Dragonfly
Its larvae are carnivorous!
Advertisement
Dragonfly Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Dragonfly Conservation Status
Dragonfly Facts
- Favorite Food
- Mosquitoes
- Common Name
- Dragonfly
- Number Of Species
- 5000
- Location
- Worldwide
- Slogan
- It's larvae are carnivorous!
View all of the Dragonfly images!

Dragonflies eat mosquitoes, gnats, and cicadas making them an important part of the ecosystem.
These amazing insects also serve as a food source for a variety of fish and birds. They are found on every continent with the exception of Antarctica. Wooded areas as well as freshwater lakes, ponds, marshes, and streams are all habitats of the dragonfly.
5 Incredible Dragonfly Facts!
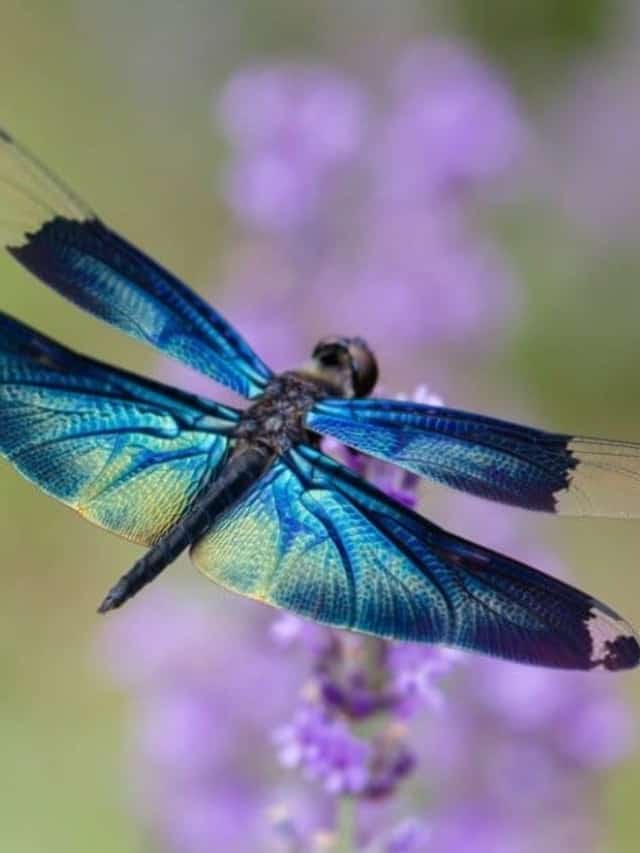

©iStock.com/H_Yasui
- There are approximately 7,000 species of true dragonflies. The largest dragonfly species in the world can reach more than 5 inches in length!
- They can fly as fast as 35 mph
- These insects have 28,000 eyes
- In the life cycle of this insect, its larvae stay in the water for up to 3 years
- These insects can see 360 degrees around them
Species, Types, and Scientific Names
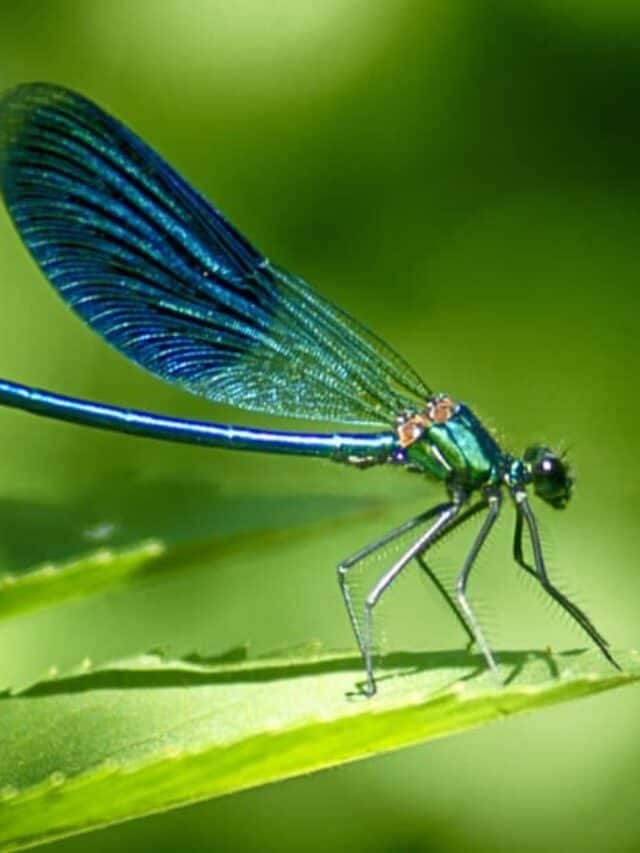

Adult dragonflies will consume any insect they catch.
©Costea Andrea M/Shutterstock.com
Anisoptera is the scientific name of these insects. While Anisoptera is its family, the dragonfly belongs to the order classification of Odonata. The word Odonata is Greek meaning ‘toothed one.’ This refers to the jaws of this insect.
There are around 7,000 species of true dragonflies. These insects are closely related to the damselfly though damselflies have the suborder classification of Zygoptera.
These insects live everywhere on the globe except for Antarctica. They live in warm climates and near bodies of water including lakes, ponds, marshes, and streams. Adults are easily recognizable by their narrow, needle-like bodies and two pairs of slender, colorful wings.
There are 14 types including:
- Petaluridae
- Aeshnidae
- Gomphidae
- Austropetaliidae
- Cordulegastridae
- Neopetalia Punctata
- Chlorogomphidae
- Corduliidae
- Libellulidae
- Macromiidae
- Synthemistidae
- Darners
- Saddlebag
- Gliders
Evolution and Origins
Dragonflies are an ancient species of insects that have existed for over 300 million years. They belong to the order Odonata, which also includes damselflies. The earliest dragonflies were much larger than the dragonflies we see today, with some species having wingspans of over two feet.
Dragonflies have undergone little evolutionary change over the past 300 million years, as they have already evolved to be perfectly adapted to their environment. Their long, slender bodies, large wings, and powerful flight muscles have allowed them to thrive in a variety of habitats, from freshwater streams to open skies.
The evolutionary success of dragonflies can be attributed to their adaptability and versatility. They feed on a variety of prey, including mosquitoes, flies, and other insects, and their larvae can live in a variety of aquatic habitats, from still ponds to fast-flowing streams. This has allowed dragonflies to spread to almost every corner of the world, and to occupy a wide variety of ecological niches.
The fossil record of dragonflies provides important insights into the evolution of insects and the ancient earth. It shows that dragonflies have been able to survive and thrive in a changing world and that they have been an important part of the food chain for millions of years.
Furthermore, dragonflies are a fascinating and ancient species of insects that have adapted and evolved over millions of years to become the highly successful creatures we see today. They continue to play a crucial role in many ecosystems, serving as both predators and prey, and providing valuable insights into the evolution of life on earth.
Appearance
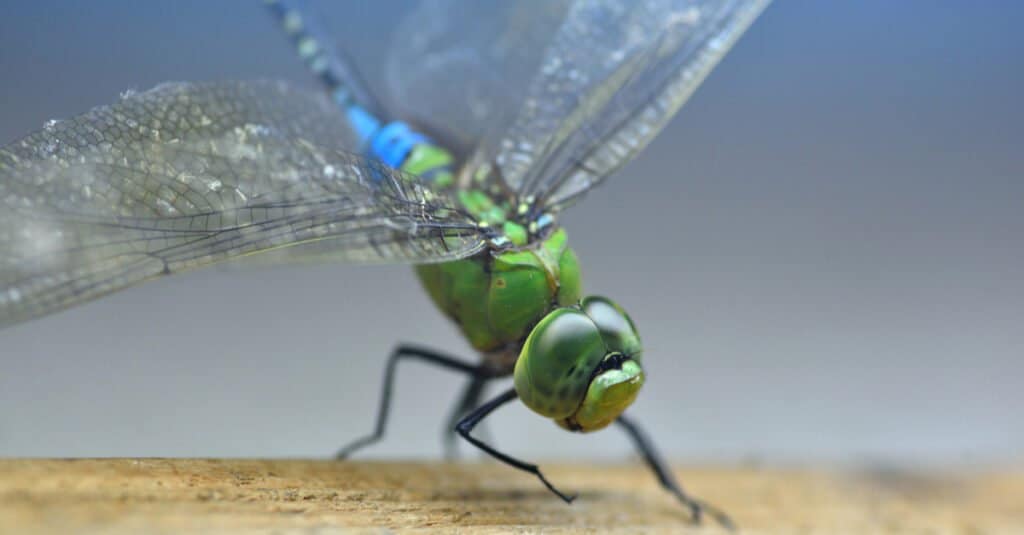

An adult measures from 1 to 5 inches long and weigh less than 1 ounce. They have 6 legs and 2 pairs of wings.
©Photoongraphy/Shutterstock.com
An adult measures from 1 to 5 inches long and weigh less than 1 ounce. They have 6 legs and 2 pairs of wings. The wingspan of the insect can measure up to 6 inches. This insect’s color depends on what type it is. They can be brown, blue, yellow, green, or red. Their wings have an iridescent or metallic appearance.
The damselfly is the closest relative of the dragonfly. They are similar in appearance with two pairs of wings and brightly colored bodies. However, a notable difference is a dragonfly rests with its wings spread out while a damselfly rests with its wings pulled together.
The largest type of dragonfly is the giant garner dragonfly. Its scientific name is Anax walsinghami. It’s 5 inches long with a 5-inch wingspan.
These insects have a few adaptations they use to protect themselves from predators. For one, they can fly up to 35 mph! Also, they can change directions mid-air allowing them to escape some predators. Their eyes provide them with a 360-degree view of their environment. So, they’re likely to see a predator soon enough to make an escape.
These insects are solitary. But, when they do form groups, they are called a flight or a cluster. Males can be aggressive when defending their territory from other males.

©Helen Cradduck/Shutterstock.com
Habitat
These insects are found throughout the world except for Antarctica. Though they don’t live in people’s homes, some do live near people. These insects make their home around bodies of water including ponds, streams, lakes, and rivers. If a homeowner has a pond on their property, there are likely to be dragonflies in the area. Or, if a family lives near a large creek or river, they may see dragonflies moving through the area.
Diet
These insects have a carnivorous diet. Specifically, they eat insects which have earned them the classification of an insectivore.
What eats dragonflies?
Frogs, fish, birds, and large spiders are all predators of adult dragonflies. A dragonfly baby also called larvae or nymph is vulnerable to the same predators.
What do dragonflies eat?
These insects eat mosquitoes, gnats, and cicadas. An adult eats from thirty to over 100 mosquitoes each day. Some types of dragonflies hunt at night while others look for food during the day.
Want to discover more about the diets of dragonflies? Check out our complete guide: ‘What Do Dragonflies Eat.’
View all 110 animals that start with DDragonfly FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Dragonflies herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Dragonflies are Carnivores, meaning they eat other animals.
What Kingdom do Dragonflies belong to?
Dragonflies belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Dragonflies belong to?
Dragonflies belong to the class Insecta.
What phylum to Dragonflies belong to?
Dragonflies belong to the phylum Arthropoda.
What family do Dragonflies belong to?
Dragonflies belong to the family Anisoptera.
What order do Dragonflies belong to?
Dragonflies belong to the order Odonata.
Where do Dragonflies live?
Dragonflies are found worldwide.
In what type of habitat do Dragonflies live?
Dragonflies live in wetlands and close to water.
What do Dragonflies eat?
Dragonflies eat mosquitoes, flies, and bees.
What are some predators of Dragonflies?
Predators of Dragonflies include birds, fish, and lizards.
How many babies do Dragonflies have?
The average number of babies a Dragonfly has is 60.
What is an interesting fact about Dragonflies?
Dragonfly larvae are carnivorous!
How many species of Dragonfly are there?
There are 5,000 species of Dragonfly.
What is a dragonfly?
A dragonfly belongs to the Anisoptera family and is in the order Odonata. It’s an insect found around ponds, streams, and rivers. Dragonflies have a long, thin body, two pairs of long wings, and six legs. They are known for their ability to hover in the air and zip away at speeds up to 35mph. They eat mosquitoes, gnats, and flies.
In the life cycle of a dragonfly, a baby aka a larvae or nymph, lives for up to 3 years in this form. After becoming an adult dragonfly, this insect lives for about 6 months.
Do dragonflies eat mosquitoes?
Yes. In fact, dragonflies play an important role in keeping the population of mosquitoes under control.
What eats dragonflies?
Some of the predators of dragonflies include frogs, fish, large spiders, and birds.
Is a dragonfly an insect or a bug?
A dragonfly falls under the classification of insect. Dragonflies have 6 legs and two pairs of wings. These are just two of the characteristics that qualify it as an insect.
What is the lifespan of a dragonfly?
The life cycle of a dragonfly has a few stages. An adult dragonfly lives about six months. However, a dragonfly baby also known as a larvae or nymph, lives up to three years before becoming an adult.
Are dragonflies dangerous?
No, not to people. They don’t bite or sting. But, a mosquito is likely to consider this insect a very dangerous creature!
How many legs does a dragonfly have?
A dragonfly has 6 legs.
How do you identify a dragonfly?
When identifying a dragonfly look for a long, needle-like body, two pairs of wings and six legs. A dragonfly has a colorful body and iridescent wings. These insects land on cattails and other vegetation growing near water. Otherwise, they hover in the air or quickly zip away at up to 35 mph.
Damselflies and dragonflies are similar in appearance and share the same type of habitat. Remember that a damselfly rests with its wings pressed together while the dragonfly rests with its wings spread out.
How do you get rid of dragonflies?
Generally, dragonflies aren’t considered pests. If you live near a pond or creek, you may see a dragonfly zip by from time to time.
These creatures with their colorful bodies and intricate flying patterns are interesting to observe and are worthy of our appreciation.
What's the difference between dragonflies and butterflies?
Dragonflies belong to a different order compared to butterflies, and most butterflies prefer to eat nectar. Dragonflies eat other insects.
How to say Dragonfly in ...
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- San Diego Zoo, Available here: https://animals.sandiegozoo.org/animals/dragonfly-and-damselfly
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dragonfly