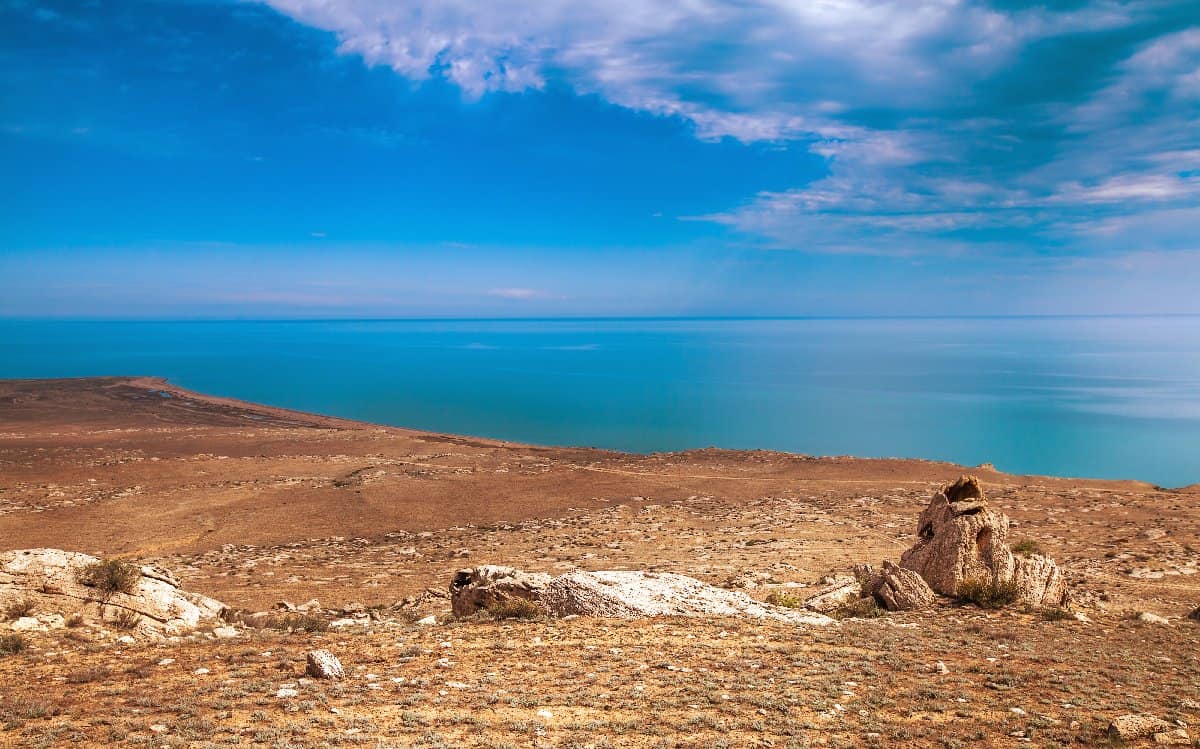
The Caspian Sea is one of the most studied, explored, popular, and historically amazing seas in the world. It is a unique body of water that is home to an abundance of marine life. The history of the Caspian Sea and its contemporary happenings are also a subject of its own.
There have been territorial disputes in the naturally rich Caspian Sea for the longest time. Why? The Caspian Sea is extremely rich in oil and natural gas and that can make a country a lot of money. The sea is also known for producing the world’s best caviar.
There are so many fascinating facts about this sea! So, let’s explore 10 mind-blowing facts about the legendary Caspian Sea. We’ll go over each point in more detail and provide you with fun facts about the sea that will mesmerize you.
1. Largest Inland Body of Water
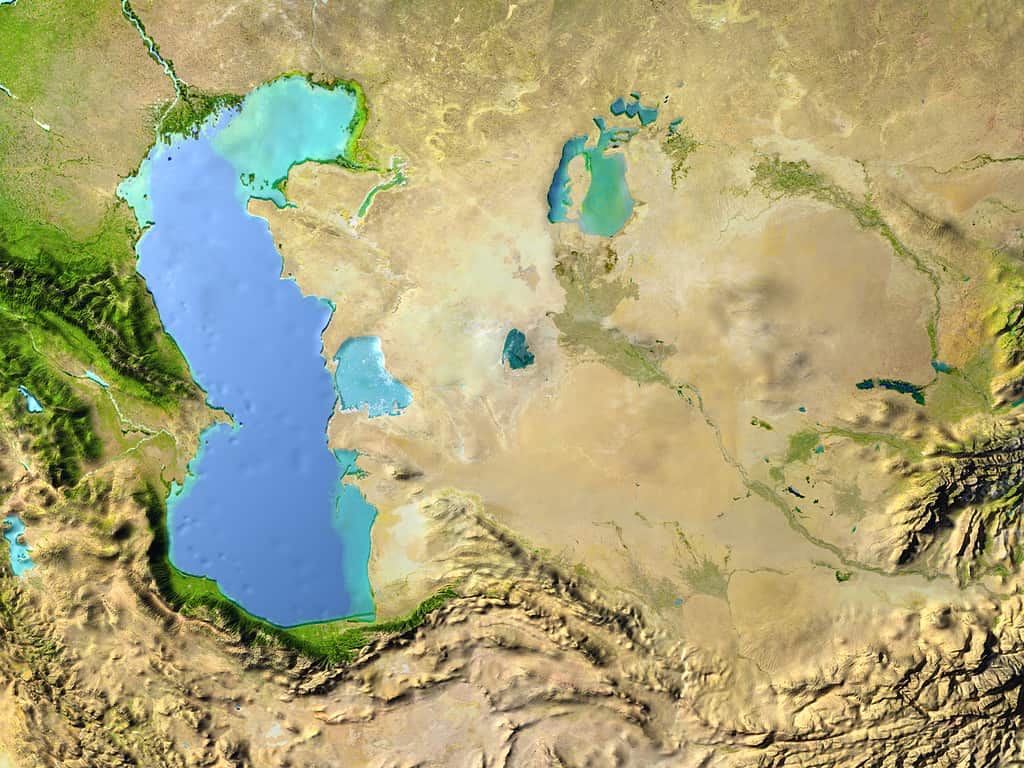
The Caspian Sea is larger than the entire country of Germany and more than three times bigger than all the Great Lakes.
©Harvepino/iStock via Getty Images
The Caspian Sea is the largest inland body of water in the world. It covers 143,200 square miles and because it’s so huge, people have erroneously called it a sea. Of course, no one truly can agree whether it is a sea or a lake. The reason why it’s big is because there are so many rivers flowing down to the Caspian Sea.
2. Endorheic Body of Water

The primary rivers that flow into the Caspian Sea are the Kura River, the Terek River, the Sefid-Rud, the Volga River, and the Ural River.
©MisoKnitl/iStock via Getty Images
The Caspian Sea is one of the few bodies of water that are endorheic in the world. Most bodies of water flow into another body of water. When it comes to lakes, the water will usually flow into a river that flows into an ocean. But for the Caspian Sea, the water goes nowhere. The rivers surrounding the sea flow into it and that’s it. The only way the Caspian Sea loses water is by evaporation.
3. Diversity Abundance

There are about 50 islands, of all shapes and sizes, located in the Caspian Sea.
©ekipaj/iStock via Getty Images
Like all bodies of water, the Caspian Sea is also rich in biodiversity. Some of the surrounding areas of the Caspian Sea are lush with forests, like the Hyrcanian forests in Iran. When it comes to fauna, you can find so much marine life in the sea, including the Caspian turtle, the Caspian seal, and the zebra mussel.
There are also six species of sturgeon (which is where caviar comes from) and they include the Russian sturgeon, Persian sturgeon, bastard sturgeon, beluga sturgeon, starry sturgeon, and sterlet sturgeon. In terms of land animals around the area, you will find Persian leopards roaming around, Asiatic cheetahs, Horsfield’s tortoises, and spur-thighed tortoises.
4. Fascinating History

The Caspian Sea is sometimes referred to as the Tarki Sea or the Kumyk Sea.
©Alexmumu/iStock via Getty Images
The Caspian Sea is about 30 million years old and got its saltwater from the now-extinct Tethys Sea. Humans have inhabited the area for about 75,000 years and it is believed that the sea is named after the Caspi Tribe that lived in the southwestern part. Oil wells have existed since the 10th century as humans discovered the sea’s rich natural resources. Europeans explored the area in the 16th century when they discovered the sea was a haven for natural resources. Historically, the Caspian Sea has been an important trade route for the region, which connects to East Asia and Europe.
5. Territorial Disputes

In Iran, the Caspian Sea is called the Mazandaran Sea.
©ekipaj/iStock via Getty Images
Over the decades, there have been territorial disputes on how to divide up the Caspian Sea. With so many natural resources in one body of water, it was bound to happen. There have been discussions with many of the countries about free access through rivers and where the lines should be drawn in the Caspian Sea. In 2018, the five nations signed an agreement to end the dispute — whether the Caspian Sea is a sea or a lake. A sea, as Iran considers it, would be subject to international maritime law. A lake, as the other countries see it, would be equally divided. Today, however, there seems to be a flaring conflict between Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Iran.
6. Delicious But Expensive Caviar
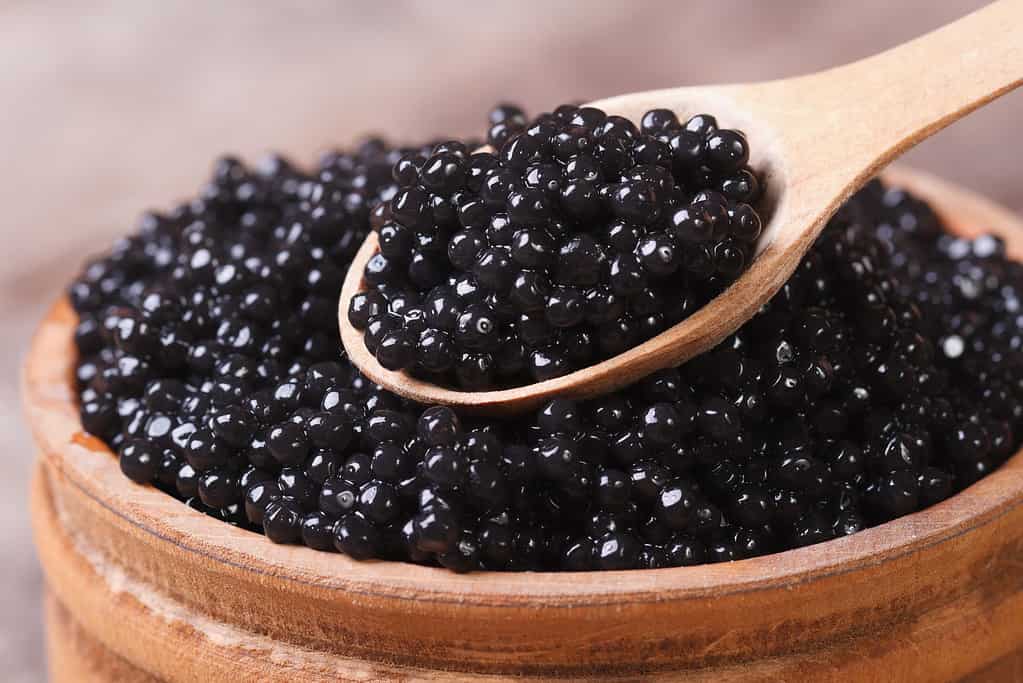

The beluga caviar comes from the beluga sturgeon in the Caspian Sea and it’s the most expensive of caviars.
©ALLEKO/iStock via Getty Images
Caviar are fish eggs. It’s roe that is cured in salt belonging to the Acipenseridae fish. Caviar is usually eaten as a spread or garnish. Usually, caviar comes from the roe of wild sturgeon found in the Caspian and Black Seas. Those caviars are called beluga, ossetra, and sevruga caviars. The most expensive caviar is the beluga caviar and that only comes from none other than the Caspian Sea. The industry is a million-dollar industry that is heavily sought after, especially by the wealthy. Unfortunately, many of the fish in the sea are at risk of extinction due to human ecocide, especially those in the caviar industry.
7. The Sea’s Oil Reserves
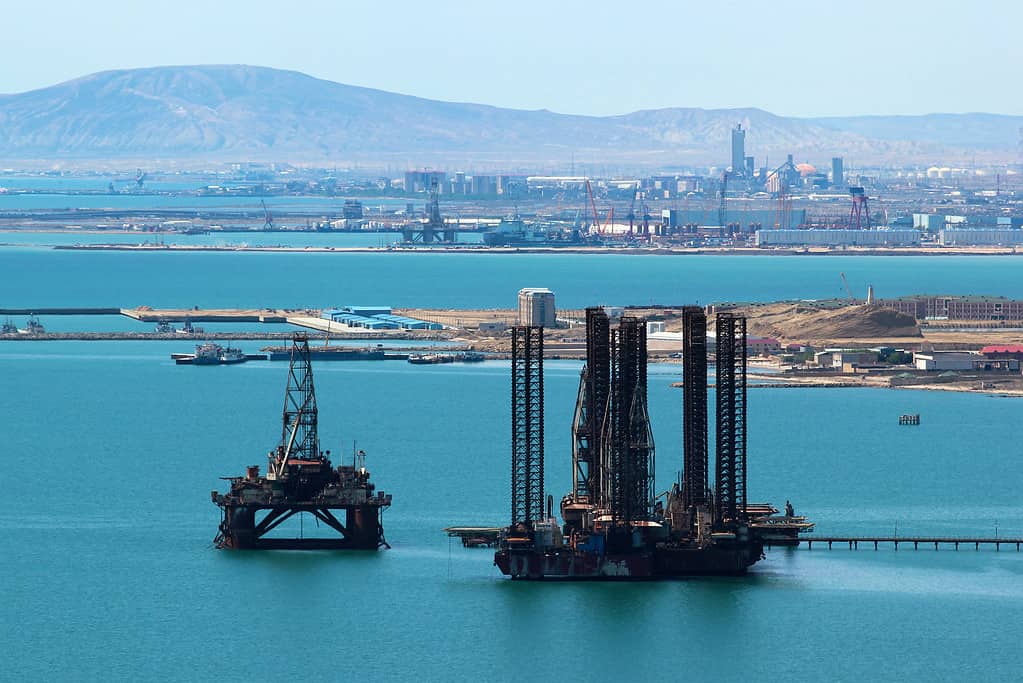

The oil production in the Caspian Sea used to be huge, but since the collapse of the Soviet Union, production has decreased.
©aquatarkus/iStock via Getty Images
The Caspian Sea is quite rich in natural resources like oil and natural gas. Oil reserves have existed in the Caspian Sea for centuries. In fact, Marco Polo described that there were oil wells in Baku, Azerbaijan when he was exploring western Asia. About 1.5 million barrels each day are taken from the Caspian Sea, for which Kazakhstan accounts for 55% and Azerbaijan about 20%. Oil is so strong in some of the bordering countries that it accounts for 10% of their GDP. Iran is number two in oil reserves in the world, whereas Russia is number two when it comes to oil and natural gas production.
8. Ecological Pollution
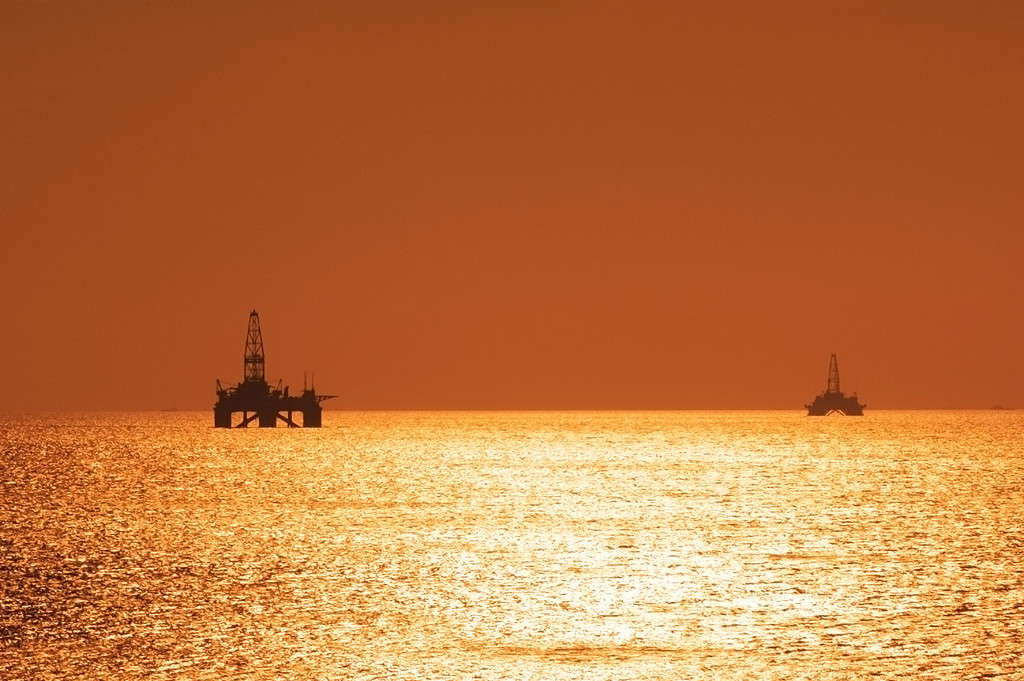

It is estimated that there are between 20 to 200 billion barrels of crude oil reserves in the Caspian Sea.
©© Elnur Amikishiyev/iStock via Getty Images
The Caspian Sea is a polluted lake, mainly because of human ecocide. The oil reserves in the sea are a huge contributor to the problem. There is also agricultural runoff that has made huge dents in the Caspian Sea’s marine life and ecosystem. And because the Caspian Sea is endorheic, it only loses water by evaporation, which means that the pollution stays in the sea.
Scientists believe that about 30 to 60 feet of the sea will be gone. Some towns rely on the sea and are seeing huge negative impacts because of the Caspian Sea’s shrinking. Furthermore, the biodiversity in the region could be destroyed because of this problem.
9. Bordering Countries

Five countries border the Caspian Sea and another four countries are what are called basin countries.
©ekipaj/iStock via Getty Images
The Caspian Sea is huge and that’s why five countries border it. The countries are Russia, Kazakhstan, Iran, Turkmenistan, and Azerbaijan. Although they do not directly border the Caspian Sea, there are also nearby basin countries, too. Those include Georgia, Armenia, Uzbekistan, and Turkey. Each country that borders the Caspian Sea relies on it for their economies.
10. Thriving Economy for Neighboring Countries

The Caspian Sea is a saltwater lake.
©Rufat Yusubov/iStock via Getty Images
The Caspian Sea is an important body of water for the neighboring countries. It provides billions of dollars for the economies of the five countries, as well. It ensures that thousands of people have jobs and millions are fed. There is also a good amount of tourism around the Caspian Sea with many different beaches and tourist towns popping up around the sea over the years.
Summary
And there you have it, these are 10 amazing facts about the Caspian Sea. The sea is unique because two of the world’s richest exports happen to take place in the sea — caviar and oil. The sea is steeped in a fascinating history that stretches out millions of years. The countries surrounding the Caspian Sea consider it an important sea for their economies but also continue to fight over which part of the sea is theirs.
If you get the chance to visit some of the five countries surrounding the Caspian Sea, you will be stunned by the azure waters before you. Just think about the beauty of the sea, the wildlife diversity, and the history of the legendary Caspian Sea.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.








