Get ready to test your knowledge of the human body and mind with this fascinating quiz! From anatomy to psychology, this quiz covers a wide range of interesting facts about what makes us human.
So, put on your thinking cap, and let’s see how much you know about the complexities of the human species:
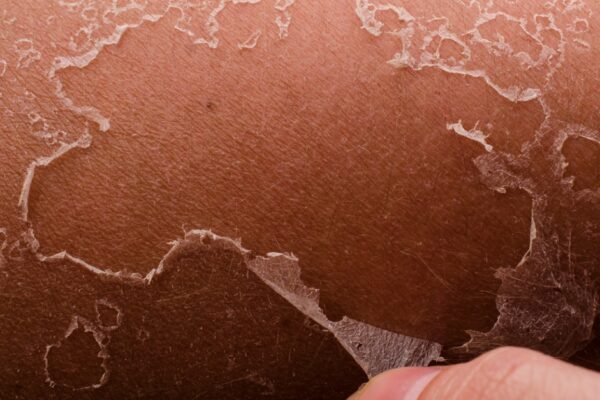
What is the Largest Organ in the Human Body?
The largest organ in the human body is the skin. It covers the entire body, including all its internal organs, and serves as the first line of defense against infection, injury, and harmful substances.
The skin is also responsible for regulating body temperature, producing vitamin D, and providing a sense of touch. It is estimated that the average adult’s skin weighs about 6 pounds and has a surface area of about 20 square feet.
The skin is composed of multiple layers, each with its own specific function. The outermost layer, the epidermis, is responsible for protecting the body and regulating the amount of water lost through the skin. The second layer, the dermis, contains sweat glands, hair follicles, and oil glands, among other structures. Finally, the subcutaneous layer is composed of fat and connective tissue provides insulation and helps regulate body temperature.
Furthermore, the skin is an incredibly important and complex organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is essential to take good care of your skin by using sunscreen, moisturizing regularly, and avoiding harmful substances that can damage it.
What is the Difference Between Homo Sapiens and Neanderthals?
Homo sapiens and Neanderthals are two closely related species of early humans that lived in the Pleistocene epoch. While they share a common ancestry, there are several key differences between the two species.
- Anatomy: Neanderthals had a more robust and muscular build compared to Homo sapiens, with a larger skull and brow ridge, shorter limbs, and a wider pelvis. Homo sapiens, on the other hand, had a more gracile and slender physique, a smaller skull, and longer limbs.
- Culture: Neanderthals are believed to have had a more primitive culture compared to Homo sapiens, with a limited range of tools and limited evidence of symbolic behavior. Homo sapiens, on the other hand, developed more complex cultures and created a wider range of tools, art, and symbols.
- DNA: Recent genetic studies have shown that Neanderthals and Homo sapiens interbred and that most non-African populations today carry some Neanderthal DNA. However, the exact extent of this interbreeding is still the subject of ongoing research.
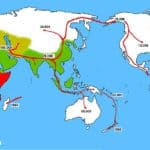
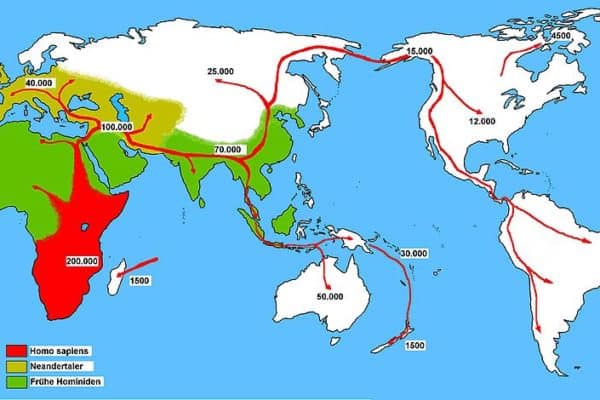
- Geographic Distribution: Neanderthals were primarily found in Europe and western Asia, while Homo sapiens first evolved in Africa and then dispersed across the globe.
In addition, Homo sapiens and Neanderthals are two distinct species of early humans that lived at the same time and shared some common ancestry. While they had some similarities, the differences in anatomy, culture, DNA, and geographic distribution set them apart from each other.
What are the Different Types of Blood Cells and their Functions?
Blood is the life-sustaining fluid that circulates throughout our bodies. It is made up of cells and plasma, and the cells are responsible for delivering oxygen to our organs and tissues. There are three different types of blood cells—red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets—and each one has its own function within the body. Let’s take a closer look at these three types of blood cells and their functions.
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs) – Red blood cells are by far the most abundant type of cell in your bloodstream
- White Blood Cells (WBCs) – White blood cells make up a much smaller portion of your total blood volume than red blood cells do, but they play an equally important role in keeping you healthy.
- Platelets – Platelets are small fragments of larger cell structures that circulate in your bloodstream, similar to red and white blood cells.
The three main types of blood cells—red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets—all have their own unique functions within our bodies.
Related Articles
Check out some of our related articles, you are sure to learn something new:






 Rawpixel.com/Shutterstock.com
Rawpixel.com/Shutterstock.com