
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes known for their distinctive rattles at the end of their tails. Although found across the American continent, they’re particularly abundant in California, where they’re essential to the state’s ecosystem.
With their fearsome reputation, rattlesnakes have captured the imagination of humans for centuries. But despite their notoriety, rattlesnakes are often misunderstood and unfairly vilified.
Today, we discover the largest rattlesnake ever caught in California. We also provide a comprehensive overview of rattlesnakes in California. The overview includes their identification, habitat, behavior, interactions with humans, conservation, and management.
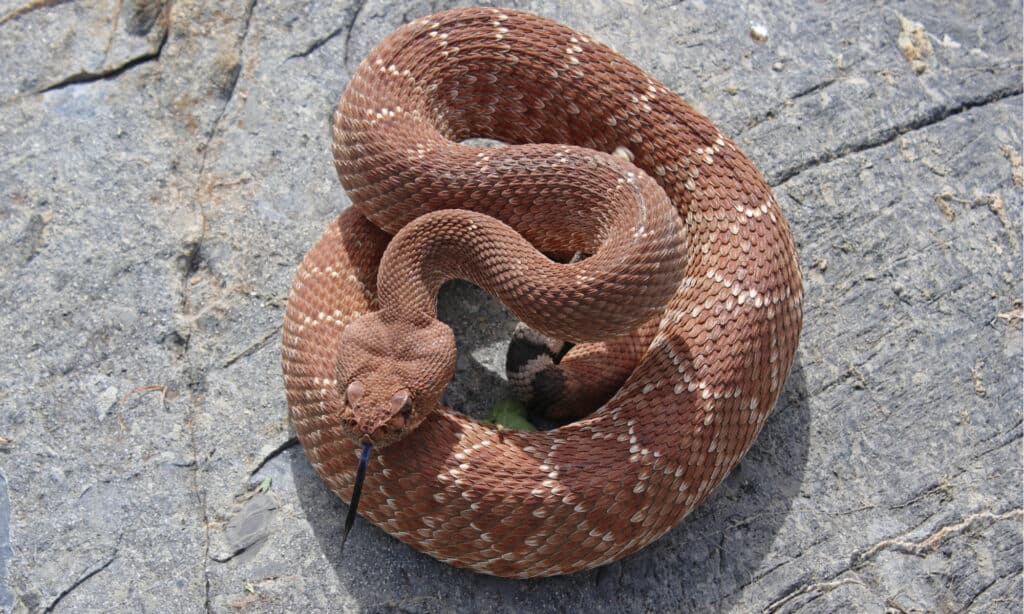

Red diamondback rattlesnakes coil up, rattle, and may strike when they’re threatened.
©Creeping Things/Shutterstock.com
The Largest Rattlesnake Ever Caught In California
Willow Godshalk spotted the largest rattlesnake ever in the history of California on July 27, 2018. Godshalk spotted the 6 ft. long rattlesnake that nearly attacked her dog on Mariposa Street in Santee, California.
Godshalk saw her dog running around when she noticed the massive red diamond rattlesnake. The snake was fed and later released back into the wild.
The Largest Rattlesnake Ever Caught Worldwide
The largest rattlesnake ever caught on record was an eastern diamondback rattlesnake (scientific name: Crotalus adamanteus). It measured 7 ft., 8 in. long, and weighed 34 lbs. Hunter Rutledge shot the massive snake in 1946.
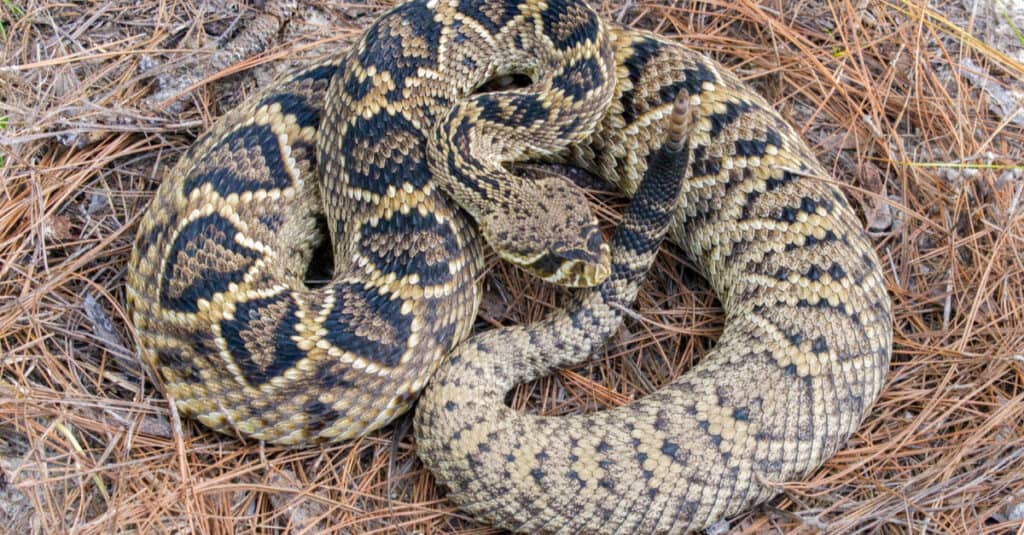

The largest rattlesnake ever caught on record was an eastern diamondback rattlesnake.
©Chase D’animulls/Shutterstock.com
About Rattlesnakes
Identifying rattlesnakes can be challenging. But there are several physical characteristics and behavioral cues to look for.
Physical Characteristics
Rattlesnakes have triangular-shaped heads that are much wider than their necks. They also have heat-sensing pits between their eyes and nostrils that help them locate prey.
In terms of coloration, rattlesnakes vary depending on the species. But many have a distinctive diamond-shaped pattern along their backs.
Additionally, some, like the Mojave rattlesnake, have shorter, stubbier tails that can make their rattles less prominent.
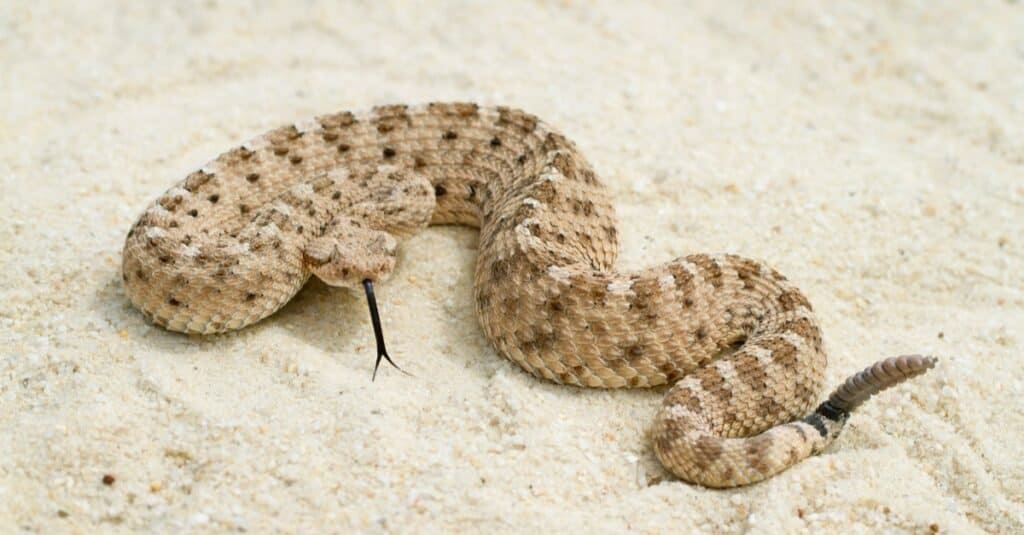

The venomous Sidewinder Rattlesnake has a unique sideways movement and distinctive horns above its eyes.
©Mark_Kostich/Shutterstock.com
Identifying Different Species Of Rattlesnakes
There are more than 30 different species of rattlesnakes in North America. Identifying them can be challenging. However, you can safely identify and appreciate rattlesnakes in their natural habitats by learning to recognize these physical characteristics and behavioral cues.
- The western diamondback rattlesnake. This has large, diamond-shaped scales on its back.
- The sidewinder rattlesnake. It has a unique sideways movement and distinctive horns above its eyes.
- The timber rattlesnake. It has a series of dark bands across its body.
- The prairie rattlesnake. It has a distinctive rattle that sounds like a buzzing insect.
Note: Some non-venomous snakes, like the gopher snake, may resemble rattlesnakes in appearance. So, it’s crucial to learn to distinguish between the two.
Distinguishing Rattlesnakes From Non-Venomous Snakes
One way to distinguish rattlesnakes from non-venomous snakes is by looking at their pupils. Rattlesnakes and other pit vipers have elliptical pupils, while most North American non-venomous snakes have round pupils. Of course, the venomous Sonoran coral snake has round pupils, so this is only one factor.
Most rattlesnakes also have very large heads with an oddly thin necks — something gopher snakes lack.
Additionally, rattlesnakes have a distinct heat-sensing pit between their eyes and nostrils, while non-venomous snakes don’t.
Finally, rattlesnakes have a rattle at the end of their tails, which non-venomous snakes lack.
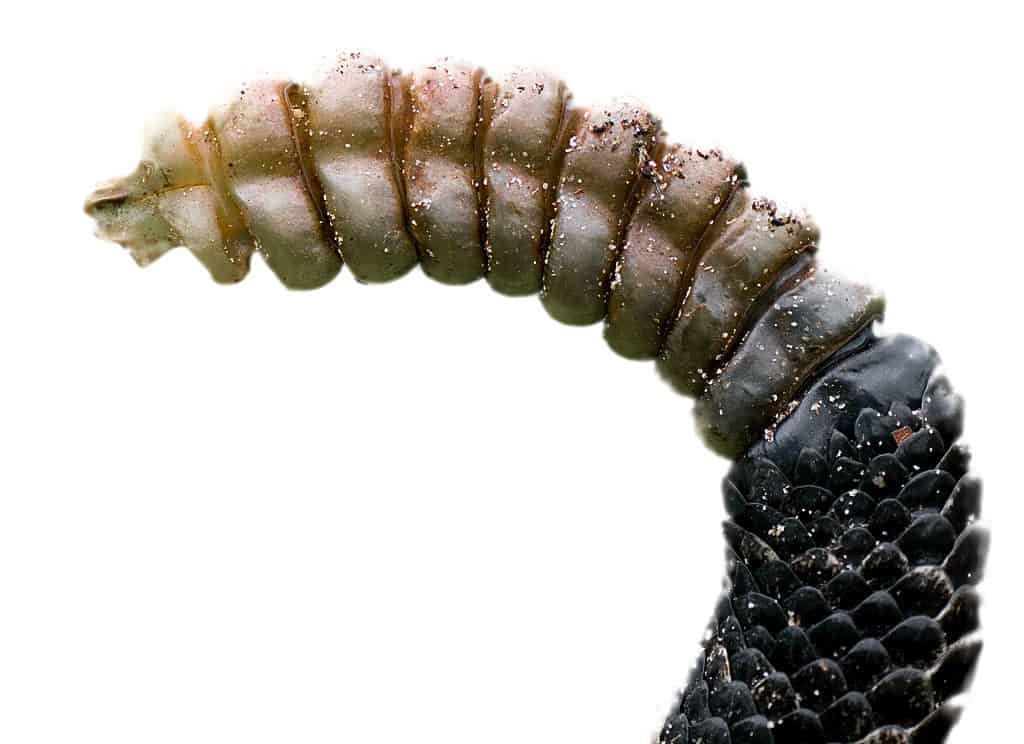

Rattlesnakes are easy to identify by the rattle at the end of their tail. Listen carefully when hiking and you may hear it.
©Chase D’animulls/Shutterstock.com
Rattlesnake Predators
While rattlesnakes are known for their venomous bite, they aren’t immune to predation. Several predators in California are known to feed on rattlesnakes. Let’s explore some of California’s most common rattlesnake predators and how they manage to hunt and consume these venomous snakes.
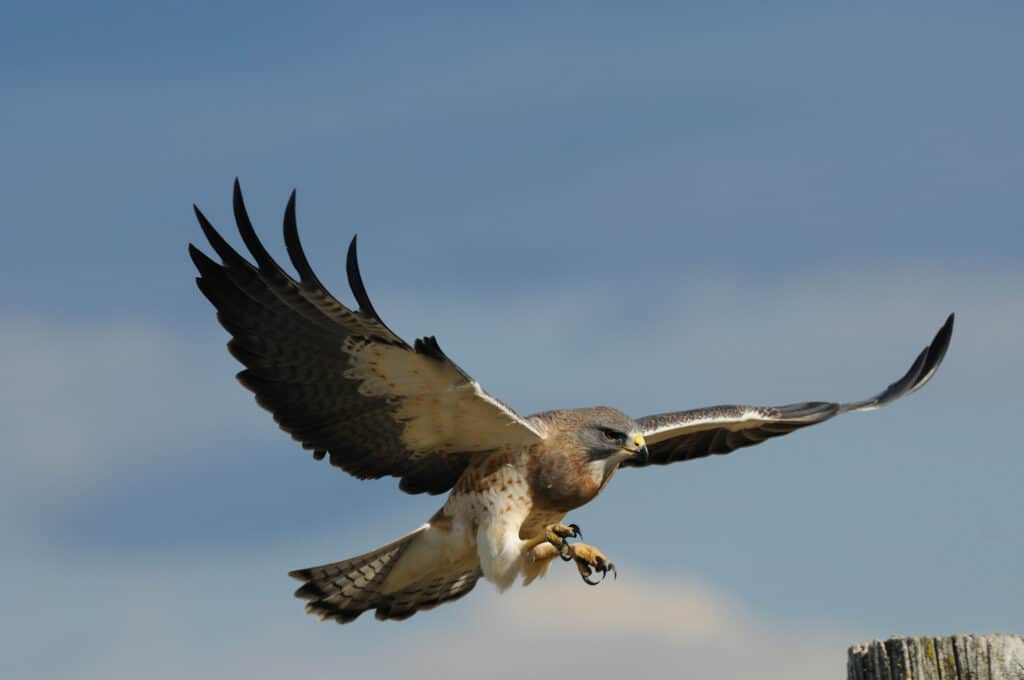

Hawks are some of California’s most common rattlesnake predators.
©Rob McKay/Shutterstock.com
Birds Of Prey
Birds of prey, such as hawks and eagles, are some of California’s most common rattlesnake predators.
These birds have keen eyesight and can spot rattlesnakes from high up in the sky. Once they spot a snake, they swoop down and grab it with their talons.
Sometimes, they kill the snake by dropping it from a height before consuming it.
Coyotes
Coyotes are another common rattlesnake predator in California. These canines are known for their keen sense of smell. They can locate snakes using their olfactory senses.
Once they find a snake, they bite and kill it or grab it in their jaws and shake it to death. Coyotes can consume the entire snake, including the venomous head.
Bobcats
Bobcats are skilled hunters that can take down a variety of prey, including rattlesnakes.
These felines use their excellent vision and stealth to stalk and pounce on snakes. They will often grab the snake behind the head and deliver a quick, fatal bite to the neck.
Like coyotes, bobcats, including the venomous head, can eat the entire kill.
Other Snakes
Believe it or not, some snakes are known to prey on other snakes.
In California, the king snake is a common predator of rattlesnakes. These non-venomous snakes are immune to rattlesnake venom and will actively seek out and consume these venomous snakes.
King snakes overpower rattlesnakes by constricting them and delivering a fatal bite to the head.
Humans
Although not natural rattlesnake predators, humans are responsible for most rattlesnake deaths in California.
Humans often kill rattlesnakes out of fear or perceived threat.
Habitat And Distribution

Rattlesnakes adapt to a variety of habitats, from deserts to forests.
©iStock.com/Banu R
Rattlesnakes are found throughout North and South America. They’re particularly abundant in California.
They’re adapted to a variety of habitats, from deserts to forests. They can be found at elevations ranging from sea level to over 11,000 ft.
Habitat
In California, rattlesnakes are found in various habitats, including:
- Deserts
- Grasslands
- Chaparral
- Forests
They’re often associated with rocky outcroppings, where they can bask in the sun and hide from predators.
Some species like the sidewinder rattlesnake, are adapted to living in sandy environments. They have evolved a unique sideways movement to navigate the loose terrain.
Distribution
Rattlesnakes are found throughout California, with the highest species diversity in the southern part of the state.
Some of the most common species in California include:
But you’ll find other species, like the Mojave rattlesnake and the northern Pacific rattlesnake, in more specific regions of the state.
It’s important to note that the distribution of rattlesnakes can change depending on factors such as:
- Climate
- Habitat
- Human activity
For example, in recent years, some species of rattlesnakes have been expanding their ranges northward due to changes in climate patterns.
Conversely, habitat destruction and fragmentation can lead to declines in rattlesnake populations and restrict their distribution.
Understanding rattlesnakes’ habitat and distribution is vital for conservation efforts and public safety. By knowing where rattlesnakes are likely to be found, people can take appropriate precautions when hiking or engaging in other outdoor activities.
Additionally, protecting and preserving rattlesnake habitats is crucial for maintaining healthy populations of these important species.
Behavior And Diet
Rattlesnakes are fascinating animals with unique behaviors and diets. Understanding their behavior and diet can help people appreciate and coexist with these important predators.
Behavior
Rattlesnakes are primarily active during the day but may also be active at night in hot weather. They’re generally solitary animals, although they may congregate in certain areas, such as communal den sites. Some rattlesnake species may exhibit co-parenting and other social behaviors, typically near their dens. During the cooler months, rattlesnakes may enter a brumation state, similar to hibernation.
When threatened, rattlesnakes often assume a defensive posture, coiling their bodies and shaking their rattles as a warning. However, if provoked, they may strike, delivering a venomous bite.
But rattlesnakes are typically not aggressive and try to avoid humans and other animals if given the opportunity.
Diet
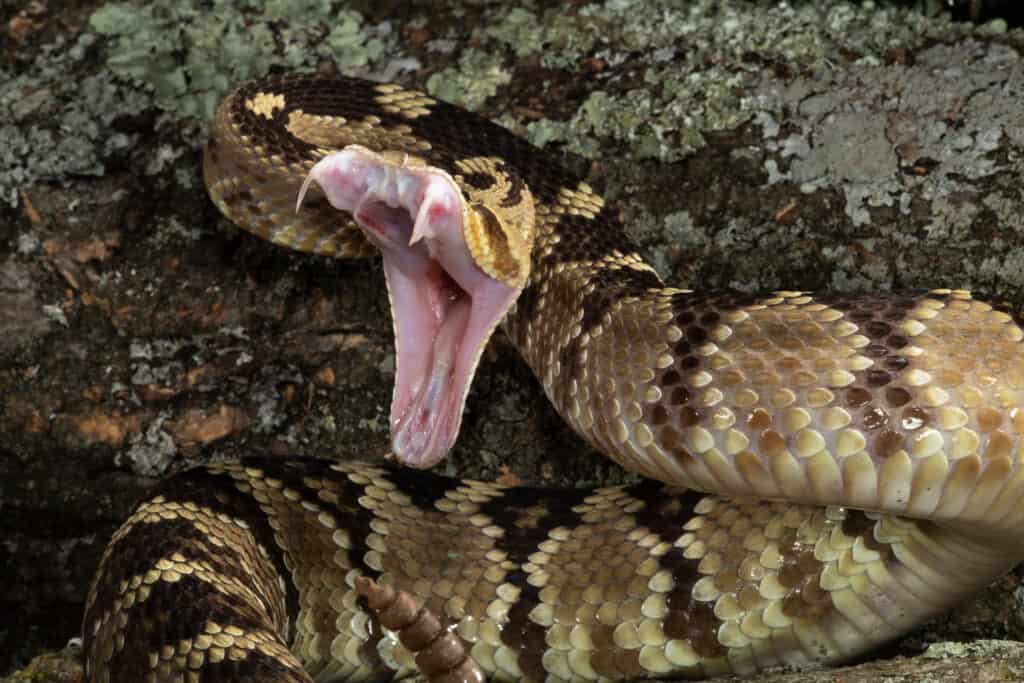

Rattlesnakes are carnivorous and primarily eat small mammals.
©Joe McDonald/Shutterstock.com
Rattlesnakes are carnivorous and primarily eat small mammals like mice, rats, and ground squirrels. However, they are also known to eat birds, lizards, and other snakes. Rattlesnakes use their heat-sensing pits to detect prey. They then strike with lightning-fast speed, injecting venom into the potential prey. Finally, they track their prey using their sense of smell and swallow it whole.
Interactions With Humans
As predators, rattlesnakes are essential to the ecosystem. But their interactions with humans can sometimes lead to conflicts.
Bites
Rattlesnake bites are relatively rare. But they can be dangerous if not treated promptly.
Most bites occur when humans accidentally step on or near a rattlesnake or attempt to handle or kill one.
Symptoms of a rattlesnake bite can include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Difficulty breathing
Anyone who a rattlesnake bites should seek medical attention immediately.
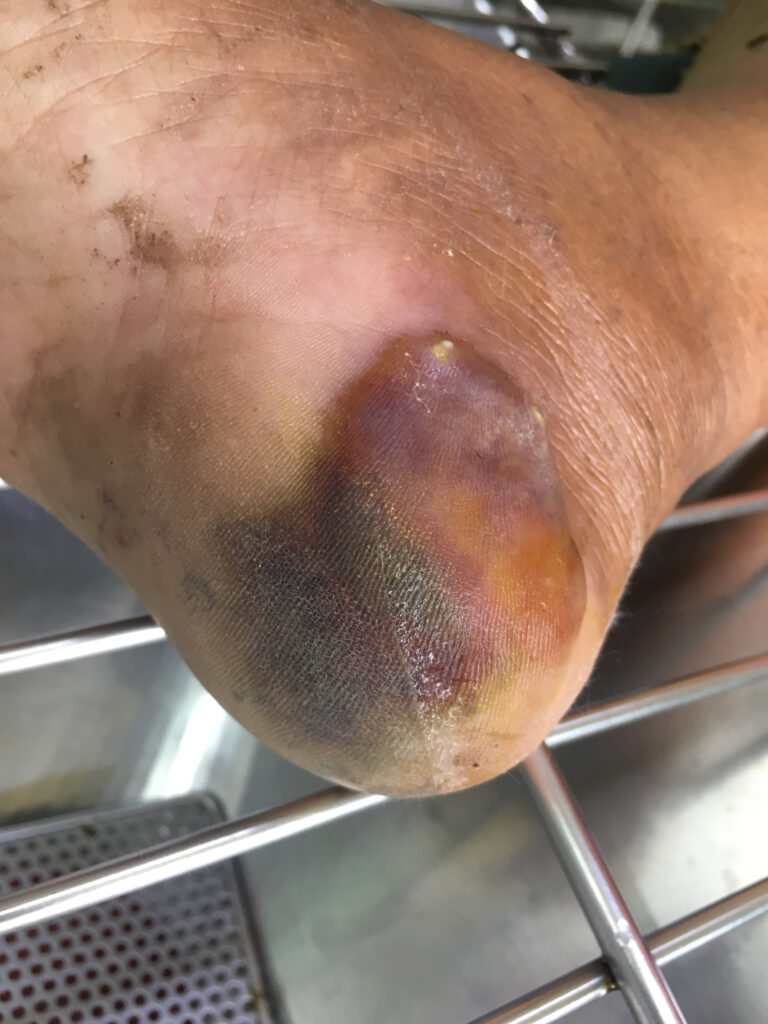
Most bites occur when humans accidentally step on or near a rattlesnake or attempt to handle or kill one.
©Chuanpit/Shutterstock.com
Conservation
As earlier noted, rattlesnakes are essential to the ecosystem. Consequently, protecting their populations is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems.
But habitat loss, fragmentation, and persecution by humans have led to declines in rattlesnake populations in many areas.
Conservation efforts, such as habitat restoration and public education, can help protect rattlesnakes and their habitats.
Public Education
Public education is one of the best ways to minimize conflicts between humans and rattlesnakes. By learning to recognize the warning signs of rattlesnakes and respecting their space, people can avoid accidentally encountering or provoking these animals.
Additionally, educating people on the importance of rattlesnakes in the ecosystem and the dangers of attempting to handle or kill them can help reduce the incidence of bites.
Management
In some areas, rattlesnake populations may need to be managed to minimize conflicts with humans. This can include relocating rattlesnakes from populated areas or using barriers to prevent them from entering areas where people are present.
There should be careful planning and execution for management to minimize harm to both humans and rattlesnakes.
Conservation And Management

Habitat loss, fragmentation, and persecution by humans have led to declines in rattlesnake populations in many areas.
©melissamn/Shutterstock.com
Conservation and management efforts are crucial for protecting rattlesnake populations and minimizing conflicts with humans. Here are some of the key strategies for rattlesnake conservation and management.
Habitat Protection
Protecting the habitats that rattlesnakes depend on is crucial for maintaining healthy populations. This can include efforts to restore and preserve natural habitats and create protected areas where rattlesnakes can thrive without interference from humans.
Enlightening Communities
Enlightening communities is crucial in minimizing conflicts between humans and rattlesnakes. This can include teaching people:
- How to recognize the warning signs of rattlesnakes
- How to safely coexist with these animals
- Why they are important for the ecosystem
Management Strategies
Management strategies may sometimes be necessary to minimize conflicts with humans. This can include:
- Relocating rattlesnakes from populated areas
- Using barriers to prevent them from entering areas where people are present
- Using snake aversion training to teach dogs to avoid rattlesnakes
Research
Continued research on rattlesnake populations and behavior can help inform conservation and management efforts. This can include studies on:
- Rattlesnake habitat use
- Population dynamics
- The effects of human activities on these animals
Collaboration
Collaboration between scientists, government agencies, and the public is essential for effective rattlesnake conservation and management.
By working together, we can develop and implement strategies that protect both human safety and the health of rattlesnake populations.
Other Record-Breaking Snakes
The biggest anaconda ever found was said to measure 33 feet in length, 3 feet in width at its widest point, and weigh approximately 880 lbs.
It was discovered at a construction site in Brazil, but unfortunately, it met its demise either through a controlled explosion or by construction workers who encountered it after its emergence. Regrettably, humans were responsible for killing the largest anaconda ever recorded.
The reported size of the largest anaconda could not be verified accurately due to the lack of proper measurement or recording. Although a video of the snake was available, the authenticity of the footage could not be confirmed as videos can be manipulated, and perspectives can be misleading.
There have been other alleged cases of record-breaking anacondas, but without substantial evidence or references to support them. According to one claim, the longest and heaviest snake ever discovered measured 27.7 feet in length, had a girth of 3 feet, and weighed more than 500 lbs.
Key Takeaways
Rattlesnakes are essential to California’s ecosystems, serving as top predators and playing crucial roles in maintaining biodiversity. But their interactions with humans can sometimes lead to conflicts. This makes understanding their behavior, habitat, and conservation needs crucial.
Conservation and management efforts are important to protect rattlesnakes and minimize conflicts with humans. These efforts can include habitat protection, community enlightenment, and careful management strategies. By working together to protect rattlesnakes, we’ll ensure they continue to play vital roles in California’s ecosystems for generations to come.
Humans need to learn how to coexist with rattlesnakes and appreciate their place in the natural world. By respecting their space and taking steps to avoid conflicts, we can protect both human safety and the health of our ecosystems.
Where Is California Located On A Map?
Santee is located in San Diego County, California, and is just 18 miles from the Pacific Ocean. The state of California is located in the Western United States along the Pacific Coast. It is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the west, Oregon to the north, Arizona, and Nevada to the east, and the Mexican state of Baja California to the south.
Here is California on a map:
The photo featured at the top of this post is © Creeping Things/Shutterstock.com
Discover the "Monster" Snake 5X Bigger than an Anaconda
Every day A-Z Animals sends out some of the most incredible facts in the world from our free newsletter. Want to discover the 10 most beautiful snakes in the world, a "snake island" where you're never more than 3 feet from danger, or a "monster" snake 5X larger than an anaconda? Then sign up right now and you'll start receiving our daily newsletter absolutely free.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.






