Can have a leg span of nearly 2 meters!
Advertisement
King Crab Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
King Crab Conservation Status
King Crab Facts
- Main Prey
- Molluscs, Fish, Sea Urchin
- Habitat
- Cold coastal waters and continental shelves
- Predators
- Human, Larger Fish, Octopus
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 50,000 to 500,000 eggs at once
View all of the King Crab images!

The king crab is one of the most enormous crab species known to man. It can weigh more than 11 pounds, which is heavier than a house cat, and have a total leg span of over 5 feet, which means that it can be as long as a human is tall.
Some of the most popular King crabs are Alaskan king crabs, red king crabs, or Japanese crabs. They can only grow larger through a process called molting in which they shed their old shells and grow newer, larger ones.
In general, king crabs can be found along the Alaskan coast, in the Bering Sea, and in the shallow waters surrounding the coast of Japan. They are the most popular crab to eat, and their meat is considered a delicacy in most parts of the world.

While they may look unedible, king crab meat is considered a delicacy.
3 King Crab Facts
- The heaviest king crab ever found weighed 28 pounds. This is roughly the same weight as a miniature poodle or a corgi!
- King crabs are closely related to hermit crabs, and they share the trait of having two differently-sized claws. The right claw is typically larger and used to crush things, and the left claw is smaller and shaped to make tearing food apart more convenient.
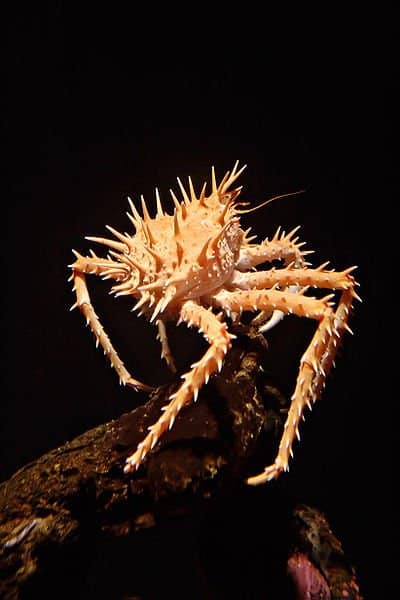
- King crabs cannot swim as adults. They move around by walking along the ocean floor.
Scientific Name
“Paralithodes” comes from the Ancient Greek prefix “para,” which means “beside,” “near” or “closely resembling,” and the Greek word “lithodes,” which means “stone-like.” This means that king crabs are a part of a group of animals that all have rigid, hard, “stone-like” shells.
Types of King Crab
There are over 120 different species of king crabs across the Earth.
Alaskan King Crab
Some of the most well-known king crabs originate near the Alaskan coast. These are the four main types:
- Red King Crab – The Red King Crab is also known as the Japanese crab or the Kamchatka crab. Its scientific name is Paralithodes camtschaticus. Red king crab is the most expensive type of crab and is very desirable. They can be caught near Bristol Bay.
- Blue King Crab – The Blue King Crab is named for the touches of blue on their otherwise brown exoskeleton. The meat from the blue king crab is sometimes mistaken for red king crab meat because of its red and orange coloration. These crabs can be caught in the areas near St. Matthew Island and the Pribilof Islands.
- Brown “Golden” King Crab – The Brown “Golden” King Crab is named for its gold and brown shell. These smaller crabs can be harvested close to the Aleutian Islands; however, they deliver less meat than their larger cousins.
- Scarlet King Crab – The Scarlet King Crab is known for its bright red shell. These crabs are not hunted in the same amount as the other Alaskan king crabs due to their smaller population.
Other King Crab
There are many other types of king crabs found around the world’s oceans.
- Southern King Crab – The Southern King Crab is another king crab that lives far to the south, close to Chile and Argentina. These crabs are sometimes known as Chilean king crabs and also centolla. They grow to be just over a half-foot long.
- Norway King Crab – The Norway King Crab is found off the coast of Northern Europe and Norway, and it’s also called the deep sea crab. They can be recognized by their spiky carapace which has a brown and orange hue.
- Puget Sound King Crab – The Puget Sound King Crab is a larger cousin of the other king crabs that grow almost a foot long. It is one of the more colorful king crabs with their hues of purple, red, and orange.
- Brown Box Crab – The Brown Box Crab can be caught along the Pacific Coast of Canada and America, including Alaska. These crabs are a little duller than other king crabs and not quite as large, yet much of their total mass is edible.

King crabs cannot swim as adults.
©Stan Shebs, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Appearance and Behavior
Despite its name, the red king crab is typically not red. Live ones tend to have a more orange or burgundy hue. Some can even be a brownish-blue color. The name actually comes from the fact that they turn bright red when cooked.
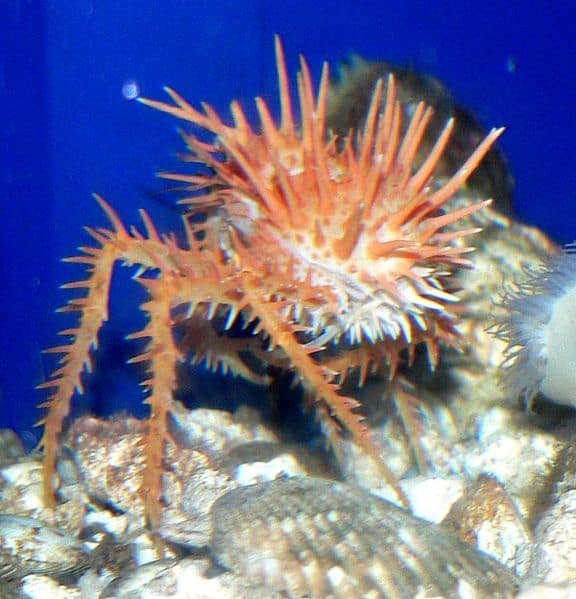
Like most crab species, king crabs are covered in a thick and heavy shell, which is usually called a carapace. In addition, their entire bodies are covered in large, sharp spines for additional protection.
Outside of the mating season, king crabs are solitary creatures. However, they have been known to group together in the face of large predators. They will stack on top of each other in what is known as a “pod” in order to appear larger and more menacing. These pods can be dozens of feet high and contain stacks of hundreds of crabs.
Male king crabs usually grow to be larger than females, and they can be easily identified by their different body shapes. Female king crabs have a wide, fan-shaped abdomen, and males have a narrow, triangle-shaped abdomen.
King crabs have five pairs of legs. The first pair of legs actually functions more like arms, and each has a sharp pincer attached to the end. The right claw is larger and thicker, and it is designed for crushing. The left claw is smaller, and it is designed to tear apart food.
The fifth set of legs is also different from the rest. These legs are smaller and specialized in aiding the crabs in egg fertilization during mating and cleaning fertilized eggs after they have been laid.

King crabs are covered in a thick and heavy shell, called a carapace.
©Stan Shebs, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
History and Evolution
King crabs are some of the largest arthropods on Earth. Evidence points to king crabs descending from the same tree as hermit crabs, despite them having weak exoskeletons and spiraling abdomens. Somewhere along the line, the king crab ancestors evolved away from living within a shell and adapted a much strong exoskeleton for protection to replace the exterior shell. Making this adaptation allowed the king crab to grow larger than hermit crabs. This roughly took place around 20 million years ago, and the hermit crabs themselves have a long history dating back 150 million years.
There also happens to be a line of thought that sees other crustaceans evolving to take a form similar to that of a crab. There must be some advantage to the evolution that a lot of these animal types are trending towards over time.
Habitat
Most species of king crabs prefer to live in relatively shallow and muddy coastal waters that are less than 200 feet deep. They can live in waters that are as deep as 650 feet, however, so they are versatile.
Adult king crabs generally prefer cold water that is between 2 to 4 degrees Celsius or 35 to 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Crab Diet
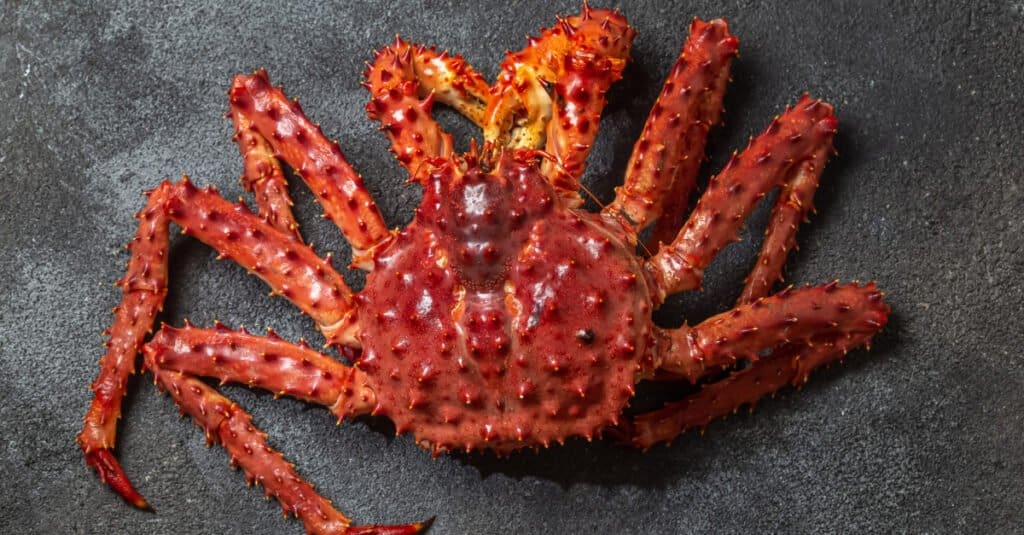

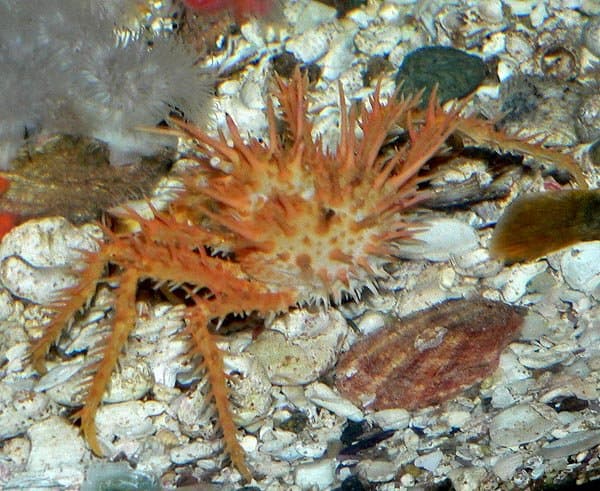
King crabs eat mussels, barnacles, sea urchins, clams, fish, and even smaller crab species.
©Larisa Blinova/Shutterstock.com
King crabs are carnivores, and they are known for eating smaller ocean creatures such as worms, snails, mussels, barnacles, sea urchins, clams, and fish. They will even eat smaller crab species.
They are also considered opportunistic feeders, which means that they are not picky eaters. They will eat whichever invertebrates are easiest to find and crush with their pincers in the nearby surroundings.
Predators and Threats
The natural predators of king crabs include large fish like cod, halibut, and other similar species as well as skates and sculpins. They are also in danger from octopuses and even other king crabs.
The largest king crabs have very few natural predators due to their sheer size and the fact that they are only vulnerable right after molting.
Human harvesting of king crabs is another threat to wild populations. However, a number of man-made fisheries have been established, and strict harvesting regulations are in place, so they are not considered to be endangered.
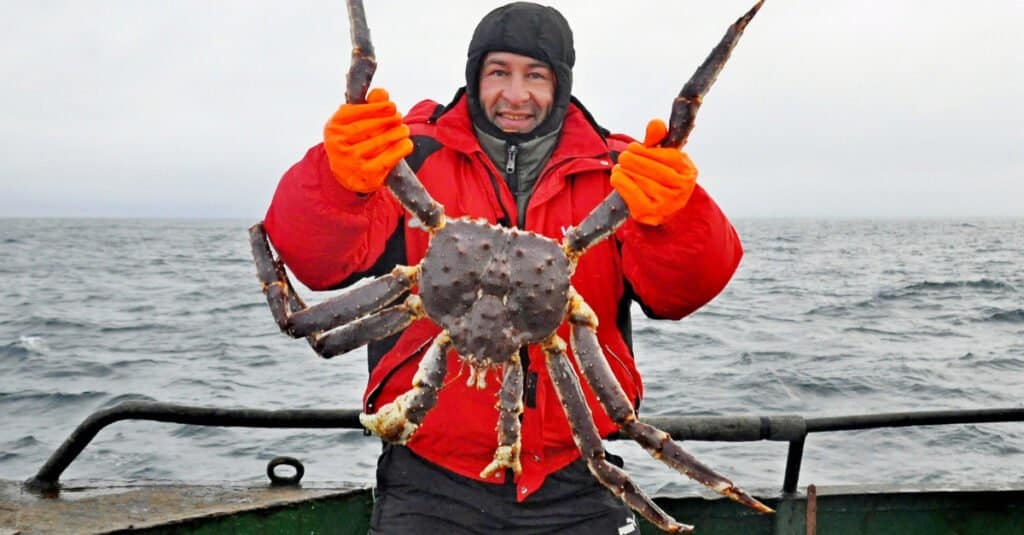

Harvest king crabs is a heavily restricted industry.
©Don Serhio/Shutterstock.com
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
In the wild, king crabs can live up to 30 years. Most do not live this long, but it is normal for a king crab to live at least 20 years when there is minimal threat of human harvesting.
King crabs reach sexual maturity after about five years, and their reproduction cycle begins in the spring.
In mid-spring, usually around May, mature female king crabs will migrate to warmer, shallower waters to ensure that they can safely spawn their eggs. They can spawn anywhere from 50,000 to 500,000 eggs at once.
Male king crabs will join the females later in the season to fertilize the eggs, and females will then carry these eggs in their abdominal flaps for up to 12 months before they hatch. After hatching, king crab larvae resemble tiny shrimp. These larvae are called zoea, and unlike their adult counterparts, they are able to swim. They do not spend any time with the mother crab.
King crab larvae will molt up to five times in the first few months of their lives, and they then metamorphose into what is called a “glaucothoe.” This is a sort of in-between stage of growth for king crabs, which is similar to how many insects have a juvenile stage that essentially looks like a less-developed adult version of the creature.
These juvenile king crabs settle onto the ocean floor when they reach this stage of growth, and as they continue to grow, they will remain on the ocean floor and begin to move around and behave like adult king crabs. During this phase, they will continue to molt regularly as they grow larger, and they also lose their ability to swim.

King crabs can live up to around 30 years in the wild.
©LELACHANOK/Shutterstock.com
Population
King crab populations are closely monitored to avoid overfishing. Because king crab population fluctuations are cyclical, fisheries maintain guidelines regarding how and when these crabs can be harvested to maximize their chances of reproducing and keeping population numbers high.
As an example, fisheries follow the “three S” rule: size, sex, and season. Only male crabs may be harvested, and they must be above a certain size threshold. Additionally, they are only allowed to be harvested outside of the mating and molting season. This helps to ensure that the species is able to replenish itself.
Populations in the Barents Sea are estimated to be around 20 million, and the numbers in the Bering Sea are slightly lower.
King Crab FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How are king crabs different than snow crabs?
King crabs are larger than snow crabs. In addition, they have spines across their bodies and are thicker than snow crabs.
Are king crabs carnivores, herbivores or omnivores?
King crabs are opportunistic carnivores. This means that they eat meat, but they are not picky about where the meat comes from. They will eat almost any invertebrates that are smaller than they are, and they will even eat smaller king crabs if they can crush them with their pincers.
Why is king crab so expensive?
Ultimately, the price of king crab is dictated by supply and demand. Because there is only a limited amount of king crab that can be harvested each year, the demand often exceeds the supply. This is also why king crab prices can fluctuate so much as well.
During seasons when there is an abundance of crab to be harvested, prices may drop somewhat. In seasons where populations are lower and regulations are tighter, prices often rise because the supply is even more limited.
How big does a king crab get?
In general, king crabs are one of the largest crab species. The males grow larger than the females, and it is common for them to be as heavy as 11 pounds and to have a leg span as long as 5 or 6 feet.
To put that in perspective, the average domestic cat weighs about 11 pounds, and the average height for an American female is 5 feet 4 inches.
The largest king crab on record weighed in at an astounding 28 pounds, which is as heavy as a small, stocky dog such as a dachshund or corgi.
Are king crabs dangerous?
Despite their size and their spiny shells, king crabs are not particularly aggressive or dangerous to humans. The profession of king crab fishing is dangerous for other reasons.
Why is king crab fishing so dangerous?
A number of factors all work together to make Alaskan crab fishing one of the most dangerous occupations.
First, it’s important to remember how heavy king crabs are. Fishermen must haul up huge nets or cages that are soaking wet and full of large, live crabs. These nets or pots can weigh hundreds of pounds each, and everything is wet and slippery.
In addition, the fishing waters are often rough, unpredictable and freezing cold. Because the fishing season occurs during the coldest part of the year, there is also the potential for strong, icy winds and dangerous winter storms to make the process even more treacherous.
What Kingdom do King Crabs belong to?
King Crabs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do King Crabs belong to?
King Crabs belong to the phylum Arthropoda.
What class do King Crabs belong to?
King Crabs belong to the class Malacostraca.
What family do King Crabs belong to?
King Crabs belong to the family Lithodidae.
What order do King Crabs belong to?
King Crabs belong to the order Decapoda.
What genus do King Crabs belong to?
King Crabs belong to the genus Lopholithodes.
What type of covering do King Crabs have?
King Crabs are covered in Shells.
In what type of habitat do King Crabs live?
King Crabs live in cold coastal waters and continental shelves.
What is the main prey for King Crabs?
King Crabs prey on mollusks, fish, and sea urchin.
What are some predators of King Crabs?
Predators of King Crabs include humans, larger fish, and octopuses.
What is the average litter size for a King Crab?
The average litter size for a King Crab is 7.
What is an interesting fact about King Crabs?
King Crabs can have a leg span of nearly 2 meters!
What is the scientific name for the King Crab?
The scientific name for the King Crab is Lopholithodes Mandtii.
What is the lifespan of a King Crab?
King Crabs can live for 15 to 30 years.
How fast is a King Crab?
A King Crab can travel at speeds of up to 7 miles per hour.
How do King Crabs have babies?
King Crabs lay eggs.
What's the difference between King Crabs and Spider Crabs?
Spider crabs are larger than King crabs. Additionally, King crabs enjoy cold waters, while spider crabs prefer temperate seas.
What's the difference between King Crabs and Dungeness Crabs?
King crabs are far larger than Dungeness crab. Additionally, King crabs live longer lives than Dungeness crabs on average.
How are king crabs different than bairdi crabs?
The key differences between bairdi crab and king crab are size, appearance, health factors, and location.
Decapod crustaceans, such as king crabs, thrive in frigid waters. The flavor of crab is heavily influenced by its environment, eating habits, and geographic location. For example, snow crab meat is firm, sweet, and has a briny taste, whereas king crab meat is richer in flavor and more tender in texture.
How are king crabs different than opilio crabs?
The key differences between opilio crabs and king crabs are size, health factors, appearance, and habitat.
King crabs are decapod crustaceans that prefer cold seas. They come in red, blue, and brown varieties. King crabs have thicker, shorter legs than queen crabs, making them richer and more appealing as a food source.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals