A species refers to a the largest grouping of organisms in a genus that has similar characteristics and can reproduce with one another to create viable offspring.
What Defines a Species?
The term species is used in biology to refer to the biggest group of organisms wherein two members with similar characteristics could reproduce and create offspring capable of reproduction. Species can be considered the basic taxonomic units of an organism.
Species is a difficult term to define in a way that satisfies disciplines within the field of biology and in other studies such as philosophy. Not counting subspecies, species refers to the most specific version of an organism without considering them as individuals.
For example, white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) are medium-sized deer that live in the Americas known for their similar morphologies including a white tail, brownish fur, antlers in some cases, and more. These creatures are similar to other members of their genus, Odocoileus, but they have distinguishing features from other species in that genus, like mule deer.
Yet, a species is just the final level of a long series of classifications used to reach the most specific version of an organism. Many ranks exist above this level of the taxonomic rank scale.
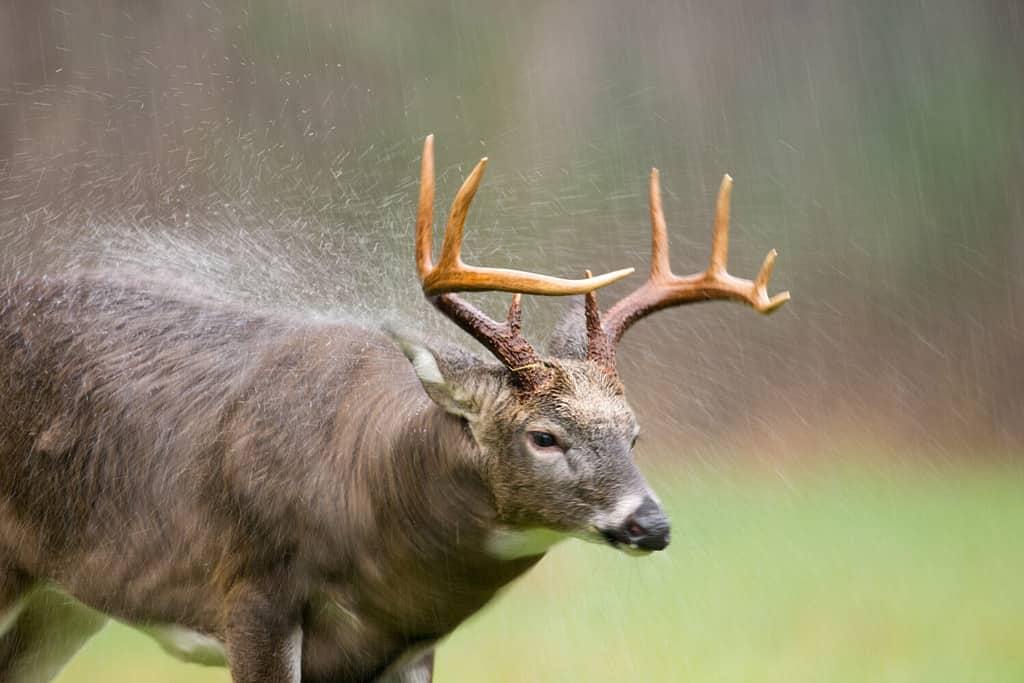

A large white-tailed deer, an individual belonging to
Odocoileus virginianus.
©Tony Campbell/Shutterstock.com
Understanding Taxonomic Rank
Biologists use seven or eight main taxonomic ranks when organizing animals into similar groups. From general to specific, they are:
- Domain
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
The domain classification is not always added over the rank of a kingdom when discussing taxonomic ranks, though. A useful way to conceptualize the taxonomic rank system is an inverted triangle where every layer gets more specific than the one before it. Every rank on the list provides information about an organism because of the shared traits of organisms within that rank.
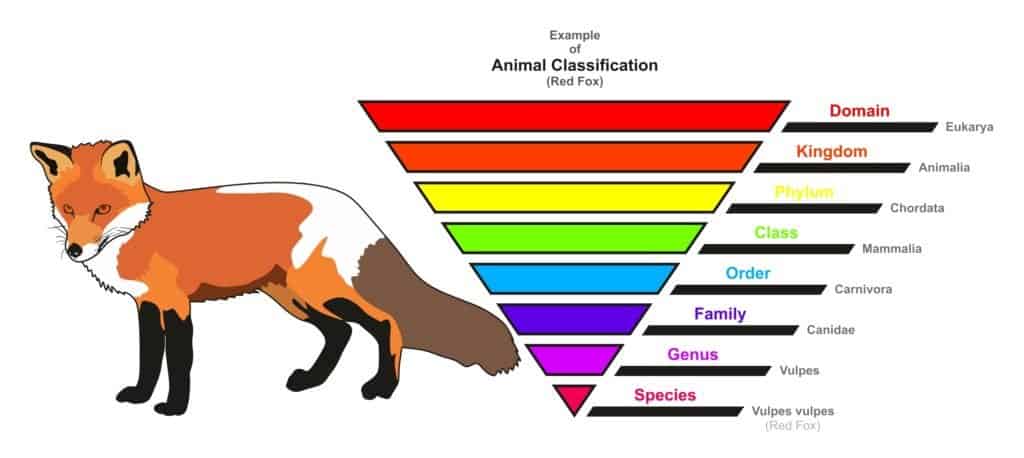
An animal classification for red fox, based on the Linnaeus Method
©udaix/Shutterstock.com
The Classification of a Lion’s Taxonomic Rank
A lionis a very large cat that primarily lives in Africa. The animal’s species name is Panthera leo. However, that is just one level of the animal’s overall taxonomic identity. Consider the following classifications and information each layer reveals about the lion on the way to the creature’s species definition.
| Taxonomic Rank | Lion |
|---|---|
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Order | Carnivora |
| Family | Felidae |
| Genus | Panthera |
| Species | Panthera leo |
Every classification on this list reveals something about the organisms contained within. For example, the lion is a member of Eukaryota, meaning they have cells with a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Most members of Animalia reproduce sexually, consume other organisms, and more. Chordates, members of the phylum Chordata, have a series of physical characteristics that separate them from other animals, like a notochord, pharyngeal slits, and more.
Members of the class Mammalia use mammary glands to feed their young, possess hair or fur, and have a developed neocortex. Lions also belong to the order Carnivora, meaning that they primarily subsist by consuming the flesh of other animals.
As a member of the family Felidae, lions have characteristics of cats. They are carnivores adapted to ambush attacks with powerful forelegs and strong bites.
The Panthera genus is a group of large cats with the ability to roar, including lions, jaguars, tigers, leopards, and snow leopards.
Within that genus is the species Panthera leo, the lion. These creatures are known for their physical qualities such as their broad chests, manes, tail, and round heads. They’re apex predators that live in social groups with a defined hierarchy.
Every level of taxonomic ranks shows a different facet of an organism until they reach the species level, making the current system of taxonomy very useful in defining animals.

What Are 5 Examples of a Species?
Every species is a unique type of organism. Consider the following examples of various species from around the world.
1. Solanum lycopersicum
Solanum lycopersicum is the name of the plant that produces tomatoes. This species originated in South and Central America where it was domesticated for food.
2. Panthera Tigris
Panthera tigris refers to the tiger, the largest cat in the world. These animals are one of the so-called “big cats” that live around the world.
3. Oreamnos americanus
Oreamnos americanus is a mountain goat, also called the Rocky Mountain goat, a mammal that lives in western North America.
4. Gorilla gorilla
The western gorilla takes its common name from its genus and species. Interestingly, the western lowland gorilla subspecies have the scientific name Gorilla gorilla gorilla.
5. Aquila chrysaetos
The golden eagle is a large bird of prey that lives throughout much of the northern hemisphere. Six subspecies of this bird are alive throughout the world.
What Species Are Humans?
The human species is called Home sapiens. This is the only extant species within the genus. Previously, several other members of the genus existed including Homo antecessor and Homo neanderthalensis.
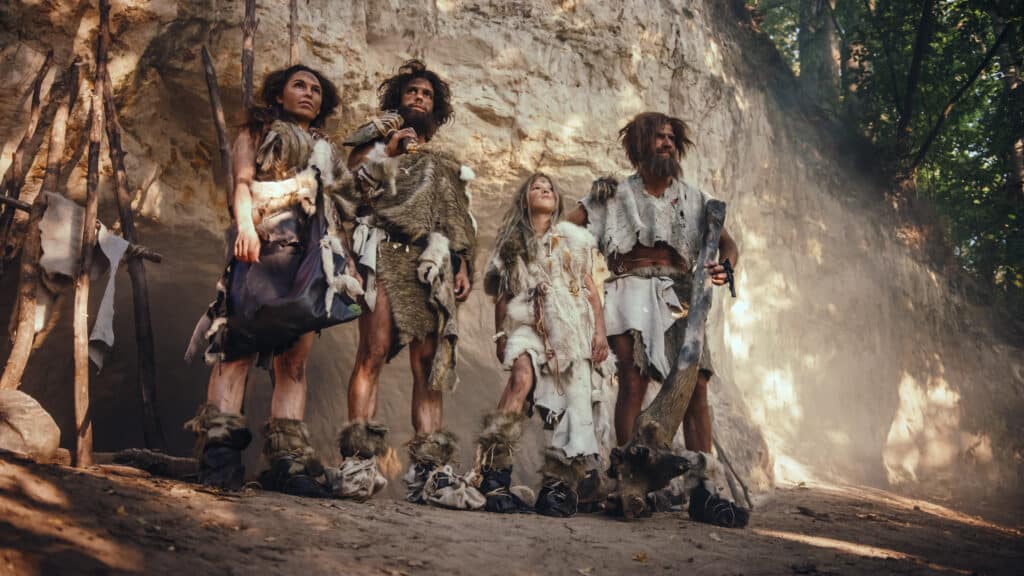

Neanderthals were also members of the genus
Homo.
©iStock.com/gorodenkoff
Species Pronunciation
The word is pronounced to sound like “spee-shees” as well as “spee-sees.”









