A jet stream is a narrow flow of air or wind that acts as a barrier between hot and cold areas of air. Jet streams always blow from west to east. However, their northern and southern boundaries shift. Jet streams are strongest in the winter.
How Many Jet Streams Does the Earth Have?
Our planet has four major jet streams. These include two polar streams: one surrounding the North Pole and one surrounding the South Pole. There are also two subtropical streams close to the equator in both the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere.
Other smaller ones can form temporarily in the summer, especially in tropical areas.
How and Why Do Jet Streams Form?
When the sun heats the Earth, it does so indirectly. Because the equator is closer to the sun, it gets hotter than other areas of the globe. Alternatively, the poles are further from the sun, so they get colder than most other portions of Earth. In the areas where warm and cool air meet, the warm air rises over the cool air. This creates the winds that form the jet stream.
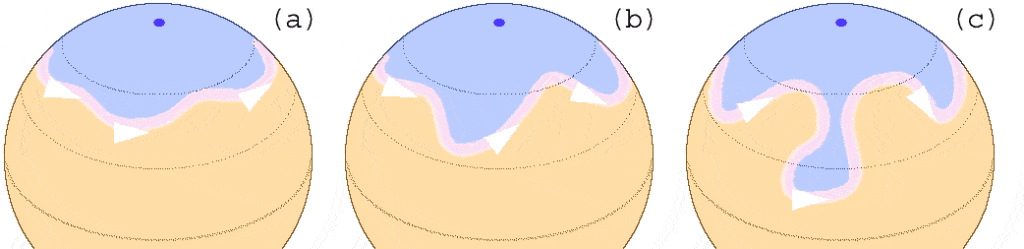
The earth has four jet streams: two polar streams: one surrounding the North Pole, one surrounding the South Pole, and two subtropical streams close to the equator.
©https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/85/N_Jetstream_Rossby_Waves_N.gif
Can You Feel the Jet Stream on Earth?
This isn’t something that people can feel on a windy day. These powerful flows of air are typically found between five and nine miles above our planet’s surface. However, even though we cannot detect it while on the ground, it benefits us greatly. Planes flying from west to east often use these winds to arrive at their destination faster.
How Fast Are Jet Stream Winds?
Jet streams flow at about 110 miles per hour on average. However, when there are drastic temperature differences between two areas, they may travel as fast as 250 miles per hour. In fact, it’s wonderful that we can’t feel these powerful forces on the ground. Their average speed equals a category two hurricane!
They are often described as ribbons of air; however, experts say they are more like rivers. The current is strongest in the middle, but there is a wide swath of air in the “river bed.” They can also split, come together, form eddies, or disappear completely before popping up elsewhere.
Why Do Jet Streams Always Blow From West to East?
These air streams blow from west to east due to the shape and rotation of the Earth, which turns in a west-to-east direction. Hot air rises from the equator and heads north. Areas near the equator spin significantly faster than areas closer to the North Pole or South Pole. In fact, you would weigh a whole pound less at the equator than at one of the poles! Because the air has such momentum, it does not go directly north. Instead, it follows its original trajectory with the velocity of the equator, which sends it from west to east as it travels north. As it nears the poles, it moves faster than the Earth is spinning, creating the powerful wind that creates a jet stream.
Why are Jet Streams Strongest in the Winter?
They are strongest in the winter because that is when the differences in temperatures are greatest between air masses. During the winter, they are more likely to reach its highest range of speeds.
What Does the Jet Stream Do?
These strong winds affect the weather on the ground. When the jet stream is strong, it is often in the shape of a circular band around Earth. However, storms and other conditions can cause it to become irregularly shaped, leading to weather phenomena like heat waves and polar vortexes. It also affects areas of high and low pressure on the surface. When there is high air pressure, the weather is likely to be clear and pleasant. In areas of low pressure, storms and inclement weather are more likely.
These powerful winds can also help weather patterns move along quickly, transporting storms across far distances. This can create problems over a wide area. On the other hand, if a storm or weather pattern forms far from a jet stream, it might stall over one area for a long time.
A country’s position in relation to the jet stream often explains its weather. For example, the arctic polar stream flows over the UK in the winter, resulting in plenty of rainy weather. However, in the summer, it usually moves north resulting in sunnier days. This is because the jet stream often follows the sun. In the spring and summer, the sun’s elevation increases each day in relation to what we see on Earth. So, in those seasons, the jet stream often moves northwards.
Because of these factors, meteorologists use satellites and other tools to monitor the jet stream constantly. They are somewhat unpredictable, but are an important indicator for forecasting the weather.
Up Next:
- The Great Flood of 1993: Here’s What Happened to the Mississippi River
- Discover the 10 Windiest States in the US
- Discover the Highest Wind Speed Ever Recorded on Earth
- The Deadliest Natural Disasters of All Time
The photo featured at the top of this post is © https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/79/Greatcircle_Jetstream_routes.svg / Original
Sources
- SciJinks, Available here: https://scijinks.gov/jet-stream/
- National Weather Service, Available here: https://www.weather.gov/jetstream/jet
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jet_stream
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the jet stream?
The jet stream is a narrow flow of air or wind that is basically a barrier between hot and cold areas of air. Jet streams always blow from west to east. However, their northern and southern boundaries shift. Jet streams are strongest in the winter.
How many jet streams does the Earth have?
Our planet has four major jet streams. There are two polar jet streams: one surrounding the North Pole and one surrounding the South Pole. There are also two subtropical jet streams close to the equator in both the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere.
Other, smaller jet streams can form temporarily in the summertime, especially in tropical areas.
How do jet streams form?
When the sun heats the earth, it does so indirectly. The equator is closer to the sun, so it gets hotter. The poles are further from the sun, so they get colder. In the areas where warm and cool air meet, the warm air rises over the cooler air. This creates the winds that form the jet stream.
Can you feel the jet stream on Earth?
The jet stream isn’t something that you would feel on a windy day. Jet streams are typically found between five and nine miles above our planet’s surface. Even though you can’t really feel it down on the ground, it does help us. Planes flying from west to east often use the jet stream to get to their destination faster.
How fast are jet stream winds?
Jet streams flow at about 110 miles per hour on average. However, when there are even more significant temperature differences between two areas, they can go as fast as 250 miles per hour. It’s really a good thing you can’t feel a jet stream on the ground. Their average speed equals a category 2 hurricane or a weak tornado!
Why do jet streams blow from west to east?
The jet stream blows from west to east due to the rotation of the Earth, which rotates in a west-to-east direction, and the shape of the planet. Hot air rises from the equator and heads north. Things at the equator spin significantly faster than things closer to the North Pole or South Pole. This momentum is enough that you would weigh a whole pound less at the equator compared to one of the poles! Because the air has this momentum, it does not go directly north but follows its original trajectory with the velocity from being at the equator, which sends it from west to east as it travels north. As it nears the poles, it is moving faster than the Earth is spinning due to its original location at the equator, creating the powerful wind that makes it a jet stream.
What does the jet stream do?
These strong winds affect the weather on the ground. When the jet stream is strong, it is often in the shape of a circular band around Earth. However, storms and other conditions can cause it to become irregularly shaped, leading to weather phenomena like heat waves and polar vortexes. It also affects areas of high and low pressure on the surface.
Jet streams can also help weather patterns move along quickly. A country’s position in relation to the jet stream often explains its weather.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.







