Ice sheets are important to most ecosystems in the world because of their interconnectivity with the ocean. But what is an ice sheet? How many ice sheets are left today?
What Is an Ice Sheet?
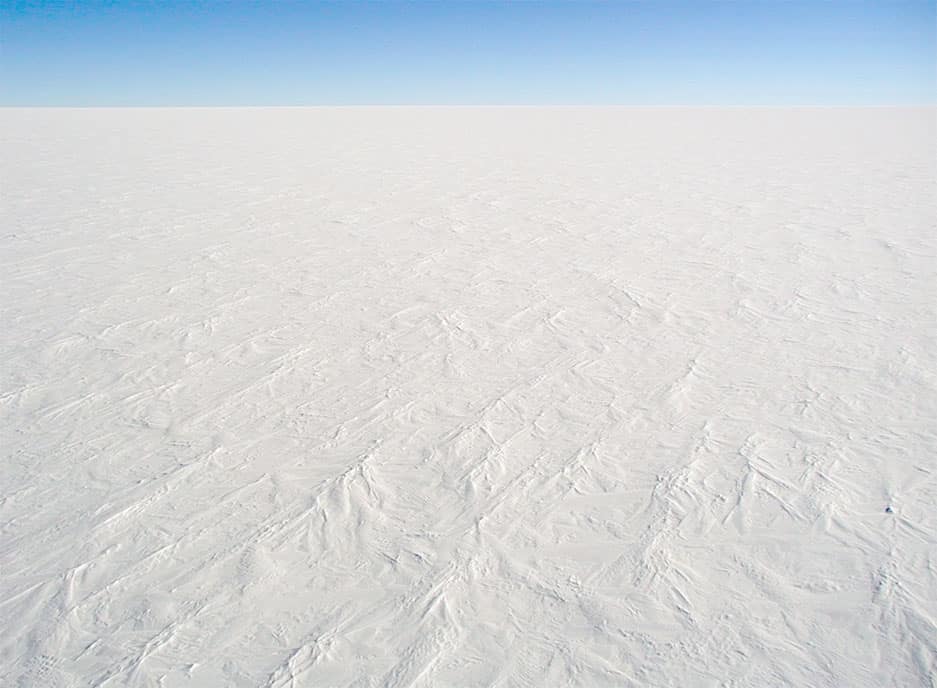

Ice sheets are glacial ice that covers more than 20 thousand square miles.
An ice sheet is defined as glacial ice covering land that’s over 20 thousand square miles in size. Today’s extant examples hold a little more than 68 percent of all of the fresh water on the planet. They also represent 99 percent of all freshwater ice on solid ground in the world.
How Many Are Left Today?

As the planet warms due to climate change, melting is causing a rise in sea levels.
©Maridav/Shutterstock.com
There are two ice sheets left on the planet today. They are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet.
At the end of the last Ice Age, about 10 thousand years ago, ice sheets that covered over one-third of the planet melted. Today, glacial ice only covers about one-tenth of the planet.
The two extant examples have been melting at an increasing rate since 2002. About 33 percent of the total sea level rise that’s occurred since 1993 is a direct result of melting caused by climate change.
If today’s ice sheets completely melted, sea levels around the world would rise about 224 feet. In today’s climactic conditions, sea levels are rising a little less than one-fifth of an inch per year. The speed of this melt is expected to ramp up, though no one is sure what this escalating melt will look like.
What Is the Biggest on Earth?
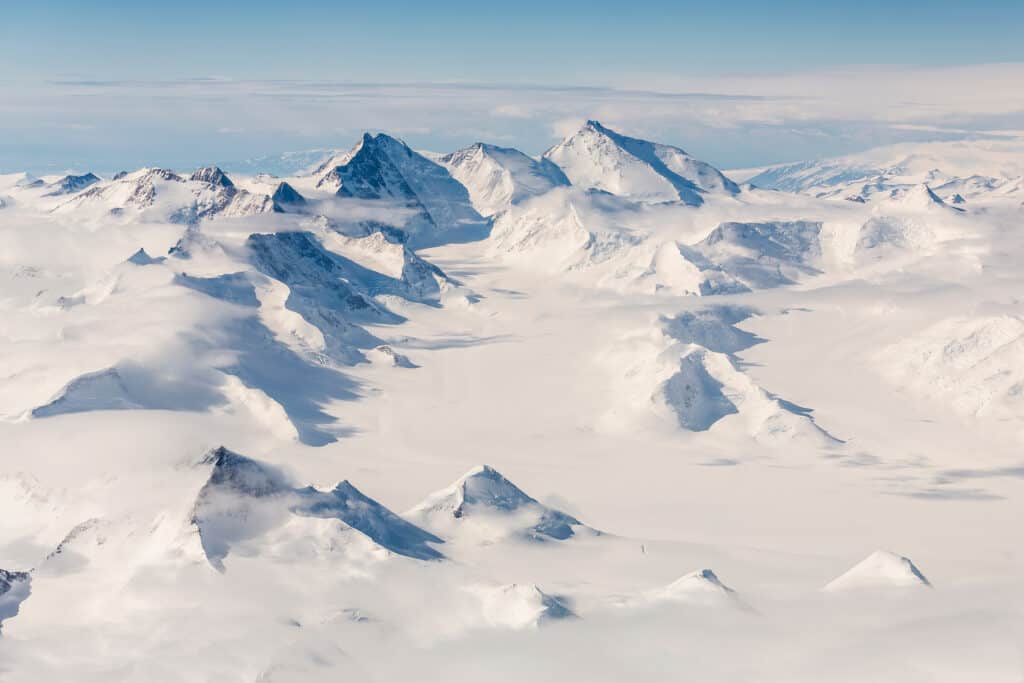

The Transantarctic Mountains divide Antarctica into east and west.
©Matt Makes Photos/Shutterstock.com
The biggest ice sheet on Earth is in Antarctica. It is almost 3 miles thick at its deepest point at the South Pole though it averages under a mile and a half thick. It occupies an area of just under 5.5 million square miles.
The Antarctic ice sheet is so heavy that it’s caused parts of the land making up the Antarctic continent to sink about half of a mile below sea level. Currently, about 40 percent rests on bedrock that’s below sea level.
Over 95 percent of the continent of Antarctica is covered by its ice sheet. However, about 95 miles disappear per year, though this number is debated in the scientific community. This equates to approximately 150 billion tons of mass loss annually.
There are two parts to the Antarctic ice sheet separated by the Transantarctic Mountains that run across the continent. The West Antarctic ice sheet covers the area west of the mountains, and the East Antarctic Ice sheet covers the eastern part of the continent. Both combined are by far the biggest repository of fresh water on the planet.
What’s on the east of the continent is dramatically bigger than what is on the west. It is also the coldest, driest, and windiest place on the planet, with temperatures as low as negative 148 degrees Fahrenheit. It also contains the South Pole.
How Big Is the Greenland Ice Sheet?
Greenland is melting about 55 percent faster than Antarctica.
©Uwe Dedering / CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – Original / License
The Greenland ice sheet is much smaller than the one in Antarctica at about 656 thousand square miles. At its deepest point, it is just about 2 miles thick. On average, it is about a mile thick.
Greenland is the globe’s biggest island, and the Greenland ice sheet covers 80 percent of its land. If the entire thing melted into water, the world’s oceans would rise about 24 feet.
Currently, around 270 billion tons of mass is lost to melting annually in Greenland. This is about 55 percent faster than the melt taking place in Antarctica due to the different dynamics at play based on location and composition. Scientists predict that the entire thing is going to be gone by 3000 CE if climate change continues at the rate it is now.
Is Antarctic Sea Ice the Same?
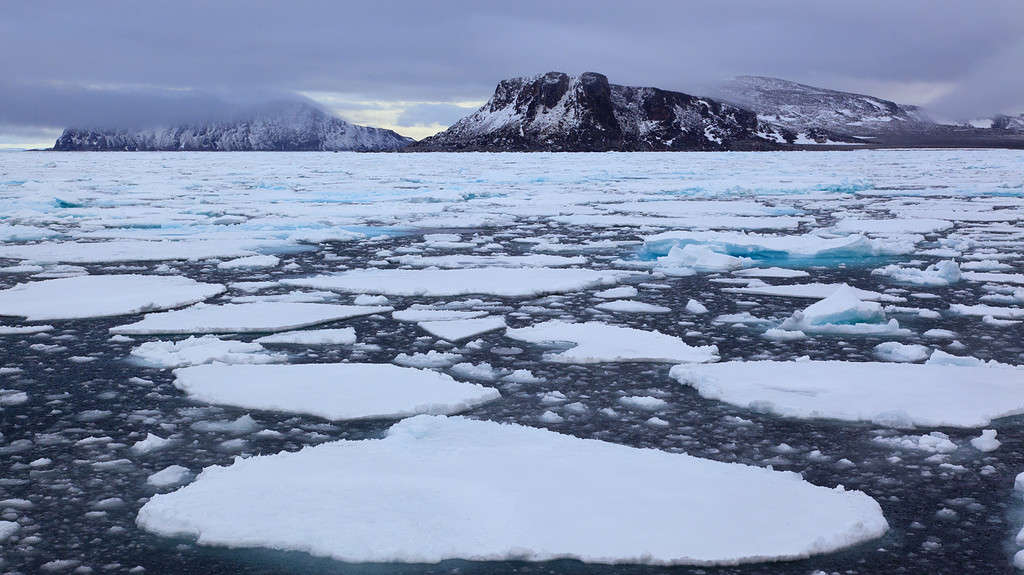

Sea ice is made of salt water.
©pum_eva/iStock via Getty Images
No, Antarctic sea ice is not the same thing. What is known as Antarctic sea ice is the ice in the Southern Ocean around the continent. The Antarctic ice sheet is on land, not floating on top of the ocean.
The sea ice around Antarctica is frozen ocean salt water whereas what’s on land is made up of freshwater precipitation. Antarctic sea ice is usually only up to 6 feet thick, though under the right conditions, this can increase dramatically. This is much thinner than the Antarctic ice sheet that is miles deep.
The photo featured at the top of this post is © Daphne Nilsson/Shutterstock.com
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.







