The Antarctic sigma event, a term that has riled the scientific community, refers to a worrisome and unprecedented fall in Antarctic sea ice levels. We are seeing significantly lower sea ice levels this year. The extent of which would take centuries to regain and recover. This so-called “sigma event” is measured in terms of standard deviations from the average. Currently, we have reached the level of a “five-sigma event,” or even a “six-sigma event” in some reports. Several experts peg the rarity of such an event occurring outside of climate change at once per 7.5 million years. Its significance extends beyond Antarctica, showing underlying changes that could affect the entire planet.

Melting glaciers are a clear sign of climate change and global warming
©Bernhard_Staehli/iStock via Getty Images
Understanding Sigma Events
Sigma events are statistical anomalies, representing significant deviations from the mean or average. In the context of Antarctic sea ice, the sigma events reveal extreme and sudden changes. They offer valuable, if worrying, insights into climate patterns and environmental interconnectedness.
Five-Sigma in the Scientific Community
A five-sigma event is strongly ingrained in scientific practice. Notably in particle physics, where it is regarded as the “gold standard” for discovery. This level of significance corresponds to a p-value of 3×10^-7, indicating a mere 0.00003% likelihood that the observed data would be as extreme if the underlying hypothesis (e.g., the existence of a new particle) were false.
In layperson’s terms, imagine you’re trying to prove something truly extraordinary, like finding a new particle. Scientists use a mathematical test to see how likely it is that what they observed is just a fluke.
Here, the test gave them a result known as a p-value, and it’s tiny. Like 3 chances in 10 million (that’s what 3×10^-7 means) tiny. Hence there’s only a 0.00003% chance that what they found is just a coincidence or random blip that looks significant but isn’t. So, when scientists get a p-value this small, they feel very, very, very confident that what they observed isn’t just a random accident.

The prediction for the existence of the Higgs boson received confirmation at CERN, the European Council for Nuclear Research, using the five sigma criterion for verification
©Naeblys/iStock via Getty Images
Application to Antarctic Sea Ice
Applying this strict statistical approach to Antarctic sea ice enables researchers to detect profound changes in climate patterns with high confidence. A five-sigma event in this context would represent an extreme and sudden change in sea ice levels, far from the expected mean. What is happening in Antarctica is almost certainly because of human-induced climate change and not natural variability.
Experts have been using words like “unprecedented,” “gobsmacking,” “truly remarkable,” and “unprecedented isn’t strong enough” of a word.
Significant variations like these provide critical insights into the interdependence of climate systems, suggesting larger environmental shifts.

Climate change has forced penguins in Antarctica to venture further out to find food
©iStock.com/axily
The Beyond Unprecedented Decline in Antarctic Sea Ice and What’s At Stake
Since the late 1970s, Antarctic sea ice has been slowly melting, losing approximately 12.6% of its mass per decade. This slow decrease has been more severe in specific times and places. It offers a complicated image of a continent in upheaval.
The melting of Antarctic sea ice has ramifications well beyond the polar regions. It has far-reaching and nuanced ramifications for global warming, weather patterns, and extreme weather events. With so much pent-up climatological energy in our seas and skies, this Antarctic event (ironically) adds gasoline to the fire.
A recent study found that the Antarctic region is approaching tipping points that could result in permanent changes. These changes aren’t limited to Antarctica but have global consequences.
The stakes are high, as changes in Antarctic sea ice will likely have a global impact on weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems. Here’s a closer look at the risks and what’s at stake:
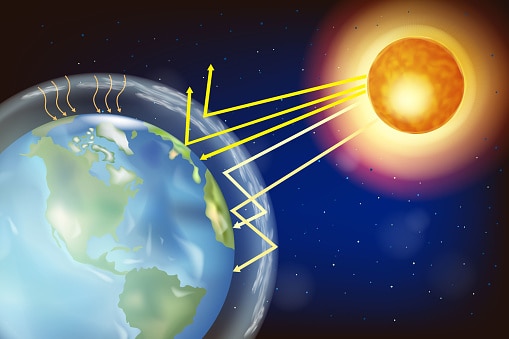
Sea ice is able to reflect back into space incoming solar radiation
©Sakurra/iStock via Getty Images
Antarctic Sea Ice Melt and Increased Uncertainty
Complex Variables
Ocean currents, air temperatures, and human-caused climate change all add to the difficulty of predicting sea ice behavior.
Challenging Predictions
Despite advanced scientific models, predicting the exact outcomes of these variables remains a difficult task.
Not Only Are the Stakes High, but Also Deep and Wide
Approaching Tipping Points
Some projections indicate that the region is nearing points of no return, leading to permanent changes with far-reaching consequences.
Global Implications
Antarctic sea ice changes can have an impact on global weather patterns, contribute to increasing sea levels, and damage ecosystems. As part of this downward spiral, the less Antarctic ice there is, the more sunlight our planet absorbs. Sea ice reflects the sun’s heat back to outer space. The less there is, the more heat the planet takes.
The Role of Sigma Events
The dramatic changes in Antarctic sea ice are not entirely the result of human activity. They’re also linked to natural variability, which is sometimes punctuated by rare and significant sigma events. It’s a tricky beast to nail down. But whatever the cause, these statistical anomalies amplify the complexity and accelerate the pace of our changing climate. It presents us with challenges that have no simple solutions.
Ecological Impact on Antarctica
Penguins that once roamed the icy plains, and krill, tiny creatures at the bottom of the food chain, are now facing new challenges. Penguins must travel further for food, which may have cascading effects on their numbers. The loss of sea ice, if it continues at the same rate, will likely disrupt the entire food chain, from krill to whales, and eventually to us. In this delicate balance, even minor changes can have a ripple effect throughout the ecosystem. A decrease in krill, for example, can alter whale feeding patterns, changing migratory routes and reproductive strategies. It’s a vivid depiction of the intricate web that binds all ocean life together, illustrating how interconnected and fragile the Antarctic ecosystem truly is.

Melting sea ice means habit loss for many species, including the endangered
polar bear
©avstraliavasin/iStock via Getty Images
Importance of Antarctic Sea Ice Research and Monitoring
We can only hope and pray that this five-sigma event is a fluke, though we’d never bet money on such odds. But if we do nothing, then we’re wagering our very existence as a thriving species on a goldilocks planet. Thus, it’s imperative that we continue to engage with the iciest continent on our planet and try to decode what ails it. Doing so involves our continued investment in efforts like:
Understanding Complexity
The Antarctic sea ice system is complicated. Research helps us to understand how components such as wind patterns, ocean currents, and temperatures interact with one another.
Guiding Response to Changes
Scientific insights guide policy decisions, conservation efforts, and global initiatives to mitigate the effects of climate change. While monied interests lobby politicians the most, as the effects of climate change hit more industries, science-based guidance will hopefully have a louder voice in the halls of power.
Predicting Changes
Vigilant monitoring helps in early detection of anomalies and extreme events, allowing for timely response and adaptation. We have learned such lessons from the history of strong storms like hurricanes and destructive tornadoes, as well as the recent wildfires. Our responses and adaption methods will have to evolve with the changing climate realities.
Conclusion
The interplay between environment, humans, and research in the Antarctic’s continual development is intricate. This shift is more than a mental challenge or a collection of curious facts. It’s an opportunity for introspection about our place on this planet.
Important markers adopted from particle physics, such as the five-sigma threshold, reveal that sigma events in Antarctic sea ice are more than mere statistical oddities. They provide a dependable means of distinguishing between genuine shifts and background fluctuations in data. They also reveal multilayered entanglement between the movement of sea ice, ocean currents, and weather patterns.
As the sea ice melts, our understanding will need to evolve to incorporate not just the hard data but also the profound truths it reveals. The way we handle the most pressing environmental issues of our day will decide whether we preserve or wreck the delicate equilibrium of our one and only planet.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.








