Detects prey using echolocation!
Advertisement
Bat Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Chiroptera
- Family
- Microchiroptera
- Genus
- Emballonuridae
- Scientific Name
- Chiroptera
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Bat Conservation Status
Bat Facts
- Main Prey
- Mice, Frogs, Fruit
- Distinctive Feature
- Large ears detect prey using echolocation and have strong, flexible wings
- Habitat
- Woodland and caves
- Predators
- Owls, Eagles, Snakes
- Diet
- Omnivore
“A mother bat gives birth to her babies while hanging upside down.”
There are 47 species of bats living in the United States and 1300 species of bats in total. Bats live in many types of environments except in extremely cold places (polar regions) and extremely hot ones (deserts). Bats are important pollinators and help to control the population of insects. These animals are social and live in groups that can number in the hundreds of thousands! Though vampire bats are the most well-known, there are only three species of bats that use another animal’s blood as food.

5 Bat Facts
- Some bats travel up to 2,400 miles each year to spend the winter in a place with a warm climate
- 70% of all bats feed on beetles, moths, flies, mosquitoes, and other insects
- The biggest type of bat in the world is known as the Pteropus
- Bats have been known to survive for over 20 years
- A bat is a mammal that can fly without ever gliding. Some bats are extremely fast. The Mexican free-tailed bat can reach speeds of more than 100 miles per hour, making it the fastest animal in North America.
Scientific Name
Bat is the common name of this remarkable animal, while Chiroptera is its scientific name. The bat has a classification as Mammalia and is in the Microchiroptera family.
The Brazilian free-tailed bat has a subspecies called the Mexican free-tailed bat that lives in the southern part of the United States. Also, the Virginia big-eared bat is a subspecies of Townsend’s big-eared bat.
A bat’s scientific name is taken from the Greek words cheir, meaning hand, and pteron, meaning wing. This is because the parts of a bat’s wing resemble that of a hand with four ‘fingers’ covered with a thin membrane.
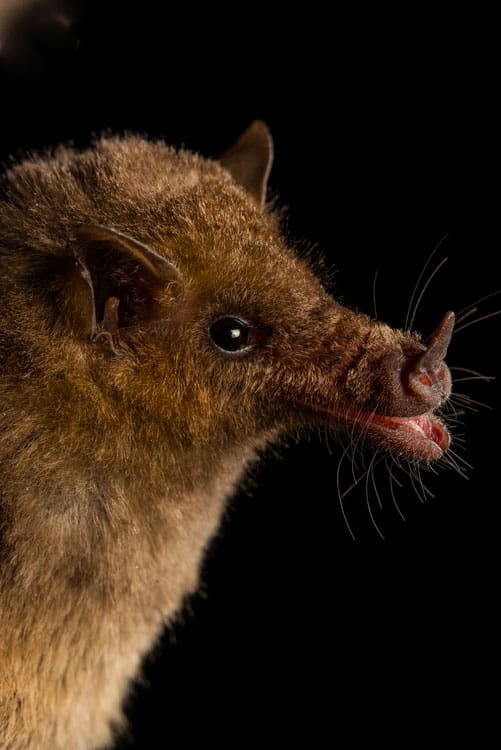

A bat’s scientific name is taken from the Greek words cheir, meaning hand, and pteron, meaning wing. This is because the parts of a bat’s wing resemble that of a hand with four ‘fingers’ covered with a thin membrane.
©svaldvard/Shutterstock.com
Evolution and Origins
Most scientists agree that bats must have evolved from mammals, but there is not enough evidence to know which ancestor they came from. Bats first appeared in the fossil record around 50 million years ago, during the Eocene. Scientists have found remains ranging from teeth and bits of the jaw to full skeletons in places like Wyoming, Paris, Australia, and India. They now think that bats evolved from small, rodent-like animals, including animals such as rats.
The first bats were different from their modern relatives in some ways. For example, scientists know from the ear anatomy of better-preserved specimens that the first bats couldn’t echolocate. They used only sight, smell, and touch to find their meals. Today, bats have a claw only on the equivalent of our thumb, but early bats kept some additional finger claws from their ancestors. A bat fossil dating to about 52 million years ago, called Onychonycteris finneryi, had claws on each of its five fingers. New technology is helping fill in a few of the gaps. A recent study of coloration in the fossil record found that two 48 million-year-old bats found in Germany were mostly brown.
Despite the progress made, scientists are still left with some big questions. For example, they are unsure where the 50-million-year-old bat specimens came from. They are also uncertain about when, where, why, and how the first bats became airborne. This information is hidden by the vast amount of time that has passed.
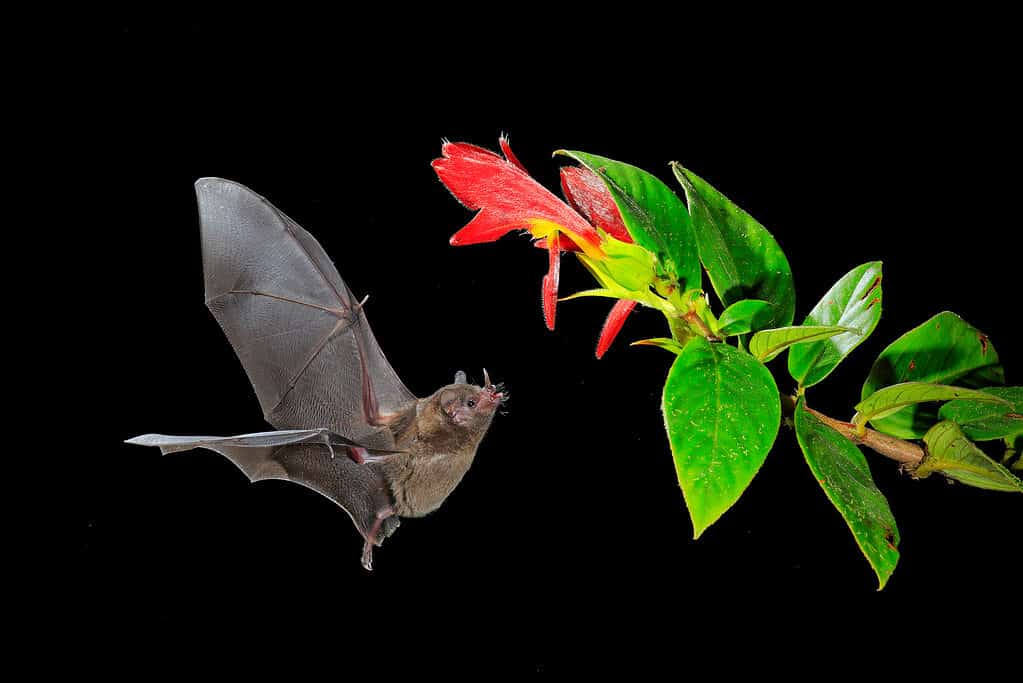

Early bats did not have echolocation. They used sight, sound, and smell to locat their food.
©iStock.com/Ondrej Prosicky
Appearance and Behavior
A bat has a thin layer of brown, black, or gray fur. They have small or large ears and small black eyes. Depending on its species, a bat can weigh as little as .07 ounces. Think of a bat that weighs .07 ounces as being lighter than a single penny. The largest species of bat can weigh up to 3.3 pounds. A bat weighing 3.3 pounds is about as heavy as half of an average-sized brick.
The wings of a bat are its most memorable feature. A bat’s wing has four bones that you can think of as its fingers, as well as a bone serving as a thumb. A thin layer of skin called a membrane connects these bones creating a bat’s flexible wing. If you’ve ever watched a bat fly, you know it can change direction in an instant. It’s these flexible finger bones in their wings that give them that skill. A bat’s wings also give it speed. The fastest bat can travel 99 mph.
When it comes to wingspan, the largest species of bat, known as a flying fox, has a wingspan of five feet! When a flying fox stretches its wings to full length, it would be almost as long/tall as a home’s refrigerator. The smallest species of bat, the Kitti-hognosed bat, has a wingspan of a little less than six inches. This is less than half the length of a ruler you may use in school.
Bats are social animals and live in groups called colonies. (Though they like being around other bats, they are shy and will avoid people.) Sometimes a colony of bats can number in the hundreds of thousands. Living together is how a bat protects itself from predators. If an owl invades a colony of bats, most of the bats will be able to escape. The largest colony of bats is located in the Philippines. The Monfort bat colony there has 3 million bats and counting. Safety in numbers!

Habitat
Bats live on many continents, including Asia, North America, South America, Africa, Europe, and Australia. However, there are no bats living in Antarctica because they prefer warm climates.
When you think of a bat’s home, you may imagine a colony of bats hanging from the ceiling of a cave. Bats also live in trees, under bridges, in burrows, and even in manmade bat houses. They choose a place to roost where they’ll be hidden from predators and able to sleep during the day. Bats wrap their flexible wings around them when they sleep.
Some bats migrate to warmer places for the winter months. These flying mammals hibernate from about October or November until spring arrives in March. A bat living in a place where the temperature doesn’t fall below 45 degrees may not migrate to a warmer climate.
Learn more about other animal species that hibernate here.
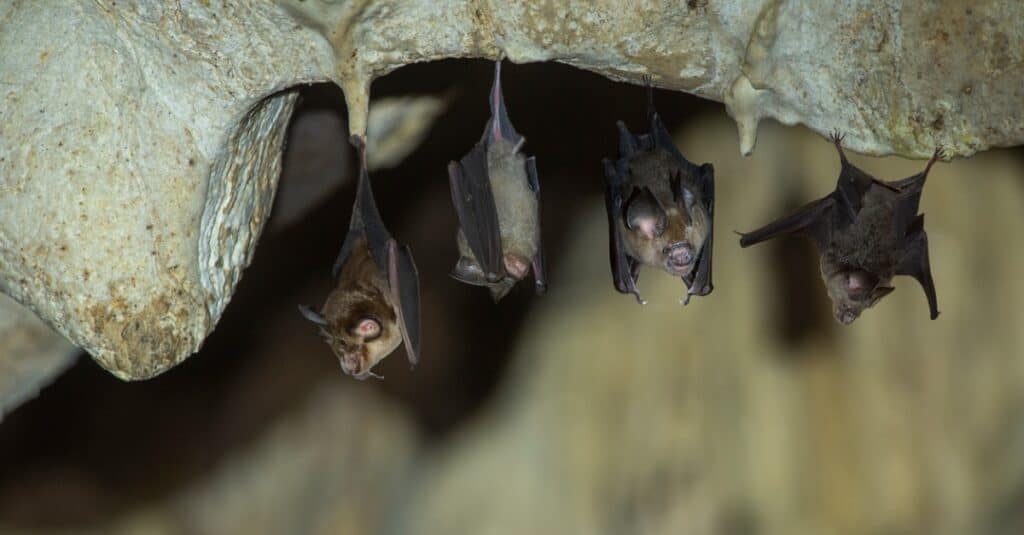

Bats live on every continent except Antarctica.
©iStock.com/BirdHunter591
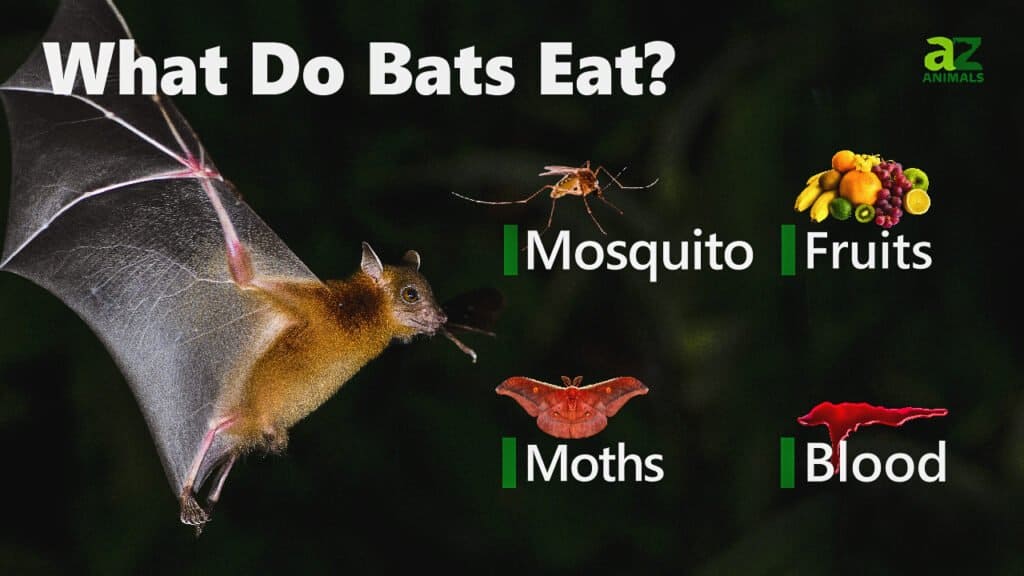
Diet
What do bats eat? Many bats eat insects such as mosquitoes, moths, cockroaches, and beetles. A little brown bat can eat 500 insects in one hour. A colony of bats can consume 500,000 pounds of bugs per night. 500,000 pounds of bugs is equal to the weight of two blue whales!
Bats use echolocation to find their prey. As a bat flies, it lets out high-pitched squeaks and clicks that humans can’t hear. When the sound waves created by a bat’s squeak hit an object, the sound echoes back to the bat. Think of echolocation as a bat’s personal radar system.
Other bats have a diet of nectar. These bats drink nectar from flowers just as hummingbirds do. Some bats eat fruit by sucking the juices of a ripe piece of fruit and spitting out the seeds. In addition, there are bats that eat fish. They fly over the water, grabbing fish with their claws.
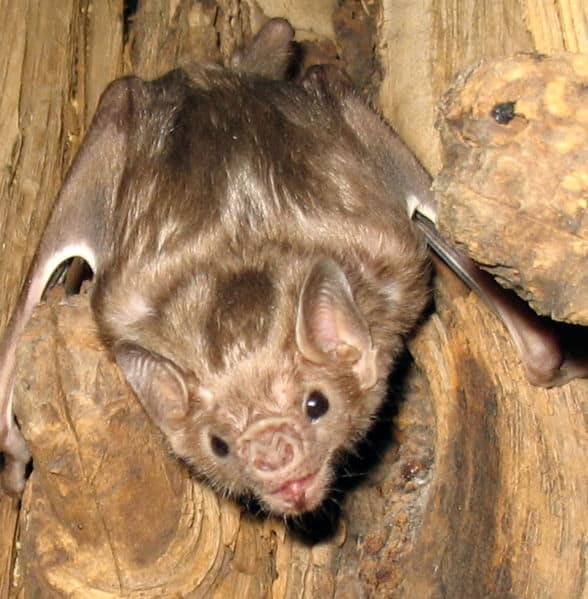
You’re probably familiar with the vampire bat. There are three types of these bats that drink blood from mammals such as cows or birds. They are found in South America and Mexico. It’s a myth that vampire bats suck the blood from these animals. Instead, they bite a cow, a sheep, or a bird while it’s sleeping and lick the blood as it seeps out of the animal’s leg or other body parts. This bat only takes in about two teaspoons of an animal’s blood.

Predators and Threats
Bats have a few predators, including owls, falcons, eagles, snakes, raccoons, and cats. An owl may sit on a tree near a cave or bridge where a bat is sleeping and capture it as it flies out to hunt in the evening. Alternatively, a raccoon or snake may pick up a baby bat that’s fallen from its mother’s grasp and landed on the ground.
Bats face the threat of loss of habitat due to people clearing trees to build homes and businesses. If they’re disturbed during the hibernation period, they can starve or die due to exposure to the cold. Also, when land and crops are cleared, it can remove the food source of bats. Some bats are threatened in cultures that use them for food or medicine.
The conservation status of bats is the Least Concerned. Many bat conservation groups offer suggestions to the public on how they can help make sure bats continue to thrive and grow in population. Some of those suggestions include avoiding the use of pesticides in gardens and building a bat house to provide protection for local bats. Also, if you find a bat in hibernation, don’t disturb it.

Bats face the threat of loss of habitat due to people clearing trees to build homes and businesses.
©iStock.com/nymphoenix
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
Did you know a bat can sing? Male bats sing and unfold their wings to attract female bats during mating season. Unfortunately, people can’t hear the high-pitched song of bats. A male bat marks its territory during mating time with liquid from its scent glands. Bats swarm during this time, allowing them to find a mate. A female bat can be pregnant for 40 days or six months, depending on its species. Most have one baby once a year.
A mother bat gives birth to her baby or pup while she is hanging upside down. She must catch her pup with her wings after it’s born! A pup weighs about ¼ of the total weight of its mother. So, if a pup’s mom weighs one pound, the baby weighs just ¼ of a pound. A pup of this size is not quite as heavy as a hamster. A pup is born blind and without hair. It drinks milk from its mother for up to six months and clings to her as she flies. After six months, a mother teaches her pup to fly and hunt for food. Once a pup learns these skills, it’s able to survive on its own.
Depending on its species, a bat can live from 5 to 30 years. Scientists have observed that hibernating bats have a tendency to live longer than non-hibernating ones. In many species of bats, females live longer than males. The oldest bat on record lived to be 41 years old!
A disease known as White-nose syndrome is responsible for killing both young and older bats as they hibernate. This disease takes away from a bat’s store of fat as it sleeps. This can cause the bat to wake up and fly out of the cave in search of food. Chances are that the weakened bat will starve because the supply of insects is low in the wintertime.

A mother bat gives birth to her baby or pup while she is hanging upside down. She must catch her pup with her wings after it’s born! A pup weighs about ¼ of the total weight of its mother.
©Corina Daniela Obertas/Shutterstock.com
Population
There are 1,300 species of bats throughout the world. The highest concentration of bat species lives near the equator. The conservation status of bats is Least Threatened, and the population is holding fairly steady. However, conservation efforts are always in place for bats because most have just one pup per year.
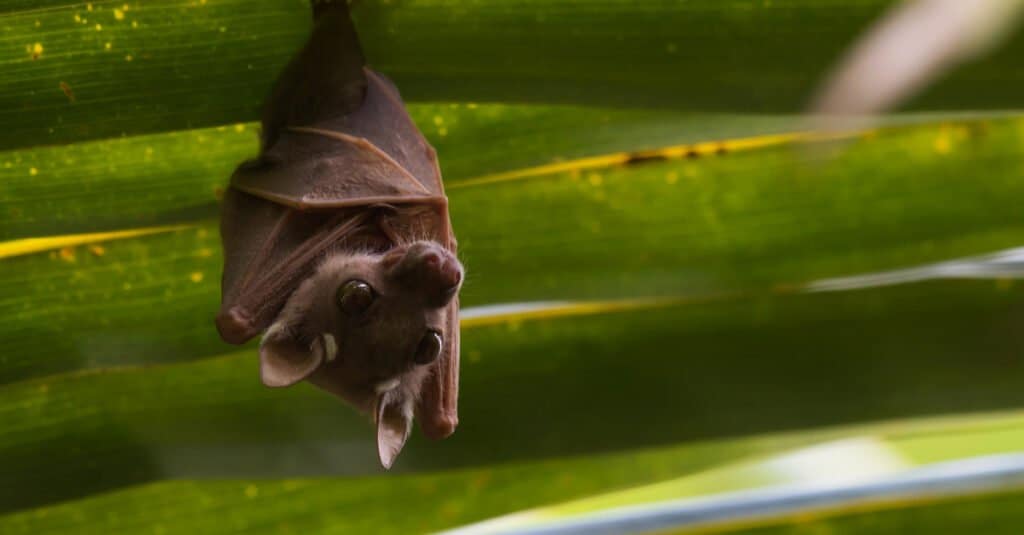

There are more than 1,200 species of bats throughout the world
©Dave Montreuil/Shutterstock.com
Types of Bats
- Pygmy fruit bat (Aethalops alecto)
- Borneo fruit bat (Aethalops aequalis)
- Mindanao pygmy fruit bat (Alionycteris paucidentata)
- Spotted-winged fruit bat (Balionycteris maculata)
- Black-capped fruit bat (Chironax melanocephalus)
- Lesser short-nosed fruit bat (Cynopterus brachyotis)
- Horsfield’s fruit bat (Cynopterus horsfieldii)
- Peters’s fruit bat (Cynopterus luzoniensis)
- Minute fruit bat (Cynopterus minutus)
- Nusatenggara short-nosed fruit bat (Cynopterus nusatenggara)
- Greater short-nosed fruit bat (Cynopterus sphinx)
- Indonesian short-nosed fruit bat (Cynopterus titthaecheilus)
- Brooks’s dyak fruit bat (Dyacopterus brooksi)
- Rickart’s dyak fruit bat (Dyacopterus rickarti)
- Dayak fruit bat (Dyacopterus spadiceus)
- Philippine pygmy fruit bat (Haplonycteris fischeri)
- Salim Ali’s fruit bat (Latidens salimalii)
- Tailless fruit bat (Megaerops ecaudatus)
- Javan tailless fruit bat (Megaerops kusnotoi)
- Ratanaworabhan’s fruit bat (Megaerops niphanae)
- White-collared fruit bat (Megaerops wetmorei)
- Luzon fruit bat (Otopteropus cartilagonodus)
- Dusky fruit bat (Penthetor lucasi)
- Greater musky fruit bat (Ptenochirus jagori)
- Lesser musky fruit bat (Ptenochirus minor)
- Blanford’s fruit bat (Sphaeria blanfordi)
- Swift fruit bat (Thoopterus nigrescens)
- Madagascan fruit bat (Eidolon dupreanum)
- Straw-coloured fruit bat (Eidolon helvum)
- Bulmer’s fruit bat (Aproteles bulmerae)
- Manado fruit bat (Boneia bidens)
- Andersen’s naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia anderseni)
- Beaufort’s naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia beauforti)
- Negros naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia chapmani)
- Halmahera naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia crenulata)
- Biak naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia emersa)
- Sulawesi naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia exoleta)
- Solomon’s naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia inermis)
- Lesser naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia minor)
- Moluccan naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia moluccensis)
- Panniet naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia pannietensis)
- Western naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia peronii)
- New Britain naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia praedatrix)
- Greenish naked-backed fruit bat (Dobsonia viridis)
- Sulawesi harpy fruit bat (Harpyionycteris celebensis)
- Harpy fruit bat (Harpyionycteris whiteheadi)
- Long-tongued nectar bat (Macroglossus minimus)
- Long-tongued fruit bat (Macroglossus sobrinus)
- Long-tailed fruit bat (Notopteris macdonaldi)
- New Caledonia blossom bat (Notopteris neocaledonica)
- Common blossom bat (Syconycteris australis)
- Halmahera blossom bat (Syconycteris carolinae)
- Moss-forest blossom bat (Syconycteris hobbit)
- Broad-striped tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene aello)
- Common tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene albiventer)
- Pallas’s tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene cephalotes)
- Mountain tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene certans)
- Round-eared tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene cyclotis)
- Dragon tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene draconilla)
- Keast’s tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene keasti)
- Island tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene major)
- Malaita tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene malaitensis)
- Demonic tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene masalai)
- Lesser tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene minutus)
- Philippine tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene rabori)
- Eastern tube-nosed bat (Nyctimene robinsoni)
- Nendo tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene sanctacrucis)
- Umboi tube-nosed fruit bat (Nyctimene vizcaccia)
- Lesser tube-nosed fruit bat (Paranyctimene raptor)
- Steadfast tube-nosed fruit bat (Paranyctimene tenax)
- Sulawesi fruit bat (Acerodon celebensis)
- Talaud fruit bat (Acerodon humilis)
- Golden-capped fruit bat (Acerodon jubatus)
- Palawan fruit bat (Acerodon leucotis)
- Sunda fruit bat (Acerodon mackloti)
- White-winged flying fox (Desmalopex leucopterus)
- Small white-winged flying fox (Desmalopex microleucopterus)
- Fardoulis’ blossom bat (Melonycteris fardoulisi)
- Black-bellied fruit bat (Melonycteris melanops)
- Woodford’s fruit bat (Melonycteris woodfordi)
- Fijian monkey-faced bat (Mirimiri acrodonta)
- Small-toothed fruit bat (Neopteryx frosti)
- Bougainville monkey-faced bat (Pteralopex anceps)
- Guadalcanal monkey-faced bat (Pteralopex atrata)
- Greater monkey-faced bat (Pteralopex flanneryi)
- Montane monkey-faced bat (Pteralopex pulchra)
- New Georgian monkey-faced bat (Pteralopex taki)
- Admiralty flying fox (Pteropus admiralitatum)
- Aldabra flying fox (Pteropus aldabrensis)
- Black flying fox (Pteropus alecto)
- Small Samoan flying fox (Pteropus allenorum)
- Vanuatu flying fox (Pteropus anetianus)
- Silvery flying fox (Pteropus argentatus)
- Aru flying fox (Pteropus aruensis)
- Dusky flying fox (Pteropus brunneus)
- Ashy-headed flying fox (Pteropus caniceps)
- Bismark masked flying fox (Pteropus capistratus)
- Moluccan flying fox (Pteropus chrysoproctus)
- Makira flying fox (Pteropus cognatus)
- Spectacled flying fox (Pteropus conspicillatus)
- Large Samoan flying fox (Pteropus coxi)
- Ryukyu flying fox (Pteropus dasymallus)
- Nicobar flying fox (Pteropus faunulus)
- Banks flying fox (Pteropus fundatus)
- Gilliard’s flying fox (Pteropus gilliardorum)
- Gray flying fox (Pteropus griseus)
- Ontong Java flying fox (Pteropus howensis)
- Small flying fox (Pteropus hypomelanus)
- Andersen’s flying fox (Pteropus intermedius)
- Kei flying fox (Pteropus keyensis)
- Livingstone’s fruit bat (Pteropus livingstonii)
- Lombok flying fox (Pteropus lombocensis)
- Okinawa flying fox (Pteropus loochoensis)
- Lyle’s flying fox (Pteropus lylei)
- Big-eared flying fox (Pteropus macrotis)
- Lesser flying fox (Pteropus mahaganus)
- Mariana fruit bat (Pteropus mariannus)
- Indian flying fox (Pteropus medius)
- Black-bearded flying fox (Pteropus melanopogon)
- Black-eared flying fox (Pteropus melanotus)
- Caroline flying fox (Pteropus molossinus)
- Great flying fox (Pteropus neohibernicus)
- Mauritian flying fox (Pteropus niger)
- Temotu flying fox (Pteropus nitendiensis)
- Ceram fruit bat (Pteropus ocularis)
- Ornate flying fox (Pteropus ornatus)
- Chuuk flying fox (Pteropus pelagicus)
- Pelew flying fox (Pteropus pelewensis)
- Masked flying fox (Pteropus personatus)
- Large Palau flying fox (Pteropus pilosus)
- Geelvink Bay flying fox (Pteropus pohlei)
- Grey-headed flying fox (Pteropus poliocephalus)
- Bonin flying fox (Pteropus pselaphon)
- Little golden-mantled flying fox (Pteropus pumilus)
- Solomons flying fox (Pteropus rayneri)
- Rennell flying fox (Pteropus rennelli)
- Rodrigues flying fox (Pteropus rodricensis)
- Madagascan flying fox (Pteropus rufus)
- Samoa flying fox (Pteropus samoensis)
- Little red flying fox (Pteropus scapulatus)
- Seychelles fruit bat (Pteropus seychellensis)
- Philippine gray flying fox (Pteropus speciosus)
- Small Mauritian flying fox (Pteropus subniger)
- Temminck’s flying fox (Pteropus temminckii)
- Guam flying fox (Pteropus tokudae)
- Insular flying fox (Pteropus tonganus)
- Vanikoro flying fox (Pteropus tuberculatus)
- Kosrae flying fox (Pteropus ualanus)
- Large flying fox (Pteropus vampyrus)
- New Caledonia flying fox (Pteropus vetulus)
- Pemba flying fox (Pteropus voeltzkowi)
- Dwarf flying fox (Pteropus woodfordi)
- Yap flying fox (Pteropus yapensis)
- Mindoro stripe-faced fruit bat (Styloctenium mindorensis)
- Sulawesi stripe-faced fruit bat (Styloctenium wallacei)
- Short-palated fruit bat (Casinycteris argynnis)
- Campo-Ma’an fruit bat (Casinycteris campomaanensis)
- Angolan epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus angolensis)
- Ansell’s epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus anselli)
- Peters’s epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus crypturus)
- Dobson’s epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus dobsonii)
- Gambian epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus gambianus)
- Lesser Angolan epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus grandis)
- Ethiopian epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus labiatus)
- East African epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus minimus)
- Minor epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus minor)
- Wahlberg’s epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus wahlbergi)
- Buettikofer’s epauletted fruit bat (Epomops buettikoferi)
- Franquet’s epauletted fruit bat (Epomops franqueti)
- Greater dawn bat (Eonycteris major)
- Philippine dawn bat (Eonycteris robusta)
- Lesser dawn bat (Eonycteris spelaea)
- Hammer-headed bat (Hypsignathus monstrosus)
- Azagnyi fruit bat (Megaloglossus azagny)
- Woermann’s bat (Megaloglossus woermanni)
- Hayman’s dwarf epauletted fruit bat (Micropteropus intermedius)
- Peters’s dwarf epauletted fruit bat (Micropteropus pusillus)
- Angolan fruit bat (Myonycteris angolensis)
- São Tomé collared fruit bat (Myonycteris brachycephala)
- East African little collared fruit bat (Myonycteris relicta)
- Little collared fruit bat (Myonycteris torquata)
- Veldkamp’s dwarf epauletted fruit bat (Nanonycteris veldkampii)
- D’Anchieta’s fruit bat (Plerotes anchietae)
- Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus)
- Geoffroy’s rousette (Rousettus amplexicaudatus)
- Sulawesi rousette (Rousettus celebensis)
- Long-haired rousette (Rousettus lanosus)
- Leschenault’s rousette (Rousettus leschenaulti)
- Linduan rousette (Rousettus linduensis)
- Madagascan rousette (Rousettus madagascariensis)
- Comoro rousette (Rousettus obliviosus)
- Bare-backed rousette (Rousettus spinalatus)
- Zenker’s fruit bat (Scotonycteris zenkeri)
- Kitti’s hog-nosed bat (Craseonycteris thonglongyai)
- Egyptian mouse-tailed bat (Rhinopoma cystops)
- Yemeni mouse-tailed bat (Rhinopoma hadramauticum)
- Lesser mouse-tailed bat (Rhinopoma hardwickei)
- Macinnes’s mouse-tailed bat (Rhinopoma macinnesi)
- Greater mouse-tailed bat (Rhinopoma microphyllum)
- Small mouse-tailed bat (Rhinopoma muscatellum)
- Heart-nosed bat (Cardioderma cor)
- Ghost bat (Macroderma gigas)
- Greater false vampire bat (Megaderma lyra)
- Lesser false vampire bat (Megaderma spasma)
- Acuminate horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus acuminatus)
- Adam’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus adami)
- Intermediate horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus affinis)
- Halcyon horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus alcyone)
- Arcuate horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus arcuatus)
- Lesser woolly horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus beddomei)
- Blasius’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus blasii)
- Bokhara horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus bocharicus)
- Bornean horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus borneensis)
- Canut’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus canuti)
- Cape horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus capensis)
- Sulawesi horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus celebensis)
- Geoffroy’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus clivosus)
- Croslet horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus coelophyllus)
- Andaman horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus cognatus)
- Cohen’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus cohenae)
- Convex horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus convexus)
- Little Japanese horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus cornutus)
- Creagh’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus creaghi)
- Darling’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus darlingi)
- Decken’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus deckenii)
- Dent’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus denti)
- Eloquent horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus eloquens)
- Mediterranean horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus euryale)
- Broad-eared horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus euryotis)
- Greater horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus ferrumequinum)
- Formosan woolly horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus formosae)
- Francis’s woolly horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus francisi)
- Rüppell’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus fumigatus)
- Guinean horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus guineensis)
- Hildebrandt’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus hildebrandti)
- Hill’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus hilli)
- Upland horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus hillorum)
- Lesser horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus hipposideros)
- Imaizumi’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus imaizumii)
- Philippine forest horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus inops)
- Insular horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus keyensis)
- Lander’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus landeri)
- Blyth’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus lepidus)
- Woolly horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus luctus)
- Mount Mabu horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus mabuensis)
- Maclaud’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus maclaudi)
- Big-eared horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus macrotis)
- Madura horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus madurensis)
- Maendeleo horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus maendeleo)
- Malayan horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus malayanus)
- Marshall’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus marshalli)
- Smaller horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus megaphyllus)
- Mehely’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus mehelyi)
- Mitred horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus mitratus)
- Formosan lesser horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus monoceros)
- Timorese horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus montanus)
- Neriad horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus nereis)
- Osgood’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus osgoodi)
- Bourret’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus paradoxolophus)
- Pearson’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus pearsonii)
- Large-eared horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus philippinensis)
- Least horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus pusillus)
- King horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus rex)
- Peninsular horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus robinsoni)
- Rufous horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus rouxii)
- Large rufous horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus rufus)
- Ruwenzori horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus ruwenzorii)
- Sakeji horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus sakejiensis)
- Schnitzler’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus schnitzleri)
- Lesser woolly horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus sedulus)
- Shamel’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus shameli)
- Shortridge’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus shortridgei)
- Thai horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus siamensis)
- Forest horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus silvestris)
- Bushveld horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus simulator)
- Chinese rufous horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus sinicus)
- Smithers’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus smithersi)
- Lesser brown horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus stheno)
- Little Nepalese horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus subbadius)
- Small rufous horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus subrufus)
- Swinny’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus swinnyi)
- Thomas’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus thomasi)
- Trefoil horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus trifoliatus)
- Yellow-faced horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus virgo)
- Dobson’s horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus yunanensis)
- Ziama horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus ziama)
- Flower-faced bat (Anthops ornatus)
- Arabian trident bat (Asellia arabica)
- Somalian trident bat (Asellia italosomalica)
- Patrizi’s trident leaf-nosed bat (Asellia patrizii)
- Trident bat (Asellia tridens)
- Dong Bac’s trident bat (Aselliscus dongbacana)
- Stoliczka’s trident bat (Aselliscus stoliczkanus)
- Temminck’s trident bat (Aselliscus tricuspidatus)
- Percival’s trident bat (Cloeotis percivali)
- East Asian tailless leaf-nosed bat (Coelops frithii)
- Malayan tailless leaf-nosed bat (Coelops robinsoni)
- Cyclops roundleaf bat (Doryrhina cyclops)
- Aba roundleaf bat (Hipposideros abae)
- Great roundleaf bat (Hipposideros armiger)
- Dusky leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros ater)
- Benito roundleaf bat (Hipposideros beatus)
- Bicolored roundleaf bat (Hipposideros bicolor)
- Short-headed roundleaf bat (Hipposideros breviceps)
- Sundevall’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros caffer)
- Spurred roundleaf bat (Hipposideros calcaratus)
- Greater roundleaf bat (Hipposideros camerunensis)
- Fawn leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros cervinus)
- Ashy roundleaf bat (Hipposideros cineraceus)
- Large Mindanao roundleaf bat (Hipposideros coronatus)
- Telefomin roundleaf bat (Hipposideros corynophyllus)
- Cox’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros coxi)
- Timor roundleaf bat (Hipposideros crumeniferus)
- Short-tailed roundleaf bat (Hipposideros curtus)
- Makira roundleaf bat (Hipposideros demissus)
- Diadem roundleaf bat (Hipposideros diadema)
- Fierce roundleaf bat (Hipposideros dinops)
- Borneo roundleaf bat (Hipposideros doriae)
- Khajuria’s leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros durgadasi)
- Dayak roundleaf bat (Hipposideros dyacorum)
- Hill’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros edwardshilli)
- Sooty roundleaf bat (Hipposideros fuliginosus)
- Fulvus roundleaf bat (Hipposideros fulvus)
- Cantor’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros galeritus)
- Grand roundleaf bat (Hipposideros grandis)
- Griffin’s leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros griffini)
- Thailand roundleaf bat (Hipposideros halophyllus)
- Kolar leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros hypophyllus)
- Crested roundleaf bat (Hipposideros inexpectatus)
- Arnhem leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros inordinatus)
- Jones’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros jonesi)
- Phou Khao Khouay leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros khaokhouayensis)
- Khasian leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros khasiana)
- Lamotte’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros lamottei)
- Indian roundleaf bat (Hipposideros lankadiva)
- Intermediate roundleaf bat (Hipposideros larvatus)
- Large Asian roundleaf bat (Hipposideros lekaguli)
- Shield-faced roundleaf bat (Hipposideros lylei)
- Big-eared roundleaf bat (Hipposideros macrobullatus)
- Maduran leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros madurae)
- Maggie Taylor’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros maggietaylorae)
- Aellen’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros marisae)
- Ethiopian large-eared roundleaf bat (Hipposideros megalotis)
- Fly River roundleaf bat (Hipposideros muscinus)
- Malayan roundleaf bat (Hipposideros nequam)
- Philippine forest roundleaf bat (Hipposideros obscurus)
- Orbiculus leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros orbiculus)
- Biak roundleaf bat (Hipposideros papua)
- Peleng leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros pelingensis)
- Pomona roundleaf bat (Hipposideros pomona)
- Pratt’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros pratti)
- Philippine pygmy roundleaf bat (Hipposideros pygmaeus)
- Ridley’s leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros ridleyi)
- Laotian leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros rotalis)
- Noack’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros ruber)
- Shield-nosed leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros scutinares)
- Semon’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros semoni)
- Sorensen’s leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros sorenseni)
- Schneider’s leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros speoris)
- Northern leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros stenotis)
- Sumba roundleaf bat (Hipposideros sumbae)
- Lesser great leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros turpis)
- Wollaston’s roundleaf bat (Hipposideros wollastoni)
- Orange leaf-nosed bat (Rhinonicteris aurantia)
- Commerson’s roundleaf bat (Macronycteris commersoni)
- Giant roundleaf bat (Macronycteris gigas)
- Saõ Tomé leaf-nosed bat (Macronycteris thomensis)
- Striped leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros vittatus)
- Grandidier’s trident bat Paratriaenops auritus
- Rufous trident bat (Triaenops persicus)
- Hairy-winged bat (Harpiocephalus harpia)
- Peter’s tube-nosed bat (Harpiola grisea)
- Taiwan tube-nosed bat (Harpiola isodon)
- Bronze tube-nosed bat (Murina aenea)
- Little tube-nosed bat (Murina aurata)
- Bala tube-nosed bat (Murina balaensis)
- Beelzebub’s tube-nosed bat (Murina beelzebub)
- Bicolored tube-nosed bat (Murina bicolor)
- Ashy-gray tube-nosed bat (Murina cineracea)
- Round-eared tube-nosed bat (Murina cyclotis)
- Elery’s tube-nosed bat (Murina eleryi)
- Flute-nosed bat (Murina florium)
- Dusky tube-nosed bat (Murina fusca)
- Slender tube-nosed bat (Murina gracilis)
- Harrison’s tube-nosed bat (Murina harrisoni)
- Hilgendorf’s tube-nosed bat (Murina hilgendorfi)
- Hutton’s tube-nosed bat (Murina huttoni)
- Greater tube-nosed bat (Murina leucogaster)
- Lorelie’s tube-nosed bat (Murina loreliae)
- Peninsular tube-nosed bat (Murina peninsularis)
- Rainforest tube-nosed bat (Murina pluvialis)
- Taiwan tube-nosed bat (Murina puta)
- Hidden tube-nosed bat (Murina recondita)
- Gilded tube-nosed bat (Murina rozendaali)
- Ryukyu tube-nosed bat (Murina ryukyuana)
- Shuipu tube-nosed bat (Murina shuipuensis)
- Brown tube-nosed bat (Murina suilla)
- Gloomy tube-nosed bat (Murina tenebrosa)
- Scully’s tube-nosed bat (Murina tubinaris)
- Ussuri tube-nosed bat (Murina ussuriensis)
- Walston’s tube-nosed bat (Murina walstoni)
- Southeastern myotis (Myotis austroriparius)
- Sakhalin myotis (Myotis abei)
- Kon Tum Tube-nosed Bat (Murina kontumensis)
- Large-footed bat (Myotis adversus)
- Southern myotis (Myotis aelleni)
- Silver-tipped myotis (Myotis albescens)
- Alcathoe bat (Myotis alcathoe)
- Szechwan myotis (Myotis altarium)
- Anjouan myotis (Myotis anjouanensis)
- Annamit myotis (Myotis annamiticus)
- Hairy-faced bat (Myotis annectans)
- Atacama myotis (Myotis atacamensis)
- Peters’s myotis (Myotis ater)
- Southwestern myotis (Myotis auriculus)
- Australian myotis (Myotis australis)
- Southeastern myotis (Myotis austroriparius)
- Bechstein’s bat (Myotis bechsteini)
- Lesser mouse-eared bat (Myotis blythii)
- Rufous mouse-eared bat (Myotis bocagii)
- Far Eastern myotis (Myotis bombinus)
- Brandt’s bat (Myotis brandti)
- Bocharic myotis (Myotis bucharensis)
- California myotis (Myotis californicus)
- Long-fingered bat (Myotis capaccinii)
- Chilean myotis (Myotis chiloensis)
- Large myotis (Myotis chinensis)
- Western small-footed myotis (Myotis ciliolabrum)
- Guatemalan myotis (Myotis cobanensis)
- Cryptic myotis (Myotis crypticus)
- Csorba’s mouse-eared bat (Myotis csorbai)
- Pond bat (Myotis dasycneme)
- Daubenton’s bat (Myotis daubentoni)
- David’s myotis (Myotis davidii)
- Dominican myotis (Myotis dominicensis)
- Elegant myotis (Myotis elegans)
- Geoffroy’s bat (Myotis emarginatus)
- Western long-eared myotis (Myotis evotis)
- Fringed long-footed myotis (Myotis fimbriatus)
- Findley’s myotis (Myotis findleyi)
- Hodgson’s bat (Myotis formosus)
- Cinnamon myotis (Myotis fortidens)
- Fraternal myotis (Myotis frater)
- Gomantong myotis (Myotis gomantongensis)
- Malagasy mouse-eared bat (Myotis goudoti)
- Gray bat (Myotis grisescens)
- Armenian whiskered bat (Myotis hajastanicus)
- Lesser large-footed bat (Myotis hasseltii)
- Herman’s myotis (Myotis hermani)
- Horsfield’s bat (Myotis horsfieldii)
- Hosono’s myotis (Myotis hosonoi)
- Ikonnikov’s bat (Myotis ikonnikovi)
- Insular myotis (Myotis insularum)
- Izecksohn’s Myotis (Myotis izecksohni)
- Hairy-legged myotis (Myotis keaysi)
- Keen’s myotis (Myotis keenii)
- Chinese water myotis (Myotis laniger)
- Eastern small-footed myotis (Myotis leibii)
- Yellowish myotis (Myotis levis)
- Kashmir cave bat (Myotis longipes)
- Little brown bat (Myotis lucifugus)
- Big-footed myotis (Myotis macrodactylus)
- Southern myotis (Myotis macropus)
- Pallid large-footed myotis (Myotis macrotarsus)
- Schwartz’s myotis (Myotis martiniquensis)
- Dark-nosed small-footed myotis (Myotis melanorhinus)
- Maluku myotis (Myotis moluccarum)
- Burmese whiskered bat (Myotis montivagus)
- Morris’s bat (Myotis morrisi)
- Whiskered myotis (Myotis muricola)
- Greater mouse-eared bat (Myotis myotis)
- Whiskered bat (Myotis mystacinus)
- Natterer’s bat (Myotis nattereri)
- Curacao myotis (Myotis nesopolus)
- Black myotis (Myotis nigricans)
- Nepal myotis (Myotis nipalensis)
- Arizona myotis (Myotis occultus)
- Singapore whiskered bat (Myotis oreias)
- Montane myotis (Myotis oxyotus)
- Honshu myotis (Myotis ozensis)
- Peninsular myotis (Myotis peninsularis)
- Peking myotis (Myotis pequinius)
- Flat-headed myotis (Myotis planiceps)
- Frosted myotis (Myotis pruinosus)
- Felten’s myotis (Myotis punicus)
- Rickett’s big-footed bat (Myotis ricketti)
- Ridley’s bat (Myotis ridleyi)
- Riparian myotis (Myotis riparius)
- Thick-thumbed myotis (Myotis rosseti)
- Red myotis (Myotis ruber)
- Schaub’s myotis (Myotis schaubi)
- Scott’s mouse-eared bat (Myotis scotti)
- Northern long-eared myotis (Myotis septentrionalis)
- Mandelli’s mouse-eared bat (Myotis sicarius)
- Himalayan whiskered bat (Myotis siligorensis)
- Velvety myotis (Myotis simus)
- Indiana bat (Myotis sodalis)
- Kei myotis (Myotis stalkeri)
- Fringed myotis (Myotis thysanodes)
- Cape hairy bat (Myotis tricolor)
- Cave myotis (Myotis velifer)
- Fish-eating bat (Myotis vivesi)
- Long-legged myotis (Myotis volans)
- Welwitsch’s bat (Myotis welwitschii)
- Yanbaru whiskered bat (Myotis yanbarensis)
- Yoshiyuki’s myotis (Myotis yesoensis)
- Yuma myotis (Myotis yumanensis)
- Zenati myotis (Myotis zenatius)
- Himalayan Broad-muzzled Bat (Submyotodon caliginosus)
- Taiwan broad-muzzled myotis (Submyotodon latirostris)
- Tanzanian woolly bat (Kerivoula africana)
- St. Aignan’s trumpet-eared bat (Kerivoula agnella)
- Damara woolly bat (Kerivoula argentata)
- Copper woolly bat (Kerivoula cuprosa)
- Ethiopian woolly bat (Kerivoula eriophora)
- Flores woolly bat (Kerivoula flora)
- Hardwicke’s woolly bat (Kerivoula hardwickii)
- Small woolly bat (Kerivoula intermedia)
- Lesser woolly bat (Kerivoula lanosa)
- Lenis woolly bat (Kerivoula lenis)
- Least woolly bat (Kerivoula minuta)
- Fly River trumpet-eared bat (Kerivoula muscina)
- Bismarck’s trumpet-eared bat (Kerivoula myrella)
- Papillose woolly bat (Kerivoula papillosa)
- Clear-winged woolly bat (Kerivoula pellucida)
- Spurrell’s woolly bat (Kerivoula phalaena)
- Painted bat (Kerivoula picta)
- Smith’s woolly bat (Kerivoula smithii)
- Whitehead’s woolly bat (Kerivoula whiteheadi)
- Pallid bat (Antrozous pallidus)
- Collared pipistrelle (Arielulus aureocollaris)
- Black-gilded pipistrelle (Arielulus circumdatus)
- Coppery pipistrelle (Arielulus cuprosus)
- Social pipistrelle (Arielulus societatis)
- Necklace pipistrelle (Arielulus torquatus)
- Van Gelder’s bat (Bauerus dubiaquercus)
- Allen’s yellow bat (Baeodon alleni)
- Western barbastelle (Barbastella barbastellus)
- Beijing barbastelle (Barbastella beijingensis)
- Eastern barbastelle (Barbastella leucomelas)
- Large-eared pied bat (Chalinolobus dwyeri)
- Gould’s wattled bat (Chalinolobus gouldii)
- Chocolate wattled bat (Chalinolobus morio)
- New Caledonia wattled bat (Chalinolobus neocaledonicus)
- Hoary wattled bat (Chalinolobus nigrogriseus)
- Little pied bat (Chalinolobus picatus)
- New Zealand long-tailed bat (Chalinolobus tuberculatus)
- Rafinesque’s big-eared bat (Corynorhinus rafinesqii)
- Mexican big-eared bat (Corynorhinus mexicanus)
- Townsend’s big-eared bat (Corynorhinus townsendii)
- Little black serotine (Eptesicus andinus)
- Bobrinski’s serotine (Eptesicus bobrinskoi)
- Botta’s serotine (Eptesicus bottae)
- Brazilian brown bat (Eptesicus brasiliensis)
- Chiriquinan serotine (Eptesicus chiriquinus)
- Diminutive serotine (Eptesicus diminutus)
- Surat serotine (Eptesicus dimissus)
- Horn-skinned bat (Eptesicus floweri)
- Argentine brown bat (Eptesicus furinalis)
- Big brown bat (Eptesicus fuscus)
- Gobi big brown bat (Eptesicus gobiensis)
- Guadeloupe big brown bat (Eptesicus guadeloupensis)
- Long-tailed house bat (Eptesicus hottentotus)
- Harmless serotine (Eptesicus innoxius)
- Meridional serotine (Eptesicus isabellinus)
- Japanese short-tailed bat (Eptesicus japonensis)
- Kobayashi’s bat (Eptesicus kobayashii)
- Sind bat (Eptesicus nasutus)
- Northern bat (Eptesicus nilssonii)
- Thick-eared bat (Eptesicus pachyotis)
- Lagos serotine (Eptesicus platyops)
- Serotine bat (Eptesicus serotinus)
- Taddei’s Serotine (Eptesicus taddeii)
- Sombre bat (Eptesicus tatei)
- Spotted bat (Euderma maculatum)
- Disk-footed bat (Eudiscopus denticulus)
- Chocolate pipistrelle (Falsistrellus affinis)
- Western false pipistrelle (Falsistrellus mackenziei)
- Pungent pipistrelle (Falsistrellus mordax)
- Peters’s pipistrelle (Falsistrellus petersi)
- Eastern false pipistrelle (Falsistrellus tasmaniensis)
- Allen’s striped bat (Glauconycteris alboguttata)
- Silvered bat (Glauconycteris argentata)
- Beatrix’s bat (Glauconycteris beatrix)
- Curry’s bat (Glauconycteris curryae)
- Bibundi bat (Glauconycteris egeria)
- Glen’s wattled bat (Glauconycteris gleni)
- Allen’s spotted bat (Glauconycteris humeralis)
- Kenyan wattled bat (Glauconycteris kenyacola)
- Machado’s butterfly bat (Glauconycteris machadoi)
- Abo bat (Glauconycteris poensis)
- Butterfly bat (Glauconycteris variegata)
- Javan thick-thumbed bat (Glischropus javanus)
- Common thick-thumbed bat (Glischropus tylopus)
- Blanford’s bat (Hesperoptenus blanfordi)
- False serotine bat (Hesperoptenus doriae)
- Gaskell’s false serotine (Hesperoptenus gaskelli)
- Tickell’s bat (Hesperoptenus tickelli)
- Large false serotine (Hesperoptenus tomesi)
- Strange big-eared brown bat (Histiotus alienus)
- Humboldt big-eared brown bat (Histiotus humboldti)
- Thomas’s big-eared brown bat (Histiotus laephotis)
- Big-eared brown bat (Histiotus macrotus)
- Southern big-eared brown bat (Histiotus magellanicus)
- Small big-eared brown bat (Histiotus montanus)
- Tropical big-eared brown bat (Histiotus velatus)
- Korean Pipistrelle (Hypsugo alaschanicus)
- Anchieta’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo anchietae)
- Anthony’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo anthonyi)
- Arabian pipistrelle (Hypsugo arabicus)
- Desert pipistrelle (Hypsugo ariel)
- Dark Madagascar pipistrelle (Hypsugo bemainty)
- Cadorna’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo cadornae)
- Broad-headed pipistrelle (Hypsugo crassulus)
- Long-toothed Pipistrelle (Hypsugo dolichodon)
- Eisentraut’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo eisentrauti)
- Brown pipistrelle (Hypsugo imbricatus)
- Joffre’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo joffrei)
- Red-brown pipistrelle (Hypsugo kitcheneri)
- Lanza’s Pipistrelle (Hypsugo lanzai)
- Burma pipistrelle (Hypsugo lophurus)
- Big-eared pipistrelle (Hypsugo macrotis)
- Mouselike pipistrelle (Hypsugo musciculus)
- Chinese pipistrelle (Hypsugo pulveratus)
- Savi’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo savii)
- Vordermann’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo vordermanni)
- Great evening bat (Ia io)
- Allen’s big-eared bat (Idionycteris phyllotis)
- Angolan long-eared bat (Laephotis angolensis)
- Botswanan long-eared bat (Laephotis botswanae)
- Namib long-eared bat (Laephotis namibensis)
- De Winton’s long-eared bat (Laephotis wintoni)
- Silver-haired bat (Lasionycteris noctivagans)
- Greater red bat (Lasiurus atratus)
- Desert red bat (Lasiurus blossevillii)
- Eastern red bat (Lasiurus borealis)
- Tacarcuna bat (Lasiurus castaneus)
- Hoary bat (Lasiurus cinereus)
- Hawaiian hoary bat (Lasiurus cinereus semotus)
- Jamaican red bat (Lasiurus degelidus)
- Hairy-tailed bat (Lasiurus ebenus)
- Southern yellow bat (Lasiurus ega)
- Big red bat (Lasiurus egregius)
- Cuban yellow bat (Lasiurus insularis)
- Northern yellow bat (Lasiurus intermedius)
- Minor red bat (Lasiurus minor)
- Pfeiffer’s red bat (Lasiurus pfeifferi)
- Saline red bat (Lasiurus salinae)
- Seminole bat (Lasiurus seminolus)
- Cinnamon red bat (Lasiurus varius)
- Western yellow bat (Lasiurus xanthinus)
- Moloney’s mimic bat (Mimetillus moloneyi)
- Dark-brown serotine (Neoromicia brunneus)
- Cape serotine (Neoromicia capensis)
- Yellow serotine (Neoromicia flavescens)
- Tiny serotine (Neoromicia guineensis)
- Heller’s pipistrelle (Neoromicia helios)
- Isalo serotine (Neoromicia malagasyensis)
- Malagasy serotine (Neoromicia matroka)
- Melck’s house bat (Neoromicia melckorum)
- Banana pipistrelle (Neoromicia nana)
- Rendall’s serotine (Neoromicia rendalli)
- Rosevear’s serotine (Neoromicia roseveari)
- White-winged serotine (Neoromicia tenuipinnis)
- Zulu serotine (Neoromicia zuluensis)
- Pied bat (Niumbaha superba)
- Birdlike noctule (Nyctalus aviator)
- Azores noctule (Nyctalus azoreum)
- Japanese noctule (Nyctalus furvus)
- Greater noctule bat (Nyctalus lasiopterus)
- Lesser noctule (Nyctalus leisleri)
- Mountain noctule (Nyctalus montanus)
- Common noctule (Nyctalus noctula)
- Chinese noctule (Nyctalus plancyi)
- Schlieffen’s twilight bat (Nycticeinops schlieffeni)
- Temminck’s mysterious bat (Nycticeius aenobarbus)
- Cuban evening bat (Nycticeius cubanus)
- Evening bat (Nycticeius humeralis)
- Northern long-eared bat (Nyctophilus arnhemensis)
- Eastern long-eared bat (Nyctophilus bifax)
- Corben’s Long-eared Bat (Nyctophilus corbeni)
- Lesser long-eared bat (Nyctophilus geoffroyi)
- Gould’s long-eared bat (Nyctophilus gouldi)
- Sunda long-eared bat (Nyctophilus heran)
- Lord Howe long-eared bat (Nyctophilus howensis)
- Western long-eared bat (Nyctophilus major)
- Small-toothed long-eared bat (Nyctophilus microdon)
- New Guinea long-eared bat (Nyctophilus microtis)
- New Caledonian long-eared bat (Nyctophilus nebulosus)
- Tasmanian long-eared bat (Nyctophilus sherrini)
- Mt. Missim long-eared bat (Nyctophilus shirleyae)
- Greater long-eared bat (Nyctophilus timoriensis)
- Pygmy long-eared bat (Nyctophilus walkeri)
- Desert long-eared bat (Otonycteris hemprichii)
- Canyon bat (Parastrellus hesperus)
- Tricolored bat (Perimyotis subflavus)
- New Guinea big-eared bat (Pharotis imogene)
- Rohu’s bat (Philetor brachypterus)
- Japanese pipistrelle (Pipistrellus abramus)
- Forest pipistrelle (Pipistrellus adamsi)
- Mount Gargues pipistrelle (Pipistrellus aero)
- Angulate pipistrelle (Pipistrellus angulatus)
- Kelaart’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus ceylonicus)
- Greater Papuan pipistrelle (Pipistrellus collinus)
- Indian pipistrelle (Pipistrellus coromandra)
- Egyptian pipistrelle (Pipistrellus deserti)
- Endo’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus endoi)
- Hanaki’s dwarf bat (Pipistrellus hanaki)
- Dusky pipistrelle (Pipistrellus hesperidus)
- Aellen’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus inexspectatus)
- Java pipistrelle (Pipistrellus javanicus)
- Kuhl’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus kuhlii)
- Madeira pipistrelle (Pipistrellus maderensis)
- Minahassa pipistrelle (Pipistrellus minahassae)
- Christmas Island pipistrelle (Pipistrellus murrayi)]
- Tiny pipistrelle (Pipistrellus nanulus)
- Nathusius’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus nathusii)
- Lesser Papuan pipistrelle (Pipistrellus papuanus)
- Mount Popa pipistrelle (Pipistrellus paterculus)
- Dar es Salaam pipistrelle (Pipistrellus permixtus)
- Common pipistrelle (Pipistrellus pipistrellus)
- Soprano pipistrelle (Pipistrellus pygmaeus)
- Racey’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus raceyi)
- Rüppell’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus rueppellii)
- Rusty pipistrelle (Pipistrellus rusticus)
- Narrow-winged pipistrelle (Pipistrellus stenopterus)
- Sturdee’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus sturdeei)
- Least pipistrelle (Pipistrellus tenuis)
- Watts’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus wattsi)
- Northern pipistrelle (Pipistrellus westralis)
- Sichuan Long-eared Bat (Plecotus ariel)
- Brown long-eared bat (Plecotus auritus)
- Grey long-eared bat (Plecotus austriacus)
- Ethiopian big-eared bat (Plecotus balensis)
- Christie’s big-eared bat (Plecotus christii)
- Mediterranean long-eared bat (Plecotus kolombatovici)
- Alpine long-eared bat (Plecotus macrobullaris)
- Japanese long-eared bat (Plecotus sacrimontis)
- Sardinian long-eared bat (Plecotus sardus)
- Taiwan big-eared bat (Plecotus taivanus)
- Strelkov’s big-eared bat (Plecotus strelkovi)
- Canary big-eared bat (Plecotus teneriffae)
- Yucatan yellow bat (Rhogeessa aeneus)
- Bickham’s little yellow bat (Rhogeessa bickhami)
- Genoways’s yellow bat (Rhogeessa genowaysi)
- Slender yellow bat (Rhogeessa gracilis)
- Husson’s yellow bat (Rhogeessa hussoni)
- Thomas’s yellow bat (Rhogeessa io)
- Tiny yellow bat (Rhogeessa minutilla)
- Least yellow bat (Rhogeessa mira)
- Little yellow bat (Rhogeessa parvula)
- Black-winged little yellow bat (Rhogeessa tumida)
- Rüppell’s broad-nosed bat (Scoteanax rueppellii)
- White-bellied lesser house bat (Scotoecus albigula)
- Light-winged lesser house bat (Scotoecus albofuscus)
- Hinde’s lesser house bat (Scotoecus hindei)
- Dark-winged lesser house bat (Scotoecus hirundo)
- Desert yellow bat (Scotoecus pallidus)
- Harlequin bat (Scotomanes ornatus)
- Andrew Rebori’s house bat (Scotophilus andrewreborii)
- Lesser yellow bat (Scotophilus borbonicus)
- Sulawesi yellow bat (Scotophilus celebensis)
- Sody’s yellow house bat (Scotophilus collinus)
- African yellow bat (Scotophilus dinganii)
- Greater Asiatic yellow bat (Scotophilus heathi)
- Lesser Asiatic yellow bat (Scotophilus kuhlii)
- White-bellied yellow bat (Scotophilus leucogaster)
- Schreber’s yellow bat (Scotophilus nigrita)
- Robbins’s yellow bat (Scotophilus nucella)
- Nut-colored yellow bat (Scotophilus nux)
- Robust yellow bat (Scotophilus robustus)
- Greenish yellow bat (Scotophilus viridis)
- Western broad-nosed bat (Scotorepens balstoni)
- Little broad-nosed bat (Scotorepens greyii)
- Eastern broad-nosed bat (Scotorepens orion)
- Northern broad-nosed bat (Scotorepens sanborni)
- Dormer’s bat (Scotozous dormeri)
- Lesser bamboo bat (Tylonycteris pachypus)
- Greater bamboo bat (Tylonycteris robustula)
- Inland forest bat (Vespadelus baverstocki)
- Northern cave bat (Vespadelus caurinus)
- Large forest bat (Vespadelus darlingtoni)
- Yellow-lipped bat (Vespadelus douglasorum)
- Finlayson’s cave bat (Vespadelus finlaysoni)
- Eastern forest bat (Vespadelus pumilus)
- Southern forest bat (Vespadelus regulus)
- Troughton’s forest bat (Vespadelus troughtoni)
- Little forest bat (Vespadelus vulturnus)
- Parti-coloured bat (Vespertilio murinus)
- Asian parti-coloured bat (Vespertilio sinensis)
- Cuban funnel-eared bat (Chilonatalus micropus)
- Bahaman funnel-eared bat (Chilonatalus tumidifrons)
- Brazilian funnel-eared bat (Natalus espiritosantensis)
- Jamaican greater funnel-eared bat (Natalus jamaicensis)
- Hispaniolan greater funnel-eared bat (Natalus major)
- Mexican greater funnel-eared bat (Natalus mexicanus)
- Cuban greater funnel-eared bat (Natalus primus)
- Mexican funnel-eared bat (Natalus stramineus)
- Trinidadian funnel-eared bat (Natalus tumidirostris)
- Gervais’s funnel-eared bat (Nyctiellus lepidus)
- Lesueur’s hairy bat (Cistugo lesueuri)
- Angolan hairy bat (Cistugo seabrai)
- Aellen’s Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus aelleni)
- (Montagne d’Ambre Long-fingered BatMiniopterus ambohitrensis)
- African long-fingered bat (Miniopterus africanus)
- Little bent-wing bat (Miniopterus australis)
- Madagascar Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus brachytragos)
- Eger’s Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus egeri)
- Lesser long-fingered bat (Miniopterus fraterculus)
- Southeast Asian long-fingered bat (Miniopterus fuscus)
- Glen’s Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus gleni)
- Griffiths’s Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus griffithsi)
- Griveaud’s Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus griveaudi)
- Greater long-fingered bat (Miniopterus inflatus)
- Small Melanesian Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus macrocneme)
- Maghrebian Bent-wing Bat (Miniopterus maghrebensis)
- Western bent-winged bat (Miniopterus magnater)
- Mahafaly Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus mahafaliensis)
- Major’s Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus majori)
- Manavi long-fingered bat (Miniopterus manavi)
- Intermediate long-fingered bat (Miniopterus medius)
- Least long-fingered bat (Miniopterus minor)
- Natal long-fingered bat (Miniopterus natalensis)
- Newton’s Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus newtoni)
- Philippine long-fingered bat (Minopterus paululus)
- Peterson’s long-fingered bat (Miniopterus petersoni)
- Small bent-winged bat (Miniopterus pusillus)
- Loyalty bent-winged bat (Miniopterus robustior)
- Common bent-wing bat (Miniopterus schreibersii)
- Shortridge’s Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus shortridgei)
- Sorocula Long-fingered Bat (Miniopterus sororculus)
- Great bent-winged bat (Miniopterus tristis)
- Duke of Abruzzi’s free-tailed bat (Chaerephon aloysiisabaudiae)
- Ansorge’s free-tailed bat (Chaerephon ansorgei)
- Madagascar Free-tailed Bat (Chaerephon atsinanana)
- Gland-tailed free-tailed bat (Chaerephon bemmeleni)
- Spotted free-tailed bat (Chaerephon bivittatus)
- Fijian mastiff bat (Chaerephon bregullae)
- Chapin’s free-tailed bat (Chaerephon chapini)
- Gallagher’s free-tailed bat (Chaerephon gallagheri)
- Northern freetail bat (Chaerephon jobensis)
- Black and red free-tailed bat (Chaerephon jobimena)
- Northern free-tailed bat (Chaerephon johorensis)
- Lappet-eared free-tailed bat (Chaerephon major)
- Nigerian free-tailed bat (Chaerephon nigeriae)
- Wrinkle-lipped free-tailed bat (Chaerephon plicatus)
- Little free-tailed bat (Chaerephon pumilus)
- Russet free-tailed bat (Chaerephon russatus)
- Solomons mastiff bat (Chaerephon solomonis)
- São Tomé free-tailed bat (Chaerephon tomensis)
- Lesser naked bat (Cheiromeles parvidens)
- Hairless bat (Cheiromeles torquatus)
- Cinnamon dog-faced bat (Cynomops abrasus)
- Greenhall’s dog-faced bat (Cynomops greenhalli)
- Mexican dog-faced bat (Cynomops mexicanus)
- Miller’s Dog-faced Bat (Cynomops milleri)
- Para dog-faced bat (Cynomops paranus)
- Southern dog-faced bat (Cynomops planirostris)
- Black bonneted bat (Eumops auripendulus)
- Dwarf bonneted bat (Eumops bonariensis)
- Big bonneted bat (Eumops dabbenei)
- Delta Bonneted Bat (Eumops delticus)
- Florida bonneted bat (Eumops floridanus)
- Wagner’s bonneted bat (Eumops glaucinus)
- Sanborn’s bonneted bat (Eumops hansae)
- Guianan bonneted bat (Eumops maurus)
- Northern Dwarf Bonneted Bat (Eumops nanus)
- Patagonian bonneted bat (Eumops patagonicus)
- Western mastiff bat (Eumops perotis)
- Colombian bonneted bat (Eumops trumbulli)
- Underwood’s bonneted bat (Eumops underwoodi)
- Equatorial dog-faced bat (Molossops aequatorianus)
- Mato Grosso dog-faced bat (Molossops mattogrossensis)
- Rufous dog-faced bat (Molossops neglectus)
- Dwarf dog-faced bat (Molossops temminckii)
- Alvarez’s Mastiff Bat (Molossus alvarezi)
- Aztec mastiff bat (Molossus aztecus)
- Barnes’ mastiff bat (Molossus barnesi)
- Bonda Mastiff Bat (Molossus bondae)
- Coiban mastiff bat (Molossus coibensis)
- Bonda mastiff bat (Molossus currentium)
- Velvety free-tailed bat (Molossus molossus)
- Miller’s mastiff bat (Molossus pretiosus)
- Black mastiff bat (Molossus rufus)
- Sinaloan mastiff bat (Molossus sinaloae)
- Bakari’s Free-tailed Bat (Mops bakarii)
- Sierra Leone free-tailed bat (Mops brachyptera)
- Angolan free-tailed bat (Mops condylurus)
- Medje free-tailed bat (Mops congicus)
- Mongalla free-tailed bat (Mops demonstrator)
- Malagasy white-bellied free-tailed bat (Mops leucostigma)
- Midas free-tailed bat (Mops midas)
- Malayan free-tailed bat (Mops mops)
- Dwarf free-tailed bat (Mops nanulus)
- Niangara free-tailed bat (Mops niangarae)
- White-bellied free-tailed bat (Mops niveiventer)
- Peterson’s free-tailed bat (Mops petersoni)
- Sulawesi free-tailed bat (Mops sarasinorum)
- Spurrell’s free-tailed bat (Mops spurrelli)
- Railer bat (Mops thersites)
- Trevor’s free-tailed bat (Mops trevori)
- Natal free-tailed bat (Mormopterus acetabulosus)
- Beccari’s mastiff bat (Mormopterus beccarii)
- North-western Free-tailed Bat (Mormopterus cobourgianus)
- Sumatran mastiff bat (Mormopterus doriae)
- Bristle-faced free-tailed bat (Mormopterus eleryi)
- Reunion Little Mastiff Bat (Mormopterus francoismoutoui)
- Cape York Free-tailed Bat (Mormopterus halli)
- Peter’s wrinkle-lipped bat (Mormopterus jugularis)
- Kalinowski’s mastiff bat (Mormopterus kalinowskii)
- South-western Free-tailed Bat (Mormopterus kitcheneri)
- Loria’s mastiff bat (Mormopterus loriae)
- Northern Free-tailed Bat (Mormopterus lumsdenae)
- Little goblin bat (Mormopterus minutus)
- East-coast free-tailed bat (Mormopterus norfolkensis)
- Inland Free-tailed Bat (Mormopterus petersi)
- Incan little mastiff bat (Mormopterus phrudus)
- Southern free-tailed bat (Mormopterus planiceps)
- Eastern Free-tailed Bat (Mormopterus ridei)
- Daubenton’s free-tailed bat (Myopterus daubentonii)
- Bini free-tailed bat (Myopterus whitleyi)
- Peale’s free-tailed bat (Nyctinomops aurispinosus)
- Pocketed free-tailed bat (Nyctinomops femorosaccus)
- Broad-eared bat (Nyctinomops laticaudatus)
- Big free-tailed bat (Nyctinomops macrotis)
- Javan mastiff bat (Otomops formosus)
- Harrison’s large-eared giant mastiff bat (Otomops harrisoni)
- Johnstone’s mastiff bat (Otomops johnstonei)
- Madagascar free-tailed bat (Otomops madagascariensis)
- Large-eared free-tailed bat (Otomops martiensseni)
- Big-eared mastiff bat (Otomops papuensis)
- Mantled mastiff bat (Otomops secundus)
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat (Otomops wroughtoni)
- Peters’s flat-headed bat (Platymops setiger)
- Big crested mastiff bat (Promops centralis)
- Davison’s Mastiff Bat (Promops davisoni)
- Brown mastiff bat (Promops nasutus)
- Roberts’s flat-headed bat (Sauromys petrophilus)
- Egyptian free-tailed bat (Tadarida aegyptiaca)
- White-striped free-tailed bat (Tadarida australis)
- Mexican free-tailed bat (Tadarida brasiliensis)
- Madagascan large free-tailed bat (Tadarida fulminans)
- East Asian free-tailed bat (Tadarida insignis)
- New Guinea free-tailed bat (Tadarida kuboriensis)
- La Touche’s free-tailed bat (Tadarida latouchei)
- Kenyan big-eared free-tailed bat (Tadarida lobata)
- European free-tailed bat (Tadarida teniotis)
- African giant free-tailed bat (Tadarida ventralis)
- Blunt-eared bat (Tomopeas ravus)
- Ecuadorian sac-winged bat (Balantiopteryx infusca)
- Thomas’s sac-winged bat (Balantiopteryx io)
- Gray sac-winged bat (Balantiopteryx plicata)
- Thomas’s shaggy bat (Centronycteris centralis)
- Shaggy bat (Centronycteris maximiliani)
- African sheath-tailed bat (Coleura afra)
- Madagascar Sheath-tailed Bat (Coleura kibomalandy)
- Seychelles sheath-tailed bat (Coleura seychellensis)
- Chestnut sac-winged bat (Cormura brevirostris)
- Short-eared bat (Cyttarops alecto)
- Northern ghost bat (Diclidurus albus)
- Greater ghost bat (Diclidurus ingens)
- Isabelle’s ghost bat (Diclidurus isabella)
- Lesser ghost bat (Diclidurus scutatus)
- Small Asian sheath-tailed bat (Emballonura alecto)
- Beccari’s sheath-tailed bat (Emballonura beccarii)
- Large-eared sheath-tailed bat (Emballonura dianae)
- Greater sheath-tailed bat (Emballonura furax)
- Lesser sheath-tailed bat (Emballonura monticola)
- Raffray’s sheath-tailed bat (Emballonura raffrayana)
- Pacific sheath-tailed bat (Emballonura semicaudata)
- Seri’s sheath-tailed bat (Emballonura serii)
- Dark sheath-tailed bat (Mosia nigrescens)
- Peters’s sheath-tailed bat (Paremballonura atrata)
- Western sheath-tailed bat (Paremballonura tiavato)
- Greater dog-like bat (Peropteryx kappleri)
- White-winged dog-like bat (Peropteryx leucoptera)
- Lesser dog-like bat (Peropteryx macrotis)
- Pale-winged dog-like bat (Peropteryx pallidoptera)
- Trinidad dog-like bat (Peropteryx trinitatis)
- Proboscis bat (Rhynchonycteris naso)
- Antioquian sac-winged bat (Saccopteryx antioquensis)
- Greater sac-winged bat (Saccopteryx bilineata)
- Frosted sac-winged bat (Saccopteryx canescens)
- Amazonian sac-winged bat (Saccopteryx gymnura)
- Lesser sac-winged bat (Saccopteryx leptura)
- Yellow-bellied pouched bat (Saccolaimus flaviventris)
- Troughton’s pouched bat (Saccolaimus mixtus)
- Pel’s pouched bat (Saccolaimus peli)
- Naked-rumped pouched bat (Saccolaimus saccolaimus)
- Indonesian tomb bat (Taphozous achates)
- Coastal sheath-tailed bat (Taphozous australis)
- Common sheath-tailed bat (Taphozous georgianus)
- Hamilton’s tomb bat (Taphozous hamiltoni)
- Hildegarde’s tomb bat (Taphozous hildegardeae)
- Hill’s sheath-tailed bat (Taphozous hilli)
- Arnhem sheath-tailed bat (Taphozous kapalgensis)
- Long-winged tomb bat (Taphozous longimanus)
- Mauritian tomb bat (Taphozous mauritianus)
- Black-bearded tomb bat (Taphozous melanopogon)
- Naked-rumped tomb bat (Taphozous nudiventris)
- Egyptian tomb bat (Taphozous perforatus)
- Theobald’s tomb bat (Taphozous theobaldi)
- Troughton’s sheath-tailed bat (Taphozous troughtoni)
- Bate’s slit-faced bat (Nycteris arge)
- Andersen’s slit-faced bat (Nycteris aurita)
- Gambian slit-faced bat (Nycteris gambiensis)
- Large slit-faced bat (Nycteris grandis)
- Hairy slit-faced bat (Nycteris hispida)
- Intermediate slit-faced bat (Nycteris intermedia)
- Javan slit-faced bat (Nycteris javanica)
- Large-eared slit-faced bat (Nycteris macrotis)
- Malagasy slit-faced bat (Nycteris madagascariensis)
- Ja slit-faced bat (Nycteris major)
- Dwarf slit-faced bat (Nycteris nana)
- Parissi’s slit-faced bat (Nycteris parisii)
- Egyptian slit-faced bat (Nycteris thebaica)
- Malayan slit-faced bat (Nycteris tragata)
- Vinson’s slit-faced bat (Nycteris vinsoni)
- Wood’s slit-faced bat (Nycteris woodi)
- Greater bulldog bat (Noctilio leporinus)
- Lesser bulldog bat (Noctilio albiventris)
- New Zealand greater short-tailed bat (Mystacina robusta)
- New Zealand lesser short-tailed bat (Mystacina tuberculata)
- Antillean ghost-faced bat (Mormoops blainvillii)
- Giant ghost-faced bat (Mormoops magna)
- Ghost-faced bat (Mormoops megalophylla)
- Davy’s naked-backed bat (Pteronotus davy)
- Big naked-backed bat (Pteronotus gymnonotus)
- Macleay’s mustached bat (Pteronotus macleayi)
- Mesoamerican Common Mustached Bat (Pteronotus mesoamericanus)
- Paraguana moustached bat (Pteronotus paraguanensis)
- Parnell’s mustached bat (Pteronotus parnellii)
- Wagner’s mustached bat (Pteronotus personatus)
- Sooty mustached bat (Pteronotus quadridens)
- Antillean fruit-eating bat (Brachyphylla cavernarum)
- Cuban fruit-eating bat (Brachyphylla nana)
- Benkeith’s short-tailed bat (Carollia benkeithi)
- Silky short-tailed bat (Carollia brevicauda)
- Chestnut short-tailed bat (Carollia castanea)
- Silky short-tailed bat (Carollia colombiana)
- Manu short-tailed bat (Carollia manu)
- Mono’s short-tailed bat (Carollia monohernandezi)
- Seba’s short-tailed bat (Carollia perspicillata)
- Sowell’s short-tailed bat (Carollia sowelli)
- Gray short-tailed bat (Carollia subrufa)
- Hairy little fruit bat (Rhinophylla alethina)
- Fischer’s little fruit bat (Rhinophylla fischerae)
- Dwarf little fruit bat (Rhinophylla pumilio)
- Common vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus)
- White-winged vampire bat (Diaemus youngi)
- Hairy-legged vampire bat (Diphylla ecaudata)
- Cadena’s tailless bat (Anoura cadenai)
- Tailed tailless bat (Anoura caudifer)
- Handley’s tailless bat (Anoura cultrata))
- Tube-lipped nectar bat (Anoura fistulata)
- Geoffroy’s tailless bat (Anoura geoffroyi)
- Broad-toothed tailless bat (Anoura latidens)
- Godman’s long-tailed bat (Choeroniscus godmani)
- Intermediate long-tailed bat (Choeroniscus intermedius)
- Greater long-tailed bat (Choeroniscus periosus)
- Minor long-nosed long-tongued bat (Choeroniscus minor)
- Mexican long-tongued bat (Choeronycteris mexicana)
- Commissaris’s long-tongued bat (Glossophaga commissarisi)
- Miller’s long-tongued bat (Glossophaga longirostris)
- Pallas’s long-tongued bat (Glossophaga soricina)
- Underwood’s long-tongued bat (Hylonycteris underwoodi)
- Southern long-nosed bat (Leptonycteris curasoae)
- Greater long-nosed bat (Leptonycteris nivalis)
- Lesser long-nosed bat (Leptonycteris yerbabuenae)
- Dark long-tongued bat (Lichonycteris obscura)
- Insular single leaf bat (Monophyllus plethodon)
- Leach’s single leaf bat (Monophyllus redmani)
- Banana bat (Musonycteris harrisoni)
- Ega long-tongued bat (Scleronycteris ega)
- Chestnut long-tongued bat (Lionycteris spurrelli)
- Bokermann’s nectar bat (Lonchophylla bokermanni)
- Cadena’s Nectar Bat (Lonchophylla cadenai)
- Dekeyser’s nectar bat (Lonchophylla dekeyseri)
- Handley’s nectar bat (Lonchophylla handleyi)
- Western nectar bat (Lonchophylla hesperia)
- Goldman’s nectar bat (Lonchophylla mordax)
- Orces’s Long-tongued Bat (Lonchophylla orcesi)
- Eastern Cordilleran Nectar Bat (Lonchophylla orienticollina)
- Patton’s Nectar Bat (Lonchophylla pattoni)
- Orange nectar bat (Lonchophylla robusta)
- Thomas’s nectar bat (Lonchophylla thomasi)
- Long-snouted bat (Platalina genovensium)
- Big-eared woolly bat (Chrotopterus auritus)
- Tomes’s sword-nosed bat (Lonchorhina aurita)
- Northern sword-nosed bat (Lonchorhina inusitata)
- Marinkelle’s sword-nosed bat (Lonchorhina marinkellei)
- Pygmy round-eared bat (Lophostoma brasiliense)
- Carriker’s round-eared bat (Lophostoma carrikeri)
- Davis’s round-eared bat (Lophostoma evotis)
- Kalko’s round-eared bat (Lophostoma kalkoae)
- Western Round-eared Bat (Lophostoma occidentalis)
- Schultz’s round-eared bat (Lophostoma schulzi)
- White-throated round-eared bat (Lophostoma silvicolum)
- Yasuni round-eared bat (Lophostoma yasuni)
- Long-legged bat (Macrophyllum macrophyllum)
- California leaf-nosed bat (Macrotus californicus)
- Waterhouse’s leaf-nosed bat (Macrotus waterhousii)
- Behn’s bat (Micronycteris behnii)
- Brosset’s big-eared bat (Micronycteris brosseti)
- Giovanni’s Big-eared Bat (Micronycteris giovanniae)
- Hairy big-eared bat (Micronycteris hirsuta)
- White-bellied big-eared bat (Micronycteris homezi)
- Matses’ big-eared bat (Micronycteris matses)
- Little big-eared bat (Micronycteris megalotis)
- Common big-eared bat (Micronycteris microtis)
- White-bellied big-eared bat (Micronycteris minuta)
- Sanborn’s big-eared bat (Micronycteris sanborni)
- Schmidts’s big-eared bat (Micronycteris schmidtorum)
- Yates’s big-eared bat (Micronycteris yatesi)
- Golden bat (Mimon bennettii)
- Cozumelan golden bat (Mimon cozumelae)
- Striped hairy-nosed bat (Mimon crenulatum)
- Koepcke’s hairy-nosed bat (Mimon koepckeae)
- Pale-faced bat (Phylloderma stenops)
- Pale spear-nosed bat (Phyllostomus discolor)
- Lesser spear-nosed bat (Phyllostomus elongatus)
- Greater spear-nosed bat (Phyllostomus hastatus)
- Guianan spear-nosed bat (Phyllostomus latifolius)
- Greater round-eared bat (Tonatia bidens)
- Stripe-headed round-eared bat (Tonatia saurophila)
- Fringe-lipped bat (Trachops cirrhosus)
- Spectral bat (Vampyrum spectrum)
- Buffy flower bat (Erophylla sezekorni)
- Jamaican flower bat (Phyllonycteris aphylla)
- Puerto Rican flower bat (Phyllonycteris major)
- Cuban flower bat (Phyllonycteris poeyi)
- Little white-shouldered bat (Ametrida centurio)
- Tree bat (Ardops nichollsi)
- Jamaican fig-eating bat (Ariteus flavescens)
- Large fruit-eating bat (Artibeus amplus)
- Brown fruit-eating bat (Artibeus concolor)
- Fringed fruit-eating bat (Artibeus fimbriatus)
- Fraternal fruit-eating bat (Artibeus fraterculus)
- Hairy fruit-eating bat (Artibeus hirsutus)
- Honduran fruit-eating bat (Artibeus inopinatus)
- Jamaican fruit bat (Artibeus jamaicensis)
- Great fruit-eating bat (Artibeus lituratus)
- Dark fruit-eating bat (Artibeus obscurus)
- Wrinkle-faced bat (Centurio senex)
- Brazilian big-eyed bat (Chiroderma doriae)
- Guadeloupe big-eyed bat (Chiroderma improvisum)
- Salvin’s big-eyed bat (Chiroderma salvini)
- Little big-eyed bat (Chiroderma trinitatum)
- Hairy big-eyed bat (Chiroderma villosum)
- Vizotto’s Big-eyed Bat (Chiroderma vizottoi)
- Andersen’s fruit-eating bat (Dermanura anderseni)
- Aztec fruit-eating bat (Dermanura azteca)
- Bogota fruit-eating bat (Dermanura bogotensis)
- Gervais’s fruit-eating bat (Dermanura cinerea)
- Silver fruit-eating bat (Dermanura glauca)
- Gnome fruit-eating bat (Dermanura gnoma)
- Pygmy fruit-eating bat (Dermanura phaeotis)
- Rosenberg’s fruit-eating bat (Dermanura rosenbergi)
- Toltec fruit-eating bat (Dermanura tolteca)
- Thomas’s fruit-eating bat (Dermanura watsoni)
- Honduran white bat (Ectophylla alba)
- MacConnell’s bat (Mesophylla macconnelli)
- Cuban fig-eating bat (Phyllops falcatus)
- Ipanema bat (Pygoderma bilabiatum)
- Visored bat (Sphaeronycteris toxophyllum)
- Red fruit bat (Stenoderma rufum)
- Aratathomas’s yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira aratathomasi)
- Bidentate yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira bidens)
- Bogota yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira bogotensis)
- Burton’s yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira burtonlimi)
- Hairy yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira erythromos)
- Choco Yellow-shouldered Bat (Sturnira koopmanhilli)
- Little yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira lilium)
- Highland yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira ludovici)
- Louis’s yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira luisi)
- Greater yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira magna)
- Talamancan yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira mordax)
- Lesser yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira nana)
- Soriano’s yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira sorianoi)
- Thomas’s yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira thomasi)
- Tilda’s yellow-shouldered bat (Sturnira tildae)
- Tent-making bat (Uroderma bilobatum)
- Brown tent-making bat (Uroderma magnirostrum)
- Bidentate yellow-eared bat (Vampyressa bidens)
- Brock’s yellow-eared bat (Vampyressa brocki)
- Melissa’s yellow-eared bat (Vampyressa melissa)
- Striped Yellow-eared Bat (Vampyressa nymphaea)
- Southern little yellow-eared bat (Vampyressa pusilla)
- Northern little yellow-eared bat (Vampyressa thyone)
- Great stripe-faced bat (Vampyrodes caraccioli)
- Alberico’s Broad-nosed Bat (Platyrrhinus albericoi)
- Eldorado broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus aurarius)
- Short-headed broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus brachycephalus)
- Choco broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus chocoensis)
- Thomas’s broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus dorsalis)
- Heller’s broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus helleri)
- Buffy broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus infuscus)
- Ismael’s Broad-nosed Bat (Platyrrhinus ismaeli)
- White-lined broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus lineatus)
- Quechuan Broad-nosed Bat (Platyrrhinus masu)
- Matapalo broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus matapalensis)
- Recife broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus recifinus)
- Shadowy broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus umbratus)
- Greater broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus vittatus)
- Smoky bat (Amorphochilus schnablii)
- Thumbless bat (Furipterus horrens)
- Peter’s disk-winged bat (Thyroptera discifera)
- LaVal’s disk-winged bat (Thyroptera lavali)
- Spix’s disk-winged bat (Thyroptera tricolor)
- Madagascar sucker-footed bat (Myzopoda aurita)
- Western sucker-footed bat (Myzopoda schliemanni)
- New Ireland Masked Flying Fox (Pteropus ennisae)
- Sierra Leone Collared Fruit Bat (Myonycteris leptodon)
- Bergmans’s Fruit Bat (Scotonycteris bergmansi)
- Hayman’s Fruit Bat (Scotonycteris occidentalis)
- Indochinese Horseshoe Bat (Rhinolophus chaseni)
- Chiew Kwee’s Horseshoe Bat (Rhinolophus chiewkweea)
- Glossy Horseshoe Bat (Rhinolophus refulgens)
- Nicobar Leaf-nosed Bat (Hipposideros nicobarulae)
- Annam Tube-nosed Bat (Murina annamitica)
- Golden-haired Tube-nosed Bat (Murina chrysochaetes)
- Fanjingshan Tube-nosed Bat (Murina fanjingshanensis)
- Ashy Tube-nosed Bat (Murina feae)
- Fiona’s Tube-nosed Bat (Murina fionae)
- Guillén’s Tube-nosed bat (Murina guilleni)
- Vietnamese Tube-nosed Bat (Murina harpioloides)
- Jaintia Tube-nosed Bat (Murina jaintiana)
- Kon Tum Tube-nosed Bat (Murina kontumensis)
Bat FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are bats carnivores, herbivores or omnivores?
Bats are omnivores. Fruit bats eat avocados, mangoes, bananas, wild dates and more. Three species of vampire bats live on blood from other mammals. Some bats drink nectar from flowers including honey suckle, yucca and evening primrose. Not surprisingly, these bats especially love the nectar of moonflowers! Some species of bats eat fish, mice and frogs.
Do bats bite?
Yes, bats do bite. Vampire bats usually bite the leg of a cow or goat to get the blood to leak out so it can drink a little of it. A bat would only bite a human if it felt threatened. But, bats are known to keep away from people.
Are bats blind?
No, bats aren’t blind. This is one of the biggest myths out there. Bats are nocturnal so they look for food when it’s dark. They don’t see well in the dark, but they aren’t blind.
Are bats dangerous?
No, bats aren’t dangerous. In fact, just the opposite! Like butterflies and bees, bats are important pollinators that help trees and flowers to grow. They spread seeds that help to grow breadfruit, figs, peaches, dates, bananas, avocados and other fruits. Plus, they eat insects helping to keep the bug population to a manageable number. As a note, bats have a reputation for carrying rabies. In reality, a very small number of bats carry this disease. Still, if you come into contact with a bat it’s good to see medical help. In the United States, five people died from contracting rabies from a bat in 2021, none received a PEP vaccination that could have prevented the spread of rabies if applied shortly after exposure.
What does it mean when you see a bat?
When you see a bat you know that the sun has gone down and it’s time to find food. If you see a bat in your backyard, you know the bat has made its home in a nearby tree or has found a cozy place in an attic. Finally, you know the bat has found its food source in your area. Whether it’s nectar, insects or fruit, the bat will stick around just as long as it finds its dinner each night!
What Kingdom do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the class Mammalia.
What family do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the family Microchiroptera.
What order do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the order Chiroptera.
What genus do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the genus Emballonuridae.
What type of covering do Bats have?
Bats are covered in Fur.
In what type of habitat do Bats live?
Bats live in woodlands and caves.
What is the main prey for Bats?
Bats prey on mice, frogs, and fruit.
What are some distinguishing features of Bats?
Bats have strong, flexible wings and large ears that detect prey using echolocation.
What are some predators of Bats?
Predators of Bats include owls, eagles, and snakes.
What is the average litter size for a Bat?
The average litter size for a Bat is 1.
What is an interesting fact about Bats?
Bats detect prey using echolocation!
What is the scientific name for the Bat?
The scientific name for the Bat is Chiroptera.
What is the lifespan of a Bat?
Bats can live for 10 to 30 years.
How fast is a Bat?
A Bat can travel at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour.
What are the key differences between mouse poop and bat poop?
The key differences between mouse poop and bat poop are appearance and characteristics.
How to say Bat in ...
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife / Accessed November 10, 2008
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals / Accessed November 10, 2008
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia / Accessed November 10, 2008
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species / Accessed November 10, 2008
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals / Accessed November 10, 2008
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals / Accessed November 10, 2008
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals / Accessed November 10, 2008