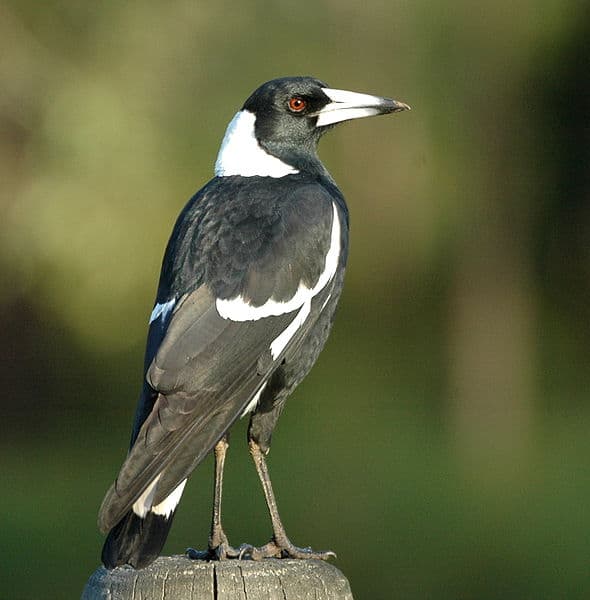
Magpie
Pica Pica
They are found across Europe, Asia and Africa!
Advertisement
Magpie Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Passeriformes
- Family
- Corvidae
- Genus
- Pica
- Scientific Name
- Pica Pica
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Magpie Conservation Status
Magpie Facts
- Lifestyle
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Fruit
- Type
- Bird
- Average Clutch Size
- 3
- Slogan
- They are found across Europe, Asia and Africa!
View all of the Magpie images!

“Magpies are able to recognize their own reflection in a mirror.”
Magpies are birds that live in various habitats including grasslands, meadows, and on the edges of dense forests. These birds are omnivores and insects, berries, nuts, and even small rodents. They build large nests often with two entrances. Magpies are well known for their variety of chirps, squeals, warbles, whistles, and other sounds. They live in flocks or murders.
5 Magpie Facts
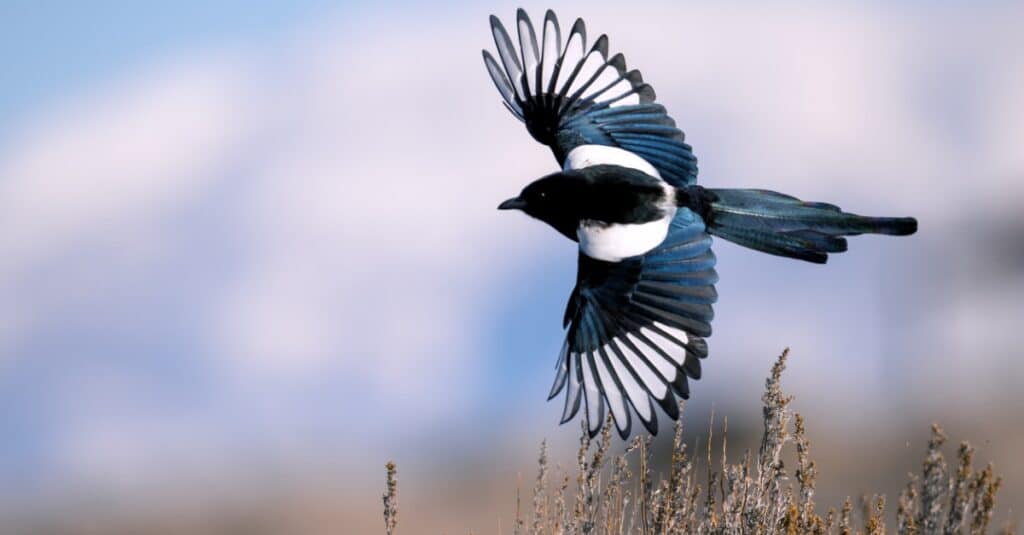

Magpies can often form friendships with people.
©iStock.com/kojihirano
• A magpie’s tail is as long as its body.
• These birds sometimes eat ticks found on deer, elk, and other large mammals.
• The magpie bird is in the same family as jays and crows.
• A splash of white feathers on their wings makes them stand out when taking flight.
• This bird lays from 6 to 9 eggs that are green/brown in color.
Magpie Scientific Name

The scientific name of a Black-billed magpie is
Pica hudsonia
.
The scientific name of a Black-billed magpie is Pica hudsonia. The word Pica is medieval Latin. It was given to a magpie because the bird has a reputation for eating almost anything. Some other common names for this bird include the American magpie, Maggie, and Flute-bird.
It belongs to the Corvidae family and its class is Aves. There are at least 17 species. The Black-billed magpie, the Australian magpie, the Eurasian magpie, the Oriental, and the Yellow-billed magpie are just a few examples of this species.
There are several species of magpies, which belong to the family Corvidae. The following is a list of magpie species, organized by genus:
- Genus Pica
- Black-billed magpie (Pica hudsonia)
- Yellow-billed magpie (Pica nuttalli)
- Eurasian magpie (Pica pica)
- Korean magpie (Pica sericea)
- Taiwan blue magpie (Urocissa caerulea)
- Genus Cyanopica
- Azure-winged magpie (Cyanopica cyana)
- Iberian magpie (Cyanopica cooki)
- Genus Urocissa
- Sri Lanka blue magpie (Urocissa ornata)
- Red-billed blue magpie (Urocissa erythroryncha)
- White-winged magpie (Urocissa whiteheadi)
It’s important to note that the term “magpie” is sometimes used to refer to other species of corvids that are not technically magpies.
Magpie Appearance
The Black-billed magpie has a collection of black and white feathers. In addition, its wings feature feathers that are glowing bluish/green. The Eurasian magpie is very similar in appearance to the Black-billed magpie.
The Australian magpie has black and white feathers too. However, unlike the other two, it has white feathers running up the back of its neck. Plus, its bill is both white and black.
Magpies have tiny dark eyes that are always searching the environment. They have two dark feet with three thin toes pointing forward and one pointing backward. When these birds move, they take long, slow steps and seem to be strutting instead of just walking. This is another characteristic that has earned them a reputation for being aggressive birds.
Magpie birds usually grow to be around 19 inches long. Line up two-and-a-half pencils end to end, and you have the length of a 19-inch magpie. However, they can grow to be close to 2 feet long.
Magpies weigh approximately 6 ounces, which is a little bit lighter than a hamster you’d see at a pet store. The Eurasian magpie is the largest species of this bird weighing up to 9.6 ounces.
Evolution and Origins
Magpies are a group of birds that are found throughout the world, known for their striking black and white plumage, long tails, and raucous calls. The evolution and origins of magpies are fascinating, as they have a long history and have adapted to a wide range of habitats.
Magpies are part of the Corvidae family, which also includes crows, ravens, and jays. The family is believed to have originated in the Paleogene period, around 60 million years ago, and has since diversified into more than 120 species. Magpies are believed to have evolved from an ancestral crow-like bird, which lived around 17 million years ago.
The earliest known magpie fossils are from the Miocene epoch, which occurred around 20 million years ago. These fossils have been found in Europe and Asia, indicating that magpies have a long history in both regions. Over time, magpies diversified into various species, each adapted to its specific environment.
One of the most well-known magpie species is the Eurasian magpie (Pica pica), which is found throughout Europe and Asia. The Eurasian magpie has been the subject of many myths and legends and is often associated with good luck or bad omens. It is a highly intelligent bird, known for its problem-solving skills and ability to recognize itself in mirrors.
In North America, the black-billed magpie (Pica hudsonia) is a common species. It is found throughout the western United States and parts of Canada and is known for its long, wedge-shaped tail and distinctive call. The black-billed magpie is an adaptable species that can thrive in a variety of habitats, from grasslands to mountain forests.
Magpie Behavior
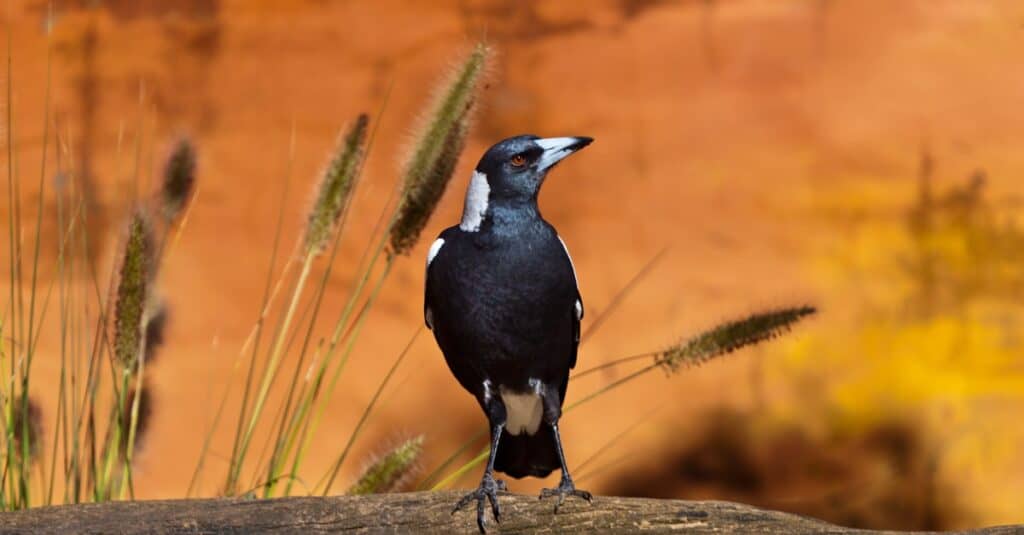

The aggressive behavior of the magpie is intended to protect its’s nest.
©iStock.com/paulacobleigh
A flock of magpies is referred to as a parliament, tribe, or mischief. Flocks of magpies are also called murders. Have you ever heard of a murder of crows? Magpies and crows are in the same family. So, there can be murders, or flocks, of both types of birds.
Generally, a flock is made up of a mating pair of magpies and their babies. So, a typical magpie flock would include about 8 birds. In colder areas, flocks of magpies are larger. This allows them to roost together to stay warm.
Living in a flock provides magpies with protection from predators such as hawks and owls. It’s not uncommon to see a flock of magpies work together to chase a predator away from a nesting area. Magpies also seek shelter from predators in dense forests and woods.
These are aggressive birds that are not afraid to land on deer, elk, and other animals to eat ticks from their fur. Also, they are familiar sights around farms, where they steal grain, seed, and other tidbits of food from inside the barn or off the ground. As a result, they are considered pests in many areas with farmland.
Habitat
Magpies make their home in different places throughout the world, including North America, parts of Europe, Africa, and Asia as well as in the southeastern Asian islands. They need a temperate climate to survive.
Magpies live in grasslands, meadows, and on the edges of forests. These birds look for food in open areas of land but live near dense forests so they can easily seek shelter from predators. Their nesting areas are usually found in shrubs or trees growing near rivers and streams. This gives the birds easy access to water without going far from their young.
Some magpies living in northern areas move slightly south when the cold weather season sets in. For instance, a Black-billed magpie living in the Rocky Mountains in Colorado may move to a lower elevation when the weather turns cold. However, they don’t stray far from their year-round home. For the most part, these birds don’t migrate.
Population
There are estimated to be over 5 million Black-billed magpies living in North America. Their official conservation status is Least Concern. Their population is holding steady though these birds face some threats. For instance, they are considered pests by some farmers because they steal seeds and grain from around barnyards. A farmer may put out poison to kill magpies that have invaded their property.
A few magpies in other parts of the world are categorized as Endangered. For example, the Asir magpie population is decreasing due to the loss of habitat. The Juniper forests in Africa where they live are being cleared.
In addition, the Javan Green magpie is Critically Endangered. The population of this magpie in southeast Asia is decreasing because they are trapped by humans in order to be sold as pets.
Scientists believe there are an estimated 19 million breeding pairs of Eurasian magpies. Their conservation status is Least Concern and their population is stable.
The Australian magpie has a conservation status of Least Concern as well and its population is increasing.
Diet

What do magpies eat? Magpies are omnivores so they aren’t limited to eating plants or animals. They eat whatever food source is most plentiful in the environment at the time. Grasshoppers, berries, nuts, beetles, caterpillars, and rodents are all on the menu.
These birds sometimes steal eggs and even chicks from the nests of other birds. Consequently, magpies are sometimes called nest predators.
In addition, magpies have been known to follow coyotes or foxes as they go out to hunt. This is so the birds can steal some of the meat from the animal killed by these predators.
For a full analysis of the magpie’s diet make sure to read our comprehensive guide, ‘What Do Magpies Eat? 25 Foods they Consume.’
Predators
Magpies have several predators including domestic cats, dogs, foxes, and owls. Also, they can have eggs as well as chicks stolen out of their nest by raccoons, hawks, weasels, and mink.
Magpies are bold birds that aren’t afraid to spend time around humans and residential neighborhoods. They steal food from trash cans and may even try to eat from a bird feeder. This activity makes them vulnerable to dogs and cats in the area.
Reproduction and Life Cycle

The breeding season for Black-billed magpies goes from March to July.
©iStock.com/Banu R
The breeding season for Black-billed magpies goes from March to July. Male magpies try to get the attention of females by showing off the glowing white feathers on their wings.
Once a male and female become a breeding pair, they are together until one of them dies. If one of the pair dies, the other magpie may find another mate, but that’s not a certainty.
A male and female magpie build a nest together. These birds create an unusually large nests out of sticks, grass, string, hair, vines, and mud. The average nest is 20 inches wide and 30 inches tall. Interestingly, the nest of a magpie has a canopy, or roof, made of sticks as well as two entrances. These birds sometimes build their nest as high as 30 feet up in the branches of a tree.
A female magpie lays from 6 to 9 eggs per clutch (group). It takes from 16 to 21 days for the eggs to hatch. Each egg is a little over an inch in length. While the female is sitting on the eggs, the male magpie looks for food to feed his mate.
A baby magpie is called a chick. Once it leaves the nest and begins to explore its environment, it’s known as a fledgling. These birds are born blind and without feathers. In the first week of life, the chicks grow a layer of downy feathers and their eyes open around day 10. Both the male and female magpies take turns bringing small insects and other food to their chicks. The baby magpies leave the nest when they reach about 25 days old.
Young magpies stay with their parents in the flock for about two years. Then, they are pushed out of the flock to form another group.
The average lifespan of a Black-billed magpie in the wild is 3.5 years for a male and 2 years for a female. Alternatively, a magpie in captivity can live to be 20 years old. The oldest magpie on record is a Eurasian magpie that lived to be 21 years and 8 months old.
As magpies get older they can develop many of the same respiratory issues as other birds. Also, they can take on parasites such as ectoparasites and lice that can contribute to shortening their life.
Zoos
• Visit and learn more about the Azure-Winged magpie at the Memphis Zoo.
• Visit the Los Angeles Zoo and Botanical Gardens to see the Yellow-Billed magpie.
• The Minnesota Zoo has an Oriental magpie on display to enjoy.
Magpie FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a magpie?
A magpie is a bird in the same family as crows and jays. It’s an omnivore that eats insects, rodents, fruits, nuts and more. There are at least 17 species of magpie living on different continents.
According to bird symbolism in western culture, magpies represent bad luck. However, in the bird symbolism embraced by eastern cultures, magpies represent good luck. Maybe they don’t represent either one!
What is a magpie known for?
Magpies are birds known for their bold personality and intelligence. They are also well-known for their calls and songs. Many birds have a song or a few calls, but magpies chatter, whistle, trill, and warble. These birds have even been known to mimic sounds around them such as wind chimes or a dog’s barking. Not surprisingly, when flocks or murders of magpies begin to call to one another it can get very loud!
Are magpies dangerous?
Magpies are not dangerous; however, they are territorial birds. This means they don’t like other animals to approach their nest. Oftentimes, when a predator such as a hawk or a raccoon tries to steal eggs from a magpie’s nest, a flock of magpies will try to chase the intruder away.
If a person ever got too close to a magpie’s nest, the bird may flutter and flap its wings trying to frighten the person away. The magpie would do this in an effort to protect its young even if the person meant no harm.
What is the difference between a magpie and a crow?
Crows and magpies are in the same family and they are both intelligent birds. Despite many similarities there are some differences between them.
Crows are smaller than magpies. A magpie has a tail that accounts for half of its body length. A crow’s tail is short making it smaller than a magpie.
Crows migrate in the fall season whereas magpies don’t migrate.
A crow’s body is covered in black feathers without any markings. Alternatively, a Black-billed magpie has a combination of black and white feathers along with green mixed in. Other species of magpie have feathers that are even brighter in color.
Are Magpies herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Magpies are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Magpies belong to?
Magpies belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Magpies belong to?
Magpies belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Magpies belong to?
Magpies belong to the class Aves.
What family do Magpies belong to?
Magpies belong to the family Corvidae.
What order do Magpies belong to?
Magpies belong to the order Passeriformes.
What genus do Magpies belong to?
Magpies belong to the genus Pica.
What type of covering do Magpies have?
Magpies are covered in Feathers.
In what type of habitat do Magpies live?
Magpies live in open woodlands, grasslands, and savannas.
What is the main prey for Magpies?
Magpies eat fruit, nuts, seeds, and insects.
What are some predators of Magpies?
Predators of Magpies include foxes, cats, and coyotes.
What are some distinguishing features of Magpies?
Magpies have black and white markings and long wedge-shaped tails.
How many eggs do Magpies lay?
Magpies typically lay 3 eggs.
What is an interesting fact about Magpies?
Magpies are found across Europe, Asia, and Africa!
What is the scientific name for the Magpie?
The scientific name for the Magpie is Pica Pica.
What is the lifespan of a Magpie?
Magpies can live for 8 to 15 years.
What is the Magpie's wingspan?
The Magpie has a wingspan of 52cm to 60cm (20in to 24in).
How fast is a Magpie?
A Magpie can travel at speeds of up to 20 miles per hour.
What are the differences between magpies and crows?
The main differences between magpies and crows are appearance, color, nesting, and behavior.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Christopher Perrins, Oxford University Press (2009) The Encyclopedia Of Birds