Wood Duck
Aix sponsa
Adult male wood ducks sport a striking red eye and bill year-round!
Advertisement
Wood Duck Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Anseriformes
- Family
- Anatidae
- Genus
- Aix
- Scientific Name
- Aix sponsa
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Wood Duck Conservation Status
Wood Duck Facts
- Fun Fact
- Adult male wood ducks sport a striking red eye and bill year-round!
- Estimated Population Size
- 4.6 million
- Biggest Threat
- Scarce habitats
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Red eyes and bills
- Distinctive Feature
- Colorful coats
- Other Name(s)
- Carolina duck
- Wingspan
- 26 to 29 inches
- Incubation Period
- 28 to 37 days
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Nesting Location
- In tree cavities or man-made nesting boxes
- Migratory
- 1
View all of the Wood Duck images!
Wood Duck Summary
“Adult male wood ducks sport a striking red eye and bill year-round!”
The wood duck is a species of waterfowl native to North America. It is a type of perching duck. Breeding males of this species sport a bright plumage. This has earned them the title of being one of the most colorful species of waterfowl on the continent. They will often utilize man-made nesting boxes.
Wood Duck Amazing Facts
- They will often nest share or use nesting boxes since natural nesting sites can be scarce.
- It is the only North American duck to produce two broods per year on a regular basis.
- When first leaving the nest, the ducklings may jump from up to 50 feet in the air without sustaining injuries.
- They are known for perching in trees.
Where to Find Wood Ducks
Wood ducks are native to North America. They can be found as far north as Canada and as far south as central Mexico and Cuba.
Year-round, regardless of the season, this species of duck will occupy the area on or near some type of water source. They prefer water sources with dense coverage, as this allows them to perch and forage as needed. Some of their most common habitats include bottomland forests, swamps, marshes, and beaver ponds. Unlike some other species, which can thrive in freshwater or brackish water, wood ducks prefer freshwater marshes. However, they are still found in coastal regions and islands.
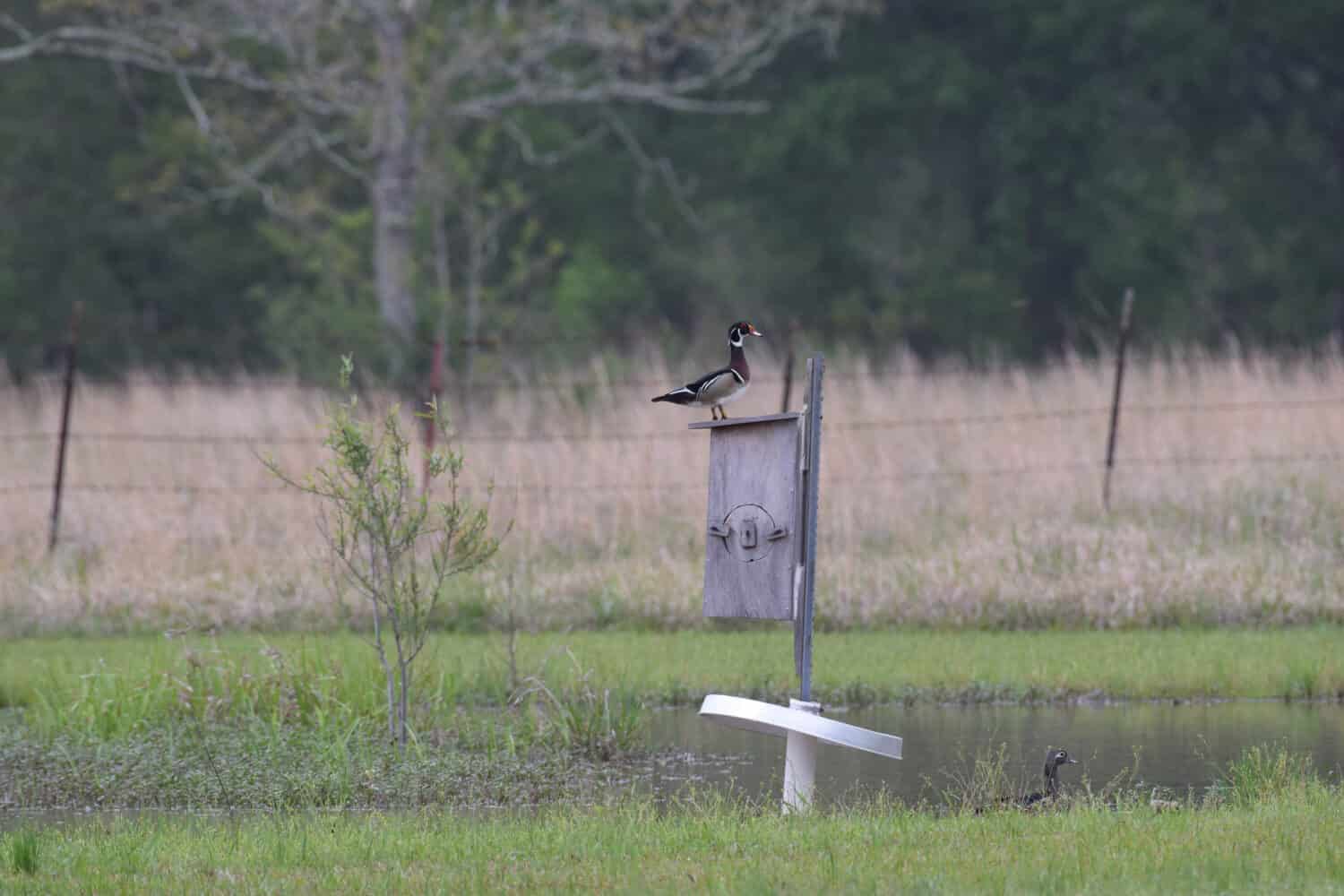

Wood ducks will nest in tree cavities or man-made nest boxes near their preferred habitats.
©albhski/Shutterstock.com
Wood Duck Nests
This species of duck takes well to man-made nesting boxes. If you would like to attract a breeding pair to your home, ensure that you have a habitat similar to that of their natural one. This includes a clean freshwater stream or pond and areas to forage and perch. You should also ensure that the nesting box has some guard to help protect the nest and hatchlings. Plastic should be avoided unless heavily shaded, as it can easily overheat.
In nature, wood ducks will build their nests in the cavities of trees. They cannot make their own cavities, and woodpecker cavities are often unused. Instead, the breeding pair will typically occupy the cavity left behind by a branch falling and the heartwood rotting away as a result.
These cavities are often up to around 60 feet from the ground, and they can nest as far as 1.2 miles away from water. However, they do prefer locations over or near water. Smaller entries are preferred to help guard away predators, although they can span several feet across.
The breeding pair will both set out in the early morning to find the right nesting location. Once the right cavity or nesting box has been found, the female will line the inside with down feathers plucked from her chest.
Wood Duck Scientific Name
The scientific name of the wood duck is Aix sponsa.
It is the class Aves and the order Anseriformes, the order which contains all species of waterfowl. Its family is Anatidae, which includes ducks, geese, and swans. There is only one other species in the genus Aix: the Mandarin duck (A. galericulata). The word aix comes from Ancient Greek, specifically from a word Aristotle used to describe an unknown diving bird species.
Another common name for this species is the Carolina duck.
Wood Duck Size, Appearance, and Behavior
The wood duck is a medium-sized species of duck. Adults of this species will grow to an average length of 19 to 21 inches. They can also weigh anywhere between 16.0 and 30.4 ounces. From wingtip to wingtip, their wingspan measures 26 to 29 inches.
Breeding males are typically more readily identifiable than females, eclipse males, or juveniles.
Male wood ducks in their breeding plumage have a green crested head with red markings, as well as bold white lines. Their faces are black with white throats and white collars, which help showcase the tell-tale red eye and beak. Males have a chestnut breast with pale yellow spots, similar to a young fawn’s coat. The sides of this duck are buff, with blue markings along the wings.
In their eclipse coats, which develop after the post-breeding season molt, males sport a grey-brown plumage. Their throats and chins still showcase a pale coloration, though it is no longer a stark white. You can still identify them by their bright red eyes and bills.
Juvenile males will still sport red eyes, while females will not. Regardless of sex, as a juvenile, their coat more closely resembles that of a female. They are grey, with pale markings along the face. There is a more noticeable coloration on their wings, usually appearing in blue with green shading.
Females have a warm brown plumage. They also sport a crested head, though it is less so than that of a breeding male. They sport a white marking around their eye, as well as a bold white strip on their wings. As mentioned above, with the juveniles, females will have bright blue markings on their wings, seen both at rest and in flight.
While flying, wood ducks are known to hold their heads high. Their heads may even bob.
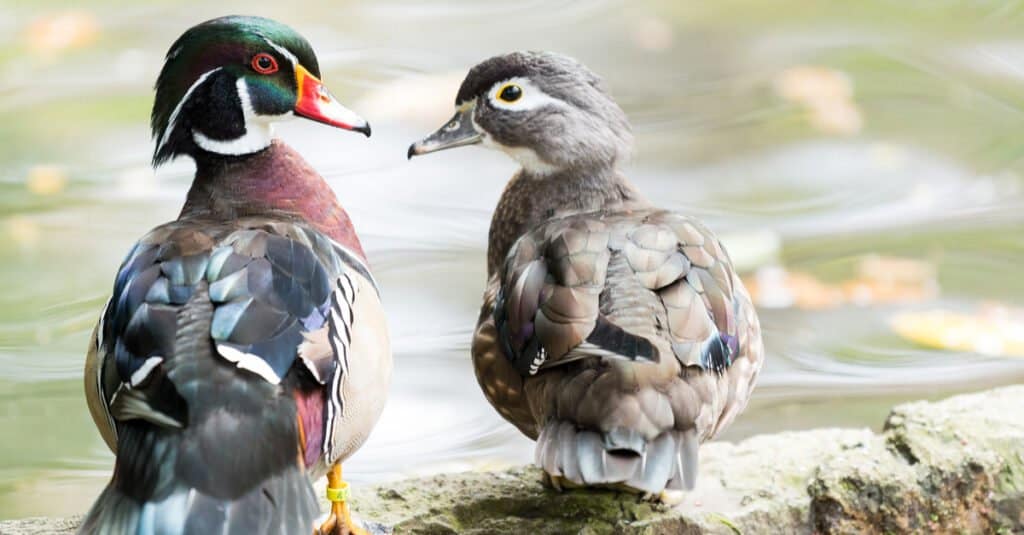

Wood ducks display sexual dimorphism, with breeding males varying greatly from females in appearance.
©JonVallejoPhotography/Shutterstock.com
Wood Duck Migration Pattern and Timing
There are several year-round populations in Cuba as well as on both the western and eastern coasts of the United States. Pairs that breed in Canada and the northernmost United States may migrate as far south as Mexico for wintering, with several wintering locations outlining the western year-round populations.
Wood Duck Diet
The wood duck has a variable omnivorous diet. However, while it may eat animal matter, the majority of its diet is plant matter. Typically, their food is aquatic in nature. However, when aquatic plants and animals are unavailable, they will forage on dry land.
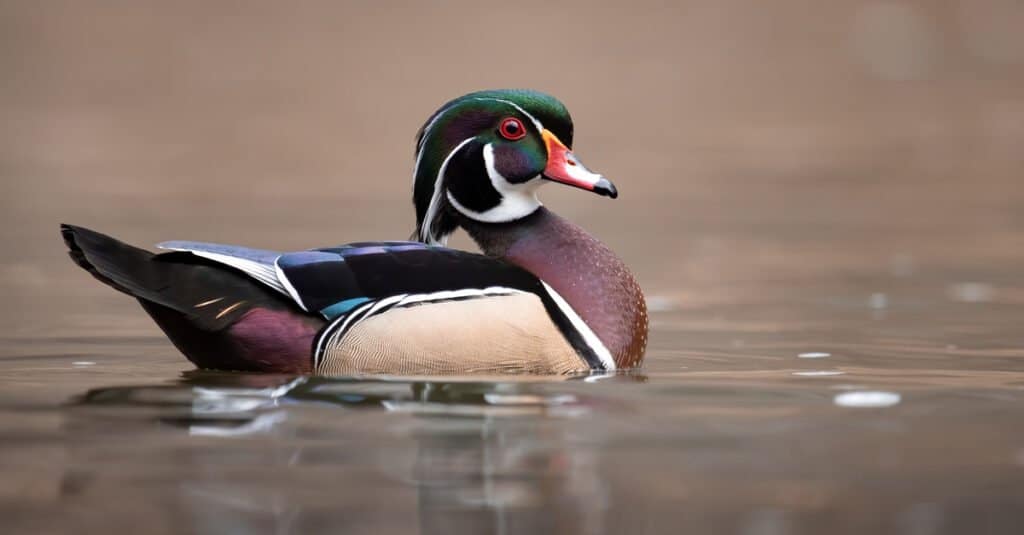

Wood ducks will dip their head beneath the surface to capture aquatic prey.
©Harry Collins Photography/Shutterstock.com
What Do Wood Ducks Eat?
This species will eat many things as available, including:
- Acorns
- Blackberries
- Duckweed
- Millet
- Smartweed
- Soybeans
- Panic grass
- Waterlily
- Water primrose
- Wild cherries
- Beetles
- Caterpillars
- Flies
- Isopods
- Snails.
Wood Duck Predators and Threats
During the late 19th century, the wood duck population faced serious declines as a result of hunting. While there have been improvements, this species is still a popular game bird and is hunted often each year. In fact, annually, they are the second-most hunted duck, behind the mallard.
One of the biggest threats to the wood duck population is the lack of habitat. Because they nest in particular tree cavities, nesting locations can be scarce. However, introducing man-made nest boxes has been beneficial in providing a solution to this concern.
There are also several predators of the wood duck.
What Eats Wood Ducks?
Some of the predators of wood ducks include the following animals.
- Owls
- Snakes
- Raccoons
- Foxes
- Coyotes
- Hawks
Wood Duck Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
Wood ducks lay one to two broods each year, each brood ranging from 6 to 16 eggs. The incubation period for these eggs is 28 to 37 days. Once the ducklings hatch, they are alert and covered in a full-down coat. Only a day after their hatching, they are able to jump down from the nesting cavity. The nesting period lasts from 56 to 70 days.
They are known to participate in intraspecific brood parasitism or egg dumping. Females will often lay their eggs in another female’s nest, leaving the latter to raise the ducklings once they hatch. Because of egg dumping, some nests have been found to have 29 eggs rather than the typical maximum of 16.
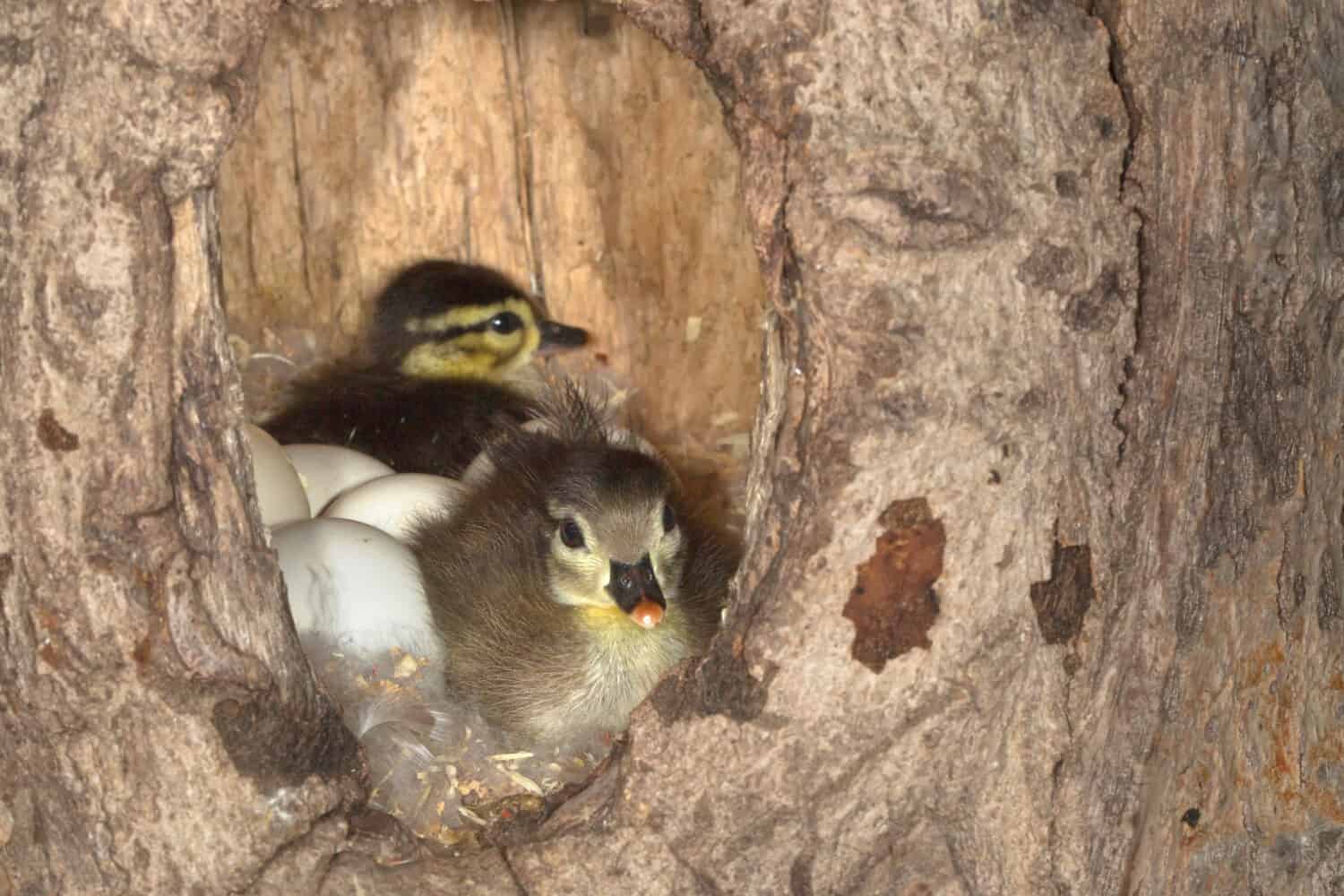

Young wood ducks will leave the nest after one day, though they remain in the care of their parents.
©Agnieszka Bacal/Shutterstock.com
Wood Duck Population
Despite threats surrounding the population, the wood duck is a species of least concern. The global breeding population is estimated to be around 4.6 million.
View all 108 animals that start with WWood Duck FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Do wood ducks migrate?
Wood ducks mainly live year-round in their locations, although some populations will breed in the north and migrate south for winter.
How many eggs do wood ducks lay?
Wood ducks lay up to 16 eggs per clutch, although because of brood parasitism, they may raise many more than that.
How fast does the wood duck fly?
Wood ducks reach a top speed of 35 miles per hour.
What is the wood duck's wingspan?
Their wingspan measures 26 to 29 inches.
When do wood ducks leave the nest?
Wood ducks leave the nest the day after they hatch.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- , Available here: https://pif.birdconservancy.org/ACAD/Database.aspx