The accidental scratches during playtime along with sweet kisses during snuggles may seem harmless. But your cat can carry diseases and transmit them to you. Some are more serious than others but the more you know, the more caution you can exercise. Discover 10 illnesses you can get from your cat!
1. Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasite that spreads via infected poop.
©Dr_Microbe/iStock via Getty Images
Dr. Colleen Wallace, a cat-only veterinarian at the Cozy Cat in Raleigh, North Carolina, told A-Z-Animals, “The most common way of developing toxoplasma is by digging in the soil, as it is prevalent in the environment. You can also be infected by eating contaminated food or by scooping an infected cat’s litter box. The toxoplasma organism can cause a miscarriage in pregnant women, but the organism is only effective after 24 hours. Scooping the litter box at least once to twice daily will prevent transmission, but if feasible, someone else should clean the box. Many people have been infected with toxoplasma and do not know it because the infection is usually asymptomatic.”
It’s not easy to tell when your cat is infected with toxoplasmosis because many cats don’t show any signs that they are sick. However, your cat may be shedding the parasite for up to three weeks after infection. If you’re infected, you may experience symptoms similar to the flu. However, some people, on rare occasions, develop eye disease. For those who are pregnant or who have weaker immune systems, symptoms may be more severe and, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, could end up causing brain disease.
2. Cat Scratch Disease
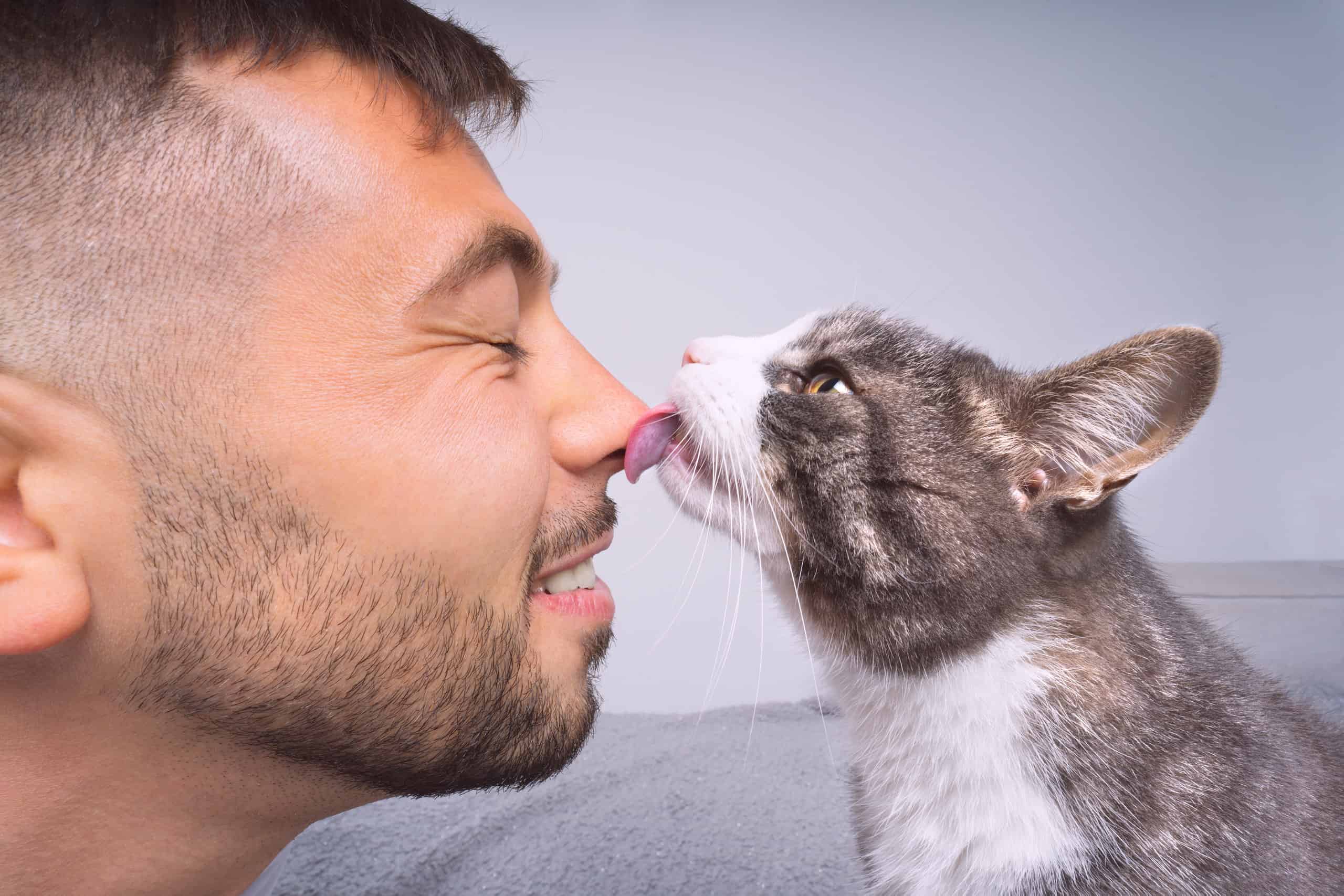

Despite what its name suggests, cat scratch disease can also be contracted via a simple, seemingly harmless lick from your cat.
©iStock.com/Daria Kulkova
This disease can be transmitted from your cat by either a scratch or a lick. Typically, cats that are living in shelters or that are under one year old are more likely to get infected. This is because the infection is transferred via flea bites on most occasions. Your cat is unlikely to show any symptoms, but some may get mildly ill and experience a fever for a couple of days.
On rare occasions, cats may develop more severe symptoms like vomiting and swollen lymph nodes. If you contract this disease, you may first notice that there is a solid, raised bump where your cat scratched or licked you. Symptoms don’t show up right away. It could take up to three weeks after the initial exposure. Symptoms include fever in most cases, but you may also experience muscle pain or eye infection.
3. Cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis may result in several symptoms, including abdominal pain and vomiting.
©Dr_Microbe/ via Getty Images
This parasitic disease spreads when you ingest your cat’s poop accidentally. This could even be when water or food is contaminated unbeknownst to you. Or it could occur if you don’t wash your hands after cleaning your cat’s litter box. Cats can typically carry this disease without any signs or symptoms.
Anyone can contract this disease from a cat, but people who have compromised immune systems are at higher risk. If contracted, symptoms such as vomiting, abdominal pain, and extremely loose stools may occur. Typically, the symptoms persist for up to two weeks.
4. Giardiasis
Your cat may transmit giardiasis to you, but usually, the type of giardiasis in humans and cats is different.
©SciePro/ via Getty Images
This parasite, like others in this list, can be transmitted via contaminated poop, soil, water, and even food. If you accidentally ingest a contaminated substance, you might get sick. The good news about giardiasis is that the type of parasite that makes people sick isn’t typically the one that makes cats sick.
When a cat has giardiasis, symptoms include dehydration and diarrhea. Typically, their stool has a greasy appearance and texture to it. In humans, giardiasis presents with several symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, gas, and diarrhea. In some cases, a person may contract giardiasis without developing any symptoms.
5. Cat Tapeworm

Cat tapeworm is contracted after ingestion of an infected flea.
©Henrik_L/ via Getty Images
Infected fleas are ultimately the culprit when it comes to cat tapeworms. When your cat ingests an infected flea (via self-grooming, for instance), the parasite spreads. It’s uncommon for humans to contract this disease from their cats because you have to swallow an infected flea yourself. But it does happen, especially with young children. This is an extremely rare infection and typically, it doesn’t present with any symptoms. However, you may be able to spot the tapeworm moving about in feces or near the anus.
6. MRSA

Your cat can be a carrier of MRSA without showing any symptoms.
©Peddalanka Ramesh Babu/ via Getty Images
MRSA is a bacterium that can manifest in a range of ways, including skin and lung infections. Cats don’t have to present symptoms or get sick, but they may still be able to transmit it to you. Although they may not always show symptoms, sometimes cats may have some skin or respiratory issues when infected. In humans, MRSA is similar in that symptoms don’t usually develop. However, the most common sign of MRSA is skin infection. When this is not treated, it can progress and become a life-threatening condition.
7. Rabies
Rabies is a deadly disease that can you can get from your cat via bites or scratches.
©jarun011/iStock via Getty Images
Your cat should already be vaccinated against rabies because this is a deadly disease that is spread via cat bites. It’s a neurologic disease that causes a quick decline in both animals and people. It’s spread when you have contact with the saliva or the brain tissue of an infected cat. Although the most common form of infection is via a bite, rabies may be transmitted via scratches. In cats, behavior changes dramatically.
After symptoms begin, cats die within just a couple of days. If you contract rabies, symptoms may appear in a couple of days, but they may also take a couple of months after exposure to begin. Once you are aware of the symptoms, the disease has already progressed too much for effective treatment. To prevent something like this from happening, always consult with your doctor after being bitten or scratched by your cat or any other animal.
8. Hookworm
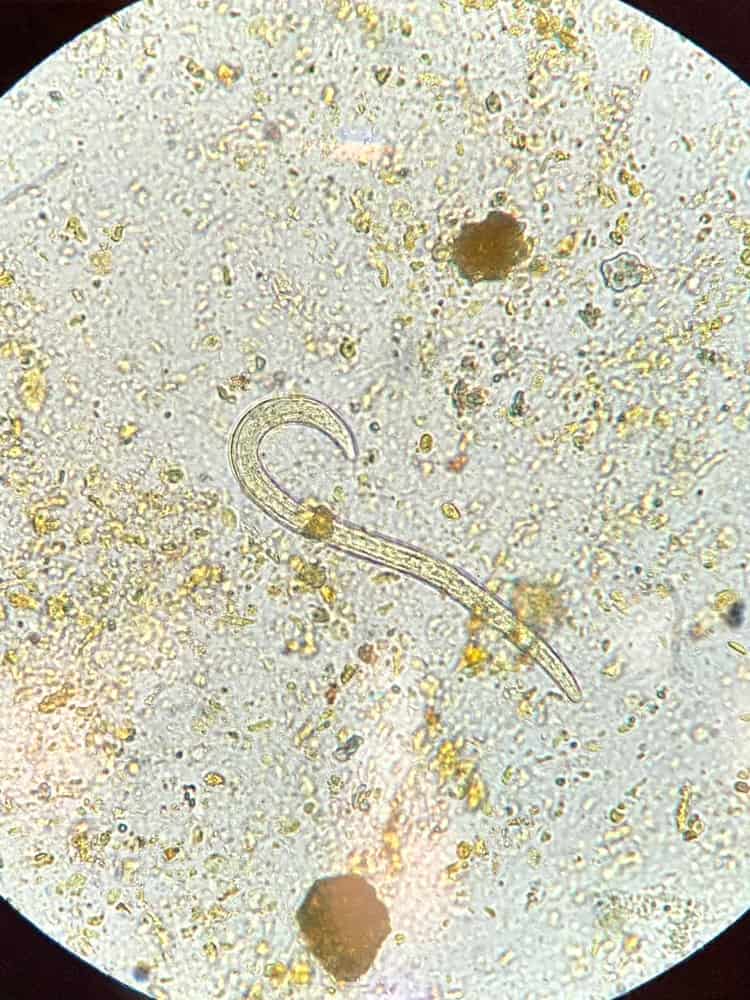
Hookworm is a parasite that’s spread via contact with contaminated environments.
©Blossom Tomorrow/Shutterstock.com
Contaminated soil may spread hookworms. These are tiny worms that may spread to you when you walk around barefoot, kneel, or sit down anywhere near areas that are contaminated with poop from your cat. When your cat is still a kitten, hookworm can cause weight loss and anemia. When the infection is severe, it could lead to death.
Symptoms of hookworm in humans present as itchiness. You may notice that there is a worm-like line where the parasite has embedded into the skin. When you contract hookworms from a cat, they can’t survive in your body for too long, so you typically see symptoms subside in about four to six weeks.
9. Roundworms
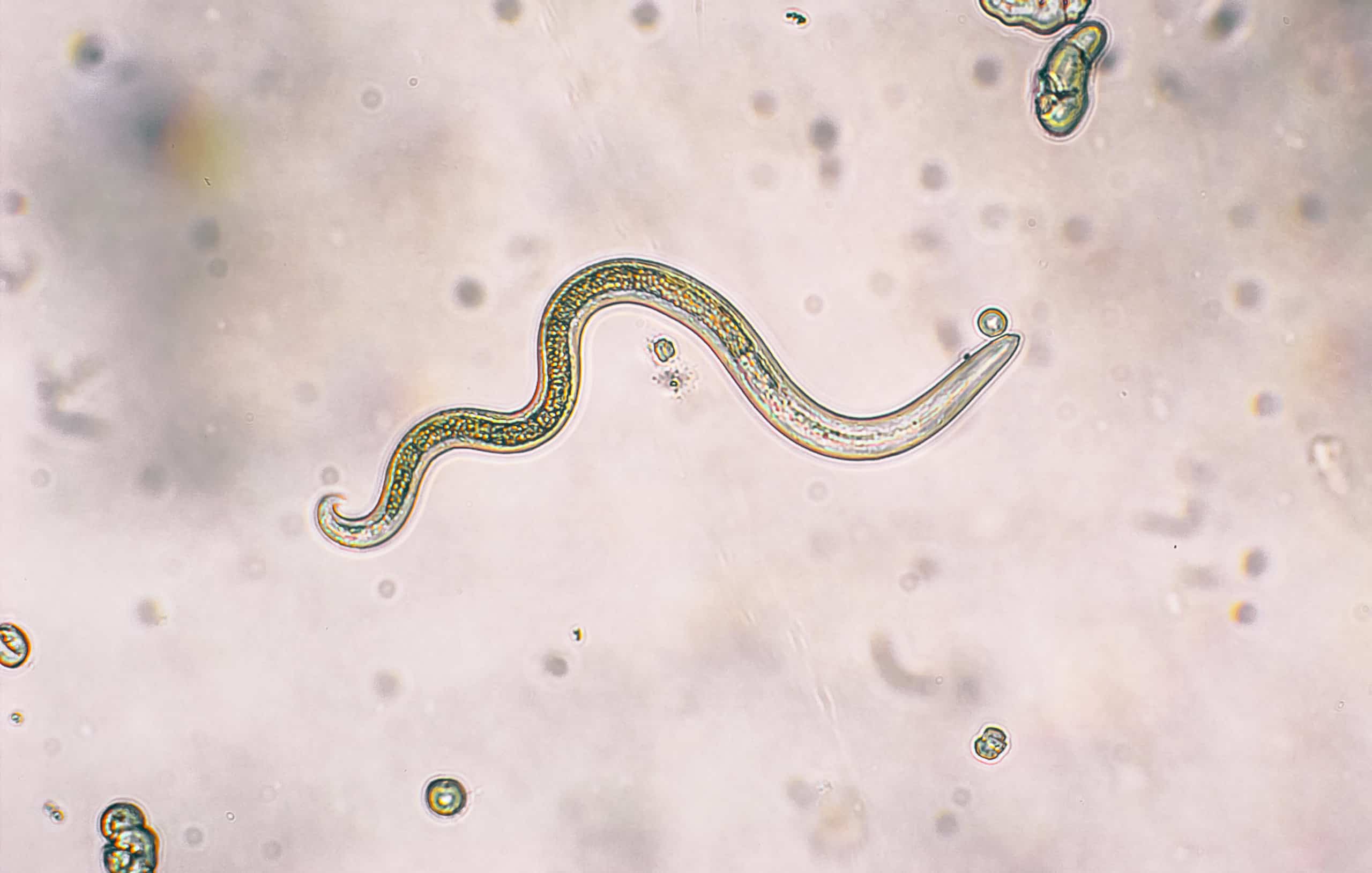
Roundworms spread via cat poop and symptoms differ depending on where they migrate.
©iStock.com/dotana
Cat poop is the culprit yet again when it comes to the spread of roundworms. When they are kittens, cats don’t usually present with symptoms, but they may be dehydrated, have diarrhea, and have a rather round, bloated belly. In people, roundworms may affect one of your eyes. The other type of illness that may develop after contracting roundworms is body organ issues like abdominal pain or fatigue. This is because roundworms may migrate to different parts of your body, which results in different symptoms.
10. Ringworm
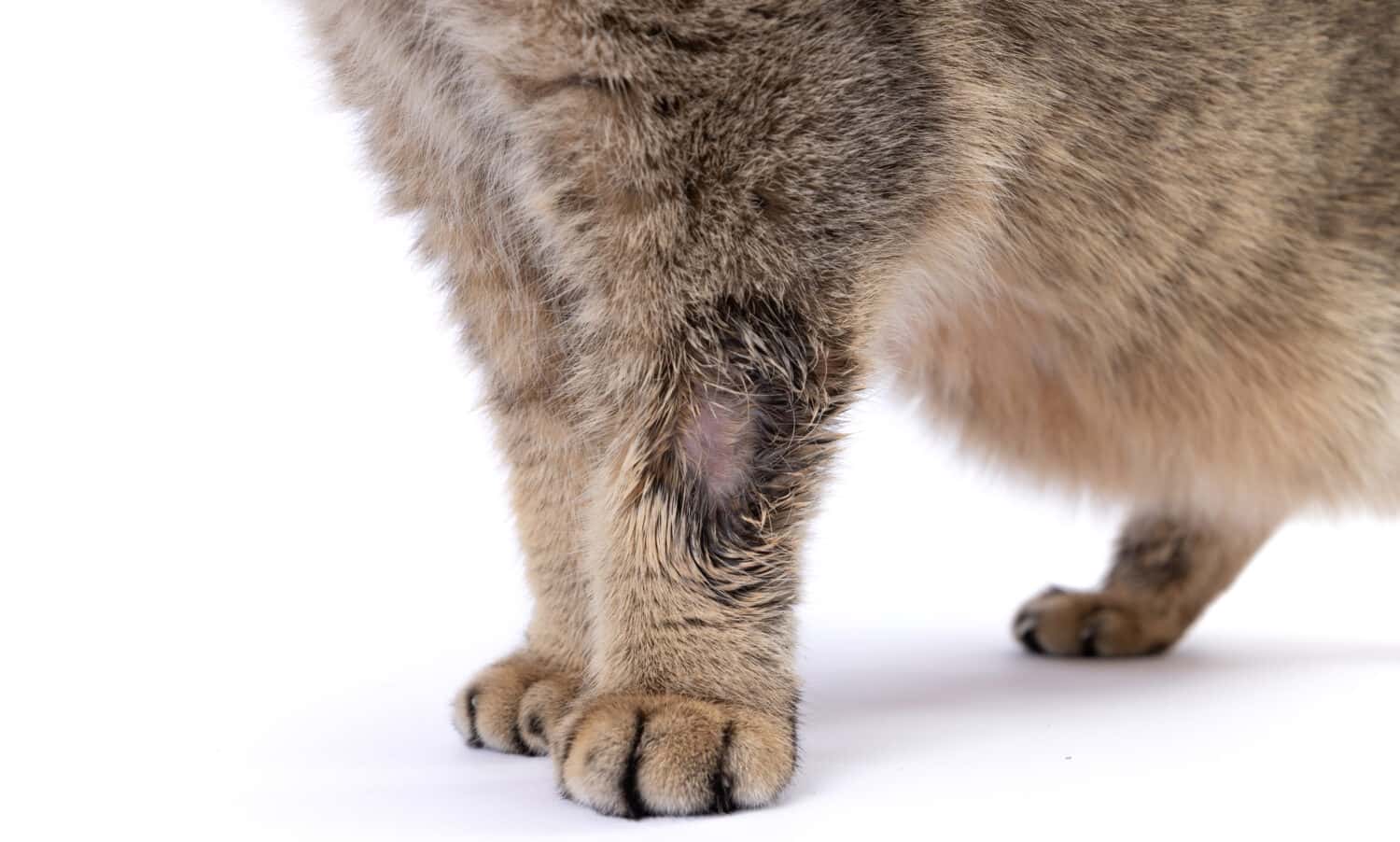
Cats that have ringworm often have bald patches on their fur along with scaly skin.
©Nadya Bessonov/Shutterstock.com
In cats and people, ringworm can affect different parts of the body. Ringworm might show up on the skin, on nails, or in hair. It spreads via touch, which means anyone can contract this infection. In some cases, cats don’t have any symptoms but most of the time, you can see that they have little areas of hair loss on their bodies.
Typically, the skin is sort of crusty. This most often occurs in kittens. If you contract this infection, you are also likely to develop scaly, itchy skin and if it spreads to your scalp, your hair may fall out. When nails are infected, they get thicker and crumbly and become discolored.
The photo featured at the top of this post is © Pogodina Natalia/Shutterstock.com
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.







