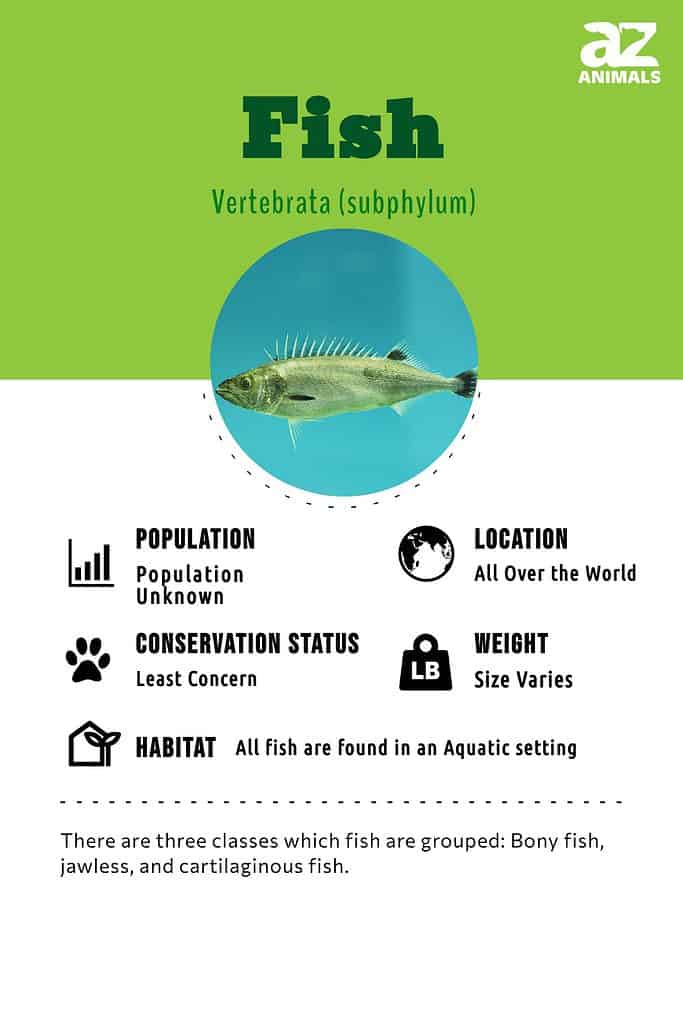
Fish are aquatic vertebrates. They usually have gills, paired fins, a long body covered with scales, and tend to be cold-blooded.
“Fish” is a term used to refer to lampreys, sharks, coelacanths, and ray-finned fishes, but is not a taxonomic group, which is a clade or group containing a common ancestor and all its descendants.
Instead, there are 3 main classes, groups, or types of fish: bony fish (Osteichthyes), jawless fish (Agnatha), and cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes). Fish are the most diverse group among vertebrates, with over 33,000 different types of fish species.
No one really knows how many different types of fish exist in the world, more are being discovered constantly. We may soon have over 35,000, or even 40,000 known species!
5 Fish Characteristics
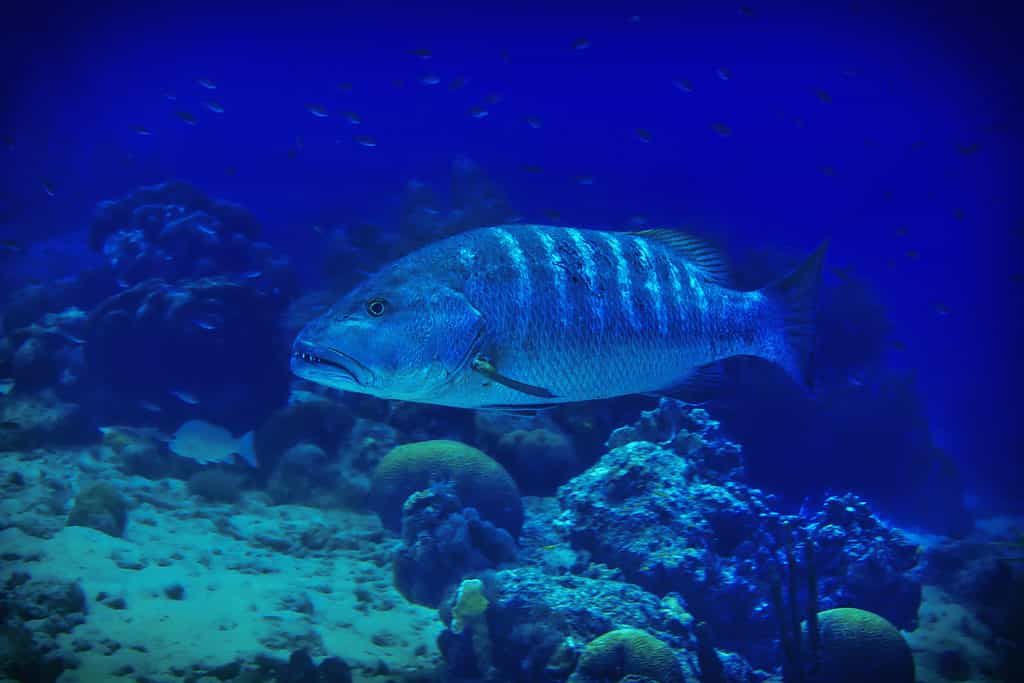

There are three superclasses into which fish are grouped: Bony fish, jawless, and cartilaginous fish.
©Lynn Archer/Shutterstock.com
There are three superclasses into which fish are grouped: Bony fish (Osteichthyes), jawless fish (Agnatha), and cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes). Ray-finned fishes are of the class Actinopterygii, while lobe-finned fishes are of the class Sarcopterygii. Both are clades of bony fishes.
Regardless, all fish have some characteristics in common that distinguish them from other animals.
- Cold-bloodedness: All fish are ectothermic or cold-blooded, meaning they cannot regulate their internal body temperature. Even warm-blooded fish such as tuna and mackerel sharks have only “regional endothermy” or warm-bloodedness limited to certain areas.
- Water habitat: All fish live in bodies of water, whether it is freshwater or saltwater. However, not all creatures that live in water are fish.
- Gills to breathe: Fish have gills throughout their life cycle. As with the water habitat, although all fish have gills, not all creatures with gills are fish.
- Swim bladders: Specialized organs fill with air to keep the fish afloat and in some species help them survive with low oxygen levels. They also help fish sleep and are sensitive enough to detect the movement of food and predators.
- Fins for movement: Most common are a tail fin, a pair of side fins, a dorsal fin, and an anal fin. Variations exist but they all provide motion, maneuverability, and stability.
For a list of incredible facts about fish, make sure to read ‘10 Incredible Fish Facts.’
Diet

What do fish eat? Most species of fish fall into the omnivore category. This means that they can eat both plants and meat. It offers a wider range of food options for aquatic animals. It also helps fish find the different nutrition they need in a variety of foods.
Additionally, pet fish may have a bit of a different diet than fish you find in the wild. For example, pet fish mostly eat freeze-dried and frozen foods including bloodworms, brine shrimp, krill, and plankton.
Evolution and Origins
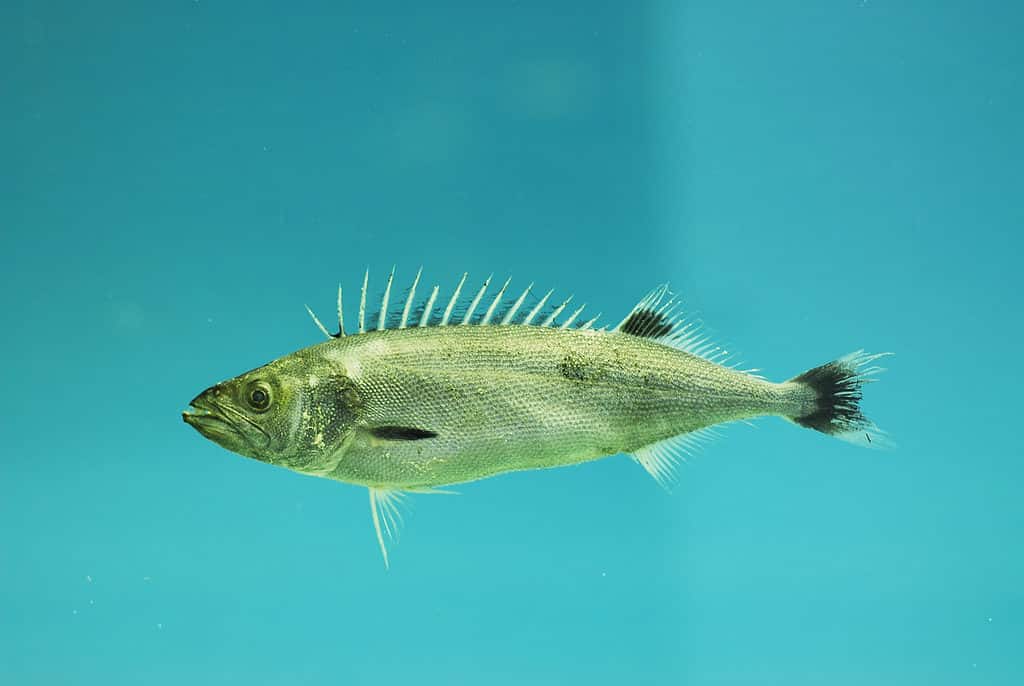

Oilfish contain high levels of wax esters, which are indigestible to humans.
©Porco_Rosso/Shutterstock.com
Fish have been evolving and changing for a very, very long time. Fish began to evolve during the Cambrian explosion approximately 530 million years ago. The earliest chordates formed skulls and spinal columns, which helped to evolve craniates and vertebrates. Additionally, the earliest fish lineages were the Agnatha or the jawless fish.
Early fish from fossil records are represented by a group of small armored and jawless fish. These were known as ostracoderm. These jawless fish lineages are mostly extinct now. However, an extant clade, the lampreys may have pre-dated the ancient pre-jawed fish. The first jaws were found in fossils and they lacked any teeth.
The diversity of these jawed creatures may prove the evolutionary advantages of a jawed mouth. Although interesting, it remains unclear if there was ever an advantage of a hinged jaw.
Furthermore, fish may have evolved from a creature similar to a coral sea squirt whose larva resembled primitive fish in very important ways.
Exceptions
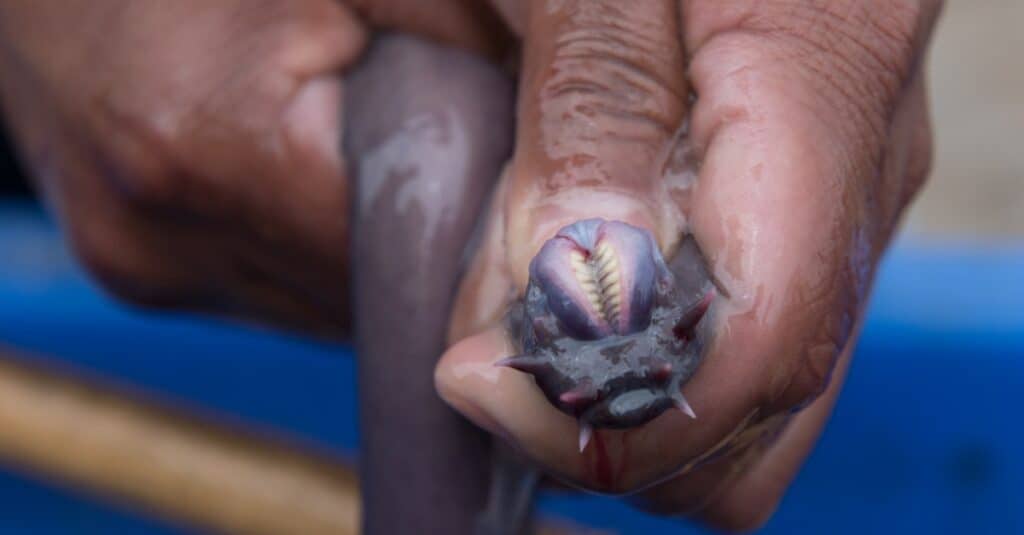

Hagfish are the only animals that have a skull but no vertebral column.
©Frank Fennema/Shutterstock.com
There are several exceptions to the common definition of a fish. For example, hagfish don’t have scales and aren’t true vertebrates (or are considered primitive vertebrates); mudskippers are amphibious fish that can live outside water; lungfish use lungs instead of gills to breathe; lampreys lack paired fins, and tuna are warm-blooded.
Also, not all fish groups come from fish lineages. The superclass Tetrapoda of the four-listed animals is considered to be a group within Sarcopterygii and includes amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Hence, Sarcopterygii includes both lobe-finned fishes and tetrapods.
Finally, not all aquatic creatures which resemble fish are considered fish. Whales, dolphins, and porpoises are aquatic mammals, for example.
You can read about some types of fish that are extinct.
Pregnancy
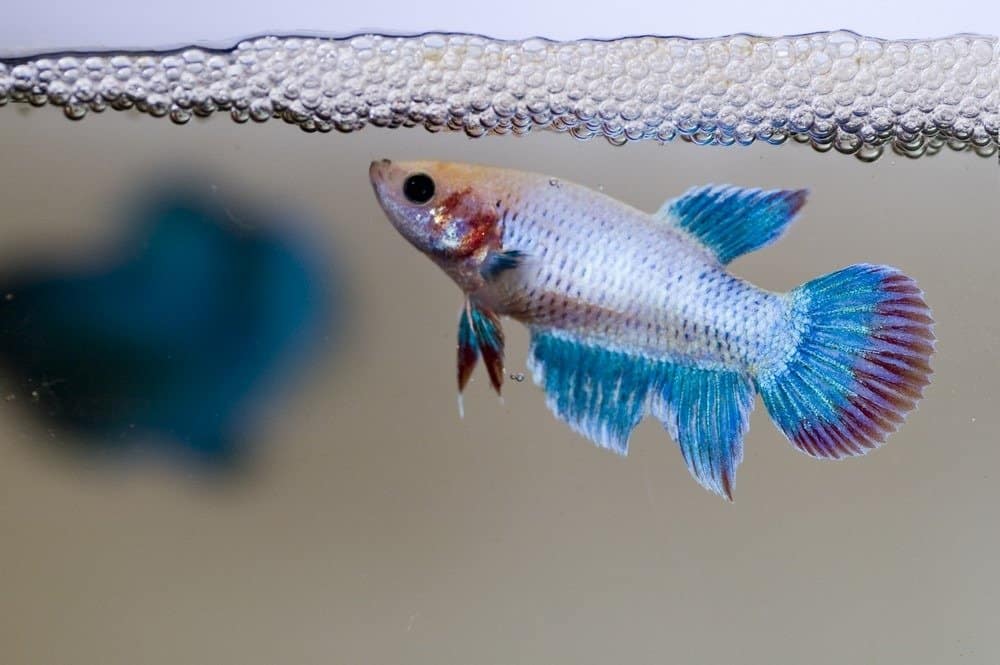

A Siamese female fighting fish guarding her newly laid eggs amongst the bubble nest.
©mnoor/Shutterstock.com
- There are two main types of fish pregnancies, ovoviviparity or aplacental viviparity (egg-bearing) and viviparous (embryo-bearing). Both are considered to be live-bearing.
- Ovoviparity has the eggs develop and hatch internally, with the young being born alive. It can express either ovuliparity (external fertilization of eggs and zygote development), oviparity (internal fertilization of eggs and external development of zygotes as eggs with yolks), or ovoviviparity (internal fertilization of eggs and internal development of embryos with yolks). Stingrays, seahorses, and some shark species are ovoviviparous. So are guppies, mollies, swordtails, halfbeaks and platies.
- Viviparity has embryos develop internally before being born live. It can express either histotrophic (“tissue-eating”) viviparity (mother provides no nutrition and embryos eat their unborn siblings or mother’s unfertilized eggs) or hemotrophic (“blood-eating) viviparity (mother provides nutrition, usually through a placenta). Many shark species are viviparous.
Check out the fish gestation period.
Different Types of Fish:

Alaskan Pollock
It's one of the most commonly eaten fish in the world

Albacore Tuna
The albacore is a very fast swimmer

Alligator Gar
The alligator gar has toxic eggs to protect against predators

Amano Shrimp
Popular kept in aquariums to keep them clean

Amberjack
Amberjack can grow up to 200 pounds

American Eel
Don't eat raw eel! Their blood is poisonous to humans when consumed raw.

Anchovies
November 12th is celebrated as National Pizza with the Works Except Anchovies Day

Angelfish
There are 70 different species!

Anglerfish
The anglerfish has a glowing lure on its head to attract unsuspecting prey

Arapaima
One of the largest freshwater fish

Archerfish
Archerfish can shoot a stream of water up to five feet with amazing accuracy.

Arctic Char
Arctic char is the northern-most fish; no other fish lives anywhere further north!

Asian Arowana
The male Asian arowana raises the eggs in its mouth

Asian Carp
Asian carp can consume 40% of their body weight in food a day!
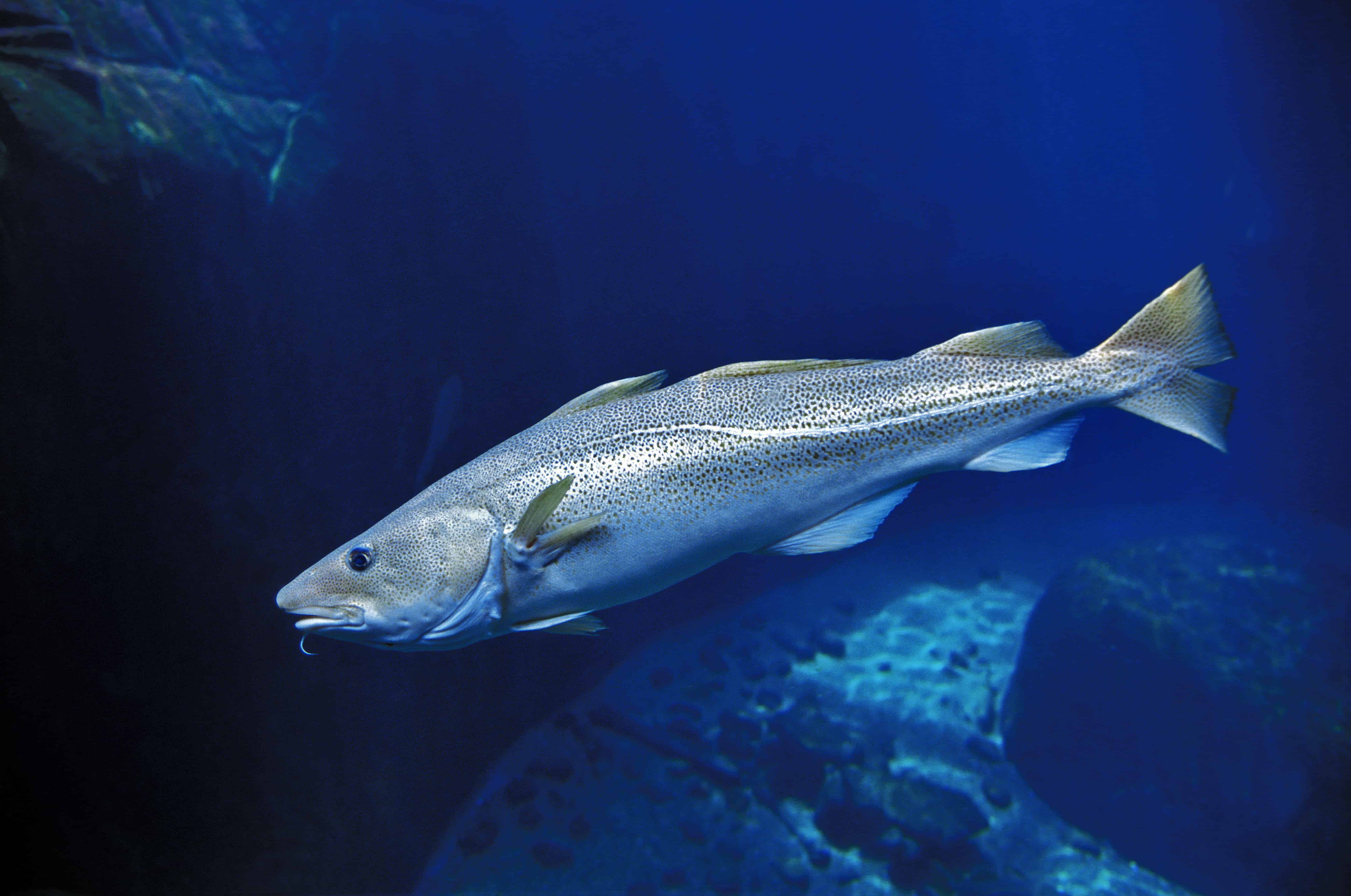

Atlantic Cod
One of the most popular food fishes in the world

Atlantic Salmon
These fish are known for their ability to leap and fight when hooked.

Atlantic Sturgeon
Atlantic Sturgeon often leap out of the water.

Australian Flathead Perch
This small fish fetches a high price tag, with individuals selling from $1,000 to $5,000.

Banana Eel
Named for the yellow body and brown spots that make it look like a banana.

Banjo Catfish
The banjo catfish is extremely shy and known for hiding from onlookers.

Barb
There are over 1768 known species!

Barracuda
Can grow to nearly 2 meters long!

Barramundi Fish
Scale rings indicate age

Barreleye Fish (Barrel Eye)
A barreleye fish's eyes can rotate in their head to look for prey.

Bass
Prized by sport fishers for their size and strength

Batfish
The batfish has a lure on its head to attract prey

Beluga Sturgeon
The beluga sturgeon is one of the largest bony fish in the world!

Betta Fish (Siamese Fighting Fish)
Can live in low-oxygen environments!

Bigfin Reef Squid
Can change color through use of chromatophores

Black Bass
The most popular game fish in North America

Black Marlin
Every black marlin is born as a female.

Blacknose Shark
When threatened, Blacknose sharks raise their head, arch their back, and lower their pectoral fins.

Bladefin Basslet
The tiny bladefin basslet belongs to the same subfamily as the giant grouper, Epinephelinae.

Blobfish
One of the ugliest creatures in existence!

Blue Catfish
It's a strong fighter when caught on a fishing line

Blue Eyed Pleco
Can live safely with many types of fish.

Blue Shark
Blue sharks can have up to 135 pups at a time.

Blue Tang
One of the most colorful members of the genus Acanthurus

Bluefin Tuna
The bluefin is one of the largest fish in the world

Bluegill
The world record for longest bluegill is 15 inches.

Bonefish
Bonefish have migratory habits, moving from shallow waters to deeper waters during different times of the year.

Bonito Fish
May eat squid or other small invertebrate ocean life

Bonnethead Shark
Bonnetheads are the only hammerhead sharks that use their pectoral fins to swim.

Bowfin
The bowfin is a primitive fish that first evolved in the Jurassic

Boxfish
Can release a toxin from its skin

Bronze Whaler Shark
The Bronze Whaler Sharks only hunt in large groups.

Brook Trout
The Brook Trout is actually part of the salmon family, making it not technically a trout.

Buffalo Fish
The oldest Buffalo fish recorded was 112 years old!

Bull Trout
The bull trout is not actually a trout, but a member of the char family.

Butterfly Fish
There are more than 100 different species!

Carp
The carp is one of the most popular pond fishes in the world

Catfish
There are nearly 3,000 different species!

Chimaera
Also called ghost shark

Chinese Paddlefish
The Chinese paddlefish is one the largest freshwater fish in the world

Chinook Salmon
The Chinook salmon undertakes a long migration for the spawning season

Cichlid
There are more than 2 000 known species!

Clearnose Skate
The skate with translucent nose patches

Clownfish
Also known as the anemonefish!

Cobia Fish
It has teeth not only in its jaws but in its tongue and the roof of its mouth

Codfish
Codfish are carnivorous and eat other fish, including young codfish.

Coelacanth
The coelacanth first evolved almost 400 million years ago.

Conger Eel
The European Conger ( Conger conger) can weigh as much as an adult human!

Cookiecutter Shark
The cookiecutter shark takes its name because it leaves a cookie-shaped bite hole in its prey.

Cory Catfish
All Cory Catfish have three pairs of barbels around their mouth that they use to detect food.

Crappie Fish
The crappie is one of the most popular freshwater fish in North America.

Cubera Snapper
While very intimidating, the cubera snapper also falls prey to other marine animals like barracudas, whale sharks, and moray eels.

Damselfish
Damselfish belong to the family Pomacentridae

Danios
These fish make a popular choice for aquarium hobbyists due to their hardy nature.

Discus
One of the only schooling Cichlids!

Dragon Eel
Dragon eels have double jaws and two sets of razor-sharp teeth

Dragonfish
Dragonfish can emit red light from their eyes

Drum Fish
The drum fish makes a croaking sound with its swimming bladder!

Dusky Shark
The Dusky Shark sometimes eats trash discarded by humans.

Dwarf Gourami
Dwarf gourami can live for over four years with proper care.

Eagle Ray
Majestic underwater bird like fish

Eel
Eels can be a mere few inches long to 13 feet!

Eel catfish
Eel catfish breathe air and reach up on land to catch beetles. Scientists think they may be a missing link between fish and lizards.

Eelpout
Not actually "eels"

Electric Catfish
The electric catfish can discharge an electric shock up to 450 volts

Electric Eel
Despite its powerful shock, electric eels have terrible vision.

Elephant Fish
Elephant fish are known as the Australian ghost shark, but they are not actually a shark species!

Ember Tetra
Ember tetras are one of the smallest shoaling fish in the world

Emperor Angelfish
One of the most beautiful fish on the planet!
Escolar
Its system can’t metabolize wax esters, which can lead to unpleasantness for diners.

Fangtooth
Has the largest teeth compared to body size of any known fish!

Fire Eel
Fire Eels are not true eels.

Fish
Respire through the gills on their heads!

Flathead Catfish
The only predators that prey on flathead catfish are members of their own species and humans who catch them for commercial and recreational purposes.

Florida Gar
The Florida gar has toxic eggs to protect against predators

Flounder
A flat fish found in the Atlantic and Pacific!

Flounder Fish
There are around 240 different species of Flounder fish

Flowerhorn Fish
The Flowerhorn fish is an artificial species; it does not exist naturally

Fluke Fish (summer flounder)
The chameleon of the seas!

Flying Fish
Can glide in the air for hundreds of feet
Football Fish
The football fish is named after its unusual round or oblong shape

Freshwater Drum
These fish are very vocal, and males make a rumbling or grunting noise during breeding season to attract a mate.

Freshwater Eel
Freshwater eels are actually catadromous, meaning they migrate to saltwater to spawn

Freshwater Jellyfish
The freshwater jellyfish is native to China but is now found all over the world

Freshwater Sunfish
Four species of the freshwater catfish have gone extinct

Frilled Shark
Frilled Sharks got their name from the six rows of gills on their throat that look like ruffled collars.

Frogfish
The frogfish can change colors, but it takes several weeks to do so

Galapagos Shark
Galapagos sharks are cannibalistic and sometimes eat their young, so the pups stay away from the adults in shallow water.

Gar
Can grow to more than 3m long!

Garden Eel
Garden eel colonies are made up of hundreds to thousands of individuals.

Ghost Catfish
You can see its heart beating

Giant Trevally
The largest fish in its genus

Goblin Shark
Goblin Sharks are called a living fossil because their family, Mitsukurinidae, can be traced back 125 million years.
Goby Fish
Some Goby species are toxic.

Golden Shiner
One of the most popular bait fish in the US.

Golden Trout
Freshwater state fish of California

Goldfish
Goldfish and common carp can mate and produce offspring

Goliath Tigerfish
Featured in "River Monsters" TV series!

Goonch Catfish
The goonch catfish, or giant devil catfish, is one of the most fierce freshwater fish.

Gourami
Gourami fishes show parental care for their young

Grass Carp
The grass carp is considered to be a natural weed control agent.

Great Hammerhead Shark
Great hammerhead sharks have a 360 view because their eyes are situated on the ends of their mallet-like heads.

Great White Shark
Can grow to more than 8 meters long!

Green Sunfish
Juvenile Green Sunfish are less colorful than their parents because they need to blend in with their surroundings to avoid predators.

Greenland Shark
This shark has the longest lifespan of any vertebrate.

Grey Reef Shark
One of the most common shark species!

Grunion
Their whole bodies are edible

Guadalupe Bass
Freshwater fish native to Texas

Gulper Catfish
Gulper catfish can consume prey twice its size

Gulper Eel
Gulper eels have a similar lifespan to humans and can live up to 85 years old. However, their age depends on their habitat and the availability of food.

Guppy
Also known as the Millionfish!

Haddock
The haddock is very popular in both recreational and commercial fishing

Hagfish
Can use slime to suffocate marine predators or escape capture

Haikouichthys
Haikouichthys was the first animal to develop a well-defined head

Hairy Frogfish
Hairy frogfish can eat prey as large as themselves by swallowing them whole.

Halibut
The word "halibut" is comes from haly meaning "holy" and butte meaning flat fish due to its popularity on Catholic holy days.

Hammerhead Shark
Found in coastal waters around the world!

Hardhead Catfish
The hardhead catfish has a sharp spine near its fin to inject venom

Herring
People enjoy the taste of the oily fish in many different ways including pickled, smoked, salted, dried and fermented.

Hogfish
Hogfish can change their sex from female to male

Horn Shark
Endemic to the Californian coast!

Horse Mackerel
Got their name from a myth that other fish would ride them over great distances

Immortal Jellyfish
Excellent hitchhiker on long-trip cargo ships

Irukandji Jellyfish
Tiny ocean killer

Jack Crevalle
One of the biggest species in the Caranx genus

Jellyfish
Have tentacles around their mouths!

John Dory
The John Dory is often labeled one of the ugliest fish in the world and has no known relatives.

Kelp Greenling
Male Kelp Greenlings participate in an unusual mating ritual by fertilizing eggs in the nests of other males.

Keta Salmon
During spawning the look of the male changes. Among other things, he grows a beak called a kype that bears fangs.

Keyhole Cichlid
When these fish feel stressed, their skin color will change from yellow-cream to brown.

Killifish
Killifish are highly sought after for their peaceful nature and ability to adapt to most aquarium communities.

King Salmon
Largest of the Pacific salmon
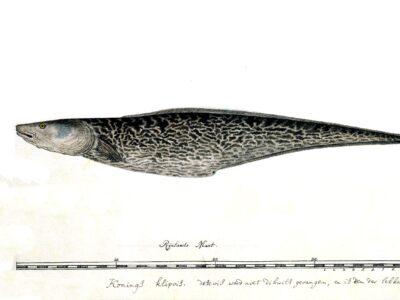
Kingklip
A delicacy in South Africa

Kissing Gourami
The kissing gesture that the kissing gourami displays is not a mating gesture

Knifefish
Produce weak electric fields

Koi Fish
In Japanese, the word koi sounds like the word for love. So the fish is a symbol of love among other good things.

Kokanee Salmon
A non-anadromous type of sockeye salmon

Krill
The krill is perhaps the most important animal in the marine ecosystem!

Labout’s Fairy Wrasse
Females are sequential hermaphrodites, which means they can convert to males anytime during their life cycle.

Lake Sturgeon
Its skeleton is part cartilage and part bone.

Lake Trout
Darker specimens are sometimes called "mud hens"

Lamprey
Not related to the eel

Lancetfish
Lancetfish live at depths up to 6,500 feet below sea level

Largemouth Bass
Georgia, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida all claim the largemouth bass as the state fish or state freshwater fish.

Lawnmower Blenny
Must be in temperatures of 78 degrees Fahrenheit to breed

Leopard Shark
Leopard Sharks have teeth with three points.

Leptocephalus
Leptocephali have flat bodies filled with jelly-like substances, surrounded by a thin layer of muscle.

Lionfish
Females can release up to 15,000 eggs at a time!

Lizardfish
The lizardfish can camouflage itself against the sandy bottom to avoid predators.

Loach
Have sharp spines below their eyes

Longnose Gar
The longnose gar species of the gar family has potentially existed for 100 million years.

Lumpfish
The lumpfish have sticky suction cups on their fins

Lungfish
The lungfish first evolved almost 400 million years ago.

Mahi Mahi (Dolphin Fish)
It's called the rabbit of the ocean because it multiplies so quickly.

Mangrove Snapper
Tagging studies have found that once adults establish a habitat they typically remain there for long periods. In fact, they found that these fish can stay in one area for up to 4 years.

Manta Ray
Can grow up to 9m wide!

Masked Angelfish
All masked angelfish are female until sometime after sexual maturity, at which point some become male.

Mayan Cichlid
Mayan cichlids live longer in captivity than they do in the wild.

Megalodon
The largest shark to ever live!

Megamouth Shark
Swims with its mouth open to capture prey

Mekong Giant Catfish
The Mekong giant catfish is the largest purely freshwater fish in the world

Milkfish
Females lay up to 5 million eggs at one time in warm, shallow and salty waters

Mojarra
The mojarra's protruding mouth allows it to sift along the seabed for food

Mola mola (Ocean Sunfish)
The ocean sunfish is the biggest bony fish in the world

Molly
Known for their calm and peaceful nature!

Monkfish
Called the poor man's lobster!

Moon Jellyfish
Moon Jellies are bioluminescent, so they glow in the dark! They can also de-age!

Moray Eel
Sometimes, groupers invite moray eels to help them hunt!

Mudskipper
They walk on land

Mullet Fish
The Striped Mullet is one of the best-known and most easily identified species, with black horizontal stripes along its body.

Muskellunge (Muskie)
In 1949, a Muskellunge set a world record by weighing 68 pounds and 8 ounces in Wisconsin.

Needlefish
no stomach to digest food

Neon Tetra
Neon Tetras are very social and peaceful fish.

Neptune Grouper
The largest recorded specimen ever caught was 17" long

Oarfish
The Giant oarfish (Regalecus glesne) holds the Guinness Book of World Records for the longest bony fish in the world.

Ocean Perch
As a scorpionfish, the ocean perch has spines along its back!

Ocean Pout
Females guard their eggs for up to 3 months
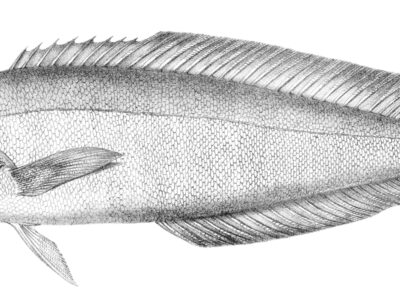
Ocean Whitefish
Common around Southern California

Oilfish
They live in deep water as far as 2,600 feet below the water’s surface.

Opah
Opah are brightly colored, with red-orange fins and a silvery body.

Opaleye (Rudderfish)
Some indigenous people of the Pacific coast of North America consider opaleye fish sacred food and use it in traditional ceremonies.

Orange Roughy
One of the oldest commercially harvested fish

Orchid Dottyback
This fish camouflages as its prey's parents to trick it into becoming dinner.

Oscar Fish
The Oscar fish has teeth in its throat!

Oyster Toadfish
The oyster toadfish can produce poison to protect itself

Ozark Bass
Ozark Bass only live in Arkansas and Missouri

Pacific Sleeper Shark
In 2015, a Pacific Sleeper Shark was filmed living underneath an active volcano near the Solomon Islands. This shark is able to survive in waters with very high temperatures and acidity!

Paddlefish
Paddlefish have existed since the Cretaceous Period

Parrotfish
The parrotfish can change from female to male at some point in its life.

Peacock Bass
Peacock bass is known for their aggressive behavior and predatory instincts, making them a challenging target for sport fishermen.

Peppermint Angelfish
The peppermint angelfish was only first described in 1992.

Perch Fish
Some of the most delicious gamefish in the world

Pictus Catfish
Pictus catfish are social fish that should be kept in groups of 4 or more

Pinfish
Pinfish make loud croaking sounds during their spawning season.

Pink Salmon
The smallest of the North American salmon

Pipefish
The male pipefish has the ability to carry fertilized eggs with him

Piranha
Generally found in fast-flowing streams!

Platinum Arowana
The male broods the eggs and baby fish in his mouth.

Pollock Fish
Pollock is a nutritious fish, generally readily available for human consumption, and more sustainable and affordable than other whitefish species like hake or haddock.

Pompano Fish
They are bottom-feeders

Porbeagle Shark
The porbeagle is one of the few sharks that jumps out of the water

Porcupinefish
The Porcupinefish secrete a potent neurotoxin known as tetrodotoxin; this poison can kill both people and predators.

Pufferfish
The second most poisonous creature in the world!

Pygmy Shark
Pygmy sharks underbelly glows to attract prey that swims beneath it.

Pyjama Shark
Pyjama Sharks like to swim in shallow inshore waters.

Rainbow Kribs (Kribensis)
Rainbow Kribs sometimes nip the fins of other fish, especially ones with long, flowing tails, which is too tempting for them not to bite.

Rainbow Shark
The rainbow shark has been genetically modified to glow in the dark

Red Drum Fish
There were a few sightings of red drums in the Mediterranean Sea off Sicily and Israel, but they do not naturally occur there, so theories are they escaped from fish farms.

Red-Lipped Batfish
Despite its weird looks, the red-lipped batfish is harmless to humans

Redhump Eartheater
The redhump eartheater are very passive fish and do well in aquariums with non-cichlid species

Redtail Catfish
One of three giant catfish species

Reef Shark
Grey reef sharks can give birth without males

Rockfish
These fish can grow up to three feet long!

Sailfish
Fast billfish with a sail-like dorsal fin

Salmon
Returns upstream every year to spawn

Salmon Shark
Salmon sharks are related to Great Whites.

Sand Tiger Shark
The sand tiger is the shark most commonly seen in aquariums.

Sardines
Schools of sardines can be miles long and are often visible from an airplane

Sawfish
Sawfish teeth keep growing as the fish gets older

Scorpion Fish
There are more than 200 recognised species!

Sculpin
Its skull bones can compress so the fish can fit in narrow spaces

Sea Dragon
Inhabits tropical coastal waters of Australia!

Sea Slug
All sea slugs have both male and female sex organs

Sea Trout
Change colors in freshwater and saltwater

Sea Urchin
Can live for up to 200 years!

Seahorse
Males give birth to up to 1,000 offspring!

Shark
No shark species has any bones in their bodies

Sheepshead Fish
This fish has teeth that resemble a human's.

Shortfin Mako Shark
Shortfin Mako sharks can jump 20 feet above the water!”

Silky Shark
Has an extremely acute sense of hearing

Silver Dollar
Closely related to the Piranha

Sixgill shark
The sixgill shark has six pairs of gills instead of the normal five

Skate Fish
More than 200 species exist!

Skipjack Tuna
The skipjack is the most commonly caught tuna in the world

Sleeper Shark
The Greenland shark is one of the longest living vertebrates in the world.

Smallmouth Bass
A fierce fighter!

Smooth Hammerhead Shark
Congregate in large groups during annual migrations
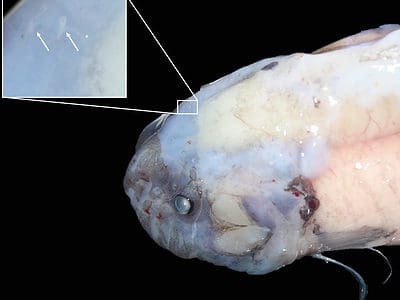
Snailfish
The deepest ocean-dweller is a snailfish who was found over 26,700 feet below sea level.

Snook Fish
Males change into females after the spawning season

Snowflake Eel
Snowflake Eel have two jaws to help them swallow their food.

Sockeye Salmon
Called "red salmon" because their skin turns bright red to dirty red during spawning season

Spanish Mackerel
Spanish mackerel typically live to the age of 12, but there have been cases of these fish living as long as 25 years!

Speckled Trout
Speckled trout are not actually a species of trout.

Spinner Shark
Can have up to 20 babies

Spiny Dogfish
Found in ocean waters worldwide!

Sponge
There are more than 9,000 known species!

Spotted Gar
They are commonly mistaken as logs in the water due to their cylindrical body.

Spotted Garden Eel
Males battle each other over females and territory

Squirrelfish
Uses vibrations to communicate with other fish

Starfish
Has 2 stomachs to aid digestion!

Stargazer Fish
Uses an electric shock to stun its prey!

Steelhead Salmon
Steelhead live in freshwater rivers and streams for 1 to 2 years before migrating into the ocean

Stingray
It's stinger is razor-sharp or serrated!

Stonefish
The most venomous fish in the world

Stoplight Loosejaw
Emit red light to hunt via bioluminescent photophores

Striped Bass
Pilgrims counted striped bass as an essential part of their diet from the time they arrived in North America.

Sturgeon
Large species can swallow whole salmon

Suckerfish
Commonly found throughout America!

Surgeonfish
Paracanthurus hepatus, the palette surgeonfish or bluetang, is the only member of its genus

Swai Fish
The edges of an iridescent shark's fins have a signature glow

Swordfish
Lose their scales and teeth as adults

Taimen Fish
The Taimen is considered one of the oldest species on earth, with fossilized remains dating back more than 40 million years!

Tang
Found around shallow coral reefs!

Tarpon
Its genus dates back to the Cretaceous period – 113 million years ago

Telescope Fish
Swallows food, much of it larger than them, whole

Tetra
Native to the freshwater streams of South America!

Thornback Ray
The skate with the biggest spines!

Thresher Shark
Thresher Sharks have a distinctive, thresher-like tail.

Tiger Muskellunge (Muskie)
Massive carnivorous hybrid fish

Tiger Shark
The fourth biggest species of shark in the world!

Tiger Trout
As tiger trout are sterile, they cannot produce offspring. However, they do have relatively long lifespans and can live up to 10 years in captivity.

Tire Track Eel
They like to burrow into aquarium sand.

Toadfish
Can be heard out of water

Triggerfish
There are 40 species of Triggerfish, all with different coloring and patterns.

Trout
They don’t have scales for their first month of life!

Tuna
The tuna has a sleek body that enables it to swim quickly through the water

Uaru Cichlid
The color of the Uaru cichlid changes during the spawning season

Urechis unicinctus (Penis Fish)
Create "inns" for other sea creatures

Viper Shark (dogfish)
Most data on these fish is based on observations near Japan.

Viperfish
Viperfish have a bioluminescent spine on their dorsal fin.

Wahoo Fish
Wahoo can change colors when they're excited and while they hunt

Walking Catfish
The walking catfish can move on land while breathing air

Walleye Fish
Has great night vision

Wels Catfish
The Wels catfish is O the largest freshwater fish in the world.

Whale Shark
The largest species of fish in the world!
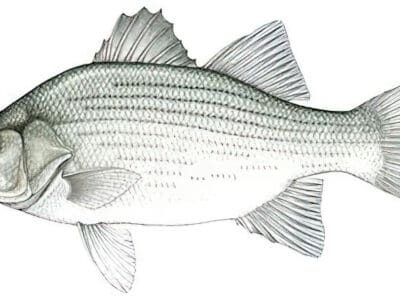
White Bass
Silvery white fish popular with anglers

White Catfish
White catfish can grow up to 37 inches in size.

White Crappie
Common freshwater fish in North America

White Sturgeon
They don't have any teeth!

Whiting
"Whiting" can refer to certain other species of ray-finned fish

Wolf Eel
Wolf Eels may become tame and interact with human in areas where people frequently dive.

Wolffish
The wolffish has impressive canines with a powerful bite force!

Wrasse
There are more than 500 different species!

Wrought Iron Butterflyfish
Is endemic to Japan.

Xingu River Ray
The Xingu River ray is only found in the Xingu River in Brazil.

Xiphactinus
Xiphactinus was the largest bony fish of the Cretaceous Period.

Yellow Bass
Largest yellow bass ever recorded weighed 2.95 pounds

Yellow Bullhead Catfish
Bottom dwelling scavenger fish

Yellow Perch
Female Yellow Perch grom larger than the males.

Yellowfin Tuna
The yellowfin forms schools with other tuna species

Yellowtail Snapper
Fast moving ocean fish with a long yellow stripe.

Zebra Pleco
The zebra pleco is a bottom feeder with a sucker mouth.

Zebra Shark
Can get to be 30 years old in the wild!

Zebrafish (Zebra Fish)
Used extensively in scientific research
List of Fish
- Alaskan Pollock
- Albacore Tuna
- Alligator Gar
- Amano Shrimp
- Amberjack
- American Eel
- American Paddlefish
- Anchovies
- Angelfish
- Anglerfish
- Arapaima
- Archerfish
- Arctic Char
- Asian Arowana
- Asian Carp
- Atlantic Cod
- Atlantic Salmon
- Atlantic Sturgeon
- Australian Flathead Perch
- Banana Eel
- Banjo Catfish
- Barb
- Barracuda
- Barramundi Fish
- Barreleye Fish (Barrel Eye)
- Basking Shark
- Bass
- Batfish
- Beluga Sturgeon
- Beluga Sturgeon
- Betta Fish (Siamese Fighting Fish)
- Bigfin Reef Squid
- Black Bass
- Black Marlin
- Blacknose Shark
- Bladefin Basslet
- Blobfish
- Blue Catfish
- Blue Eyed Pleco
- Blue Shark
- Blue Tang
- Bluefin Tuna
- Bluegill
- Bonefish
- Bonito Fish
- Bonnethead Shark
- Bowfin
- Boxfish
- Bronze Whaler Shark
- Brook Trout
- Buffalo Fish
- Bull Trout
- Butterfly Fish
- Carp
- Catfish
- Chain Pickerel
- Chimaera
- Chinese Paddlefish
- Chinook Salmon
- Cichlid
- Clearnose Skate
- Clownfish
- Cobia Fish
- Codfish
- Coelacanth
- Comb Jellyfish
- Common Carp
- Conger Eel
- Cookiecutter Shark
- Cory Catfish
- Crappie Fish
- Cubera Snapper
- Damselfish
- Danios
- Discus
- Dragon Eel
- Dragonfish
- Drum Fish
- Dusky Shark
- Dwarf Gourami
- Eagle Ray
- Eel
- Eel catfish
- Eelpout
- Electric Catfish
- Electric Eel
- Elephant Fish
- Ember Tetra
- Emperor Angelfish
- Escolar
- Fangtooth
- Fire Eel
- Fish
- Flathead Catfish
- Florida Gar
- Flounder
- Flounder Fish
- Flowerhorn Fish
- Fluke Fish (summer flounder)
- Flying Fish
- Football Fish
- Freshwater Drum
- Freshwater Eel
- Freshwater Jellyfish
- Freshwater Sunfish
- Frilled Shark
- Frogfish
- Galapagos Shark
- Gar
- Garden Eel
- Ghost Catfish
- Giant Trevally
- Goblin Shark
- Goby Fish
- Golden Shiner
- Golden Trout
- Goldfish
- Goliath Tigerfish
- Goonch Catfish
- Gourami
- Grass Carp
- Great Hammerhead Shark
- Great White Shark
- Green Sunfish
- Greenland Shark
- Grey Reef Shark
- Grunion
- Guadalupe Bass
- Gulper Catfish
- Gulper Eel
- Guppy
- Haddock
- Hagfish
- Haikouichthys
- Hairy Frogfish
- Halibut
- Hammerhead Shark
- Hardhead Catfish
- Herring
- Hogfish
- Horn Shark
- Horse Mackerel
- Immortal Jellyfish
- Irukandji Jellyfish
- Jack Crevalle
- Jellyfish
- John Dory
- Kaluga Sturgeon
- Kelp Greenling
- Keta Salmon
- Keyhole Cichlid
- Killifish
- King Mackerel
- King Salmon
- Kingklip
- Kissing Gourami
- Kitefin Shark
- Knifefish
- Koi Fish
- Kokanee Salmon
- Krill
- Labout’s Fairy Wrasse
- Lake Sturgeon
- Lake Trout
- Lamprey
- Lancetfish
- Largemouth Bass
- Lawnmower Blenny
- Leopard Shark
- Leptocephalus
- Lionfish
- Lizardfish
- Loach
- Longfin Mako Shark
- Longnose Gar
- Lumpfish
- Lungfish
- Mahi Mahi (Dolphin Fish)
- Mangrove Snapper
- Manta Ray
- Masked Angelfish
- Mayan Cichlid
- Megalodon
- Megamouth Shark
- Mekong Giant Catfish
- Milkfish
- Mojarra
- Mola mola (Ocean Sunfish)
- Molly
- Monkfish
- Moon Jellyfish
- Moray Eel
- Mudskipper
- Mullet Fish
- Muskellunge (Muskie)
- Needlefish
- Neon Tetra
- Neptune Grouper
- Oarfish
- Ocean Perch
- Ocean Pout
- Ocean Whitefish
- Oilfish
- Opah
- Opaleye (Rudderfish)
- Orange Roughy
- Orchid Dottyback
- Oscar Fish
- Oyster Toadfish
- Ozark Bass
- Pacific Sleeper Shark
- Paddlefish
- Parrotfish
- Pea Puffer
- Peacock Bass
- Peppermint Angelfish
- Perch Fish
- Pictus Catfish
- Pike Fish
- Pinfish
- Pink Salmon
- Pipefish
- Piranha
- Platinum Arowana
- Pollock Fish
- Pompano Fish
- Porbeagle Shark
- Porcupinefish
- Pufferfish
- Pygmy Shark
- Pyjama Shark
- Rainbow Kribs (Kribensis)
- Rainbow Shark
- Red Drum Fish
- Red-Lipped Batfish
- Redear Sunfish
- Redhump Eartheater
- Redtail Catfish
- Reef Shark
- Rockfish
- Sailfish
- Salmon
- Salmon Shark
- Sand Tiger Shark
- Sardines
- Sawfish
- Scorpion Fish
- Sculpin
- Sea Dragon
- Sea Slug
- Sea Trout
- Sea Urchin
- Seahorse
- Shark
- Sheepshead Fish
- Shortfin Mako Shark
- Silky Shark
- Silver Dollar
- Sixgill shark
- Skate Fish
- Skipjack Tuna
- Sleeper Shark
- Smallmouth Bass
- Smooth Hammerhead Shark
- Snailfish
- Snook Fish
- Snowflake Eel
- Sockeye Salmon
- Spanish Mackerel
- Speckled Trout
- Spinner Shark
- Spiny Dogfish
- Sponge
- Spotted Gar
- Spotted Garden Eel
- Squirrelfish
- Starfish
- Stargazer Fish
- Steelhead Salmon
- Stingray
- Stonefish
- Stoplight Loosejaw
- Striped Bass
- Sturgeon
- Suckerfish
- Surgeonfish
- Swai Fish
- Swordfish
- Taimen Fish
- Tang
- Tarpon
- Telescope Fish
- Tetra
- Thornback Ray
- Thresher Shark
- Tiger Muskellunge (Muskie)
- Tiger Shark
- Tiger Trout
- Tire Track Eel
- Toadfish
- Triggerfish
- Trout
- Tuna
- Uaru Cichlid
- Urechis unicinctus (Penis Fish)
- Viper Shark (dogfish)
- Viperfish
- Wahoo Fish
- Walking Catfish
- Walleye Fish
- Wels Catfish
- Whale Shark
- White Bass
- White Catfish
- White Crappie
- White Sturgeon
- Whiting
- Wolf Eel
- Wolffish
- Wrasse
- Wrought Iron Butterflyfish
- Xingu River Ray
- Xiphactinus
- Yellow Bass
- Yellow Bullhead Catfish
- Yellow Perch
- Yellow Tang
- Yellowfin Tuna
- Yellowtail Snapper
- Zebra Pleco
- Zebra Shark
- Zebrafish (Zebra Fish)
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the 3 types of fish?
Bony fish, jawless fish and cartilaginous fish.
What's the most famous fish?
The most famous fish is the coelacanth, which has four lobed fins resembling limbs. It is one of the world’s most ancient fish species. Its name means “hollow spine” and comes from the Greek words koilos (hollow) and akantha (spine).
Coelacanth also refers to the order Coelacanthiformes. which comes from the clade Sarcopterygii and subclass Actinistia. It includes two species in the genus Latimeria: the West Indian Ocean coelacanth (Latimeria chalumnae) and the Indonesian coelacanth (Latimeria menadoensis).
Can fish feel pain?
Yes, fish can feel pain, but it is different from the expression of pain from humans. It is difficult to test fish for pain except by looking for unusual behavior and physiological responses in reaction to certain stimuli.
What do fish eat?
Fish can be predatory, foraging or filter-feeding. Their diets can be carnivorous or omnivorous depending on the species and can include prey from zooplankton to invertebrates, crustaceans, annelids and smaller fish.
Discover a fish with human-like teeth here!
How do fish breathe?
Fish usually breathe through gills, which filters oxygen through water. However, some fish breathe using different means. Lungfish have lungs and mudskippers can breathe through wet skin and the lining of their mouth and throat.
What are the smallest and largest fish?
The smallest fish is the cyprinid fish (8mm) and the largest fish is the whale shark (12m).
What is the difference between "fish" and "fishes"?
“Fish” refers to the singular and one species or to the plural within context. “Fishes” refers to the plural, especially when talking about more than one species of fish.
What are the main differences between the flying fox fish and the Siamese algae eater?
The main differences between the flying fox fish and the Siamese algae eater are color, length and shape, mouth shape, and algae preferences.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.


















