Leopard Frog
They can jump up to three feet
Advertisement
Leopard Frog Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Leopard Frog Conservation Status
Leopard Frog Facts
- Main Prey
- Insects, Mollusks, birds, Worms, snakes, frogs
- Name Of Young
- Tadpoles
- Group Behavior
- Largely solitary
- Fun Fact
- They can jump up to three feet
- Estimated Population Size
- Millions
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss, pollution
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Leopard-like spots
- Other Name(s)
- Meadow frog, grass frog
- Gestation Period
- 70-110 days
- Average Spawn Size
- Up to 6500
- Habitat
- Forest, grassland, wetland
- Predators
- Various, including raccoons, foxes, snakes, birds, frogs, humans
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Type
- Amphibian
- Common Name
- Leopard Frog
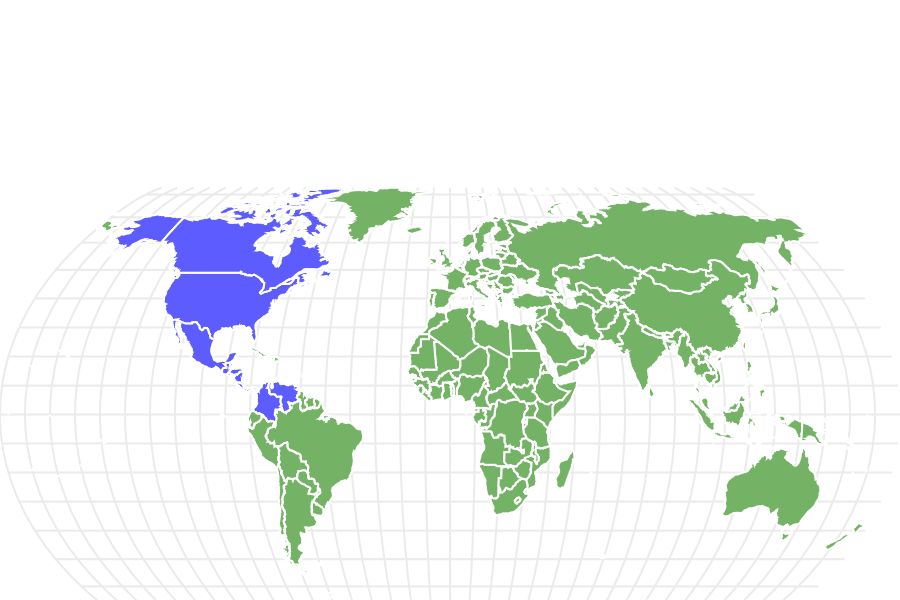
- Location
- From southern Canada through northern South America
View all of the Leopard Frog images!
“Leopard frogs are very popular with humans.”
Leopard frogs are a popular pet and a delicious food source, and they have found a calling in laboratory experiments in laboratory experiments and science classrooms. Leopard frogs, also known as meadow or grass frogs, are the common name for lithobates, the “true frog” genus. They share this name with the American Bullfrog and others.

5 Incredible Leopard Frog Facts!
- These frogs live about five years.
- A female may lay nearly 7000 eggs at one time.
- The tadpoles have eyes on top of their heads rather than on the sides like many other species.
- Not all species of these frogs have distinctive spots from which they get their name.
- Leopard frogs can be cannibals, sometimes eating other smaller leopard frogs.
Scientific Name
The scientific name for these frogs is Lithobates, which is the genus name for amphibians in the true frog family. They are in the family Ranidae, class Amphibia. They are also known as grass frogs, meadow frogs, or Rana pipiens. There are potentially twenty-three known species of these frogs:
- Atlantic Coast Frog (Lithobates kauffeldi) – These Leopard Frogs can be found in the United States and they can be noticed do to their specific mating call. They are able to create “chucking” sounds from large sacs that on each side of their head.
- Bigfoot Frog (Lithobates megapoda) – Found in western Mexico, these fairly large frogs are eaten by humans and spend the majority of their time in and around water.
- Browns’ Leopard Frog (Lithobates brownorum)
- Chiricahua Frog (Lithobates chiricahuensis)
- Forrer’s Grass Frog (Lithobates forreri)
- Guerreran Frog (Lithobates omiltemanus)
- Island Leopard Frog (Lithobates miadis)
- Lemos-Espinal’s Frog (Lithobates lemosespinali)
- Lenca Frog (Lithobates lenca) – This frog can be found high in the Honduran mountains. The nickname of this frog, “Lenca”, comes from name of the local people found in the same region.
- Lowland Frog (Lithobates yavapaiensis)
- Montezuma Frog (Lithobates montezumae)
- Northern Frog (Lithobates pipiens) – As its name suggest, this frog is found in Canada and the U.S. It is actually the state amphibian of Vermont and Minnesota. It has several color variations.
- Northwest Mexico Frog (Lithobates magnaocularis)
- Peralta Frog (Lithobates taylori)
- Pickerel Frog (Lithobates palustris) – This particular frog makes its home in North America. While almost every leopard frog has spots, the Pickerel Frog’s spots have a quality about them that makes them seem “hand-drawn”. They also have secrete toxins from their skin to help protect them from would be predators.
- Plains Frog (Lithobates blairi) – Also called “Blair’s Leopard Frog” after a famous zoologist, they are can be almost always found close to rivers, creeks, lakes, ponds, and other sources of water, despite their name. They are not very picky eaters and spend their time hunting anything their size or smaller at night.
- Relict Leopard Frog (Lithobates onca)
- Rio Grande Frog (Lithobates berlandieri)
- Showy Frog (Lithobates spectabilis)
- Southern Frog (Lithobates sphenocephalus) – This frog can be found in the eastern and southern part of the United States. It is the most common frog located in the state of Florida. With a ridge down both sides of its yellow-colored back. It has spots, like other Leopard Frogs, but they are round and dark.
- Tlaloc’s Leopard Frog (Lithobates tlaloci)
- Transverse Volcanic Frog (Lithobates neovolcanicus)
- Vegas Valley Frog (Lithobates fisheri)
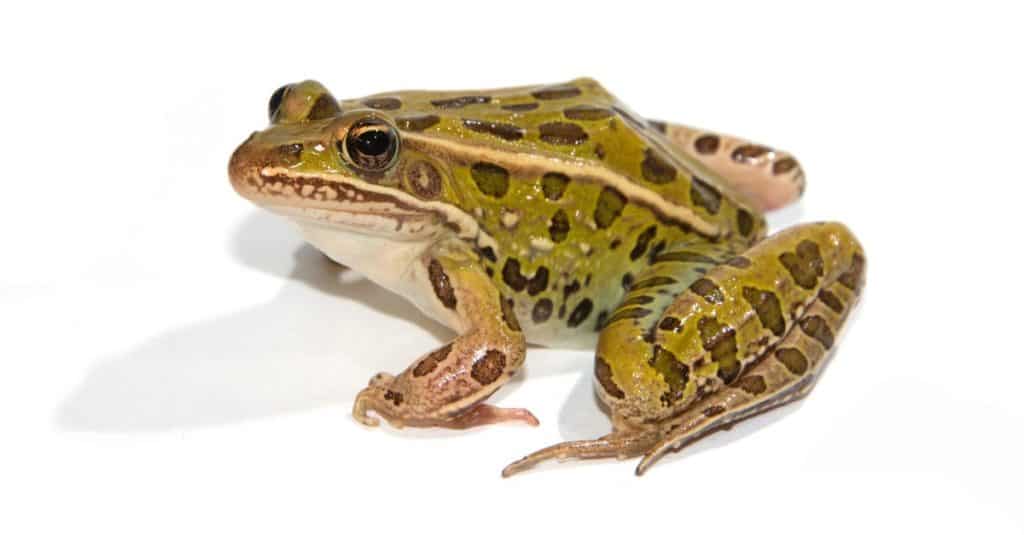

Leopard Frogs are in the family Ranidae, class Amphibia.
©Gerald A. DeBoer/Shutterstock.com
Appearance
These frogs are between two to five inches in length and vary in color between species anywhere from dull brown to bright green, and all the shades in between, many with white underbellies. Regardless of their main body color, nearly all of these frogs have dark spots in a leopard-like pattern. They are so similar in appearance that they were believed to be all one species until they came into common use in laboratories in the 1940s, at which point scientists began to note distinct differences between the species. The female of the species is larger than the male, and southern frogs tend to be smaller than northern frogs. The tadpoles are distinguishable from other frog species because they have dorsal rather than lateral eyes and a white stripe in between their nostrils.
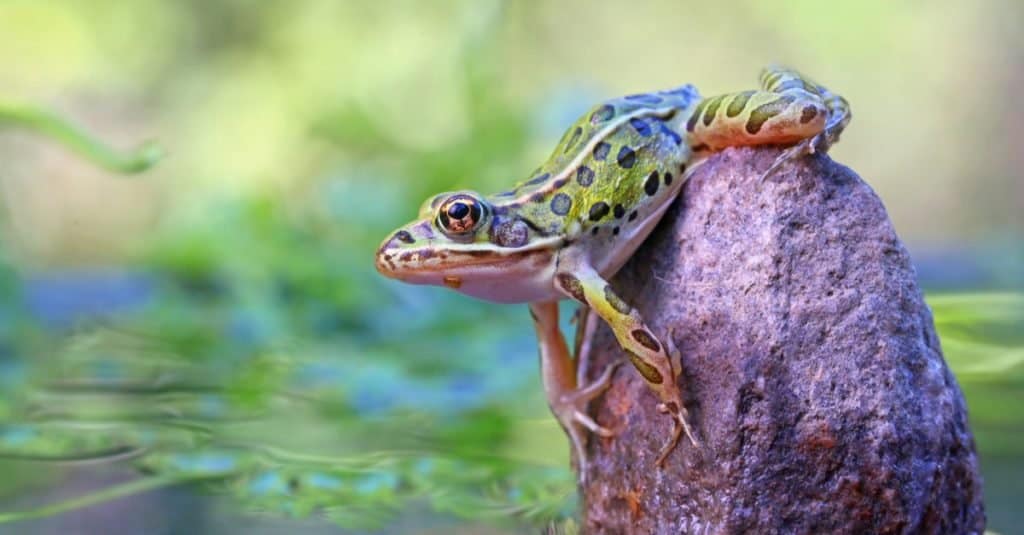

Nearly all Leopard Frogs have dark spots in a
leopard
-like pattern.
©Alexander Sviridov/Shutterstock.com
Behavior
These frogs are solitary, coming together only for mating. They do have parental care, as the offspring are briefly cared for by the females before going off on their own. These frogs are nocturnal, semi-aquatic, and hibernate in the winter, when they may stop eating for as long as three months! The tadpoles are herbivores, but fully-grown adults are carnivorous. The male’s calling noises have been likened to a snore.
Habitat
These frogs divide their time between land and water. They require moisture from the water, but most of their food is found on land since they feed primarily on insects. They favor grassland that is near water. Bodies of water also allow them to escape predators more easily. They can be found anywhere from the Hudson Bay in Canada down to Mexico and even into upper South America.
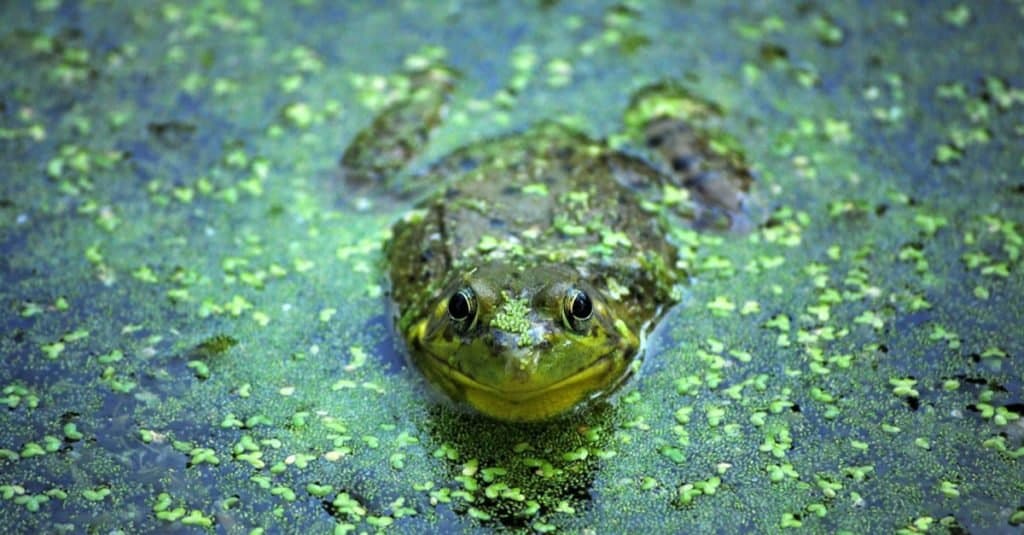

Bodies of water allow Leopard Frogs to escape predators more easily.
©tim elliott/Shutterstock.com
Diet
While these frogs primarily feed on insects, they are opportunists and will eat whatever they can find. This may even include other leopard frogs! They have been known to consume small birds and snakes. They are somewhat lazy hunters, who tend to sit and wait for prey to come along. They then catch them with long tongues that are tacky and stick to prey to keep them from escaping before it is swallowed whole.
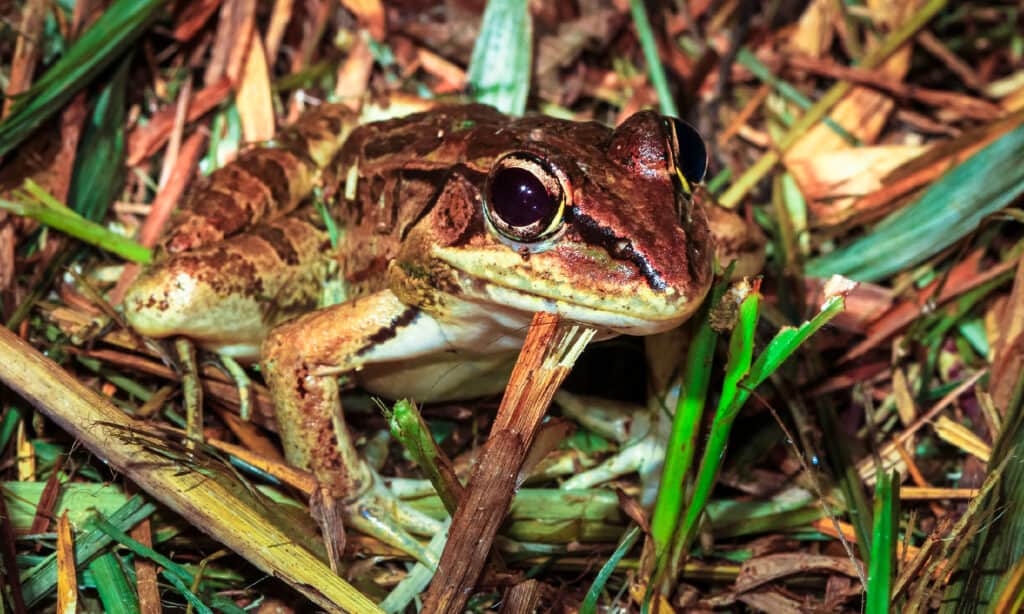

Leopard Frogs are somewhat lazy hunters, who tend to sit and wait for prey to come along.
©iStock.com/Kevin Wells
Predators and Threats
These frogs have many predators because they are not one of the species of frog that secretes a toxin through their skin. They are hunted by birds, reptiles, mammals like raccoons and foxes, and even other frogs. Humans are a threat to them not only because people consume frog legs, but because these frogs, northern leopard frogs, in particular, are commonly used in labs and also in classrooms for dissection, and due to habitat encroachment.
History and Evolution
Early on, the Lithobates genus name was used for only a few types of frogs, including the Leopard Frog and the American Bull Frog. After more studying and leaps of advancement in scientific testing, more and more species types from South and Central America were added to the group.
The Leopard Frog has been studied for its evolution because of its many different subspecies and their fairly large spread of environments. Evidence shows for some of the groups being bottlenecked evolutionary speaking in the western part of the United States compared to the eastern part. There are many factors that could have played significant roles in those evolutions, namely glacial movements over time.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
These frogs reproduce by sexual reproduction. Once a male and female mate, the female frog may lay up to 6500 eggs at one time. Depending on many factors, including weather, those eggs may take anywhere from two to four months to hatch into tadpoles and grow into adult frogs. Though adult frogs are carnivores, the tadpoles are herbivores who eat algae and decaying organic matter. These frogs generally live an average of five years in the wild, though they have been known to live as long as nine years.
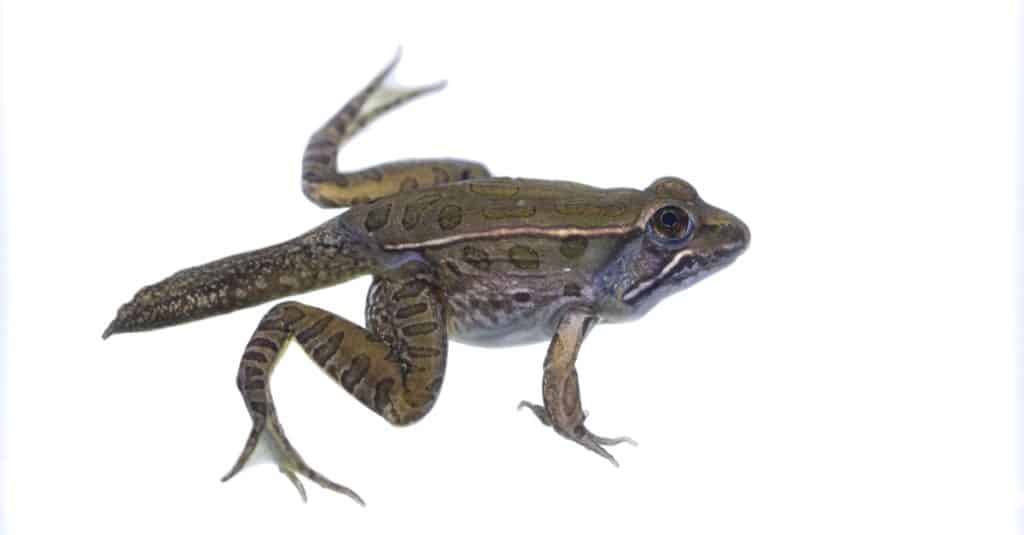

Leopard Frogs as tadpoles are herbivores who eat algae and decaying organic matter.
©Brian Magnier/Shutterstock.com
Population
The conservation status for most species of these frogs is decreasing. While many species of frogs are not considered in any danger, many other species have populations that are in decline, with several species listed as endangered or even critically endangered. At least one species, the Las Vegas or Vegas Valley Leopard Frog, is listed as extinct.
View all 98 animals that start with LLeopard Frog FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are leopard frogs carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
Leopard frogs are carnivorous, though the tadpoles are herbivores.
What is a leopard frog?
A leopard frog is a brown or green frog with dark oval spots in a pattern that resembles a leopard. The males have a calling sound similar to a human snore.
How do you care for a leopard frog?
To thrive, a leopard frog needs adequate space, temperatures between 60-80 degrees Fahrenheit, and a habitat with both terrain and freshwater. Their habitat must be cleaned every couple of weeks and they must be fed not only insects but nutritional supplements, for growth and to protect them from disease.
Do leopard frogs make good pets?
Leopard frogs do make good pets, but they do require weekly maintenance on their habitat. They do not enjoy being held and they can carry salmonella, so handling should be kept to a minimum and post-handling hygiene is important.
Are leopard frogs poisonous?
No, nor are they venomous, but they can transmit salmonella.
How big do leopard frogs get?
Leopard frogs can grow up to five inches in length.
What does a leopard frog eat?
Leopard frogs eat insects, worms, snakes, birds, and other frogs.
Can leopard frogs live with fish?
Because Leopard Frogs are carnivorous, they should not be kept with any fish that are small enough for them to ingest, but larger species of fish should be fine. They are only semi-aquatic, so they cannot be kept in a tank without an above-water land area.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/leopard-frog
- EOL, Available here: https://eol.org/pages/1019093
- IUCN Redlist, Available here: https://www.iucnredlist.org/search?query=leopard%20frog&searchType=species
- The Spruce Pets, Available here: https://www.thesprucepets.com/leopard-frogs-1236814
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leopard_frog
- Thought Co, Available here: https://www.thoughtco.com/northern-leopard-frog-facts-4588922
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/amphibians/facts/northern-leopard-frog