The word “parasite” is Greek for “one who eats at the table of another.”
Parasite Meaning
Parasites are organisms that live on or in a host organism, causing it harm. The use of hosts is essential to a parasite’s survival. Parasites can be endoparasites, meaning they live inside of a host. Or they can be ectoparasites living outside the body, typically on the surface.
Parasites operate differently from predators. For one, they are usually much smaller than their host, and their goal is not to kill them. Instead, they use the host’s resources for their own gain. The word “parasite” is Greek for “one who eats at the table of another.”
Parasite Pronunciation
You pronounce parasite as [peh | ruh | site].
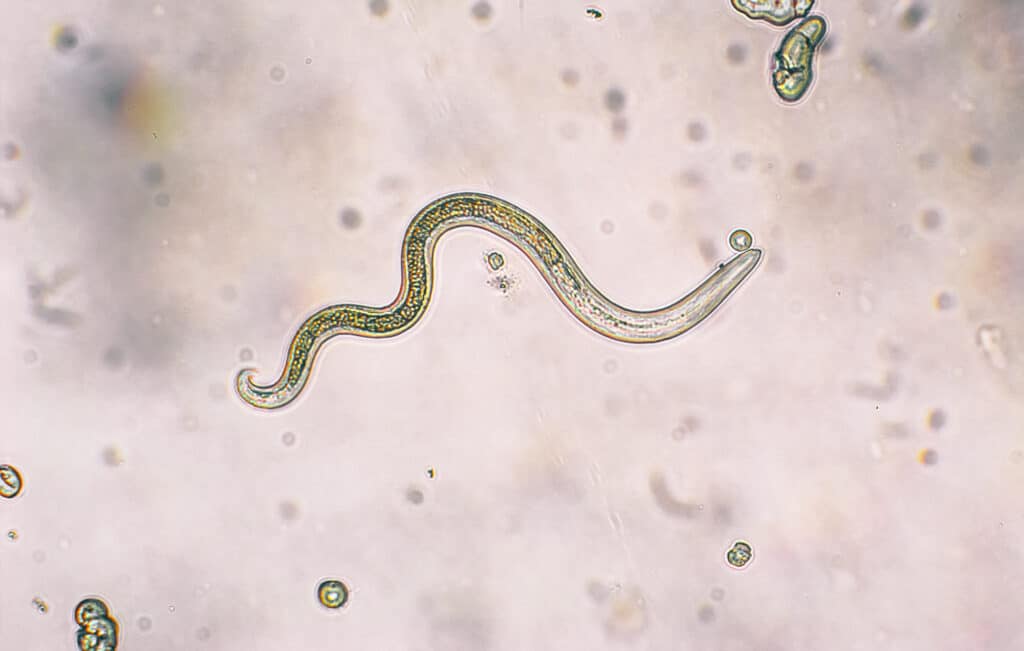
Toxocara canis second stage larvae hatch from eggs in a microscope. Toxocariasis, also known as Roundworm Infection, causes disease in humans.
©iStock.com/dotana
Example of a Parasite
Helminths, such as flatworms and roundworms, are multicellular organisms that feed on a host, using its body for food and protection. They can infect humans and animals, causing various diseases.
The tongue-eating isopod is another example of a parasite. These parasitic isopods enter through a fish’s gills, attaching to the tongue and severing the blood vessels. When the tongue falls off, the parasite attaches to the stub and acts as the fish’s new tongue.
Parasitism Evolutionary Strategies
There are six primary parasitic means of exploitation.
- Parasitic castrators – destroy the host’s reproduction system (Sacculina carini)
- Directly transmitted – do not require a vector (lice and mites)
- Trophically transmitted – transmission occurs when the host eats the parasite (roundworms)
- Vector-transmitted – needs an intermediate host (bacteria, viruses)
- Parasitoids – eventually kill their hosts (parasitoid wasps)
- Micropredators – affect more than one host and are typically vectors of disease (mosquitos)
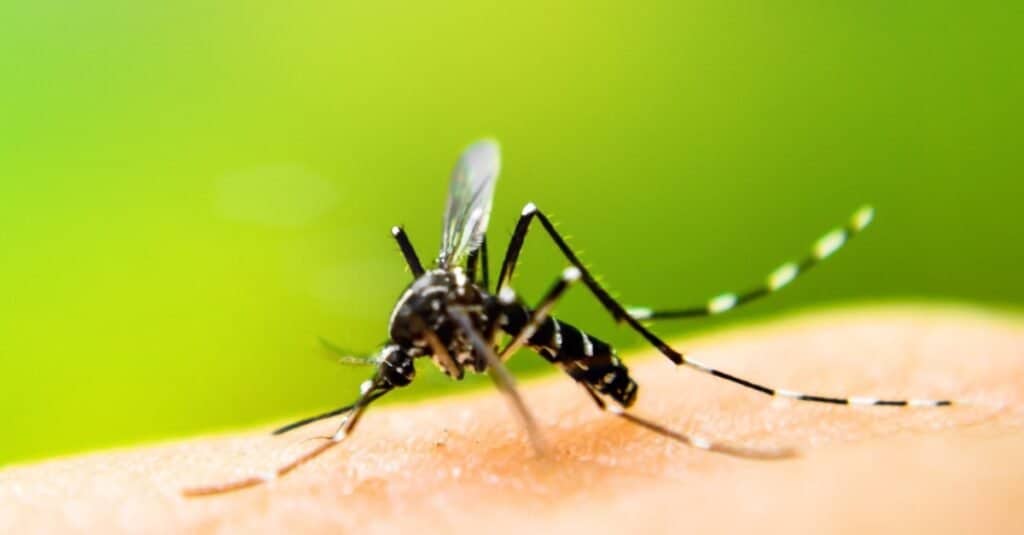

Mosquitos are micropredators, meaning they affect more than one host and are vectors of disease.
©iStock.com/auimeesri
Variations in Parasitism
There are several variations in parasitism.
- Kleptoparasites – steal food from the host (skua)
- Social parasites – take advantage of social structures within species (gypsy’s cuckoo bumblebee)
- Hyperparasites – feed on other parasites (white butterfly parasite)
- Brood parasites – hosts are tricked into raising the parasite’s young (cowbirds)
- Sexual parasites – some male species are reduced to relying solely on the female for nourishment and protection (angler fish)




