Rock Crab
Cancer productus
Males will fight each other to get to females.
Advertisement
Rock Crab Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Malacostraca
- Order
- Decapoda
- Family
- Cancridae
- Genus
- Cancer
- Scientific Name
- Cancer productus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Rock Crab Conservation Status
Rock Crab Facts
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- Males will fight each other to get to females.
- Biggest Threat
- Predators and commercial fishing.
- Most Distinctive Feature
- large brown-black claws with lighter-colored tips
- Gestation Period
- 6-8 weeks
- Habitat
- Near rocks, tide pools, and rocky marine areas.
- Predators
- Sand and kelp bass, other fish, seabirds, and sea otters.
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Favorite Food
- Worms, clams, mussels, other crabs, other invertebrates, and algae.
- Type
- Decapod
- Common Name
- red rock crab
- Number Of Species
- 1
View all of the Rock Crab images!
The rock crab molts throughout its life, shedding its former shell. Typically, younger crabs molt multiple times in the same year. It is not until they are about four inches in width that they reduce their molting to an annual occurrence.
This crustacean is a decapod, though most people refer to it as the red rock crab. Found along the Pacific Coasts, it has become a beloved dish in California, allowing them to be sold commercially and fished by locals. They prefer warm freshwater, and they are buried upwards of 300 feet below the ocean’s surface.
5 Incredible Rock Crab Facts!
Here are a few interesting facts about this crustacean.
- This species has five pairs of legs, though only the two in front are claws.
- The shell is round and flat, helping it hide beneath the sand and within rocks.
- Though they can be quick in short movements, this crustacean doesn’t move much.
- The hair-like structures on the legs allow It to feel movement and go after nearby prey.
- The average wild rock crab lives to be 5-6 years old, but the right environment can prolong their life to nearly 8 years.
Rock Crab Classification and Scientific name
The common name of the Cancer productus is the red rock crab, though there are also yellow and brown variations. They are part of the Cancridae family and the Malacostraca class.
Cancer is the Latin word for “crab,” derived from the Greek word karkinos. Productus is a conjugation of the Latin word prōdūcō, which translates to “lead forward.” Perhaps this is a nod to the rock crab’s quick and aggressive movement when they spot prey.
Species
While there aren’t many other species of rock crab, there are a variety of colors, which include:
- Yellow rock crabs – Sandy areas along the coast are the primary habitat for yellow rock crabs.
- Red rock crabs – Most commonly sold by fisheries and other commercial settings. They are primarily found on the Pacific Coast and sold in California.
- Brown rock crabs – They are found mostly on reefs. There’s no real size difference between them, but they are primarily differentiated by their preferred habitat and color.
Rock Crab Appearance
This species typically has a white to red-brown shell, which is why it is also known as the red rock crab. The body is rather chunky and heavy, but the most identifiable feature of the animal is its huge claws. Apart from their massive size, the claws are a brown-black color and have lighter-colored tips, making them easy to recognize. The claws are necessary for breaking down the shells of their prey, like snails.
The average rock crab is about 13 ounces in weight, and its shell reaches a maximum size of 4 inches. Their claws and body have a lot of meat, becoming flaky when cooked.
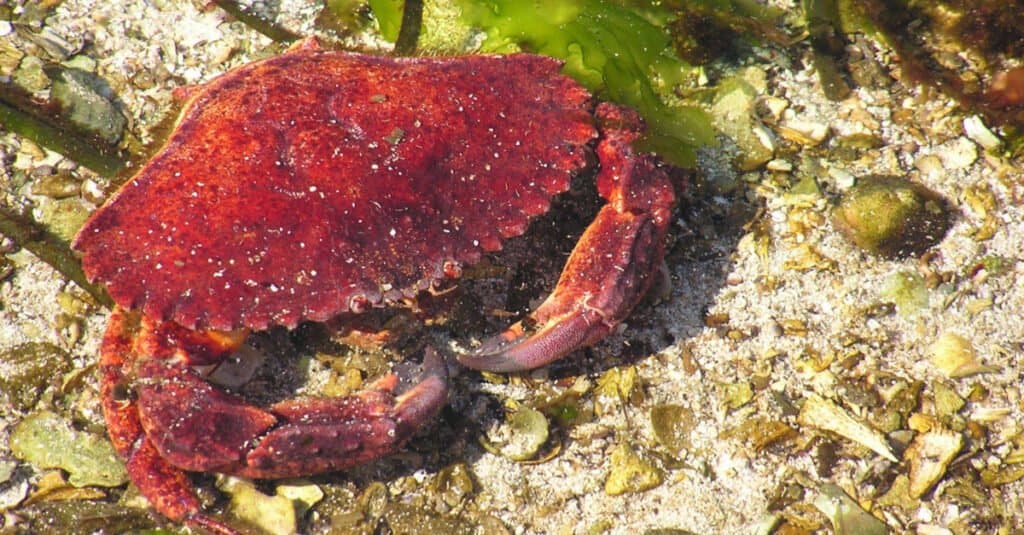

The majority of the red rock crab species is found in rocky reef areas.
©C. Rene Ammundsen/Shutterstock.com
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Due to how abundant rock crab eggs can be, it is hard to determine how many exist in the world. However, considering that over half a million pounds of this species are fished in just California every year, the numbers are fairly high, and they are currently “not extinct” (according to the IUCN). The NOAA’s current stock status shows that they are not overfished.
The majority of this species is found in rocky reef areas, though yellow rock crabs are specifically found in sandy areas of the coast. Typically, they’ll prefer bays, gravel, rocky substrates, estuaries, sand, and mud, living typically at 298 feet in the waters of California. However, away from that area of the coast, rock crabs will go deeper into the water for hunting and scavenging.
Primarily, this crustacean is found in freshwater areas.
Predators and Prey
When it comes to mealtime, this species will grab just about anything they can clamp their claws down on. As scavengers, they aren’t very picky, but they’ll mostly look for other invertebrates to eat. They’ll even indulge in other crabs and dead fish.
What does the Rock Crab eat?
As a scavenger, the diet of this crustacean primarily depends on where it is. Most of the time, they’ll enjoy worms, clams, mussels, and other invertebrates, breaking through their shell with ease. They’ll also indulge in barnacles, sea cucumbers, and amphipods. However, if a meal like a dead fish is available to them, they’ll dine on that too.
What eats Rock Crabs?
One of the biggest predators of this species is humans. Because of all of the meat that they offer, humans will fish for the crabs for different dishes. They are also hunted by crabs, fish, gulls, seabirds, and kelp bass. There’s also one breed of sea otters – Enhydra lutris – that specifically uses rock crabs as the main food in their diet.
Reproduction and Lifespan
When this species mates, it usually occurs from October to June because the female has a softer shell at this time. When she is in the molting stage, she won’t be as vulnerable as you might think because the male protects her.
About three months after this time, the female produces eggs in her abdominal sac. Before the eggs can be laid, the female migrates to where the eggs will eventually be hatched, hiding for about 12-13 days in the dirt. The female rock crab has the potential to lay up to 100,000 eggs.
They are fertilized by a sperm packet that the female stores during the mating time with the male. Once she lays the eggs, she’ll carry the eggs on her own body for about 6-8 weeks before they are ready to hatch. Baby rock crabs need to eat meat like adults, but they often will focus on invertebrates like octopuses and fish.
Fishing and Cooking
This is one of the most common species of crab for California fishermen, whether they are fishing for sport or commercial purposes. The primary place in California that they fish from is Morro Bay South. However, the California rock crab fishery seeks out several types – yellow, brown, and red. On average, this fishery takes on over one million pounds of rock crab annually.
This crustacean seems to primarily be fished in California, as the climate in Florida is much different. In Florida, you will have access to the Stone Crab, which looks like the rock crab but only the claw meat is eaten. In fact, the crab can be returned to the Florida waters to regrow their claws.
Rock crab legs can have a great taste, no matter how they are seasoned. Steaming the legs with beer and old bay seasoning brings out a bold and pub-style taste, while even just the right dipping sauce can change the flavor. Crab legs are always a delicacy, and the tender flesh is perfect for any taste.
View all 114 animals that start with RRock Crab FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is rock crab good to eat?
Yes! The tender meat of the crab is incredibly tasty. However, it should be prepared with the shell, due to the flakiness of the meat. It is difficult to remove the flesh in one piece.
Is rock crab the same as Stone Crab?
No. While the Stone Crab and the Rock Crab are quite similar in appearance, the Stone Crab is smaller. Plus, the only meat that people generally consume is from the claws, offering a taste similar to that of lobster.
How do you tell the difference between a Dungeness and a rock crab?
The Dungeness crab is much meatier with a slight sweetness, but the rock crab is much more delicate. While the red rock crab has black tips on its claws with a red body, the Dungeness has a more purple hue with a grayish-brown undertone.
Are red rock crabs dangerous?
Not particularly. These crabs typically go after algae, plants, and dead animals. However, they are fast, making them hard for anyone to catch.
Where are rock crabs found?
Rock crabs are primarily found on the Pacific Ocean coasts.
How are rock crabs and Dungeness crabs different?
Both rock crabs and Dungeness crabs are commonly found across the coasts of the Pacific Northwest and are often confused for one another. The primary difference between rock crabs vs Dungeness crabs is that Dungeness crabs are larger. In addition, rock crabs have black tips on their claws and other physical differences.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- California Ocean Protection Council / Accessed August 6, 2021
- Sea Grant California / Accessed August 6, 2021
- Animal Spot / Accessed August 6, 2021
- Animal Corner / Accessed August 6, 2021
- Chef's Resources / Accessed August 6, 2021
- Wikipedia / Accessed August 6, 2021
- Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife / Accessed August 6, 2021
- Costas Inn / Accessed August 6, 2021
- The Infinite Kitchen / Accessed August 6, 2021
- BioWeb / Accessed August 7, 2021
- University of Rhode Island Environmental Data Center / Accessed August 7, 2021
- The Spruce Eats / Accessed August 7, 2021
- Wiktionary / Accessed August 7, 2021
- Seafood Source / Accessed August 7, 2021
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration / Accessed August 7, 2021
- Animal Hype / Accessed August 7, 2021