Introduction
Texas is an incredibly big state, stretching between 800 and 1,000 miles from north to south. While Texas is the largest state in the continental United States, it is not the largest in the country overall. Nevertheless, the area and population of this state are impressive. In addition, the climate, landscape, and wildlife of Texas are diverse and beautiful. These features are sure to leave all visitors of the state in awe. Discover how big the state of Texas is and compare its size to other large states.
Texas is the largest state in the continental United States.
©Alexander Lukatskiy/Shutterstock.com
Background on Texas
Texas had previously been a part of the Spanish Empire and then incorporated into the country of Mexico. However, the state gained independence from Mexico in 1836 and joined the United States. Texas was accepted into the union as the 28th state in 1845. During its initiation into the union, many people associated the state with tales of the Wild West, where laws had little authority over the unruly cowboys throughout the region. Today, the reputation of Texas has changed, but many residents of the state keep alive the cowboy attitude of the past.
The name “Texas” comes from the Native American word “thecas,” which translates to “friends” or “allies.” When Spain settled the state, they took the word “thecas” and changed it to “Tejas,” which developed to become “Texas.” The primary industries that dominate the economy of Texas include agriculture, oil and natural gas, finance, and businesses and attractions centered in cities.
Climate in Texas
The climate of Texas varies drastically according to region and season. During winter, temperatures exceed 90ºF in the Rio Grande Valley, located just above the Rio Grande along the border between Texas and Mexico. On the other hand, the state may experience blizzards in other areas during the same season. Along the Gulf of Mexico, Texas sees temperatures averaging 70ºF, and the Panhandle of the state sees averages in the 60s.
Furthermore, precipitation is most prevalent in the southeast portion of the state; whereas the southwest region centered in the Trans-Pecos is extremely dry. Another common weather occurrence in Texas is the presence of hurricanes. Hurricanes in the state typically happen along the Gulf Coast. These hurricanes can be particularly disastrous to residents and animal life. In fact, one hurricane, which passed in the year 1900, killed 8,000 people in Texas.
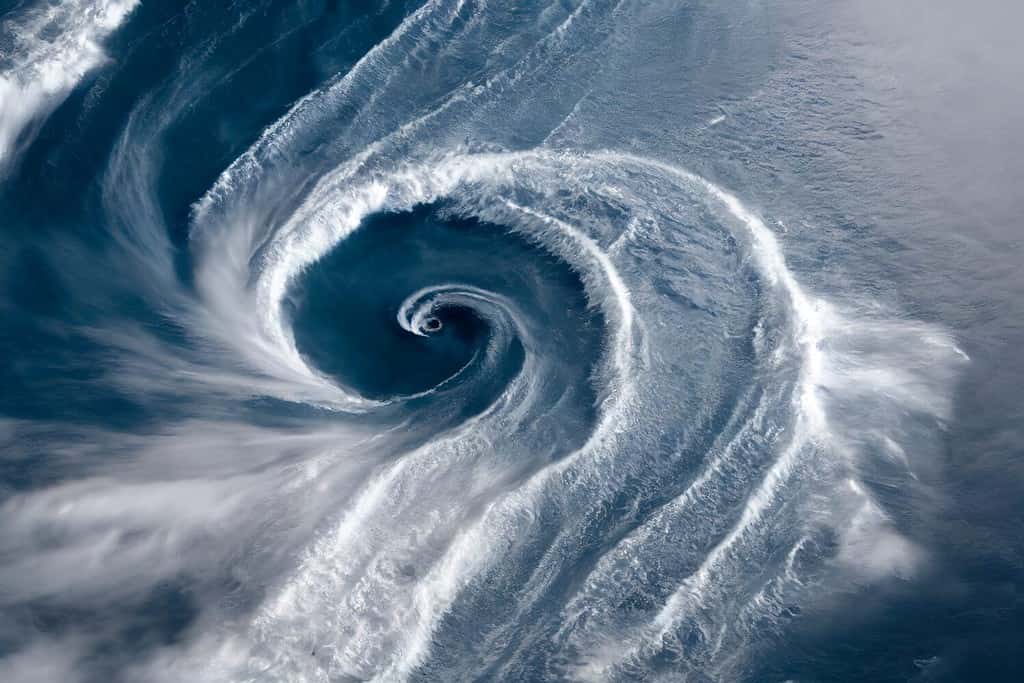

The Gulf Coast is especially prone to hurricanes.
©Vikks/Shutterstock.com
How Big is the State of Texas in Square Miles, Kilometers, and Acres?
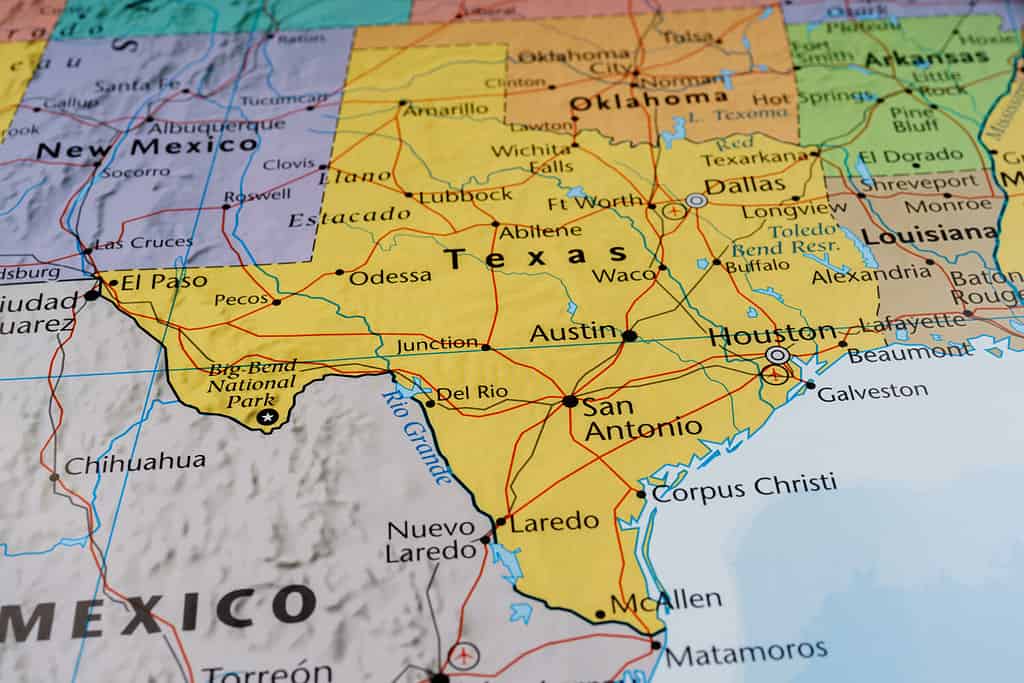
Texas is the second largest state in the United States, following behind the state of Alaska, which places first. The state of Texas covers an incredible 268,597 square miles. The square mileage of this state translates to a total of approximately 695,663 square kilometers. In addition, the state takes up around 171,902,080 acres.
Population and GDP of Texas
The population of Texas measures around 29.53 million people, which accounts for around 8.9% of the total population of the United States. Furthermore, Texas ranks as the 9th largest economy on Earth by Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at around 2.4 trillion U.S. dollars, as of 2022. Finally, the state has the second-largest economy in the United States, following California, which has a GDP of 3.7 trillion U.S. dollars, as of 2022.
Why is Texas a Large State?
Did you know that Texas used to be much larger than it is today? The state covered portions of other surrounding states, such as Colorado, New Mexico, Kansas, and more. In 1846, the southern boundary of the state was officially declared. The Rio Grande would act as the border between Texas and Mexico. During the Compromise of 1850, Texas lost around a third of its total territory. In return, the state received $10 million from the federal government.
By 1861, Texas had seceded from the union alongside other states engaged in the Civil War. The state joined the Confederacy until it was readmitted in 1870 after the Union victory. Following the Compromise of 1850 and the secession of Texas, no significant changes were made to the boundaries of the state. Thus, Texas has remained a large state since the mid-1800s.
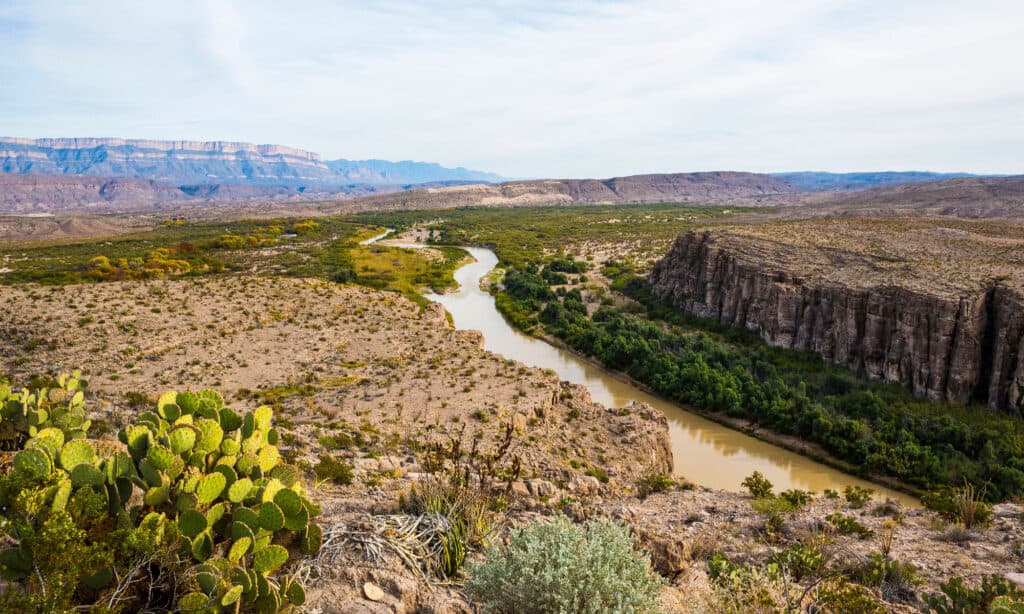

The Rio Grande marks the boundary between Texas and Mexico.
©Fred LaBounty/Shutterstock.com
Texas vs. Other Large States: A Comparison
| State and Ranking | Area (mi2) | Area (km2) | Acreage | Population | GDP (U.S. dollars) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texas (2nd) | 268,597 | 695,663 | 171,902,080 | 29.53 million | 2.4 trillion |
| Alaska (1st) | 665,384 | 1,723,337 | 425,845,760 | 732,673 | 49.63 billion |
| California (3rd) | 163,695 | 423,968 | 104,764,800 | 39.24 million | 3.7 trillion |
| Montana (4th) | 147,040 | 380,832 | 94,105,600 | 1.10 million | 49.75 billion |
| New Mexico (5th) | 121,590 | 314,917 | 77,817,600 | 2.12 million | 94.66 billion |
| Arizona (6th) | 113,990 | 295,233 | 72,953,600 | 7.28 million | 356.42 billion |
| Nevada (7th) | 110,572 | 286,380 | 70,766,080 | 3.14 million | 165.46 billion |
| Colorado (8th) | 104,094 | 269,602 | 66,620,160 | 5.81 million | 385.83 billion |
| Oregon (9th) | 98,379 | 254,798 | 62,961,920 | 4.25 million | 234.81 billion |
| Wyoming (10th) | 97,813 | 253,335 | 62,600,320 | 578,803 | 36.35 billion |
Mammals in Texas
Texas is home to hundreds of species of birds, amphibians, and mammals. In fact, around 540 bird species reside throughout the state. One animal that is abundant in this state is the bat. In fact, around 32 distinct bat species are present in Texas. Bats are commonly seen in this state during late summer, and August is one of the best months to encounter bats. For instance, the Mexican free-tailed bat is popular to see in August. As fall turns to winter, though, the Mexican free-tailed bat, alongside other bat species, will migrate south.
The nine-banded armadillo is present throughout all of Texas, excluding the Trans-Pecos, where the climate is dry. Armadillos have an outer shell that protects them from predation. In addition, they have claws that aid them in finding food. The armadillo eats larvae and insects, which are both found under the soil. Thus, armadillos use their claws to dig through the soil and find their sustenance. One fun fact about the armadillo is that it is the official state small mammal of Texas.
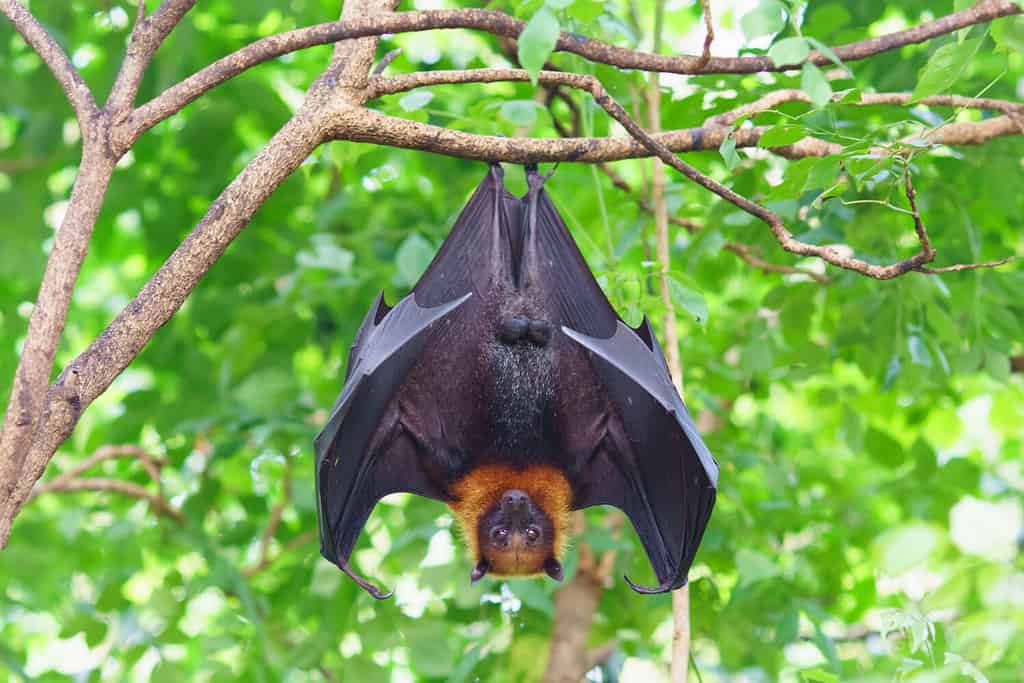

Texas is home to 32 distinct bat species, and some refer to it as the battiest state in the nation.
©jekjob/Shutterstock.com
Fish and Birds in Texas
Rivers, lakes, and other freshwater sources in Texas are home to several types of fish, including bass, crappie, carp, gar, and more. These fish are popular catches. Perhaps the most sought-after catch for fishermen is the largemouth bass. Largemouth bass measure between four and 16 inches, depending on their age. Furthermore, the coloration of largemouth bass is typically green with some darker patterning. The diet of largemouth bass includes insect larvae and zooplankton for juveniles, but adults consume other fish or crayfish.
Like fish, a diverse assortment of bird species can be encountered throughout Texas. One beautiful bird in the state is the great horned owl. The great horned owl is usually found in forested areas. The species is common across the state, excluding a region called Pineywoods. The great horned owl is often referred to as the “hoot owl” due to its unique call. Some other bird species in Texas are the ladder-backed woodpecker, Carolina wren, red-tailed hawk, great blue heron, and more.
Large Cities in Texas
Four main cities exist in the state of Texas, and all of them are relatively large, according to their populations. The largest city in the state is Houston, Texas, which has a population numbering approximately 2,293,000. One interesting fact about Houston is that it is the fourth-largest city in the nation, following behind Chicago, Los Angeles, and New York City. Perhaps some of the most important features of Houston are its growing industries, such as oil and gas and aerospace technology; diversity; and a developing appreciation for the arts.
The second-largest city in Texas is San Antonio with a population of 1,435,000 residents. San Antonio, Texas is best known for The Alamo. The Alamo is a tourist attraction in the city that was once a Spanish mission. The Alamo is well-known throughout the country because it was the site of an important battle in gaining independence for Texas.
The final two cities in Texas are Dallas and Austin with populations of 1,300,000 and 945,000, respectively. Dallas is considered the most important center of banking and finance in the entire southwest region of the United States. In addition, Dallas is the site of many significant historical events, such as the assassination of President John F. Kennedy. Austin, though the smallest city in Texas, is the state’s capital. Some unique features of Austin are its growing economy, increased job availability, and attractions, especially related to live music.

Austin, Texas is the capital of the state, but it is the least populous of the main four cities.
©Lucas Beck/Shutterstock.com
The photo featured at the top of this post is © iStock.com/leekris
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.






