Catfish Facts
- Visible heartbeat: The translucent body of this fish allows you to see its spine as well as its beating heart.
- Rainbow fish: If sunlight travels through this fish at a certain angle it can create a rainbow-like pattern of colors in an aquarium.
- Not pregnant with fertilized eggs: A female ghost catfish scatters her eggs on floating vegetation where they’re fertilized by a male. So, though she is carrying eggs inside her for a while, she is not pregnant with fertilized eggs.
Classification and Scientific Name
Kryptopterus vitreolus is the scientific name of the ghost catfish. The Latin words Kryptopterus vitreolus translate to the English words hidden glass. It’s also known as a glass catfish. It’s in the Siluridae family and the class Actinopterygii.
The ghost catfish falls into a group known as Asian glass catfish. Some examples include:
- Kryptopterus baramensis
- Kryptopterus bicirrhis
- Kryptopterus cheveyi
- Kryptopterus cryptopterus
Different Species
There are 104 subspecies in the Siluridae family of fish. Ghost catfish are in the Asian glass catfish group.
- Kryptopterus geminus: Like the Kryptopterus vitreolus, this glass/ghost catfish lives in streams and rivers in Thailand. However, the Kryptopterus geminus is larger in size at 6.7 inches long with a thinner head.
- Kryptopterus bicirrhis: This fish is another resident of streams and rivers in Thailand. One difference is at six inches this fish is larger than the Kryptopterus vitreolus. Plus, the body of the Kryptopterus bicirrhis is only transparent near its head.
- Kryptopterus piperatus: This fish shares the same type of transparent body with the Kryptopterus vitreolus. But, unlike the Kryptopterus vitreolus, the Kryptopterus piperatus is categorized as Vulnerable with a decreasing population.
- Kryptopterus cryptopterus: This member of the Asian glass catfish group is larger than a Kryptopterus vitreolus at 5.7 inches long. It also has a thicker head.
Appearance
The ghost catfish is also known as the glass catfish because of its translucent body. Its spine can clearly be seen along with its beating heart.
Like other catfish, this fish has barbels near its mouth. Barbels are spiny formations that help a catfish find food on dark river bottoms.
Ghost catfish are very small in size which makes them an appealing choice for someone who wants to stock a home aquarium. They are 1.5 to 2.5 inches long as adults and weigh less than one ounce.
The translucent body of this fish can make it appear almost invisible which helps it to hide from predators like herons and larger fish. Furthermore, ghost catfish travel in schools. This provides some protection when a predator approaches.
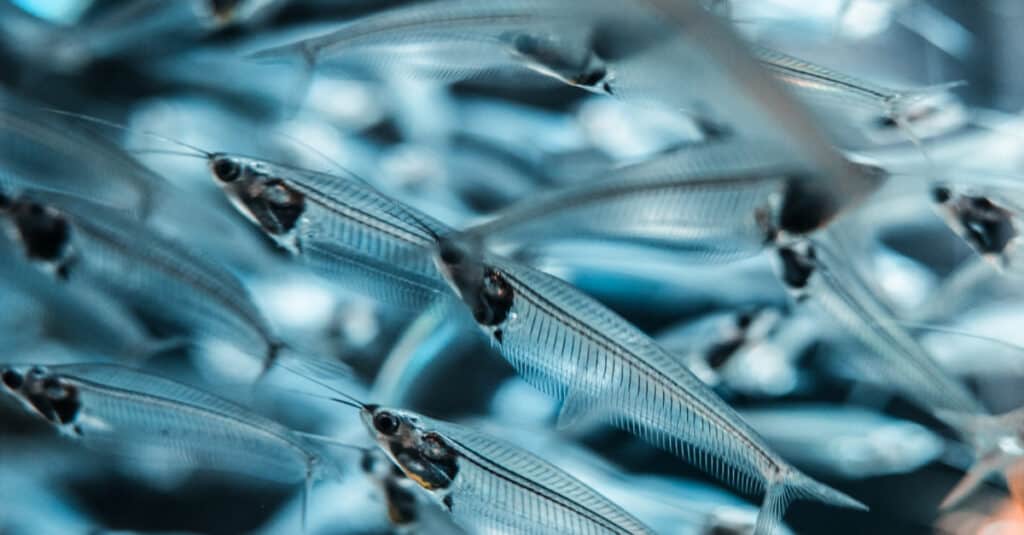

Because of their transparent skin, you can see glass catfishes’ entire skeletal system
©Volha Vasilevich/Shutterstock.com
Distribution, Population and Habitat
These fish live in inland streams and rivers in Thailand. Many of them are found in slow-moving streams. They live in a freshwater habitat with a water temperature of 75 to 79 degrees Fahrenheit.
The total population of the ghost catfish is unknown. But it’s listed as Least Concern by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. They’re captured and sold in the pet trade, but this doesn’t seem to pose a substantial threat.
Predators and Prey
Ghost catfish are carnivores. Unlike other types of catfish known as bottom-feeders, these catfish like to capture their food as it falls through the water.
What eats a ghost catfish?
These fish are sometimes eaten by larger fish. Frogs and herons eat the eggs of ghost catfish as well as newly hatched ghost catfish called fry.
What does a ghost catfish eat?
Mosquito larvae, brine shrimp, and bloodworms are all types of food eaten by ghost catfish.
These fish are caught and sold for display in home aquariums, but this has not had a major effect on its overall population. Breeding ghost catfish happens here in the U.S. This fish is listed as Least Concern.
Reproduction and Lifespan
In the wild, the breeding activity of this fish takes place in the rainy spring season. During this time, the female releases or scatters her eggs on floating vegetation in her habitat. She can release 50 to hundreds of eggs. At that point, a male ghost catfish fertilizes the scattered eggs. So, a female isn’t pregnant with fertilized eggs. Instead, the eggs are fertilized externally. They hatch in three to four days.
Someone breeding this fish in a home aquarium should take the baby fish called fry, out of the aquarium right away. This is to prevent their bigger tank mates from eating them!
Ghost Catfish in Fishing and Cooking
Though many types of catfish are caught and eaten, these fish are small in size and not included in this group. Instead, they’re kept in temperature-maintained, freshwater aquariums in homes.
View all 170 animals that start with GGhost Catfish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are ghost catfish found?
They are found in Thailand specifically in slow-moving streams and rivers.
How big do ghost catfish get?
The biggest a ghost catfish grows is 2.5 inches long.
Why is it called a ghost catfish?
A ghost catfish gets its name from its appearance. It has a translucent or clear body that makes it seem like it disappears when it swims in some areas of its habitat. It’s sometimes called a phantom catfish or even an X-ray catfish because you can see its internal organs through its skin.
Are ghost catfish aggressive?
No. These fish are mild-mannered and get along with tank mates as long as they don’t feel threatened.
Many online fish stores provide guidance on the types of fish that are compatible with ghost catfish.
Can ghost catfish live with guppies?
No. Ghost catfish, especially those that are larger in size, have been known to eat guppies.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- IUCN Red List, Available here: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/152136779/152136784
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kryptopterus_vitreolus
- Thai National Parks, Available here: https://www.thainationalparks.com/species/grey-heron
- Fish Breeding Strategies, Available here: https://fishbreedingstrategies.weebly.com/egg-scattering.html
- Aquarium Nexus, Available here: https://www.aquariumnexus.com/ghost-catfish/
- Aquariums at Home, Available here: https://aquariumsathome.com/ghost-catfish-care-guide-tank-setup-tankmates-breeding-diet/
- Betta Care Fish Guide, Available here: https://www.bettacarefishguide.com/can-glass-catfish-and-bettas-live-together/