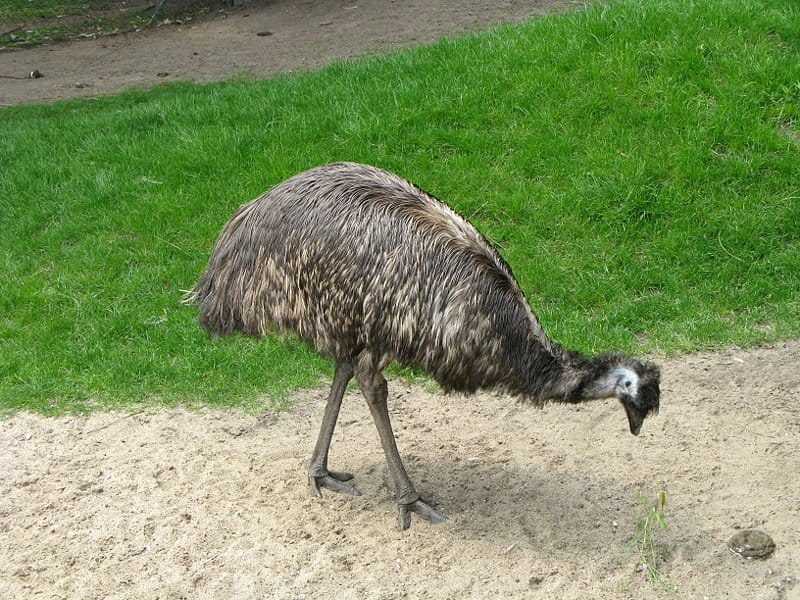
Emu
Dromaius novaehollandiae
The largest bird in Australia!
Advertisement
Emu Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Casuariiformes
- Family
- Casuariidae
- Genus
- Dromaius
- Scientific Name
- Dromaius novaehollandiae
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Emu Conservation Status
Emu Facts
- Main Prey
- Fruit, Seeds, Insects, Flowers
- Distinctive Feature
- Enormous body size and large eyes
- Habitat
- Open grasslands with bushes close to water
- Predators
- Human, Wild dogs, Birds of prey
- Diet
- Omnivore

“An emu has a running stride of 9 feet”
Emus are birds that make their home on the continent of Australia. They can grow as tall as 6.2 feet. This bird is similar in appearance to an ostrich.
Emus are omnivores eating seeds, fruits, insects, and small animals. Their lifespan is from 5 to 10 years in the wild.
An Incredible Bird: 5 Emu Facts!
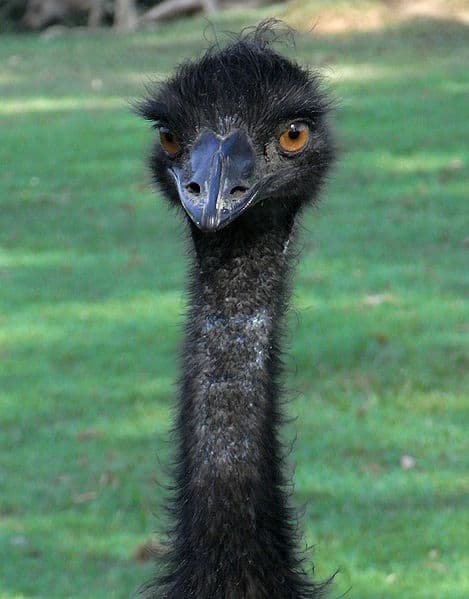

Emu birds have wings but don’t fly.
- An emu bird has a distinctive call that can be heard one mile away
- The main predators of an emu bird are dingoes, eagles, and hawks
- An emu has a clear membrane over each eye to protect it from dust in the air
- Emus are on the move all the time looking for food and water
- Emu birds have wings but don’t fly
Scientific Name
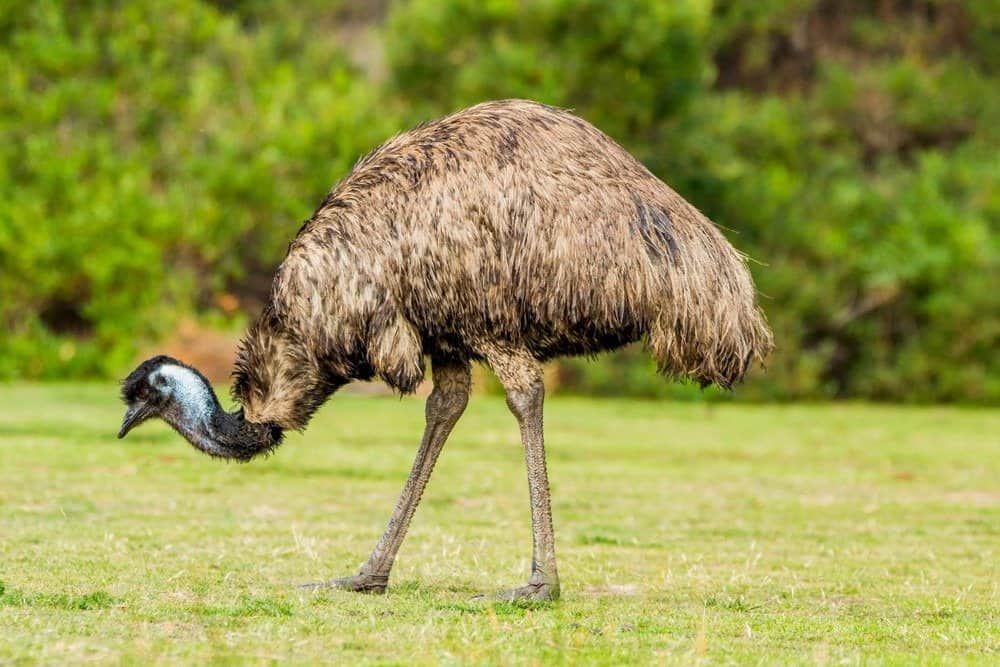

The scientific name for an emu is
Dromaius novaehollandiae.
©Lukas_Vejrik/Shutterstock.com
The scientific name for an emu is Dromaius novaehollandiae. The word Dromaius is Greek meaning runner and the word novaehollandiae means New Hollander. New Hollander refers to this bird’s initial classification as the New Holland Cassowary.
It belongs to the Dromaiidae family and is in the Aves class. There are 4 subspecies of emus.
The scientific name of each one is:
• D. novaehollandiae novaehollandiae
• D. novaehollandiae woodwardi
• D. novaehollandiae rothschildi
• D. novaehollandiae diemenensis
Appearance and Behavior

Emus have dark brown feathers that turn a lighter shade of brown as they age. They have bluish skin on their neck and head. An emu ranges from 4.9 to 6.2 feet in height.
They weigh anywhere from 66 to 121 pounds. As an example, a 6-foot-tall emu is equal in height to a stack of 5 bowling pins. A 120-pound emu weighs two-thirds as much as an adult kangaroo.
Emus have 2 long legs with 3 toes on each foot. These birds aren’t able to fly so they use their long legs to run away from predators. They also have quite a long stride when running. One stride of an emu can be 9 feet long. Just think, 9 feet is equal to half the height of an adult giraffe.
In addition to using their legs to run, emus use them to kick at predators. Their powerful kick, along with the sharp nails on their toes, can cause injury to predators giving this bird time to escape. A swift kick from an emu can even kill a dingo.
This bird makes a lot of sounds. It communicates with other emus via grunts, barks, thumping, and drumming sounds. In fact, the name emu comes from a sound it makes. E-moo! They sometimes make sounds to warn other emus in the area of an approaching predator.
Also, emus make a lot of sounds to warn other emus to stay away from their nest and eggs. Their calls can be heard as far as a mile away. In short, these are definitely not quiet birds!
Emus are solitary birds, but they can form groups when traveling to another area to find a larger food supply. A group of emus is known as a mob. A mob of emus is made up of around 20 birds.
They are non-aggressive birds unless they feel threatened by another animal or a person. They are very aggressive toward one another during the breeding season.
Emu vs. Ostrich
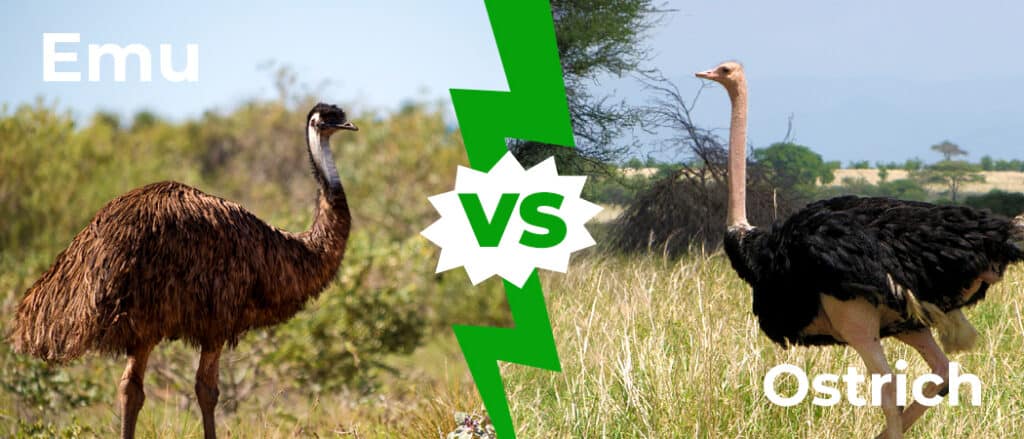

The emu and the ostrich are similar in appearance and are both flightless birds. But there are some distinct differences between them.
There is a big difference in size between these two birds. Emus are the second largest bird on the globe while the ostrich is the largest. Also, when running an emu has a stride of 9 feet while an ostrich has a running stride of 16 feet!
Ostriches can run faster than emus. The top speed of an ostrich is 43mph. The top speed of an emu is 31mph.
Emus drink a lot of water. In fact, they usually drink about two and a half gallons of water each day. Imagine 2-gallon jugs of milk in your refrigerator. Plus, another half a jug! Alternatively, the ostrich is able to go without water for 2 weeks. They get a lot of their moisture from grass and plants.
There are even differences between the eggs of these two birds. The egg of an emu is bright green while the egg of an ostrich is light brown. When it comes to size, one emu egg is equal in size to 10 chicken eggs. One ostrich egg is equal in size to 24 chicken eggs!
Evolution and Origins of Emu
Emus are from a group of flightless birds including the emu, ostrich, and the now-extinct moa. These animals were believed to have evolved from a flightless ancestor, however, recent studies suggest that each species of flightless bird evolved and lost its flight independently rather than all at once.
As mentioned in this article, emus are found in Australia and live throughout the continent. This ranges from coastal regions to the mountains. Additionally, there are two dwarf species of emus that live on Kangaroo Island and King island that have modernly become extinct.
Habitat
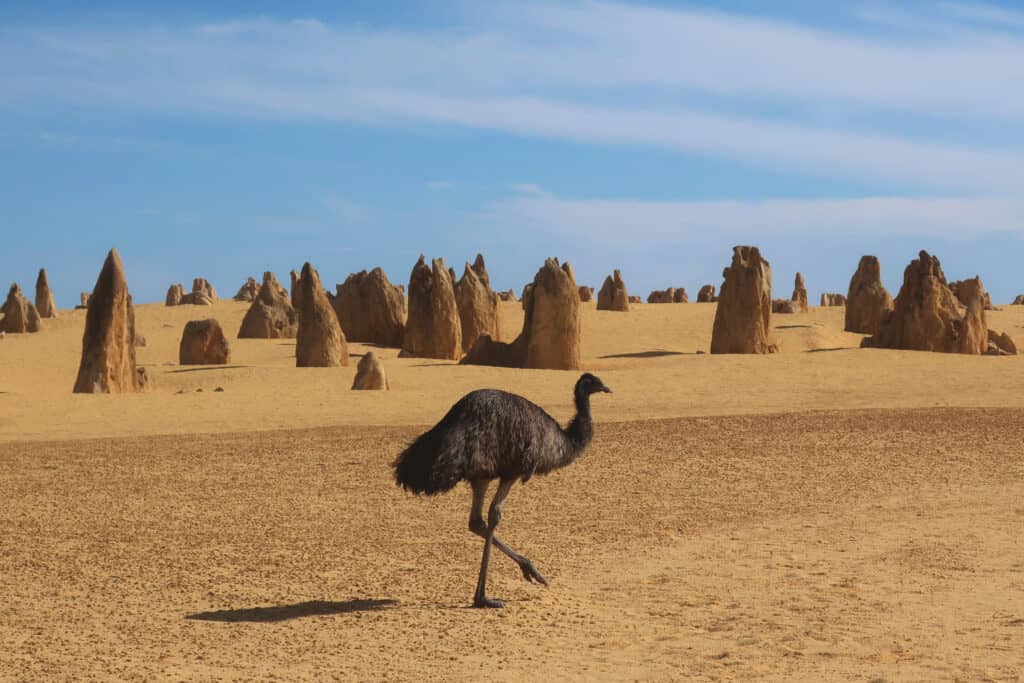

Nambung National Park, Western Australia
©iStock.com/Claudia Schmidt
Emus live on the continent of Australia. Specifically, they are found in every state within Australia except for Tasmania. Grasslands and dry forests are their main habitat. They move continually in an effort to find more food and a source of water. Normally, they travel from 9 to 15 miles per day.
An emu has a clear membrane over each eye that serves as protection against dust and debris in dry habitats. This membrane also helps to keep their eyes moist.
This bird lives in a mostly temperate climate though some of them are found in the Snowy Mountains of Australia. The long feathers of an emu contribute to maintaining a steady body temperature. If an emu is in a particularly cold area, it fluffs its long feathers in an effort to trap air beneath them.
This captured air helps to insulate the bird against cold temperatures. Sometimes they pant (like a dog) to cool down in hot areas of Australia. Have you ever seen a bird panting like a dog?
These birds migrate to the south in Australia during the winter and move north in the summertime. Fortunately, they can easily adapt to a variety of climates.
Diet

What do emus eat? Emus are omnivores. They eat fruit, seeds, beetles, small reptiles, and even the droppings of other animals.
Emus have no teeth so they can’t grind up the plants and animals they eat. So, they swallow small pebbles that go into their gizzard (a part of the emu’s stomach). The pebbles grind food pieces down for proper digestion.
Emus contribute to the ecosystem by seed dispersal. These birds eat a lot of plants, fruits, and seeds. When they leave droppings behind, they disperse seeds so more plants can grow.
Think about it. Emus wander from 9 to 15 miles each day. This means they drop seeds in a variety of areas throughout their habitat.
They also help to control the insect population by eating beetles, cockroaches, and other bugs.
Predators and Threats
Dingoes are the main predators of emus. It makes sense because dingoes share the same habitat as emus. They try to steal an emu’s eggs as well as their young.
A pair of dingoes may target a particular emu’s nest. One of them distracts the parent emu sitting on the nest while the other dingo closes in and steals an egg or a young chick. Dingoes are known for their stealthy approach to hunting prey.
Dingoes also attack adult, full-sized emus. They may try to grab a bird by the neck or head to drag it down. To defend themselves emus kick at dingoes or simply try to run away. Sometimes emus try to frighten dingoes by making a hissing sound at them.
Two other predators include eagles and hawks. These predators are difficult for an emu to fight off.
The conservation status of the emu is Least Concern. The population of emus is categorized as Stable. They are plentiful throughout Australia except in Tasmania. This is because these birds were once hunted by European settlers causing a drastic drop in their population.
Emus produce oil in their bodies which have been used for medicines, creams, and other products. Sometimes these birds are hunted and killed to obtain this oil. But this poaching activity hasn’t caused a great reduction in their overall population.
In the past, emus wandered onto farms to eat seeds causing farmers to lose parts of their crops. They were considered pests. Today, many farmers build tall fences to keep emus away from their crops. Emus can’t jump these tall fences.
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
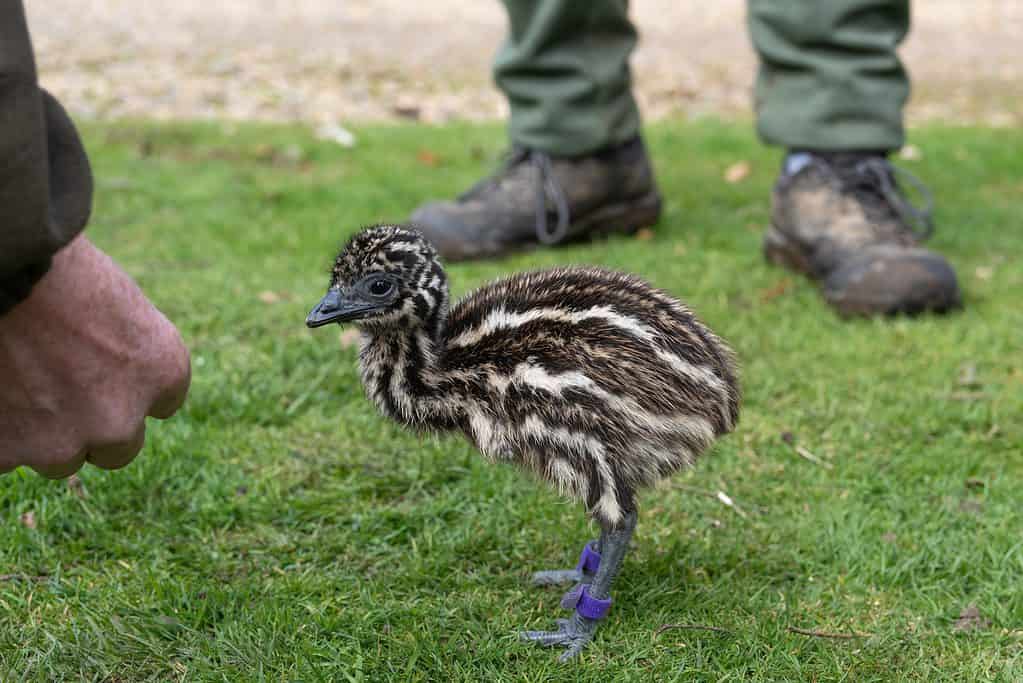

Three-day-old incubator-hatched emu chick has its first experience outdoors. A more unusual Easter chick.
©Hazel Plater/Shutterstock.com
The breeding season of emus falls in December and January. Females lay eggs in April, May, or June. A male emu struts around a female ruffling his feathers. The female has a certain call that tells the male she is interested. A female lays from 5 to 15 eggs in a group or clutch.
Each egg weighs a little over one pound. The male emu builds the nest and sits on the eggs. An emu nest is built on the ground out of grass and dry brush. The female doesn’t sit on the eggs at all. She leaves the eggs and sometimes pairs with other males during this time. Emus are polygamous (have multiple mates).
The incubation period of emu eggs is 56 days. As a comparison, the incubation period for ostrich eggs is around 40 days. While sitting on the eggs, the male doesn’t eat or drink. The fat stored in his body serves as nourishment and he drinks the dew from nearby plants for water. The male emu stands up and turns the eggs from time to time.
A newly hatched baby emu called a chick is 9.8 inches tall. Newborn chicks have a layer of downy feathers and their eyes are open. During the first several months after the chicks hatch, the father emu fiercely defends the nest and young against any threats.
The chicks stay with their parent for about 18 months before becoming independent. They eat small insects and vegetation, then are taught to hunt by the father emu.
Emus are vulnerable to internal parasites including roundworms and lungworms.
The lifespan of an emu is 5 to 10 years. They can live from 15 to 20 years in captivity. The oldest emu was 38 years old.
Population
According to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, the population of emus consists of 630,000 to 725,000 mature individuals.
The conservation status of the emu is the Least Concern with a stable population.
Where to find the Bird
• Visit the emus at the San Diego Zoo.
• Emus are on display at the Louisville Zoo.
• The Denver Zoo has emus, too!
Emu FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are emus carnivores, omnivores, or herbivores?
Omnivore is the classification for the emu diet. They eat both plants and small animals.
How long do emus live?
Emus live from 5 to 10 years in the wild. They can live from 15 to 20 years in captivity.
What is the difference between an emu and an ostrich?
An emu is smaller than an ostrich. Emus grow to be around 6 feet tall while ostriches grow as tall as 9 feet. Emus weigh as much as 121 pounds while ostriches weigh up to 320 pounds. The ostrich is the largest bird in the world while the emu is the second largest.
An emu has 3 toes on each foot while an ostrich has 2 toes on each foot.
The top speed of an emu is 31mph while the top speed of an ostrich is 43mph.
Emus live throughout Australia except for Tasmania. Alternatively, the ostrich lives in Africa.
In terms of classification, emus are in the Casuariidae family and ostriches are in the Struthionidae family.
How tall are emus?
Emus grow to be approximately 6 feet tall.
Are emus friendly?
The emu is a curious bird and is considered non-aggressive. However, they can become aggressive if their nest or young are in danger.
Remember that because an emu is such a large bird with strong legs, it has the power to injure a person or another animal if it feels threatened. So, if you ever see an emu’s nest or eggs, keep your distance.
What Kingdom do Emus belong to?
Emus belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Emus belong to?
Emus belong to the class Aves.
What phylum to Emus belong to?
Emus belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Emus belong to?
Emus belong to the family Casuariidae.
What order do Emus belong to?
Emus belong to the order Casuariiformes.
What type of covering do Emus have?
Emus are covered in Feathers.
What genus do Emus belong to?
Emus belong to the genus Dromaius.
In what type of habitat do Emus live?
Emus live in open grasslands with bushes close to water.
What is the main prey for Emus?
Emus eat fruit, seeds, insects, and flowers.
What are some predators of Emus?
Predators of Emus include humans, wild dogs, and birds of prey.
What are some distinguishing features of Emus?
Emus have enormous bodies and large eyes.
How many eggs do Emus lay?
Emus typically lay 11 eggs.
What is an interesting fact about Emus?
Emus are the largest bird in Australia!
What is the scientific name for the Emu?
The scientific name for the Emu is Dromaius novaehollandiae.
How fast is an Emu?
An Emu can travel at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour.
How do Emus have babies?
Emus lay eggs.
What are the differences between rheas and emus?
The key differences between a rhea and an emu are their size, appearance, lifespan, speed, temperament, and endangered status.
The rhea is the only member of the order Rheiformes, which is found only in South America. Two types of rheas are called the “Greater” and “Lesser” rheas. The greater rhea is the largest of all South American birds! After its ratite relative, the emu is the second-largest living bird in terms of height.
What are the key differences between an emu and a cassowary?
The key differences between an emu and a cassowary are appearance, range, habitat, and group behavior.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Christopher Perrins, Oxford University Press (2009) The Encyclopedia Of Birds
- Animal Diversity Web, Available here: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Dromaius_novaehollandiae/
- Animalia, Available here: http://animalia.bio/emu
- The Animal Facts, Available here: https://www.theanimalfacts.com/birds/emu/