In this article, we delve into the fundamental distinction between haploid vs. diploid cells. We also discuss what impact it has on genetic diversity, as well as explore the unique characteristics of these two cells, including their chromosome number and the role they play in sexual reproduction.
We will examine the mechanisms of meiosis and fertilization that lead to the formation of haploid and diploid cells, further highlighting the differences between the two. So, let’s get started on this enlightening journey into the world of genetics and discover the fascinating nuances of haploid and diploid cells!
What Are Haploid and Diploid Cells?

Flowers produce gametophytes, which in flowering plants consist of a few haploid cells.
©Sk Tanvir ali000/Shutterstock.com
Cells are the smallest units of living organisms that can function on their own. Haploid cells are cells that contain only one set of chromosomes, while diploid cells contain two sets of chromosomes. These cells are typically found in gametes, such as sperm and egg cells. Diploid cells are found in somatic cells (multicellular organisms), such as skin, muscle, and nerve cells.
Haploid vs. Diploid: 4 Key Differences

Lady finger bananas are diploid cultivars of
Musa acuminata.
©asss sssa/Shutterstock.com
Haploid vs. Diploid: Chromosome Numbers
Understanding these differences in chromosome number is crucial to understanding genetic diversity and the mechanisms of sexual reproduction. The number of chromosomes in haploid and diploid cells is the most obvious difference between the two. Haploid cells have half the number of chromosomes as diploid cells. A haploid cell only contains one complete set of chromosomes.
In contrast, diploid cells typically have two sets of chromosomes, a pair of each chromosome. They are commonly found in somatic (body) cells of sexually reproducing organisms. For example, in humans, haploid cells contain 23 chromosomes. This is in contrast to diploid cells, which contain 46 chromosomes (23 pairs).
Haploid vs. Diploid: Genetic Diversity
Haploid and diploid cells differ in the number of chromosomes they contain. They also differ in their potential for genetic diversity. These cells have fewer chromosomes and thus fewer potential genetic combinations compared to diploid cells. However, haploid cells undergo an additional round of genetic recombination through the process of meiosis. This leads to a high level of genetic variation.
In contrast, diploid cells can combine genetic material from two different individuals during fertilization, further increasing genetic diversity. Understanding how haploid and diploid cells contribute to genetic diversity is essential to the study of genetics and evolutionary biology. Research into the genetic variations of haploid and diploid populations can provide valuable insights into how genetic diversity arises and evolves over time.
Haploid vs. Diploid: Role in Sexual Reproduction
Haploid and diploid cells play different roles in sexual reproduction. Diploid cells are found in the somatic cells of sexually reproducing organisms, while haploid cells are found in the gametes – sperm and egg cells. During sexual reproduction, haploid cells from two different individuals (usually a male and a female) fuse to form a diploid zygote. The diploid zygote then develops into a new individual through a process called mitosis. In some cases, diploid cells divide by meiosis to form haploid cells, which then combine with haploid cells from another individual during sexual reproduction.
This alternation of haploid and diploid states is what enables sexual reproduction to contribute to genetic diversity. Therefore, understanding the roles of haploid and diploid cells in sexual reproduction is crucial to understanding how genetic diversity arises and develops over time.
Haploid vs. Diploid: Mechanisms of Meiosis and Fertilization
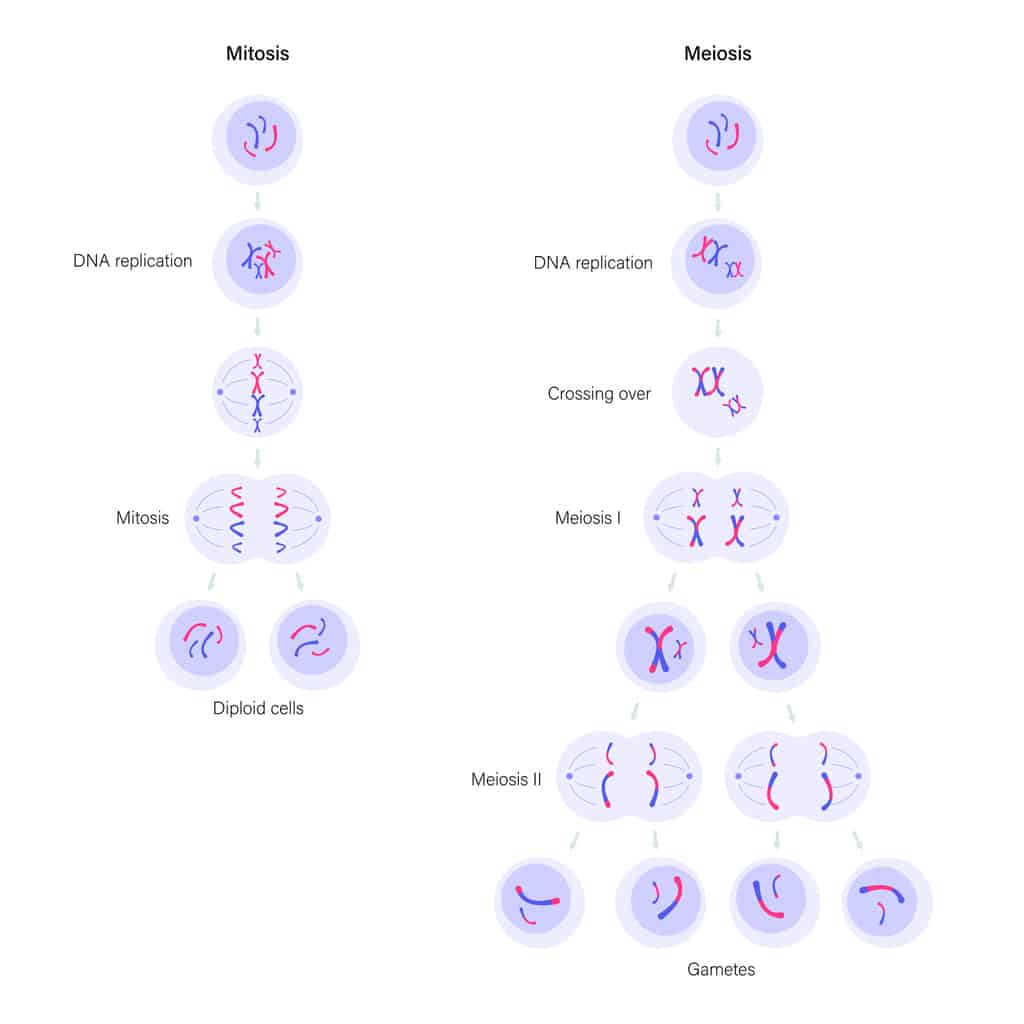
The mechanisms of meiosis and fertilization are crucial in understanding the differences between haploid and diploid cells. Meiosis is the process of cell division that forms haploid cells. During meiosis, diploid cells divide twice, each time generating cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original. This is accomplished through a series of complex molecular events, including recombination and chromosome separation. These events lead to genetic diversity and the creation of gametes, such as sperm and egg cells, which are haploid.
Fertilization, on the other hand, involves the fusion of haploid gametes to form a diploid zygote. The process of fertilization restores the diploid state, thus allowing for the transmission of genetic material from both parents. The combined genetic material from the two haploid gametes results in a genetically diverse offspring. This contributes to the variation observed within species.
Understanding the mechanisms of meiosis and fertilization is key to understanding the fundamental differences between haploid and diploid cells and how they contribute to genetic diversity.
In Conclusion
Knowledge of the differences between haploid and diploid cells is essential for understanding how genetic diversity arises and evolves over time within a species. It also helps us understand how genetic diseases and abnormalities can occur and provides essential insights into the mechanisms of sexual reproduction and inheritance. Therefore, understanding haploid and diploid cells’ unique characteristics and functions is essential to achieving a comprehensive understanding of basic cell biology.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.