Insects, invertebrates, arachnids, and other creepy crawlies are less terrifying to look at because they are tiny. But what do you think they will look like if they are about a foot long? Ants only look non-threatening because of their diminutive size. Worms also seem tolerable as they are too little to hurt you. But imagine you were transported into a fantasy world where every little critter is bigger. If you venture into the Amazon, you’ll surely find numerous animals that are not present in your typical home. One of the strangest you’ll encounter is the world’s largest leech species.
The leech is one of the most terrifying things you’ll ever see. But imagine a leech more than a foot long! That’s a gigantic, worm-looking, bloodsucking creature! You’ll surely be shocked if you see one, let alone get attached to one. Below, we uncover everything you need to know about the largest leech ever discovered.
What Is the Largest Leech Ever Discovered?
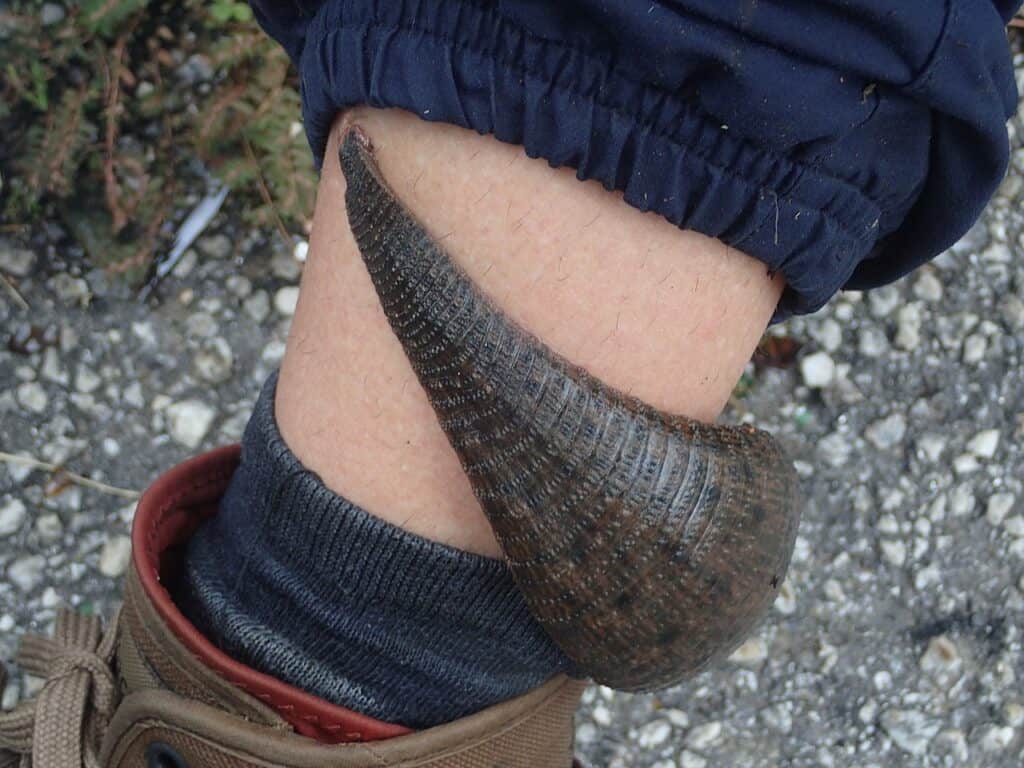
The world’s largest leech is the giant Amazon leech.
©Anonyme973 / CC BY-SA 4.0 – License
The giant Amazon leech is the world’s largest leech, reaching a length of up to 18 inches! That’s one-and-a-half feet long!
This enormous Amazon leech is reported to reach incredible sizes and spread out to a width of 3.9 inches. In contrast to juveniles, which lack a uniform color and instead have a noncontinuous palette and patchy coloring, adults of these leeches are a grayish-brown hue. From the 1890s until the 1970s, when two adults were collected in French Guiana, the species was believed to be extinct. Grandma Moses, one of these two leeches, established a fruitful reproductive colony at UC Berkeley.
In just three years, Grandma Moses, as she was known, gave birth to more than 750 baby leeches. Grandma Moses’ breeding colony was investigated by researchers in medicine, neurology, and natural history, who produced a total of 46 pieces of research. UC Berkeley selected the National Worm Collection as the leech’s final resting place after she passed away. Grandma Moses resembled the shape of a cobra’s hood in one’s hand; she was broad in the middle but tapered at either end.
According to a French scientist’s 1899 writing, a few of these huge leeches are actually enough to kill a cow or a horse.
What Does the Giant Amazon Leech Look Like?
The giant Amazon leech has 34 segments, each with its own brain (or ganglia), like all bloodsucking leeches. Not bad for a slimy little worm to have 34 brains, right? Leeches are linked to earthworms, and both have a slimy texture. When pressured, the leech secretes goopy mucus to escape.
The leech’s powerful sucker is located at its fatter end, while the head is at the narrower tip. The leech has muscles you can feel while in your palm. As it eats, those muscles move in undulating waves, likely to assist in transporting absorbed blood to the digestive system.
How Big Do Regular Leeches Get?
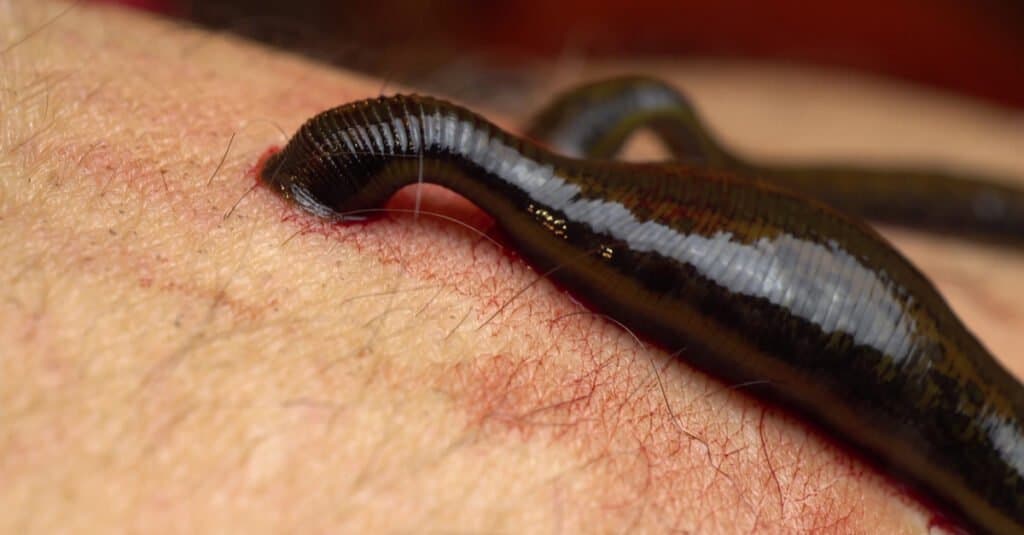

The average leech grows up to two inches long.
©Vital9s/Shutterstock.com
Leeches come in different sizes, but the average leech grows up to two inches long. Other than the giant Amazon leech, certain species in the United States can also reach lengths of 10 inches.
Leeches are segmented, flat-bodied worms. Although some species are vividly colored, they are typically black or brown in hue. They can stretch and compress to such an extent that it is challenging to measure them due to their incredible flexibility. Typically, a leech has two or three rows of small teeth, and you can’t feel a leech bite partly because of the size of its fangs.
Where Do Leeches Live?
Leeches are often located in protected, shallow areas, hidden under aquatic vegetation or beneath rocks, logs, and other debris. They are drawn to regions of disturbed water around docks and bathing places. Leeches are most active during the sweltering summer days, and they dig burrows in the mud just below the frost line in winter.
Although leeches like warm weather, they are very tolerant of their surroundings. They can go for extended periods without food, and they will modify their body temperature to suit the conditions. They can, therefore, be found anywhere besides Antarctica’s icy regions.
What Do Leeches Eat?
Leeches have a diverse diet despite their negative reputation as bloodsuckers. Freshwater leeches feed on mollusks, insects, insect larvae, fish eggs, and worms in addition to sucking blood. They like to ingest the blood of other aquatic animals, such as fish, worms, and snails.
About 25% of leech species are predators. They hunt and ambush their prey. These types of leeches eat small invertebrates like slugs, snails, and earthworms.
As soon as the leech sees a moving object, it swims toward it, utilizes one of its suckers, and attaches to the host. Then, using its tiny, pointed teeth, it makes a Y-shaped hole and injects an anticoagulant into the incision.
How Long Do Leeches Live?
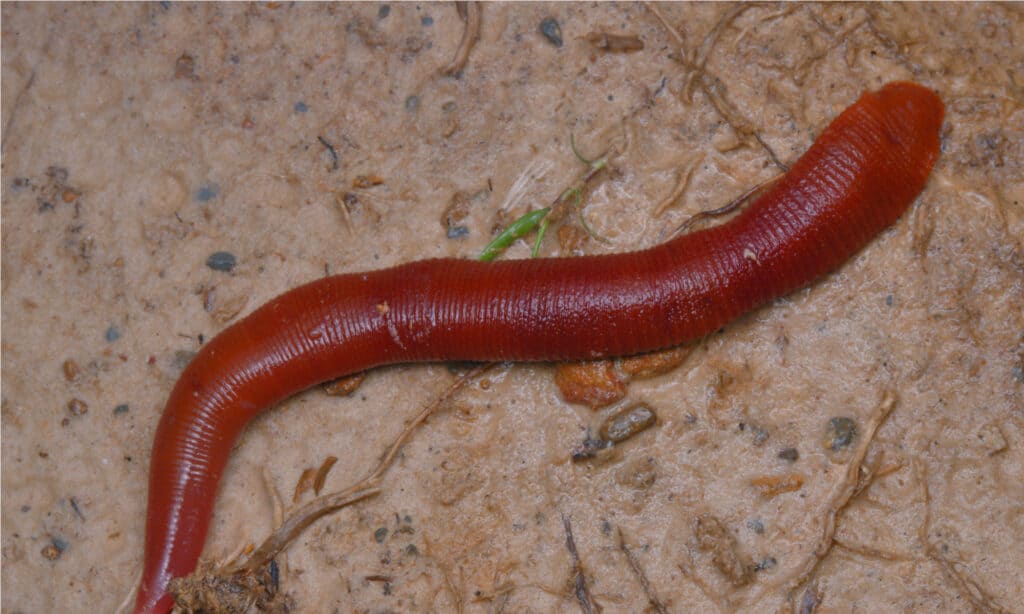

Leeches have a lifespan of two to eight years.
©SIMON SHIM/Shutterstock.com
Leeches typically have a lifespan of two to eight years, which is a long lifespan for an invertebrate. They can sometimes live for up to ten years in the wild. However, they can live much longer in captivity.
While leeches are typically found in water, some can live in dry areas by excavating mud holes. Most cannot swim and avoid going into the water, but they can withstand brief submersion.
What Happens if a Leech Enters Your Stomach?
The parasites that leeches often carry in their digestive tracts cannot survive in humans and do not serve as a threat. However, leeches can retain germs, viruses, and parasites from prior blood supplies and may pass them on to humans.
What Happens if You Get Bitten by Leeches?
People bitten by leeches may experience painless bleeding, burning, itching, bruising, irritation, and redness. A targeted physical examination may be needed depending on the region of concern.
Unlike other bloodsucking invertebrates such as mosquitos, there are no known diseases that leeches can spread to people. However, they can still pose a threat to the human body due to the parasites or germs they might carry.
Up Next:
Leech Lifespan: How Long Do Leeches Live?
3 Leech Infested Lakes in the USA You Don’t Want to Swim In!
Leeches in Texas: What Types Live in Texas and When They’re Active
The photo featured at the top of this post is © photowind/Shutterstock.com
Sources
- Missouri Department of Conservation, Available here: https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/leeches
- Nova Science Now, Available here: https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/0305/01-hunt-nf.html
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haementeria_ghilianii
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.






