Heatwaves are becoming a lot more common than they were in the past with 2023 breaking temperature records across the world. The summer of 2023 was the hottest ever recorded since temperature recording began about 140 years ago. What is a heat dome, and why do they cause soaring temperatures? We’ll go over this phenomenon and others that cause heatwaves now.
What is a Heat Dome?
The way air moves across North America affects heat dome formation.
©Алексей Белозерский/iStock via Getty Images
When an area of high pressure sits over a region for a few days or weeks, it creates a heat dome. As heat domes sit over a region, they create heat waves.
High-pressure systems don’t necessarily create heat domes. A high-pressure system causes air to sink, and as air sinks, temperatures rise. It becomes a heat dome when that sinking air cannot escape and becomes trapped.
Heat domes usually last up to a week, sometimes two, though they can last longer. In 2023, a heat dome over the Southwest United States lasted for over a month.
Heat domes in the United States are usually a result of shifts in the Pacific jet stream. This jet stream is a major air current that moves from west to east across North America in a wave-like motion.
The wave-like motion of the Pacific jet stream sometimes becomes a more dramatic wave, and the air snaking across North America may slow down. In the areas below a jet stream that has swung far to the north, stagnant air builds up and sinks. This sets the stage for a heat dome in the Southwest.
What is a Heatwave?

Heatwaves are periods of at least 2 consecutive days where the temperature is much higher than normal.
©leolintang/Shutterstock.com
A heatwave is a period where the daily temperature is much higher than normal which may be accompanied by increased humidity. For hot weather to be called a heatwave, it has to persist for two or more days. However, heatwaves can go on for months, and the most severe heatwaves usually occur under a heat dome.
While heatwaves are common, and most people have experienced them, they are the most deadly weather phenomenon in the United States. For about 2 decades, heatwaves have caused more deaths in the United States than any other extreme weather event.
Why Do Heat Domes Cause Soaring Temperatures?
Heat domes cause soaring temperatures because high pressure traps hot air underneath it almost like a pot lid. The longer the dome exists, the hotter the trapped air gets because the Sun continues to heat it. As days turn into weeks, subsequent days get hotter than the last creating a heatwave.
Heat domes also keep clouds, rain, and other weather away that could cool the ground underneath the heat dome. For example, in 2021, a heat dome over the Pacific Northwest could not be penetrated by ocean winds.
Are All Soaring Temperatures Caused by Heat Domes?
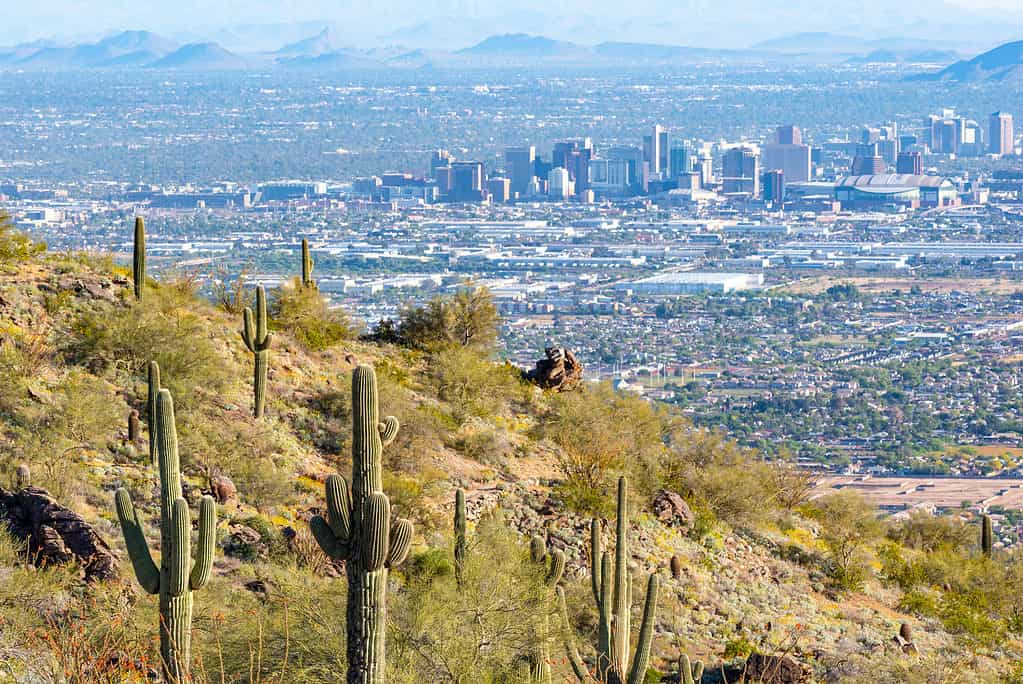

Heat domes in places like Phoenix, Arizona, are exacerbated by urban heat islands.
©iStock.com/Gregory Clifford
Most soaring temperatures resulting in heat waves are caused by heat domes. Despite this, other phenomena exacerbate the development of searing heat waves around the planet. Different heatwaves are caused by heat domes created by mechanisms unique to that area of the planet.
Anticyclones cause heat waves, and both Pacific jet stream heat domes and the domes created by anticyclones are exacerbated by El Niño. Climate change also plays a significant role in the development of heat waves.
A heat dome’s searing temperatures are sometimes exacerbated by heat islands. Major cities, like Phoenix in Arizona or New York City, absorb heat during the height of the day. They then radiate this heat at night, keeping the daytime low higher than it would be naturally.
El Niño Exacerbates Hot Conditions
El Niño refers to the warming of ocean water in the Pacific Ocean by the west coast of the Americas near the equator. This happens about every two to seven years, though exactly when this warming will occur is unpredictable. El Niño tends to last up to a year but can last much longer.
Most of the time, trade winds exist along the equator that blow in a westward direction. This wind drags warm water near South America closer to Asia. When this occurs, colder water from the depths of the ocean upwells to the surface to replace the displaced water.
When an El Niño occurs, this normal trade wind loses strength. The weakened winds do not push warm water westward which causes ocean temperatures near the Americas to be higher than normal. These warmer waters contribute to hotter temperatures in North America because the warming ocean caused by El Niño puts more heat into the atmosphere.
Anticyclones Create Heat Domes and Cause Soaring Temperatures
Anticyclones are high-pressure systems that cause hot weather. They are a little different than the heat domes common in the American Southwest, though they also cause devastating heat waves.
During an anticyclone, air flows down toward the planet’s surface, and this sinking air compresses air molecules. The air is driven toward the ground by air circulating clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. As the pressure of the sinking air increases, temperatures heat up.
Since the air of an anticyclone circulates and causes an inner spot of air that’s static and sinking, the resultant effect of anticyclones is dry and hot weather conditions. Clouds don’t form, and only light breezes affect the region. The sun bakes the static interior, and a heat dome occurs.
How Climate Change Creates More Heatwaves

Climate change creates many types of extreme weather including heat domes and tornadoes.
©EmiliaUngur/Shutterstock.com
Climate change increases the amount of hot days and nights that occur across the planet. The gradually warming lower atmosphere on Earth is caused by human factors, and this affects how air flows around the planet. It also affects how water circulates through the seas.
This increase in atmospheric heat does things like amplify the effects of El Niño events. As the jet streams shift, wind currents change, and ocean temperatures climb. This means that the necessary elements that create heat domes become more common.
Climate change may create worse heat domes in some parts of the world. It also creates other types of extreme weather. For example, hurricane frequency, storm surges, and tornadoes are also more common as climate change worsens.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.








