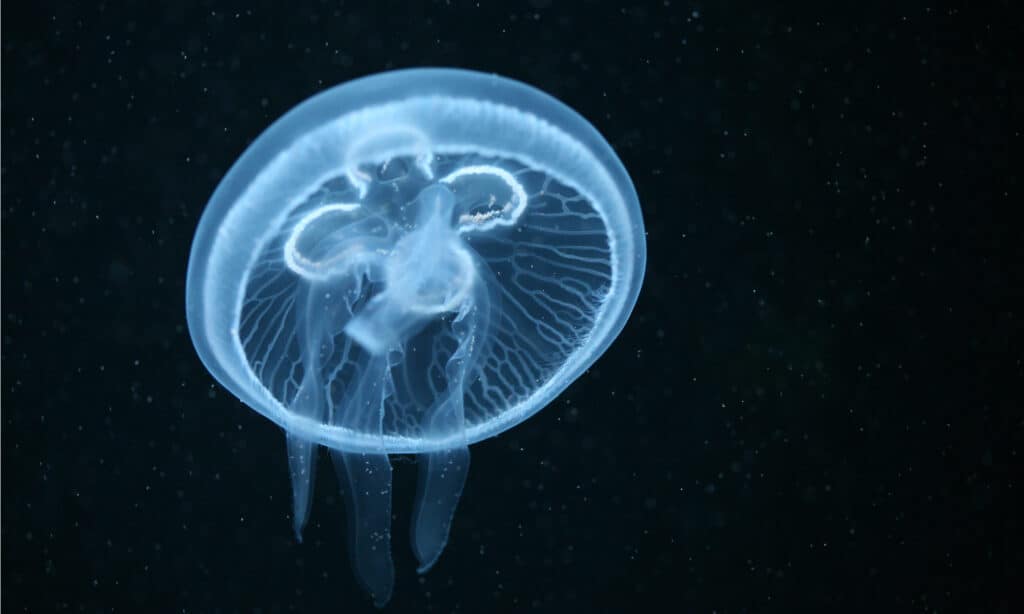
Moon Jellyfish
Aurelia aurita
Moon Jellies are bioluminescent, so they glow in the dark! They can also de-age!
Advertisement
Moon Jellyfish Facts
- Prey
- Plankton, small fish, crustaceans, larvae, eggs
- Name Of Young
- Planula, polyp, ephyra
- Group Behavior
- Smack
- Bloom
- Fun Fact
- Moon Jellies are bioluminescent, so they glow in the dark! They can also de-age!
- Estimated Population Size
- Millions
- Biggest Threat
- Humans, sea turtles, sharks, birds
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Their moon-shaped, gelatinous, glowing body
- Other Name(s)
- Saucer jelly, moon jelly, common jelly
- Gestation Period
- Varies
- Litter Size
- Can be in the 1000s
- Habitat
- Temperate ocean
- Predators
- Sea turtles, sharks, humans, fish, birds
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Lifestyle
- Smack
- Bloom
- Type
- Plankton
- Common Name
- Moon Jelly
- Number Of Species
- 25
- Location
- Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic Oceans, near the beach
View all of the Moon Jellyfish images!

The Moon Jelly is a type of jellyfish found throughout warmer waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans.
These jellyfish prefer the coastal parts of the ocean such as harbors or inlets near the beach. They often wash up on the beach because they are not strong swimmers. Unlike many other species of jellyfish, their sting is not very painful because they only have a collection of very small tentacles. They are the most common type of jelly to be kept as a pet. They are also used in cuisine in parts of Asia, in both sweet and savory dishes.
5 Moon Jellyfish Facts
Moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) in an aquarium.
©Vladimir Wrangel/Shutterstock.com
- Moon Jellyfish are actually prehistoric fish.
- Moon Jellies are a glowing species of bioluminescent fish.
- Moon Jellyfish prefer warmer coastal waters near the beach.
- Moon Jellyfish can deage and even get younger.
- Moon Jellies have been studied in space.
Classification and Scientific Name
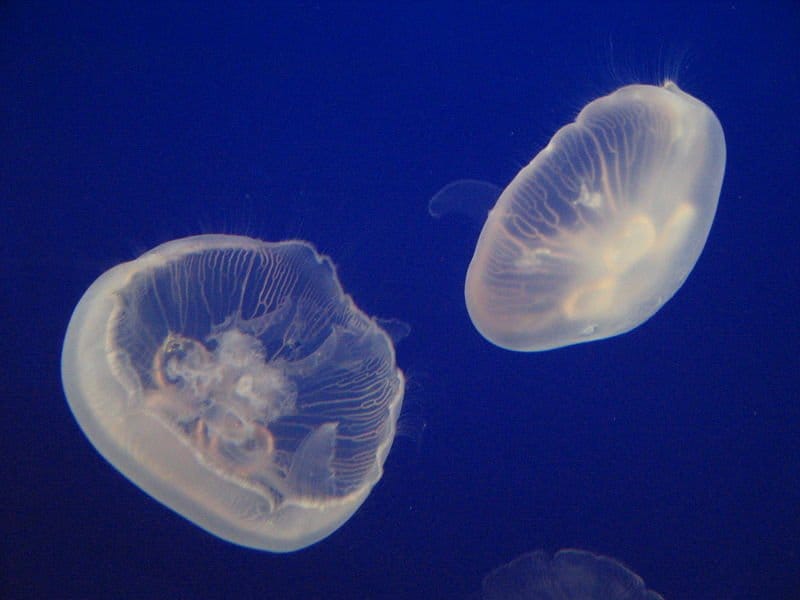

Moon Jelly fish (Aurelia aurita)
©Yosemite / Creative Commons – Original
Moon Jellyfish are known as A. aurita . Aurelia means gold-colored puppa in Greek, while aurita in Latin means furnished with hears. They may also be called moon jellies, saucer jellies, or common jellyfish. They are classified as a type of plankton, primarily because of their low swimming abilities.
They cannot swim against anything stronger than a weak current and are generally washed wherever the ocean takes them. There are currently 25 accepted species of Aurelia, with several others whose designation is pending.
Evolution and Origins
The Kavli Institute researchers have found out that the moon jellyfish’s metamorphosis was achieved without any major genetic mutations, but by utilizing a subset of pre-existing genes to transform from polyp to medusa, instead of the conventional process of mutation and natural selection.
Moon jellyfish inhabit warm oceanic waters and are commonly found near coastlines in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans, spanning across the globe.
Jellyfish possess genetic adaptations that enable them to regulate their body’s salt concentration at the molecular level, enabling them to move both vertically and horizontally to capture their prey, without being impacted by fluctuations in ocean salinity levels.
Different Types
- Immortal jellyfish
- Carybdea brevipedalia
- Staurozoa
- Keesingia gigas
- Morbakka fenneri
- Carukia barnesi
- Acraspeda
Appearance
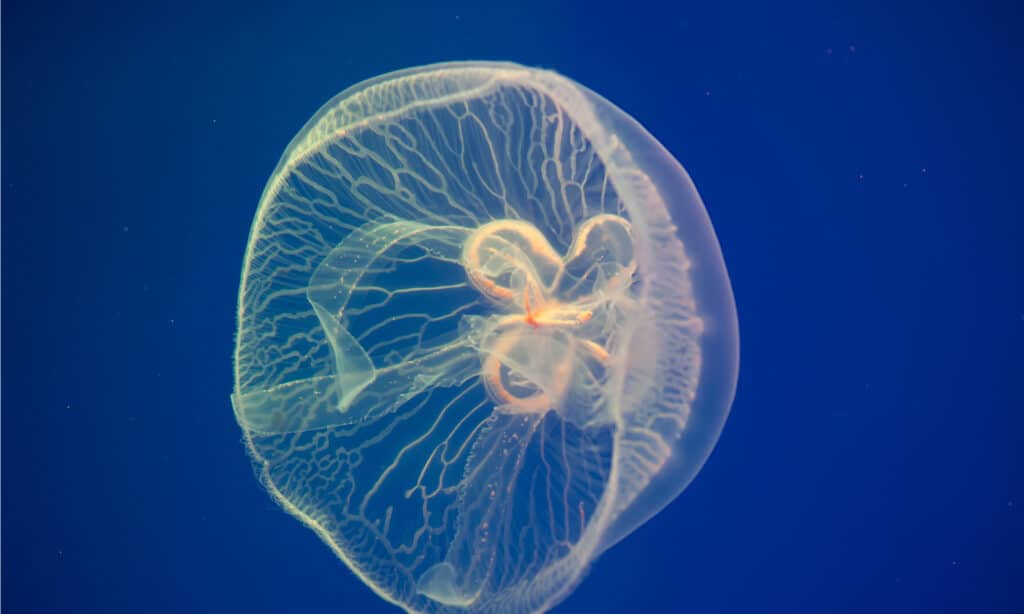

Moon jellyfish Aurelia aurita in the water. Aurelia aurita (also called the common jellyfish, moon jellyfish, moon jelly, or saucer jelly)
©Igor Kovalchuk/Shutterstock.com
Moon Jellyfish are primarily clear or transparent, with a single translucent disk in the center of their bell, which is usually blueish. Their bodies, also known as bells, are gelatinous orbs with many small tentacles. Because they are bioluminescent, they can be found glowing blue or pink in darker waters or as a means to communicate with other jellies.
Moon jelly predators may confuse a plastic bag floating in the ocean for a jellyfish and eat that instead. Moon jellies may be up to 18 inches across at the bell. They are called “moon” jellies because of their round, glowing bell and short tentacles.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Moon Jellyfish can be found in shallower areas of most of the warmer oceans. These jellies prefer to live in waters between 40 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit, but they don’t mind water that is dirty or low in oxygen. Blooms of moon jellyfish are monitored by scientists because how they grow and shrink is an indicator of other things happening in the ocean around them.
If moon jelly numbers swell, it means there is either an abundance of their prey or a dearth of their predators. These jellyfish can survive in oxygen-poor and even polluted waters that other sea creatures simply cannot.
According to the IUCN Redlist of endangered species, these moon jellies are considered not endangered or threatened.
Predators and Prey
Moon Jellyfish eat a lot of invertebrates, including other plankton, mollusk larvae, and crustaceans. They may also consume certain fish eggs and even tiny fish. Moon jellies use their tentacles to paralyze their prey and sweep them into their mucus membranes in order to ingest them.
The biggest threats to moon jellies besides humans are sea turtles and sharks, but their populations are not at risk. Other predators include marine mammals, large fish, and certain sea birds.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Moon Jellyfish lay eggs that are fertilized by sperm. This is done when a female moon jelly ingests floating sperm released by a male moon jelly and her body carries it to the eggs. Those moon jelly eggs float until they find a firm surface on which to attach, at which point they hatch and become planula, which then turns into polyps.
These moon jelly polyps may wait for up to 25 years before becoming ephyra and then adults. As adults, they usually only live about a year, although sometimes, a moon jellyfish can be triggered into de-aging or aging backward to become younger.
Many people say that jellyfish are technically immortal because of this ability to become babies and then grow up again because, in the absence of predators, the moon jellies could potentially do this de-aging and re-aging cycle indefinitely.
Fishing and Cooking
Moon Jellyfish are often used in Chinese and Japanese cooking, as well as cuisines in other parts of Southeast Asia. They are not particularly flavorful, but they do add saltiness to dishes and can be used to create items such as glowing ice cream!
Cooking with moon jellies became encouraged when jellyfish populations swelled and became a danger to fishing vessels. The jellies are not eaten fresh as they dissolve when taken from the water and killed. Instead, moon jellyfish are generally stripped of their mucus membranes and tentacles, then the moon jellies are sliced up and salt-cured.
Moon Jellyfish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Can a moon jellyfish sting you?
A moon jellyfish can sting you, yes, but because of the small size of their tentacles, their stings are virtually harmless and only someone with an allergy would be more than mildly affected.
Can you have a moon jellyfish as a pet?
Yes, some people keep Moon Jellyfish as aquarium pets in tanks.
Are moon jellyfish alive?
Yes, Moon Jellyfish ingest food and breathe oxygen, so they are alive.
Do humans use moon jellyfish?
Yes, humans do use Moon Jellies as pets in a tank or aquarium, and also sometimes they are dried and used in cuisine.
Are moon jellyfish dangerous?
No, moon jellyfish are not particularly dangerous, since their stings carry a little toxin, though they can sink shipping boats if too many get caught in the nets.
Where are moon jellyfish found?
Moon jellyfish are found in the higher, warmer levels of the oceans, especially near beaches.
What do moon jellyfish eat?
Moon jellies primarily eat plankton, mollusks, and crustaceans.
How long do moon jellyfish live?
An adult moon jellyfish lives between 12 to 15 months in tank captivity, but a polyp, or baby moon jelly, can live up to 25 years before reaching adulthood.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- S C Aquarium Moon Jelly Facts
- Cubic Aquarium Jellyfish questions and answers
- Sea Wonder Moon Jelly Fish
- Moon Jellyfish
- Moon Jellyfish Facts Gifford Zoo
- Moon Jelly Fun Facts
- Facts about Moon Jellyfish
- Pink Moon Jellies
- Aurelia Aurita "Moon Jelly" Wiki
- Moon Jelly Scientific Name Meanings and Facts
- Moon Jellyfish Facts
- Moon Jellyfish Facts Cooking with Dried Moon Jellies
- Moon Jelly Smacks, Blooms and Ecology
- Moon Jelly Predators and Behavior