Countries that start with the letter D include the Democratic People’s Republic of China, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Denmark, Djibouti, Dominica, and the Dominican Republic. Read on to learn more about these amazing countries!
We’re here to answer the question that’s on everyone’s mind: just what are the six countries that start with D? What can you do with this information? We don’t know. Win a trivia game? Perhaps plan the next phase of your plan to visit all the world’s countries in alphabetical order. We just supply the information; it’s up to you how you use it. Just remember, with great knowledge comes great power.

1. Democratic People’s Republic of Korea
History of the DPRK
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea is the official name of the country most of us know as North Korea. Its formal name gives it a place on our list of countries that start with D. We’ll refer to it as the DPRK or North Korea interchangeably. Historically, Korea has at various times been divided into warring kingdoms, united as one kingdom, dominated by China, and colonized by Japan. Like its neighbors, it was never colonized by any of the European empires.
When Japan was stripped of its overseas possessions at the end of World War II, the Korean peninsula was divided into two zones. These included a southern, American zone of occupation and a northern zone for the Soviet Union, which shares a short border with North Korea. This was supposed to be a temporary arrangement. However, as the Cold War began to take shape, separate communist and democratic governments developed in the respective occupation zones.
In 1950, North Korea tried to end the stalemate by invading the South, but an international coalition led by the United States drove the troops back. Rather than stopping at the previous border, the Allies tried to reunite the whole peninsula, sparking an intervention by communist China that pushed them back south.
In 1953, the war ended in a stalemate, with a demilitarized zone separating increasingly well-armed antagonists on each side. North Korea today, under the leadership of Kim Jong Un, has developed a nuclear arsenal and intercontinental missile capability and takes a belligerent approach toward South Korea and its allies, especially the United States.
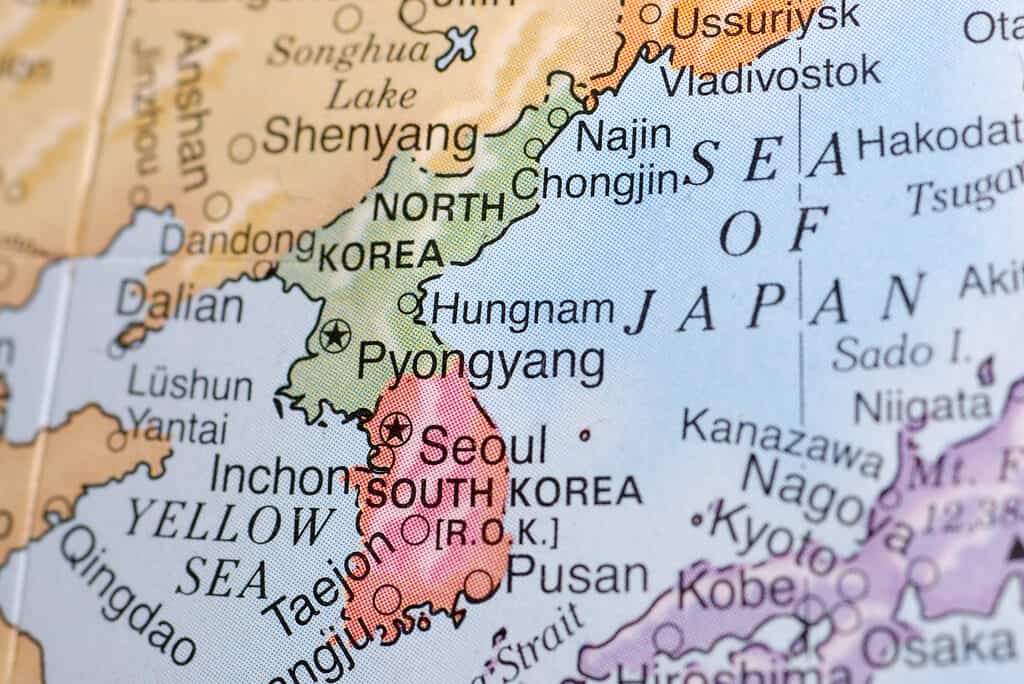
The Korean peninsula was divided into two countries after World War II.
©Kent Weakley/Shutterstock.com
Natural Environment of the DPRK
About 80% of the DPRK is mountains separated by deep valleys. Most of the country has a humid continental climate, with frigid winds from Siberia bringing heavy snow, and monsoon winds from the south bringing tropical rain. Some of the distinctive wildlife of North Korea includes over 500 species of birds, including the iconic white heron, cranes, the common pheasant, and over a million ducks and geese that winter there.
North Korean mammals include antelopes, raccoon dogs, weasels, badgers, and marten. The country has over 200 species of freshwater fish, including native species like the Korean taimen, Korean stumpy bullhead, Korean spotted hopper, south torrent catfish, and black shiner. North Korea’s environment is greatly threatened by pollution and extensive deforestation, which may have removed as much as 50% of the forest cover.
Additionally, severe food shortages have caused the population in times of famine to decimate wildlife in search of something to eat. North Korea’s environment still contains many diverse and endangered species. However conserving them with international assistance is difficult because of the government’s confrontational stance.
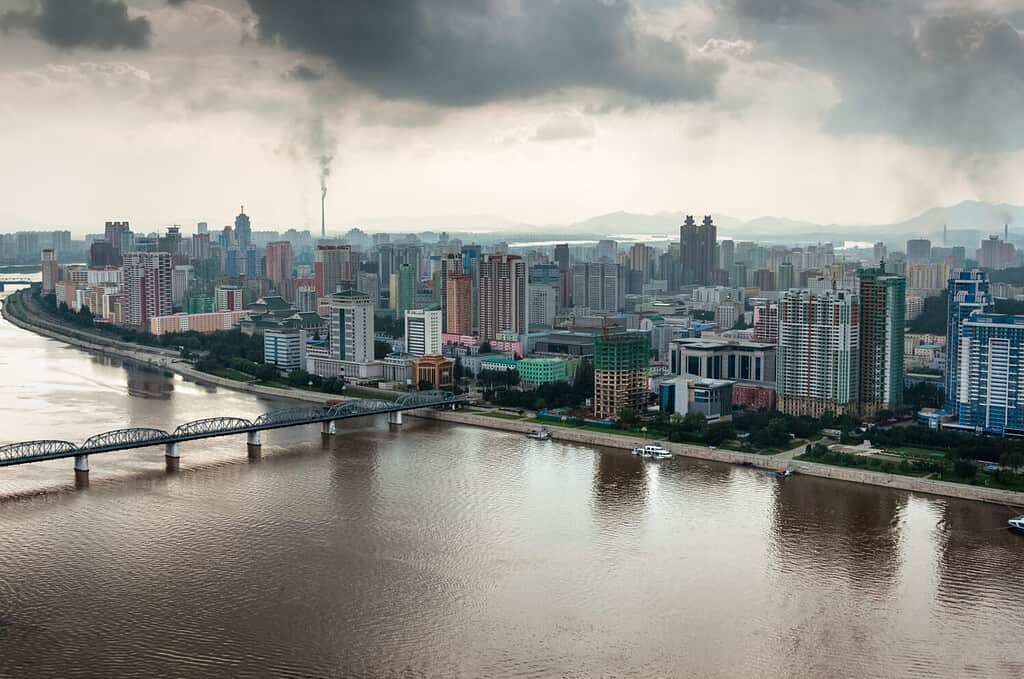

As seen in this photo of Pyongyang, the capital of the DPRK, pollution is a major environmental problem.
©Piu_Piu/Shutterstock.com
2. Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geography and History of the DRC
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is, alphabetically, the first of the modern countries that start with D. The DRC is an enormous country in south-central Africa, so big that if it sat on a map of Europe, it would reach from Stockholm to Istanbul and from France to Poland. Actually, it’s the 11th largest country in the world by land area. It’s not to be confused with the Republic of the Congo, both of which are named for the Congo River that dominates the local geography.
Despite its huge size, the country has only a small coast on the South Atlantic Ocean. Like so many ill-conceived country borders in Africa, this is the result of European colonization. After other countries had already claimed most of the coast, Belgium found a foothold at the mouth of the Congo River and went on to claim the vast river basin as the personal domain of King Leopold II.
The Belgians extracted rubber and other natural resources with unspeakable cruelty to the local population until they had a revolution in 1960 and achieved independence. With its 112 million people divided into 450 tribes speaking 240 different languages, peace and unity have been elusive in the DRC. The country has been in turmoil and armed conflict for virtually its entire history.
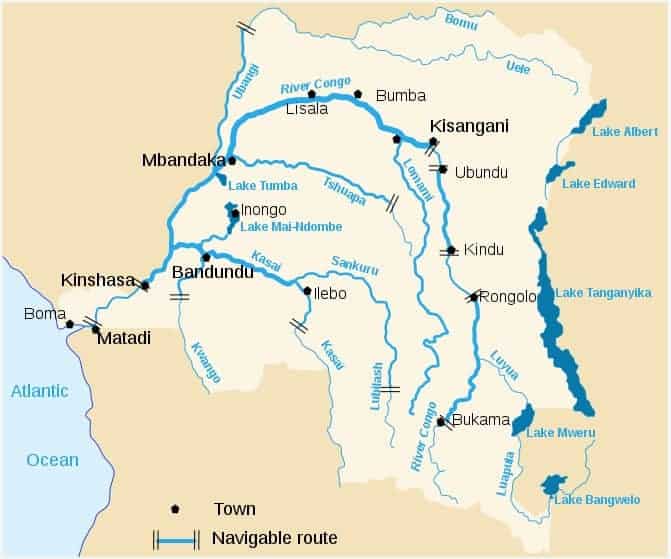
The enormous Congo River dominates the geography of the DRC.
©Kwamikagami, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Biodiversity in the DRC
It’s an incredible shame that such misery afflicts a truly remarkable country. Most of it is covered in a lush rainforest, the second-largest one in the world after the Amazon. There are highland plateaus in the south, mountains in the east, and grasslands in the northern part of the country. These habitats preserve iconic and endangered species such as chimpanzees, African forest elephants, mountain gorillas, and white rhinoceroses. The DRC is considered the most biodiverse country on the African continent. Its burgeoning population, political instability, and enormous but still not completely developed reserves of minerals and fossil fuels mean that some of the creatures in this unique habitat may struggle to survive the 21st century.
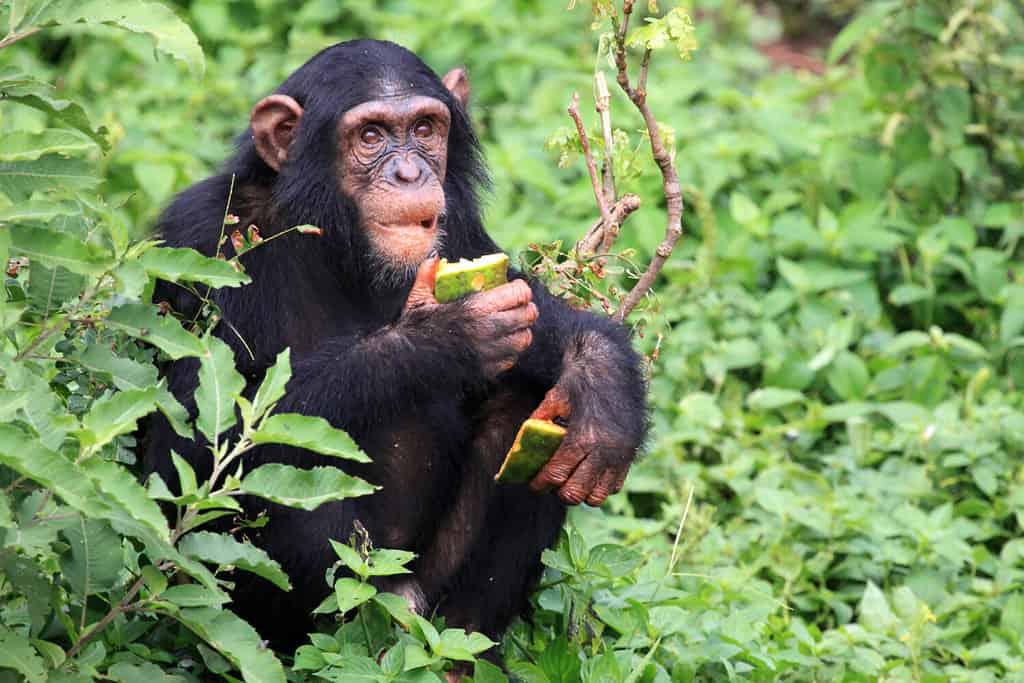

Chimpanzees are one of the vulnerable species today in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
©Sam DCruz/Shutterstock.com
3. Denmark
Denmark’s Land and People
Denmark is located on the Jutland peninsula and a cluster of neighboring islands north of Germany. It’s considered one of the Scandinavian countries and it controls the strategic entrance to the Baltic Sea. Denmark emerged as a united kingdom in the 700s and was at different times united with Norway and Sweden.
Denmark’s flag is the oldest in Europe and is the basis for the flags of its other Scandinavian neighbors. While the country is one of the smaller members of Europe, it also administers Greenland, the world’s largest island, as one of its territories. That makes Denmark the largest European landholder of territory in North America. It acquired the territory as part of its Viking history of exploration and conquest.
Back in the day, as the Roman Empire collapsed, the Danes and Jutes were among the tribes that flooded into the British Isles, leaving their mark on the language, culture, and ethnic mixture. During World War II, the Danes put their seafaring to use more constructively by evacuating their entire Jewish population to neutral Sweden in one night to save them from invading Nazis. Today, Denmark is a parliamentary democracy with a high standard of living, surrounded by allies, and focused on the well-being of its people, Europe, and the world.
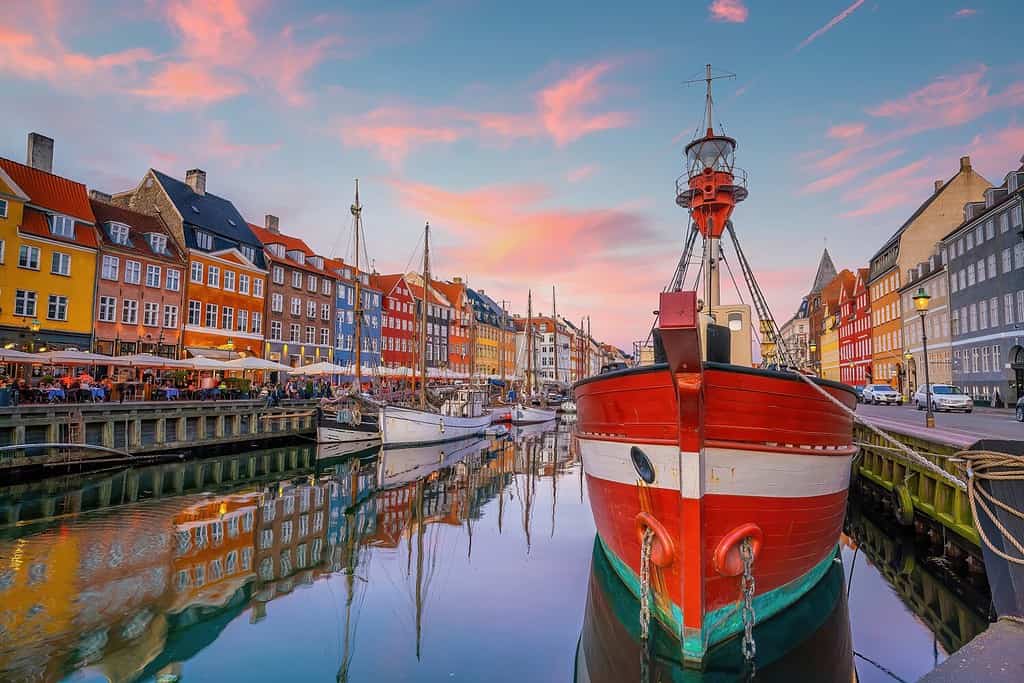

Denmark is a nation of many islands, so seafaring comes naturally. This is Copenhagen, the capital.
©f11photo/Shutterstock.com
Denmark’s Wildlife
It’s safe to say that most of the animals in Denmark are livestock today. The country has been farmed for centuries and does not have a high percentage of its land area in wild, natural spaces. Red deer and roe deer are the largest mammalian species found in forested areas. Grey wolves are the largest carnivores. Smaller mammals like the red fox, stoat, European otter, European badger, wild boar, and European polecat are in various stages of endangerment.
Denmark’s position on the sea makes fish a favorite food, as in the rest of Scandinavia. Among the many freshwater and saltwater species caught in Danish waters are the Atlantic mackerel, cod, eel, flatfish, perch, pike, pollock, salmon, and sea trout. Denmark is on the migratory route of a great many birds, which attract large numbers of birds of prey as well. Cuckoos, doves, ducks, geese, and grebes are just a few of the species that can be spotted in the thousands in season. All of this does not take into account Greenland with its own unique arctic environment. The most recognizable and endangered species in that part of Denmark’s territory is the adorable but scary polar bear.
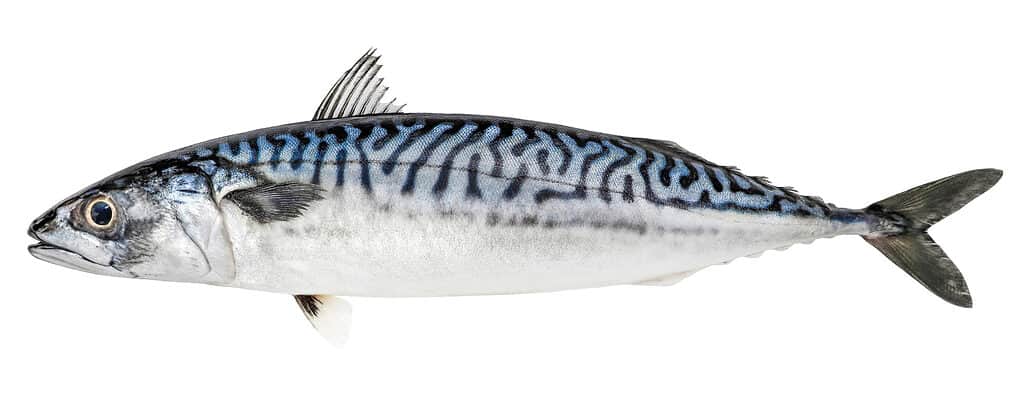

Denmark is well-known for its fishing industry. The Atlantic mackerel is a species caught in Danish waters.
©Nosyrevy/Shutterstock.com
4. Djibouti
Djibouti’s History and Geography
Djibouti is a small African country near the horn of Africa at the southern entrance to the Red Sea. Along with neighboring Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Somaliland, it was known in ancient times as the Land of Punt. During the colonial era, leaders in Djibouti made deals with France and became part of their empire in order to run a railroad to their port, making it surpass its rivals and become the main port for the whole region.
Today, the country’s port facilities continue to be its economic mainstay, as it is located at a chokepoint for trade and military activity in the Red Sea, and it is the primary port for landlocked Ethiopia. Since independence from France in 1977, Djibouti has capitalized on its geography to do lucrative deals with shipping companies and naval powers like the United States and China to build maritime facilities and maintain military bases in their country. Djibouti’s two main ethnic groups are the Somalis and the Afars. The official languages of the country are French and Arabic and the main religion is Islam.
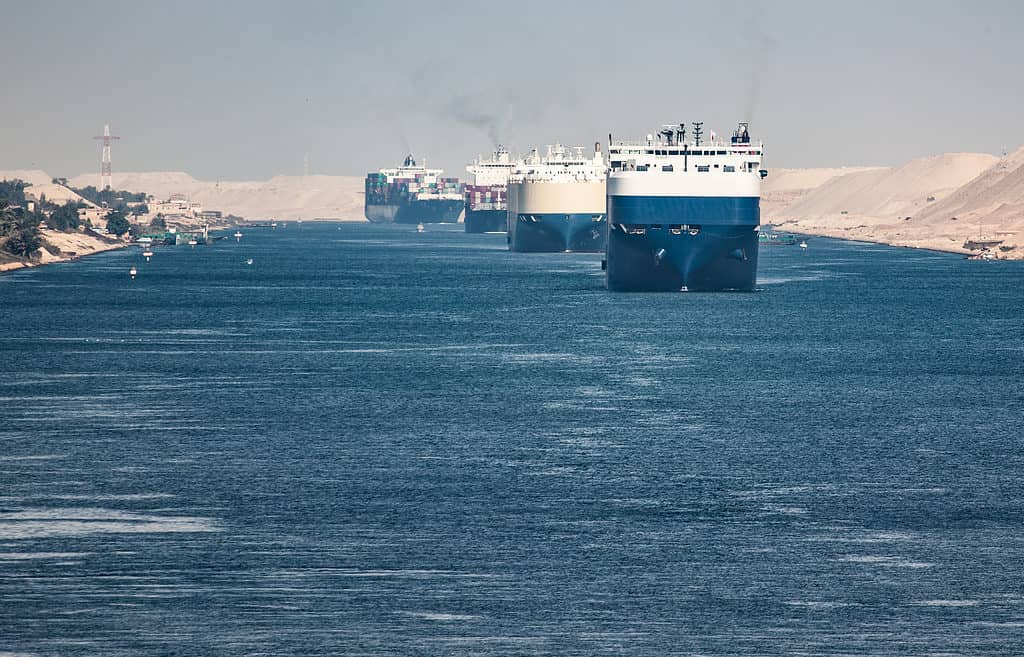

These cargo ships are traversing the Red Sea, where they’ll pass Djibouti to get to Asia and Australia.
©Dipix/Shutterstock.com
The Biosphere of Djibouti
Djibouti is in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa where two tectonic plates are pulling apart, promising to create a new ocean in the eons to come. As a consequence, Djibouti’s Lake Assal has the lowest elevation of any site in Africa. Southern Djibouti is covered by the Grand Bara desert. Its tallest mountain is a 6,564-foot peak in the Mousa Ali range. Most of the country consists of flat grasslands. Temperatures are high and less than 1% of the country is forested.
However, the forest that does exist in the mountains is home to most of the country’s animal species. These include various species of antelope, gazelles, zebras, baboons, and warthogs. Djibouti has had a hunting ban on endangered gazelles since 1970, which has helped these species rebound. Offshore, dugongs, green turtles, and hawksbill turtles live along the coast. Farther out to sea, Djibouti is part of the vast coral forest of the Red Sea, which so far has been able to survive the effects of heavy sea traffic in one of the busiest sea lanes in the world.
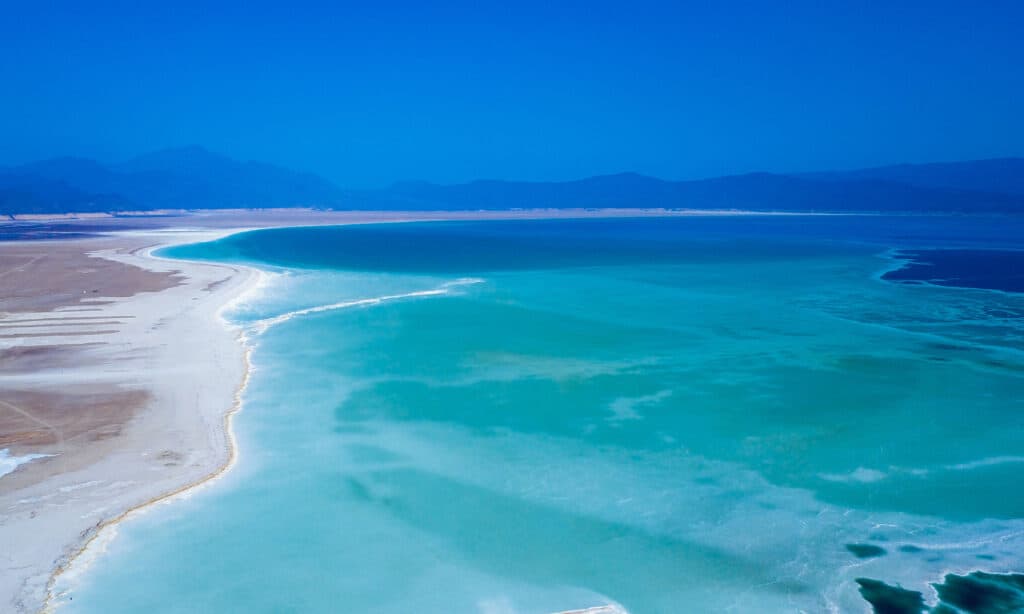

Lake Assal in Djibouti has the lowest elevation of any place in Africa.
©iStock.com/Dave Primov
5. Dominica
The Land and Its People
Dominica is a Caribbean Island country that is part of the Windward Islands chain. It was settled in ancient times by the Arawak tribe of South America but in the 17th century was colonized by the French. France was responsible for bringing large numbers of African slaves to the islands to work in coffee plantations that did well there in the island’s volcanic soil. The British took it over after they defeated France in the Seven Years’ War, a conflict that also saw France lose colonies in Canada and India.
As an independent nation since 1978, Dominica today shows the cultural influences of Latin America, Europe, and Africa in a unique blend that’s all its own. Like other islands in the region, it is a popular destination for international tourists, though it is loved for its rainforest and waterfalls, rather than beaches or luxury resorts.
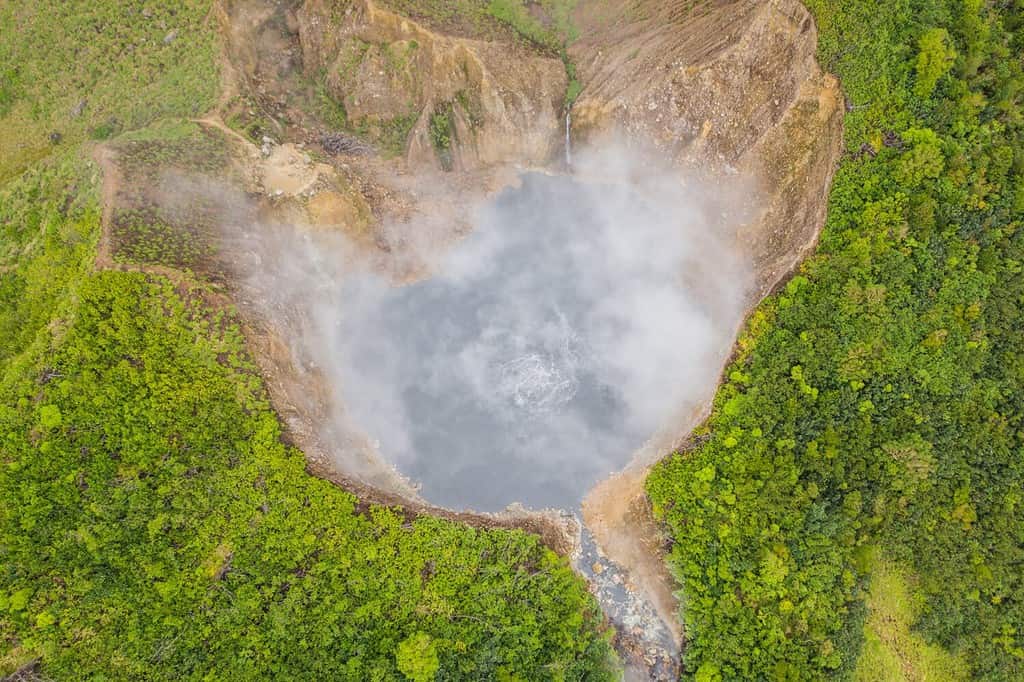

Dominica is still geologically active. This is Boiling Lake, the world’s second-largest hot spring.
©JibiBrown/Shutterstock.com
The Nature Island of the Caribbean
Because Dominica has such a verdant natural environment, it has been called the “nature island of the Caribbean.” Parts of the western coastal regions are dry, but much of the rest of this mountainous volcanic island is covered in dense rainforests. Still geologically active, Dominica is also home to the world’s second-largest hot spring, Boiling Lake.
Among the unique species on the island, one of the most intriguing, and most endangered, is the national bird, the Sisserou parrot. This beautiful bird has green and purple feathers. Dominica has included this bird on its national flag, making it one of only two countries in the world to use purple on its flag. Another parrot, the red-necked parrot, is also critically endangered due to logging and periodic hurricane damage to its habitat.
Dominica is the last place on Earth where the Lesser Antilean iguana lives in the wild. Additionally, the sea surrounding Dominica is rich in marine life, including a great many species of whales and dolphins. Whale-watching is a major tourist attraction for the local economy, due to the island’s resident sperm whale population.
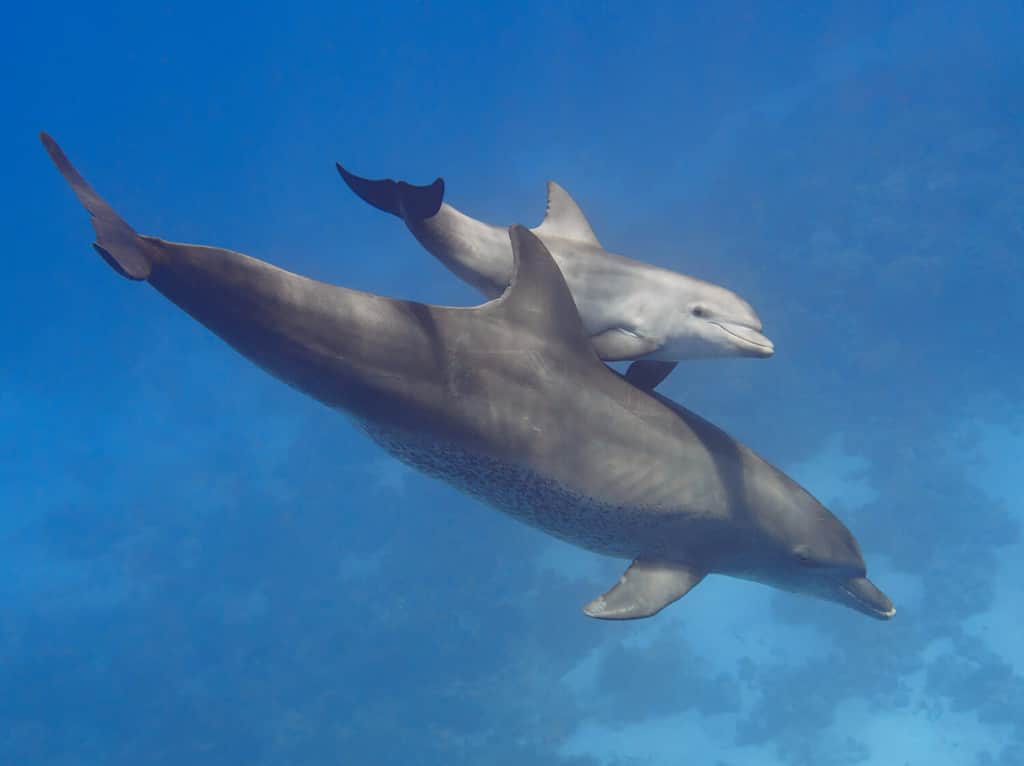

Bottlenose dolphins are one of the marine species that swim in the waters near Dominica.
©vkilikov/Shutterstock.com
6. Dominican Republic
History of the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is the last of our countries that start with D. It’s a Caribbean country that shares the island of Hispaniola with Haiti. Christopher Columbus landed there in 1492 and claimed the island for Spain, although it already had an organized and developing Taino indigenous population. As the Spanish colonized the island, most of the original inhabitants perished from disease and genocidal violence, but those who survived mixed with the Spanish and African slave populations.
This ethnic mixture is what makes up most of the population of the Dominican Republic today. Economically and politically, the Dominican Republic is more stable than neighboring Haiti, which was colonized by France. Both sides of the island are subject to earthquakes and hurricanes that periodically set back progress in development.

The Dominican Republic is a beautiful and popular international tourist destination.
©Lena Serditova/Shutterstock.com
Animals of the Dominican Republic
The waters around the Dominican Republic are popular with sport fishermen. Anglers can catch mahi mahi, marlin, sailfish, swordfish, yellowfin tuna, and wahoo there. The country’s rivers and coastal areas have West Indian manatees that can reach over 1,000 pounds. On land other vulnerable species in the Dominican Republic are the rhinoceros iguana found only on Hispaniola, and the Hispaniolan hutia, a rat-like creature related to the nutria. Boas and a handful of other non-venomous snakes live on the island. Among the many bird species, are cuckoos, doves, flamingoes, hummingbirds, guineafowl, parrots, and many others.
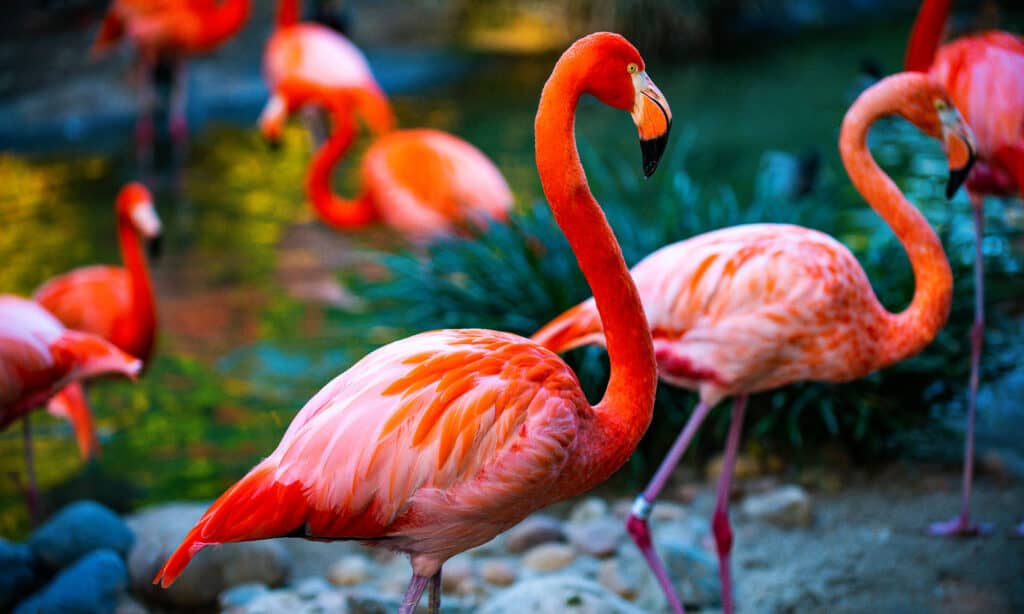

Flamingoes are some of the exotic bird species found in the Dominican Republic.
©Volodymyr TVERDOKHLIB/Shutterstock.com
Comparison of Countries That Start with D
So, those are the five countries in the world that start with D, scattered across Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Caribbean. Now let’s see how they compare with a few stats. Notice that although Greenland is a territory of Denmark, it is autonomous and will likely become a separate nation one day. That’s why it is usually not included in statistics about the size and population of Denmark. Another peculiarity is figuring out when exactly Denmark became independent. It went through various phases of independence, being united with Norway and Sweden. But it first emerged as a united Danish kingdom from its tribal roots at an unspecified point in the 700s, so that’s the date we’re going with.
The Most Populated Country That Starts with D
The Democratic Republic of the Congo wins the contest for the most populated country on our list. Its population of 111 million is almost as large as Mexico’s.
| Country | Population | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 111,859,928 |
| 2. | Democratic People’s Republic of Korea | 26,072,217 |
| 3. | Dominican Republic | 10,694,700 |
| 4. | Denmark | 5,935,619 |
| 5. | Djibouti | 957,273 |
| 6. | Dominica | 72,412 |
The Largest Country That Starts with D
Again, the Democratic Republic of the Congo wins for the largest land area of any of the countries that start with D. It’s larger than Saudi Arabia and almost as big as Algeria.
| Country | Land Area (sq. mi.) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 905,567 |
| 2. | Democratic People’s Republic of Korea | 46,540 |
| 3. | Dominican Republic | 18,792 |
| 4. | Denmark (without Greenland) | 16,580 |
| 5. | Djibouti | 8,958 |
| 6. | Dominica | 290 |
The Oldest Country That Starts with D
Denmark goes way back into the Viking days, with a founding point sometime in the 700s.
| Country | Independence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Denmark | AD 700s |
| 2. | Dominican Republic | 1821 |
| 3. | Democratic People’s Republic of Korea | 1948 |
| 4. | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 1960 |
| 5. | Djibouti | 1977 |
| 6. | Dominica | 1978 |
The Youngest Country That Starts with D
Dominica is the youngest country that starts with D. When it got its independence in 1978, the disco and bell bottom era was just getting started.
| Country | Independence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dominica | 1978 |
| 2. | Djibouti | 1977 |
| 3. | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 1960 |
| 4. | Democratic People’s Republic of Korea | 1948 |
| 5. | Dominican Republic | 1821 |
| 6. | Denmark | AD 700s |
So, which country that starts with D would you like to visit, or maybe even move to? Which has the most interesting wildlife to you? So many questions, so little time! Hopefully, we’ve satisfied most of your curiosity; that is, until you move on to countries that start with E.
Summary of the 6 Countries That Start With D
| Country | |
|---|---|
| 1. | Democratic People’s Republic of Korea |
| 2. | Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| 3. | Denmark |
| 4. | Djibouti |
| 5. | Dominica |
| 6. | Dominican Republic |
The photo featured at the top of this post is © Dashu Xinganling/Shutterstock.com
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.






