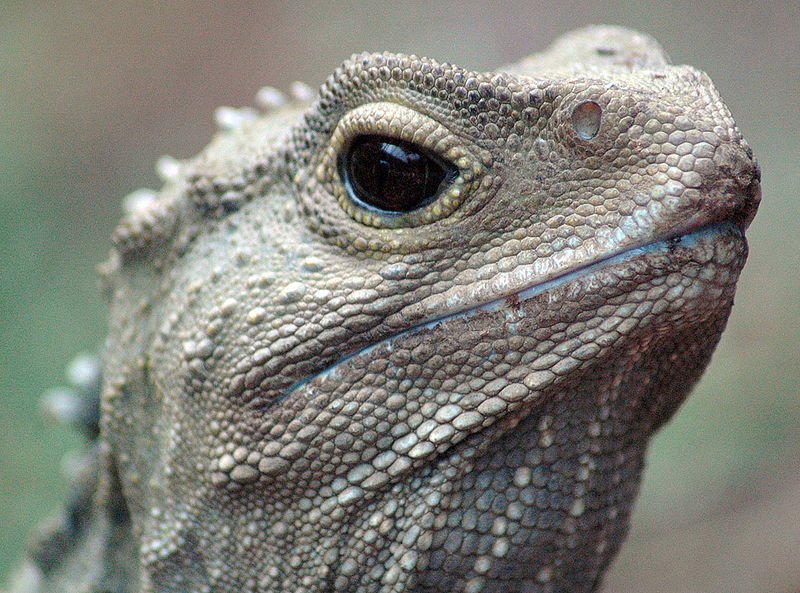
There are creatures living today that stand as relics of bygone eras in evolution. The species in question exhibit many traits that are relatively unchanged from forms that have existed for millions of years. This is well beyond the duration of many of the common species on the planet.
These organisms are known colloquially as “Living Fossils,” and there are examples of them in the plant, animal, and fungal worlds. These fascinating creatures offer scientists and laypeople glimpses into what life was like in eras past. It also offers clues into how the process of evolution transpires.
If you’re interested in the life of the past, present, and future, take a look at this list of living fossils that exist on our planet today.
1. Coelacanths
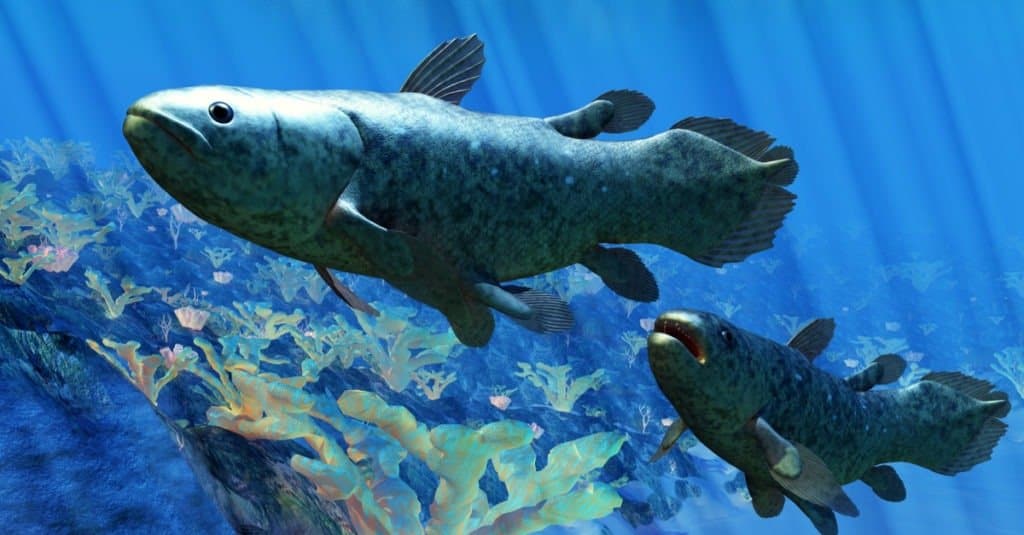

Coelacanths look quite similar to their ancient relatives.
©Catmando/Shutterstock.com
Coelacanth fish are one of the most famous living examples of animals that are living fossils. These fish stand alone amongst their genera with no other living relatives.
The Coelacanths were long considered until the species was rediscovered in the late 1800s extinct by a scientist by the name of Marjorie Eileen Doris Courtenay-Latime. After this initial discovery, it was further seen that these fish weren’t actually altogether so rare in their habitats. Prior to the discovery, it was believed to have gone extinct over 66 million years ago.
There are two subspecies of Coelacanth: The West Indian Ocean Coelacanth (Latimeria chalumnae) and the Indonesian Coelacanth (Latimeria menadoensis). The former lives off the coast of southeast Africa, primarily in the waters between the African mainland and Madagascar. The other subspecies of Coelacanth live in Indonesia. In particular, the waters surrounding the island of Java are the most common place to find it.
2. Horseshoe Crabs
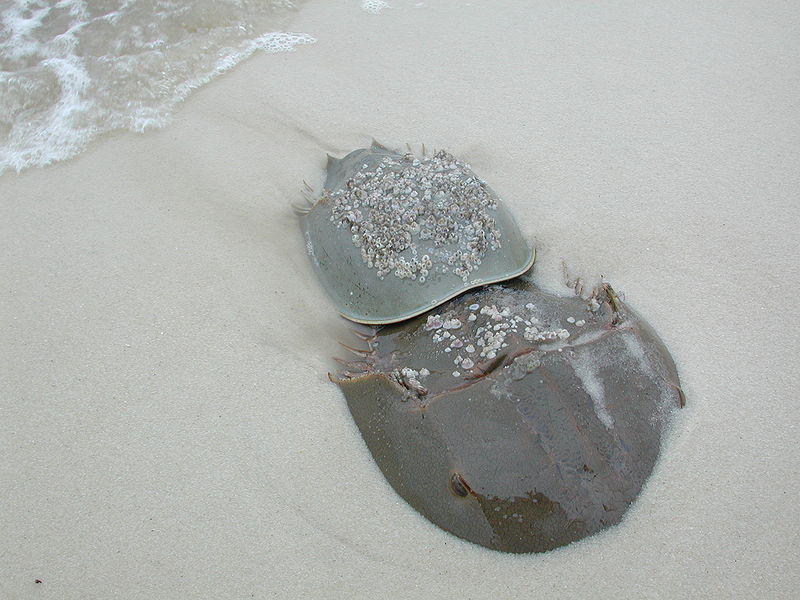

The population numbers of these creatures are plummeting worldwide.
©Coveredinsevindust at English Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Horseshoe Crabs are another example of a living fossil. These bizarre creatures aren’t even crabs or crustaceans. They’re actually a type of animal called a chelicerate. These are most closely related to arachnids such as spiders and scorpions.
These creatures initially evolved over 440 million years ago, and the forms of the most current subspecies emerged an estimated 250 million years ago. These strange creatures have many oddities surrounding their existence. For example, despite the fact that they have some of the largest eyes proportionally to any creature in the animal kingdom, horseshoe crabs have relatively poor eyesight.
3. Tuatara
The Tuatara (Sphenodon Punctatus) is native to New Zealand, where it inhabits deep forested regions of several isolated islands in the region. Despite the fact that it looks like a lizard, the Tuatara stands alone in its own distinct order, known as Rhynchcephalia. This reptile is the only surviving member of this order.
The Tuatara has some interesting physiological features. One of the most notable is its “third eye” — this parietal eye has a mysterious use. Scientists conjecture it might be for absorbing sunlight to convert to Vitamin D.
4. Gingko
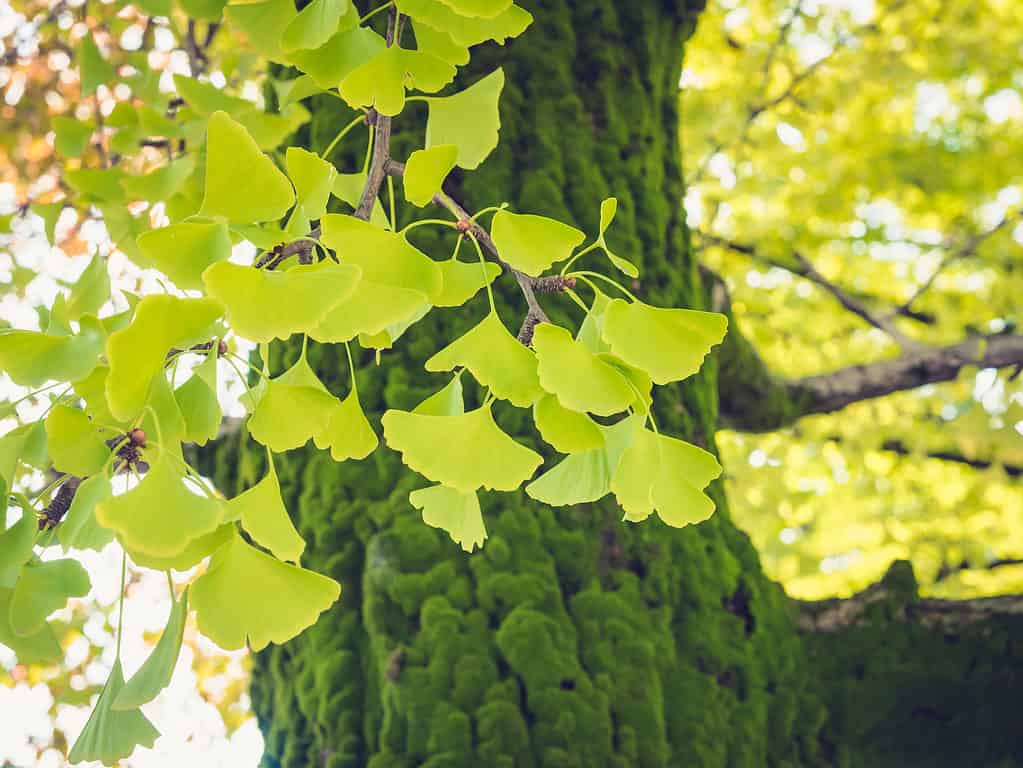

The leaves of this plant look identical to those found in fossils around the world.
©VTT Studio/Shutterstock.com
Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba) is a common decorative plant that can be seen all over the world. It exists everywhere, from sidewalks to baseball fields. However, this tree is the only surviving member of an ancient genus.
The ginkgo is closely related to a group of plants that emerged in the Permian era over 270 million years ago. The same trees that are quite commonplace today are often uncovered in fossilized form dating back millions of years.
5. Cycads
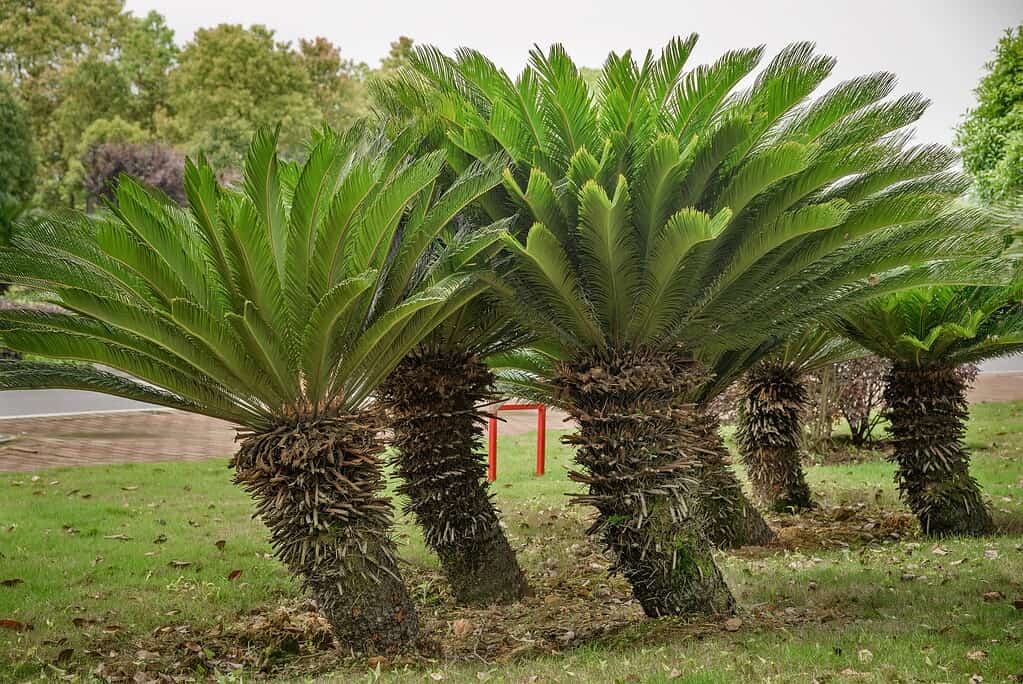

Cycads look very similar to many species of palms.
©pinholeimaging/Shutterstock.com
This member is a genus of plants that have much in common with palms. In fact, their similar appearance has contributed to much confusion surrounding these plants.
These trees have an ancient lineage and are actually vaguely related to ginkgo trees, which are also members of this list. These plants live around the world, primarily in the tropics and subtropics. These delicate plants are, unfortunately, in a steep decline worldwide. In addition, many of the subspecies of the genus are endangered or critically endangered.
6. Nautilus Mollusks
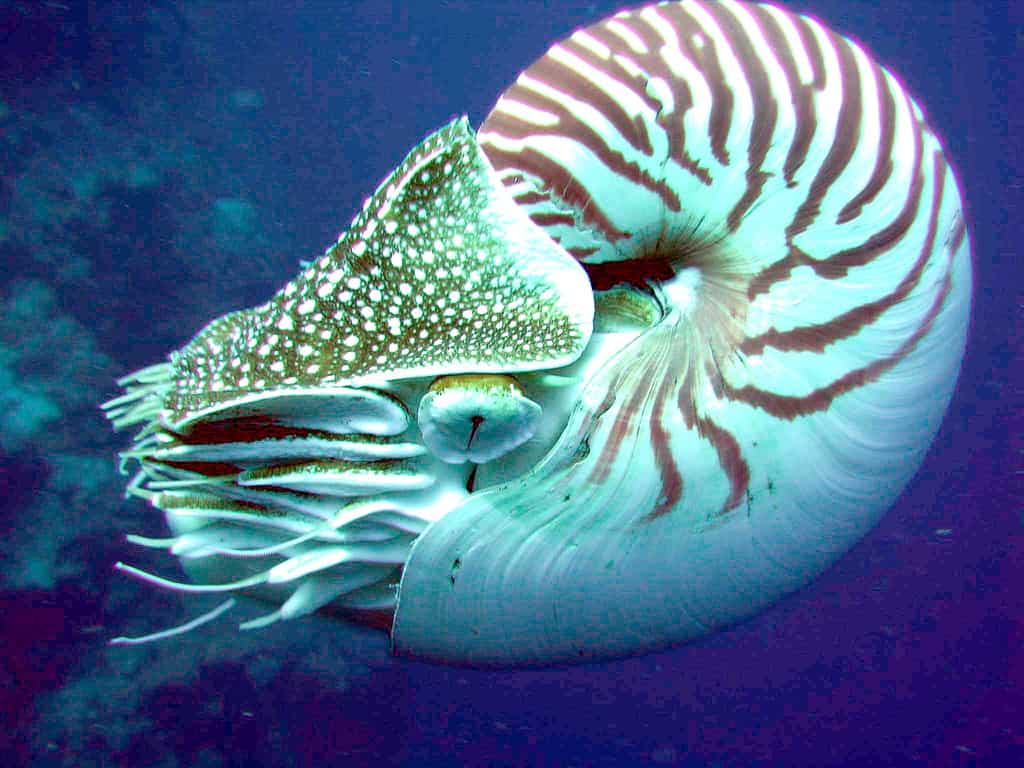

The wild appearance of the Nautilus Mollusk has inspired works of science fiction.
©Profberger at English Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0 <http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/>, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Nautilus Mollusks (Nautilus pompilius)have a form that has remained essentially unchanged for millions of years. The mollusks that live today are members of the family Nautilodea, which includes many living and extinct animals.
These mollusks move about by sucking up water from their surrounding environment. They subsequently shoot the water out of a tube protruding out of their body called a hyponome. This allows the mollusks to propel themselves around the water using jet propulsion.
These creatures also have the distinctive ability to survive rapid changes in pressure when removed from their home environments. This is a process that can have disastrous effects on the health of other types of creatures.
7. Elephant Sharks

The somewhat bizarre-looking
Elephant
Shark is not actually a shark.
©Totti, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Elephant Sharks (Callorhinchus milii) are a type of cartilaginous fish that live in the deep sea surrounding Australia and New Zealand. Also known as “Australian Ghostsharks,” these creatures are not sharks but closely related types of fish.
These fish are caught in fisherman’s nets in the seas surrounding Australia. Their meat is sold at fish ‘n chip stands in both Australia and New Zealand. In the past, these fish were somewhat threatened, though in recent decades, their numbers have rebounded. They are now a species in recovery.
8. Cedar Wood Wasp

Cedar Wood Wasps lay their eggs in the still-smoldering ruins of burnt trees.
©Katja Seltmann / CC0 1.0, from Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository – License
These strange wasps first emerged in the Mesozoic fossil record, leading to their classification as living fossils. Cedar Wood Wasps (Syntexis libocedrii) have the interesting quality of laying their eggs in the freshly burnt wood of trees of the cedar family. This includes incense cedar, junipers, and the like.
Cedar Wood Wasps live along the west coast of North America, from the high mountains of California to British Columbia. These wasps are fairly elusive and are rarely seen.
9. Scorpionflies
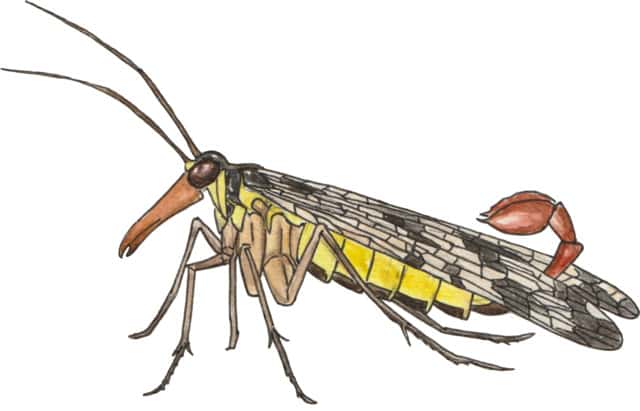
Scorpionflies are so-called due to their stinger-like tails.
©Lisa Nicvert, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
This is a type of insect that is closely related to fleas. However, the earliest fossils of these creatures date all the way back to the Permian age, and the evidence suggests that they proliferated in the Cretaceous era of the dinosaurs.
These flies are predators and primarily consume other insects. Male flies will oftentimes present females with dead insects in courtship rituals. Despite the fact that many of these flies have stinger-shaped tails, these flies do not actually have venomous stings.
The evolutionary record seems to suggest that these flies predated butterflies and bees in terms of pollinating flowers by feeding on nectar. Studying them may lead to clues as to how this characteristic came about.
10. Soft Sea Urchins
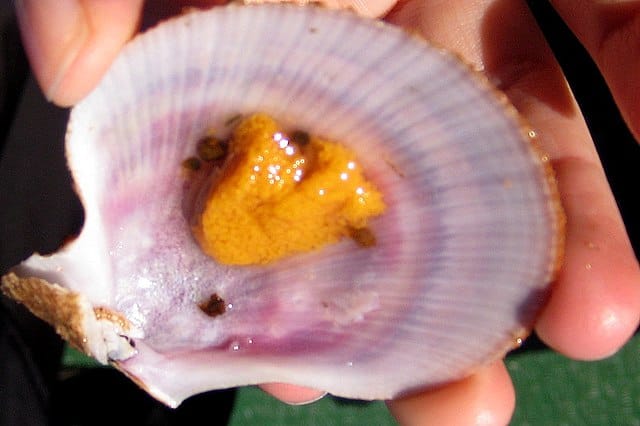

Sea Urchin
is eaten as a delicacy around the world.
©yashima from Karlsruhe, Germany, CC BY-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Soft Sea Urchins are a subtype of urchin that lacks the hard outer carapace of many other types of urchins. The earliest fossils of this order of sea creatures date back to over 465 million years ago. This makes them some of the most ancient creatures alive on earth today.
Sea Urchins have a complex relationship with humanity and have found uses in biological studies and as a foodstuff. Some species of urchins have potent neurotoxins in their spines, which can cause severe reactions in people at times.
Despite their simplistic appearance, there’s more to urchins than meets the eye. These creatures have digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems hidden within their rather primitive-looking bodies.
| Number | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Coelacanth |
| 2 | Horseshoe Crab |
| 3 | Tuatara |
| 4 | Gingko |
| 5 | Cycad |
| 6 | Nautilus Mollusks |
| 7 | Elephant Shark |
| 8 | Cedar Wood Wasp |
| 9 | Scorpionflies |
| 10 | Soft Sea Urchins |
The photo featured at the top of this post is © Pavinee Chareonpanich/Shutterstock.com
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.








