Fangtooth
Anoplogaster spp.
Has the largest teeth compared to body size of any known fish!
Advertisement
Fangtooth Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Beryciformes
- Family
- Anoplogastridae
- Genus
- Anoplogaster
- Scientific Name
- Anoplogaster spp.
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Fangtooth Conservation Status
Fangtooth Facts
- Group Behavior
- Solitary/Group
- Fun Fact
- Has the largest teeth compared to body size of any known fish!
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Tuna, marlin, small sharks
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Protruding jaw and fangs
View all of the Fangtooth images!
Fangtooth fish live in the deep sea in a region known as “the midnight zone.”
The fangtooth is a carnivorous fish that lives in the deep sea. These fish have grotesquely huge jaws with enormous, protruding fangs, and they prey on smaller fish and crustaceans as well as much larger fish and even squids. It should not be confused with the fangtooth moray, which is an eel that lives in a completely different habitat than the fangtooth fish.

4 Incredible Fangtooth Facts!
- Fangtooth fish are carnivores that will eat anything they can kill.
- They have the largest teeth proportionate to their body size of any fish in the ocean.
- They have extremely compressed bodies with huge heads, enormous jaws and a gruesome, corpse-like appearance.
- Fangtooth fish live in the deep sea in the bathyal zone, also known as “the midnight zone.”
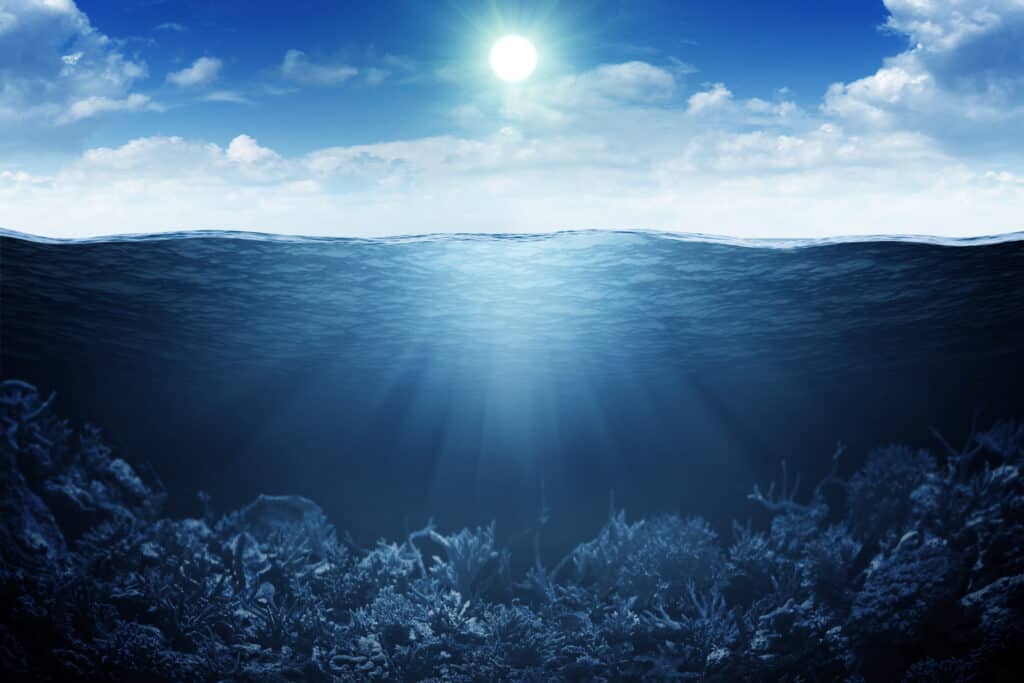

Fangtooth fish can be found in the bathyal zone of the sea.
©iStock.com/Korovin
Scientific Name
The fangtooth fish is part of the genus Anoplogaster. This name comes from the Greek words anoplo translating to “unarmed” and gaster meaning “stomach.” It is a member of family Anoplogastridae.
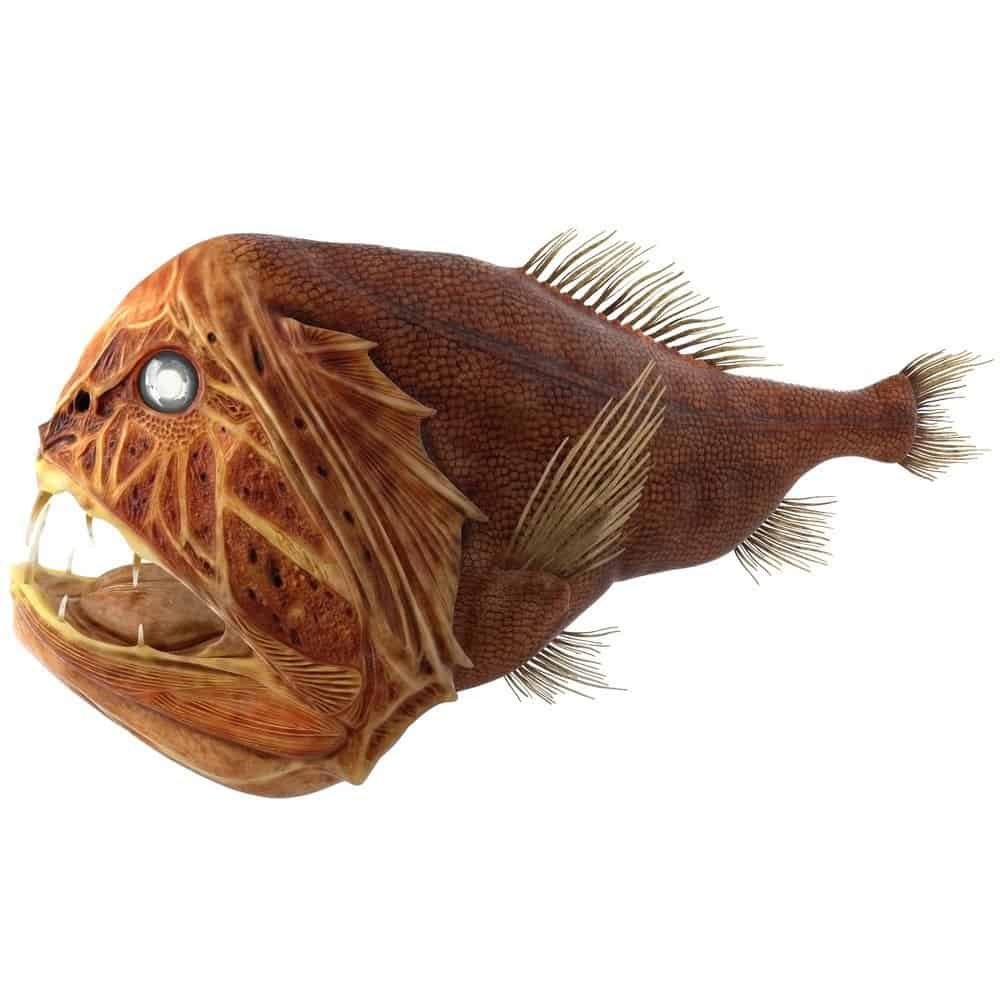

The fangtooth fish belongs to the genus
Anoplogaster.
©3DMI/Shutterstock.com
2 Types of Fangtooth
The two recognized species are the shorthorn fangtooth (Anoplogaster brachycera) and the common fangtooth (Anoplogaster cornuta).
The common fangtooth is the larger of the two and grow to 6.3 in in length at most, while the shorthorn fangtooth is believed to be less than half this size, based on measurements of young fish.
Shorthorn fangtooths are found in tropical zones of the Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean, and common fangtooths are present in more temperate waters in the Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific oceans.
Although they share a name, the fangtooth should not be confused with the fangtooth moray, which is a large, brightly-colored eel.
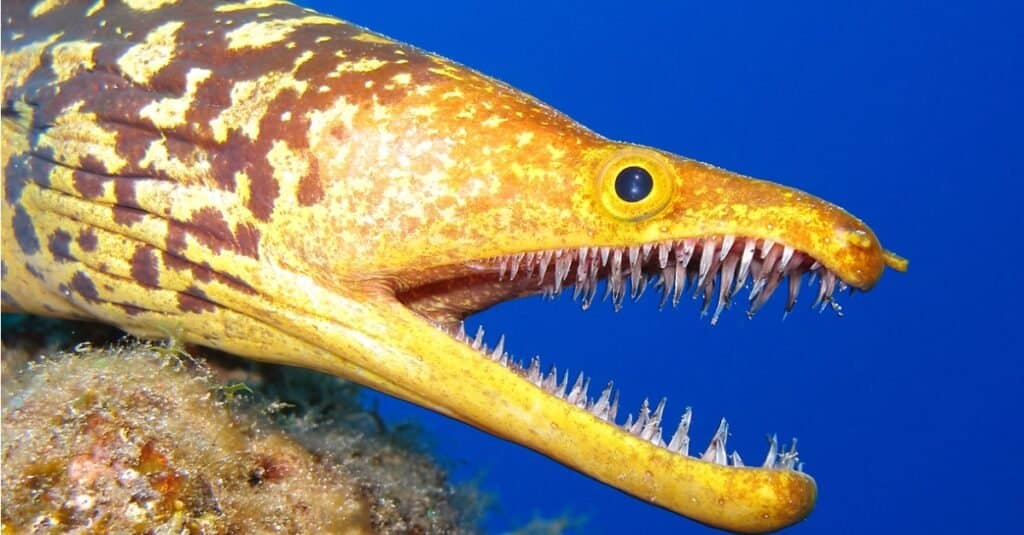

They both share the “fangtooth” name, but the fish is very different from the eel.
©Natursports/Shutterstock.com
Evolution and Origins
There is limited data on the fangtooth due to its deep-ocean habitat, and scientists have not identified any close relatives of this species. While the dragonfish might belong to the same class of Actinopterygii bony fish as the fangtooth, share the same habitats, and is similar in its large head and long, sharp teeth, it is not related and belongs to the Stomiidae family.
Some adaptations to their environment that have been observed include the development of sockets on either side of their heads to allow for their large fangs and sensory lateral lines that are highly sensitive to make up for their limited vision.
In 2020, scientists found the fangtooth can be considered an ultra-black fish as its body absorbs 99.5% of the light that touches it. The skin is covered with tightly packed melanosomes that absorb light through pigment particles. Studying 15 other species of ultra-black fish, they believe that each species evolved the ability to absorb light independently and do not have any common ancestors. They believe the ultra-black could provide camouflage from any predators as well as keep them hidden in the depths of the sea so they can more efficiently catch prey.
The fangtooth is not related to the dragonfish despite its similar head, jaw and teeth.
©OZGIOUN SAMPRI/Shutterstock.com
Appearance
Fangtooth fish, like many other deep-sea creatures, are dark in color and somewhat grotesque in appearance. Similar to anglerfish, the fangtooth fish has an enormous jaw with huge, vicious-looking teeth. In fact, the fangtooth fish has the largest teeth proportionate to its body size of any known fish. The fangs of their lower jaws are so big they had to evolve special sockets on either side of their head to accommodate them.
Because it lives so deep in the ocean, its body is extremely laterally compressed, which means it appears quite thin when viewed from above. Its disproportionately large jaw and thin skin give it a cadaverous look, especially when combined with its sharp, spiny scales and small, ragged fins. As far as researchers know, both males and females have similar appearances, but males tend to be smaller than females. This is true of many deep-sea fish species.
Fangtooths have small, cloudy eyes, and they are believed to have extremely poor eyesight. To compensate for this, they have exceptionally well-developed lateral lines that can be easily seen on either side of their bodies. A lateral line is a special sensory organ system that fish have to help them detect movement and pressure changes in the water around them.
Despite their vicious appearance, fangtooth fish are quite small and essentially harmless to humans. When they are fully grown, they typically only reach about 6 inches in length. For reference, this is about the same length as a dollar bill. Scientists do not know what the average weight of a fangtooth fish is.
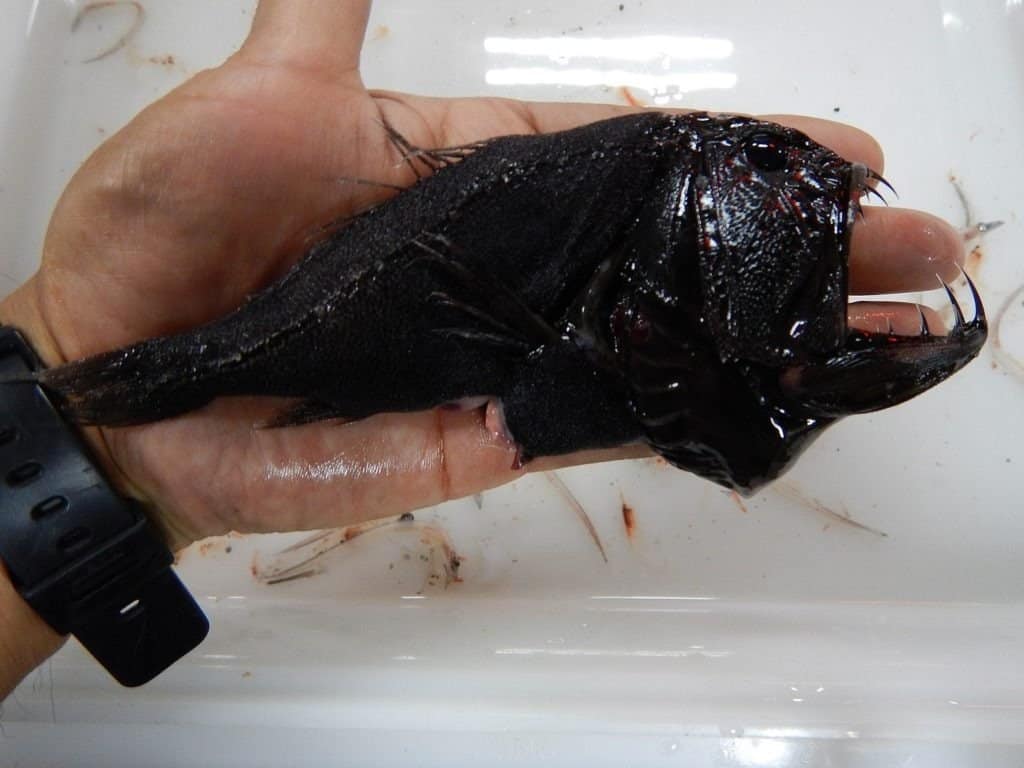

The fangtooth has a huge jaw and intimidating teeth but only measures around 6 inches.
©NOAA Photo Library / CC BY 2.0, Flickr – Original / License
Habitat
The fangtooth fish can be found across the world. It lives in what is known as the “bathyal zone” of the ocean, which means that it is classified as a “bathypelagic” fish. The bathyal zone is the region of the deep sea that stretches from 3,300 feet to 9,800 feet below the surface and is also home to other fish species such as anglerfish, dragonfish, gulper eel, and amphipods.
Although that may sound incredibly deep, the bathyal zone actually is nowhere near the bottom of the ocean. It exists above two deeper layers of the ocean: the abyssal zone and the hadal zone. However, it is deep enough that no sunlight reaches this region.
Because no sunlight touches those waters, the bathyal zone is also known as the “midnight zone.” The temperature typically stays around 40 degrees Fahrenheit. Between the lack of sunlight and freezing temperatures, there is no plant life in this part of the ocean.
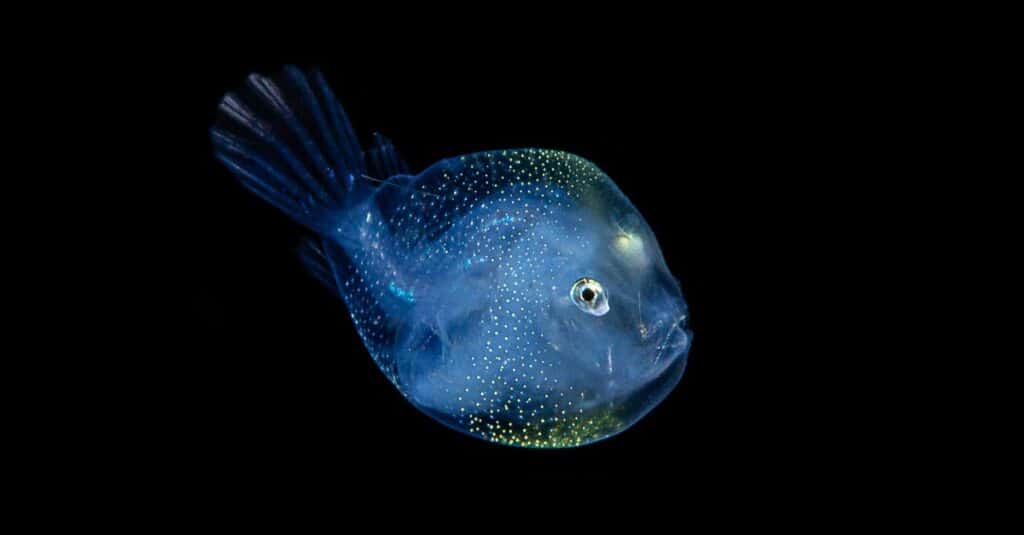

Anglerfish also live in the bathyal zone with fangtooth fish.
©Sam Robertshaw/Shutterstock.com
Diet
Fangtooth fish are part of a larger order of fish known as bericyformes. All bericyformes are carnivorous, which means that they are fish with teeth that feed on other animals like crustaceans. Unfortunately, because they are also nocturnal, deep-sea dwellers, scientists do not know much about them because they are difficult to study.
They do know that adult fangtooths feed on small fish, but they are also known to prey on larger squid as well. Their enormous teeth help them more easily hunt their meals. Juvenile fangtooths eat by filtering zooplankton from the water. Scientists don’t know for certain, but they believe that fangtooths likely follow what is known as “diurnal vertical migration.” This means that they rise to the surface at night to feed and then return to the depths as the sun rises.
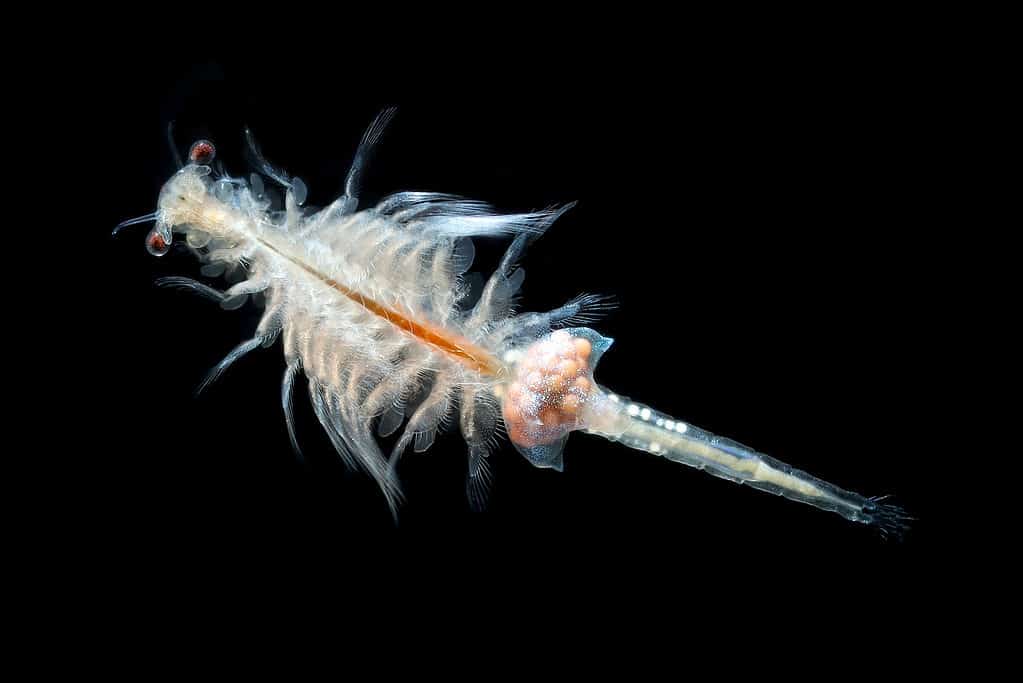

Young fangtooth fish eat a diet of zooplankton, which includes microscopic crustaceans like brine shrimp..
©Dan Olsen/Shutterstock.com
Predators and Threats
Despite their small size, fangtooths do not have many predators. They primarily are hunted by much larger tuna and marlins, but those are their only main threats.
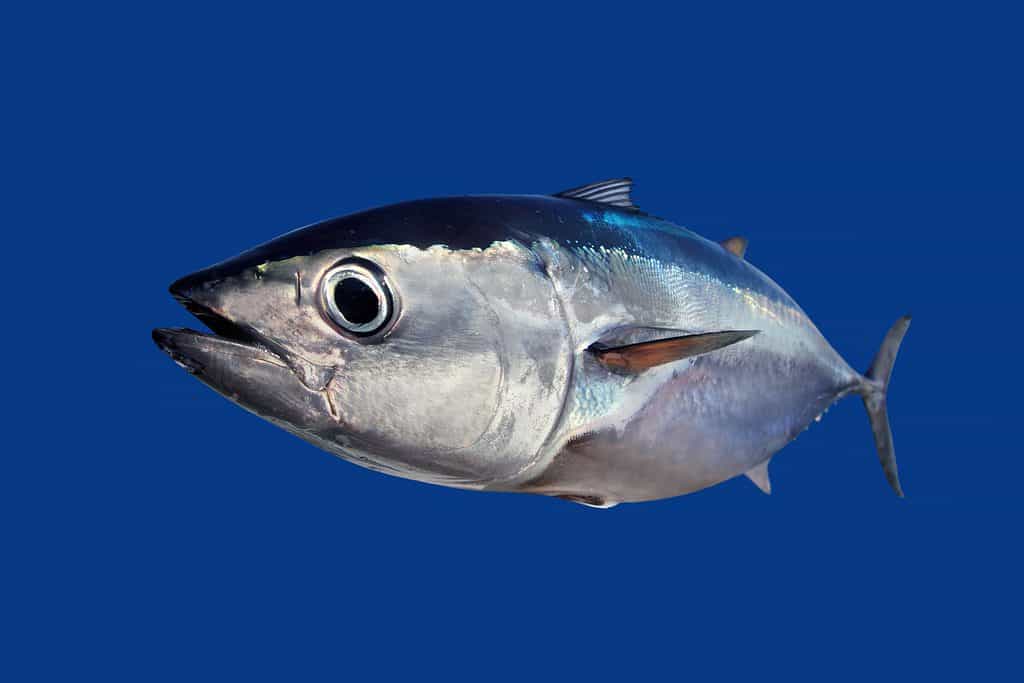

Larger tuna prey upon the fangtooth fish.
©lunamarina/Shutterstock.com
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
Little is known about the lifespan and reproduction habits of fangtooth fish simply because they live so far down in the depths of the ocean. However, scientists do know that they are oviparous, which means that the females lay a large clutch of eggs, and the males then fertilize them.
They do not appear to guard their eggs; instead, the larvae are left to fend for themselves when they hatch. This is a common trait for deep-sea fish. In fact, larvae, juveniles, and adults all live in different depths of the ocean, so they tend to exist completely separately.
Juvenile fangtooths look so different from the adult counterparts that scientists originally classified them as a completely different species of fish. They are gray instead of black and have much larger eyes and a functional gas bladder, which helps to control buoyancy. Juveniles also have long gill rakers, slender spines on their heads, and much smaller teeth, so it’s no surprise that they were thought to be a different species at first.
It is not known how long fangtooth fish can live. Researchers have noted that fangtooth fish are incredibly tough and adaptable, however. A few specimens that have been caught and kept in aquariums have survived many months despite the wildly different water pressure and overall habitat.
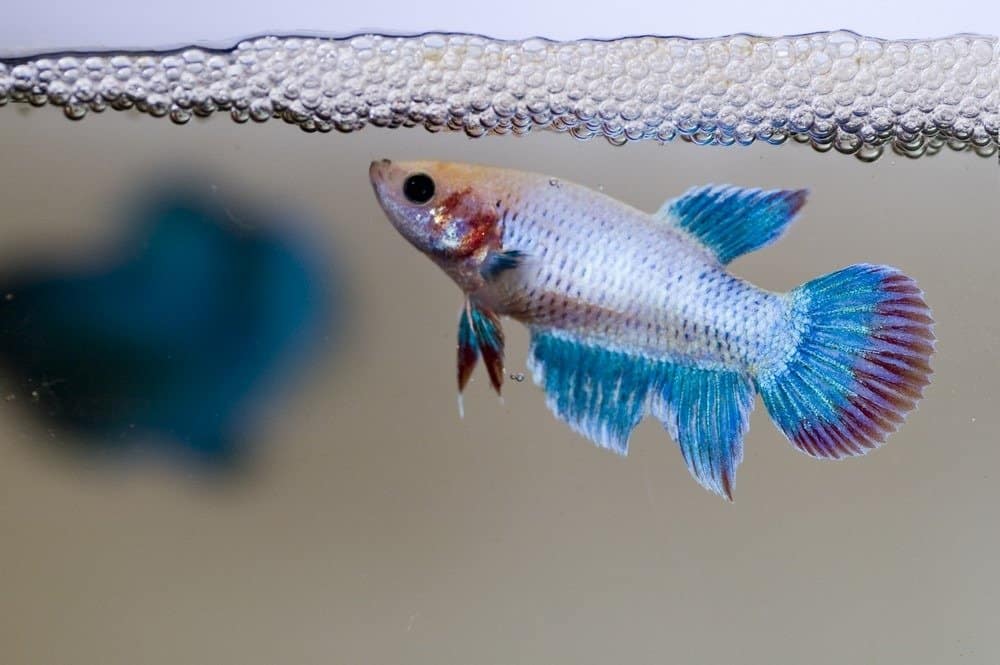

Fangtooths are oviparous like other species of fish including the Siamese female fighting fish.
©mnoor/Shutterstock.com
Fangtooth in Fishing and Cooking
Eating fish with teeth might sound appealing to some of the more adventurous seafood lovers of the world, but in general, fangtooth fish are of little interest to fishermen.
Fishermen may occasionally catch these fish in their nets, but they do not actively seek to catch them commercially or recreationally.
Fangtooth Population
As with many fish found in the deep sea, scientists are not exactly sure how many fangtooth fish exist in the wild. However, they are listed as a species of Least Concern by the IUCN, so they are not in danger of extinction.

The IUCN’s Red List categorizes the fangtooth as of Least Concern.
©Tobias Arhelger/Shutterstock.com
Fangtooth FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are fangtooths found?
Fangtooth fish are found in the deep sea, typically around 5,000 feet below the ocean’s surface.
It’s important to note that these are different from the fangtooth eel, which is a species of moray eel that is nothing like the fangtooth fish.
What do fangtooth fish eat?
As the name suggests, fangtooths are fish with teeth. They are carnivores that feed on crustaceans, invertebrates, small fish, and squids.
Where do fangtooth fish live?
Fangtooth fish live in the deep sea, in a region known as the bathyal zone. This is sometimes referred to as the bathypelagic zone and the midnight zone.
Are fangtooth fish dangerous?
While the fangtooth does look like a menacing predator, the truth is that fangtooth fish are quite small and harmless to humans.
Which ocean zone do fangtooth fish live in?
Fangtooth fish live in the bathypelagic zone, which extends from about 3,300 to 9,800 feet below the surface of the ocean.
Can you eat fangtooth fish?
As far as researchers know, it is not harmful to eat a fangtooth fish. However, they are not ever caught with the purpose of eating them. They are extremely unappealing to look at and only grow to be about 6 inches long, so they would not make a good meal.
What kingdom do fangtooths belong to?
Fangtooths belong to the kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do fangtooths belong to?
Fangtooths belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do fangtooths belong to?
Fangtooths belong to the class Actinopterygii.
What family do fangtooths belong to?
Fangtooths belong to the family Anoplogastridae.
What order do fangtooths belong to?
Fangtooths belong to the order Beryciformes.
What type of covering do fangtooths have?
Fangtooths are covered in scales.
What type of habitat do fangtooths live in?
Fangtooths live in deep ocean habitats.
What are some predators of fangtooths?
Predators of fangtooths include tuna, marlin, and small sharks.
What is the scientific name for the fangtooth?
The scientific name for the fangtooth is Anoplogaster.
What is a distinguishing feature of the fangtooth?
Fangtooths have a protruding jaw and fangs and an expanding hood.
What is the biggest threat to the fangtooth?
The biggest threats to fangtooths are tuna, marlin, and small sharks.
What is another name for the fangtooth?
The fangtooth has two species known as the common fangtooth and shorthorn fangtooth.
How many fangtooths are left in the world?
The population size of the fangtooth is unknown.
What is an interesting fact about fangtooths?
The fangtooth has the largest teeth compared to body size of any known fish.
How do fangtooths have babies?
Fangtooths lay eggs.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.