Dinopithecus
D. ingens
The only species currently recognized of this ancient baboon is Dinopithecus ingens.
Advertisement
Dinopithecus Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Primates
- Family
- Cercopithecidae
- Genus
- Dinopithecus
- Scientific Name
- D. ingens
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Dinopithecus Conservation Status
Dinopithecus Facts
- Prey
- Unknown
- Fun Fact
- The only species currently recognized of this ancient baboon is Dinopithecus ingens.
- Biggest Threat
- Climate change
View all of the Dinopithecus images!
Description & Size
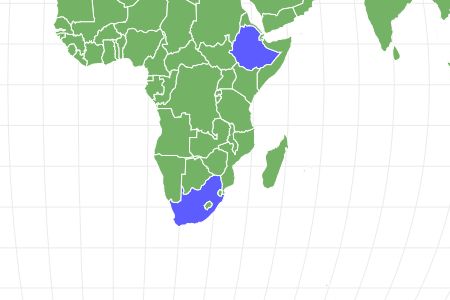
The Dinopithecus is an extinct genus, the name of which means “terrible ape”. They were a large primate closely related to the baboon. They lived in South Africa and Ethiopia from the Pliocene to the Pleistocene Epochs. Because they were only found in certain areas, it is believed they lived in specific habitats.
One of the largest known baboons in the history of the world, Dinopithecus was approximately twice the size of the largest baboons alive today. Males are estimated to have been 1.5 meters (5 feet) tall at the shoulder. Females were smaller than that, at 1.2 meters (4 feet). The Dinopithecus males tended to weigh around 46 kilograms (about 100 pounds), while the females weighed 29 kilograms (about 63 pounds) on average. Despite knowledge of Dinopithecus, currently, only partial remains have been found. Because of this, its appearance can only be approximated.
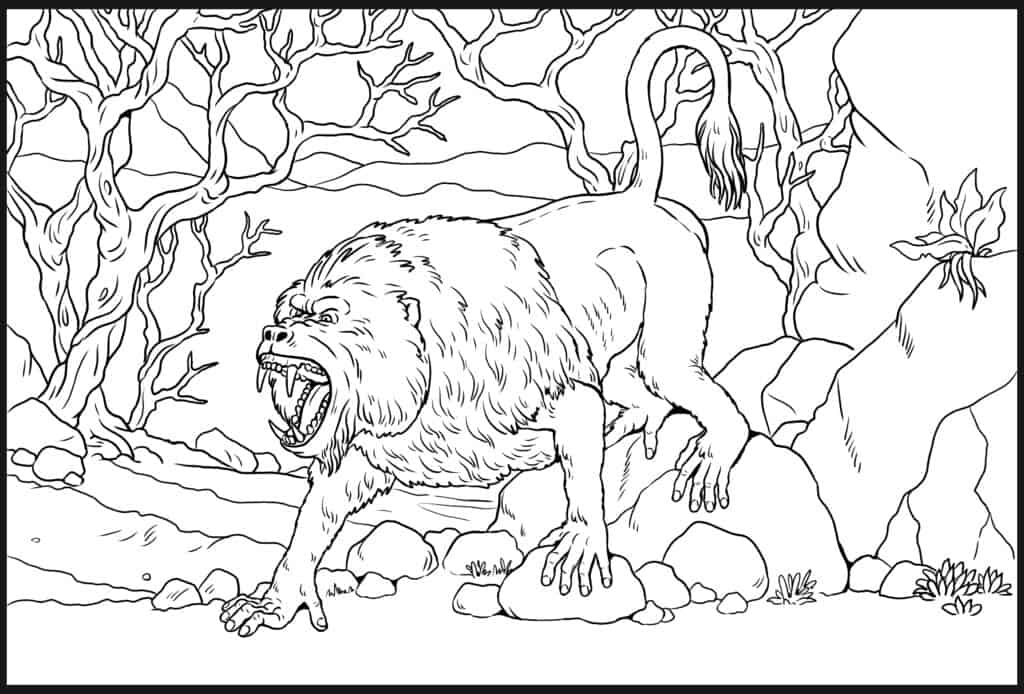
An approximation of the appearance of Dinopithecus.
©Sammy33/Shutterstock.com
Diet – What Did Dinopithecus Eat?
Details on what Dinopithecus ate are largely unknown. It is believed that they had a much more varied diet than current baboons, possibly due to climate changes at the time. Studies on the shape of their teeth indicate Dinopithecus probably had a coarse diet, primarily consisting of underground storage organs, fruits, and other savanna resources.
Dinopithecus are believed to have been omnivorous creatures. If so, they highly likely supplemented their diet of plants with meat; however, it is unknown what specifically.
Habitat – When and Where It lived
Dinopithecus lived in South Africa and Ethiopia during the Pliocene and the Pleistocene Epochs. They were most commonly found in the Ethiopian area of the Matabaietu Formation.
They also likely lived around water holes, as they weren’t suited to travel long distances for water. A home near water is essential for any baboon as it can ensure safety. It’s possible that the Dinopithecus, like the hamadryas baboon, lived near cliff faces but occasionally would find shelter in trees. Like the yellow baboon, they may have inhabited savannas and light forests.
In a study by Caroline M. Bettridge and Robin Dunbar, it was found that due to their size, they would have to have lived in very specific climates to ensure they could get enough food to survive. Generally, fossils of the Dinopithecus are rarely seen outside of the small caves where they are found in South Africa.
Threats And Predators
Exact predators of the Dinopithecus are unknown. The best candidates for what could have been their primary predators are large, sabre-toothed cats, such as Dinofelis and Machairdodus.
In addition to prehistoric big cats, relatives of the modern crocodile – like Crocodylus thorbjarnarsoni – also could have been great predators of this large primate. Crocodylus thorbjarnarsoni are known for having grown to very large sizes with powerful bites and armored skin. With such features, they easily would have been capable of killing a Dinopithecus.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where It was Found
The Dinopithecus fossils are known to be broken and incomplete, forcing paleontologists to make common guesses on how this genus lived.
Fossils from the early Pleistocene age have been found in several sites in South Africa. It is known from having been found in caves in the country, such as Swartkrans and Sterkfontein
Extinction – When Did It Die Out?
The Dinopithecus are thought to have gone extinct during the Pleistocene Epoch, which took place between 2,580,000 and 11,700 years ago.
Climate changes caused the size of Dinopithecus to become its downfall. Food became more scarce as climate changed, and the Dinopithecus required large quantities of food to stay healthy.
Related Animals…
View all 110 animals that start with DDinopithecus FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Unknown
The Dinopithecus lived from the Pliocene to the Pleistocene Epochs. They have only been found in a specific area of South Africa, showing that they were very specific about their climate and habitat.
How big was the Dinopithecus?
The Dinopithecus was estimated to have been up to 5 feet tall at the shoulder, which is very large for a primate, much more a baboon.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Georgia Journal of Science / Accessed September 1, 2022
- International Journal of Primatology / Published December 1, 2012 / Accessed September 1, 2022
- Wikipedia