Teddy Bear Hamster
Mesocricetus auratus
The oldest recorded teddy bear hamster was six and a half.
Advertisement
Teddy Bear Hamster Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Rodentia
- Family
- Cricetidae
- Genus
- Mesocricetus
- Scientific Name
- Mesocricetus auratus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Teddy Bear Hamster Conservation Status
Teddy Bear Hamster Facts
- Prey
- Seed, fruit, vegetables, and grains
- Name Of Young
- Pup
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- The oldest recorded teddy bear hamster was six and a half.
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Large ears
- Other Name(s)
- Long-haired Syrian hamsters
- Gestation Period
- 16 days
- Litter Size
- 6-12 pups
- Habitat
- Cage, aquarium
- Predators
- Snakes, domesticated dogs and cats, foxes, and birds
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Type
- Mammal
- Common Name
- Teddy Bear Hamster
- Location
- Originated in Syria
- Group
- Solitary
Teddy Bear Hamster Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Grey
- Black
- White
- Gold
- Cream
- Dark Grey
- White-Brown
- Golden
- Skin Type
- Fur
- Lifespan
- 2-3 years
- Weight
- 3.5-5.3 ounces
- Length
- 6 inches
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 6 months
- Age of Weaning
- 4 weeks
View all of the Teddy Bear Hamster images!
“A teddy bear hamster can stuff its cheek pouches with an amount of food equal to 20 percent of its body weight”
The teddy bear hamster is also known as a long-haired Syrian hamster. These tiny mammals are herbivores eating grains, vegetables, and fruit. A teddy bear hamster’s tail is very short at about half an inch long. They are solitary animals with an average lifespan of 2-3 years.
5 Incredible Teddy Bear Hamster Facts!
- Teddy bear hamsters are originally from Syria.
- They can carry food along with bedding in their cheek pouches.
- These hamsters are nocturnal.
- Their large ears and small dark eyes make them look similar to teddy bears.
- They are an easy pet to tame with gentleness and patience.

Teddy Bear Hamster Scientific Name

Syrian hamsters belong to a vast family comprising over 20 species
©stock_shot/Shutterstock.com
The scientific name of a teddy bear hamster is Mesocricetus auratus. The word Mesocricetus is Latin for hamster and the word auratus means gold. It’s also known as a long-haired Syrian hamster and sometimes a golden hamster. These small creatures belong to the Cricetidae family and are in the class Mammalia.
There are over 20 species of hamsters. Some of those include:
- Winter white dwarf hamster
- Roborovski dwarf hamster
- Chinese hamster
- Campbell’s dwarf hamster
- Turkish hamster
Evolution and Origins

The Syrian hamsters loved by many pet enthusiasts were taken from Aleppo, Syria, hence their name
©Happy monkey/Shutterstock.com
The ancestors of the teddy bear hamsters’ wider family are believed to have shown up in North Africa and Europe during the Miocene about 11.2 million to 16.4 million years ago and about 6 million to 11 million years ago in Asia. During this same epoch, a particular forbear belonging to the genus Cricetus roamed North Africa and it is this same prehistoric rodent which gave rise to the critter known as the common or European hamster.
Syrian hamsters’ first known literary mention dates back to the very end of the 18th century, in a Natural History of Aleppo written by Scottish physician Alexander Russell.
Four decades later they were bestowed with the name of golden hamster by the curator of the London Zoological Society, George Robert Waterhouse.
Approximately one century later in 1930, scientist Israel Aharoni arrived in Aleppo where it had all begun, in search of the famed critter. He was richly rewarded when he discovered a female of the species along with 11 pups.
Aharoni was able to make it back to the Hebrew University with four siblings which he bred — most of the rest had energetically chewed their way out of captivity.
The progeny of the four were sent to the United Kingdom and the United States during that same decade and the next, too. The cuddly little critters soon won the hearts of pet owners on either side of the Atlantic, and as a result soon became cherished members of several homes — a trend which has continued right up until today.
Appearance and Behavior

©Anastasia Solovykh/Shutterstock.com
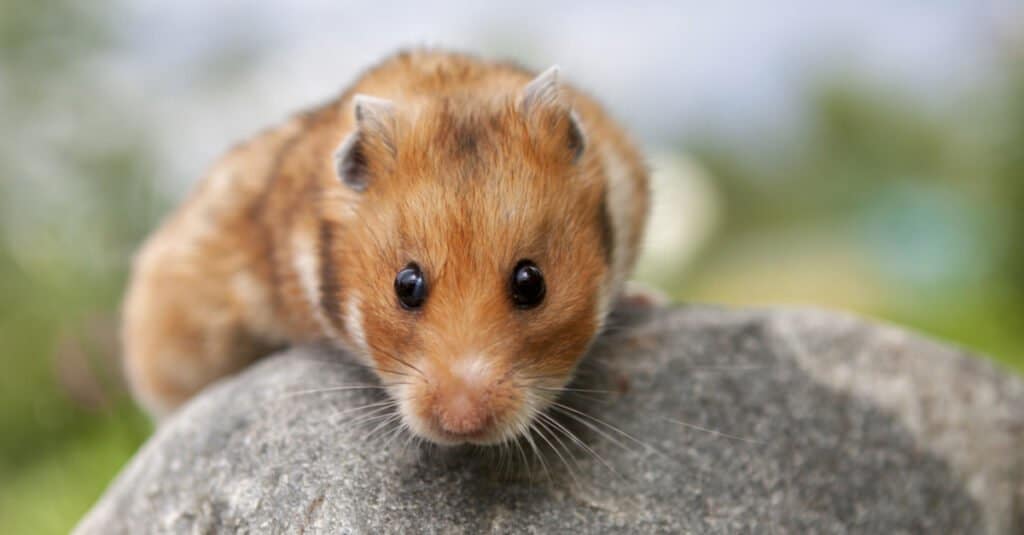
The coat of a teddy bear hamster can be a solid color or a combination of colors. Their hair can be solid black, brown, gold, or dark gray. Other teddy bear hamsters feature a mixture of colors such as gray or black with a white chest, brown with bands of white, or gold with splotches of white. The combinations are endless!
These hamsters grow to be around 6 inches long and weigh just 3.5 to 5.3 ounces. Dwarf hamsters are about half the size of teddy bear hamsters. Picture a one-dollar bill and you’re looking at something equal in length to an adult 6-inch teddy bear hamster. A teddy bear hamster weighing around 5 ounces is equal in weight to a baseball. The longest a teddy bear hamster can be is 7 inches, but that’s rare.
A gerbil is another popular pet from a different family that grows as long as 4 inches. But its tail adds another 4 inches to its length!
Though we are most familiar with these hamsters as pets, they do have some defensive features they use in the wild. They stuff their cheek pouches full of food and bedding to make a fast getaway when a predator approaches. This allows them to move to a more secure place without losing these items.
They’re nocturnal so moving from one place to another during the night may give them some cover from threats. A hamster with a black or dark coat would be even harder for predators to see.
Teddy bear hamsters also have sharp teeth to defend themselves. But even sharp teeth aren’t likely to help if this small animal is attacked by a dog or an owl.
Teddy bear hamsters are solitary. They don’t get along with dwarf hamsters or any other type. These animals can be shy with people but they can be tamed. It’s important to move slowly with a hamster because they may bite if frightened.
Fancy Hamster vs Teddy Bear Hamster
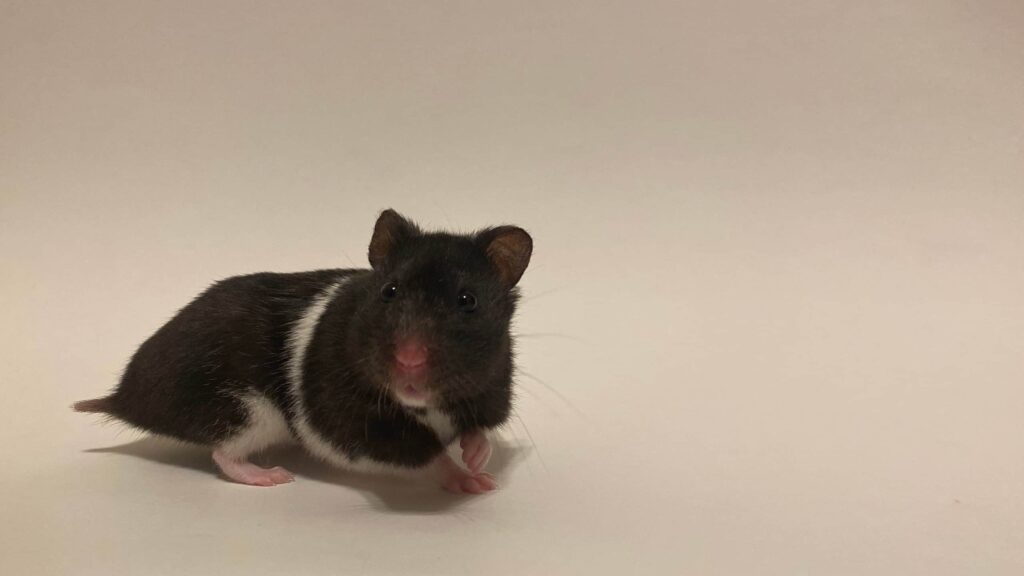

Fancy Bear hamsters are teddy bear hamsters’ short-haired cousins and are easier to care for as a result
©Shadow526/Shutterstock.com
Fancy hamsters and teddy bear hamsters have a lot of similar features. They’re both Syrian hamsters kept as pets. These hamsters eat the same type of food and are nocturnal. But some differences are existing between these two.
A significant difference has to do with their coat. A teddy bear hamster is long-haired while a fancy hamster has short hair.
This leads to a difference relating to coat maintenance. Shavings and dirt can become caught in the long coat of a teddy bear hamster. A toothbrush with soft bristles is perfect for gently removing this debris.
The third difference between these critters has to do with price. Some pet shops charge a higher price for fancy hamsters. Why? The name fancy implies the hamster is a little better quality than other hamsters. This isn’t true. There’s very little difference between these hamsters. In addition, a fancy hamster’s hair is shorter, so it requires less maintenance than a teddy bear hamster’s coat. Some pet shop owners charge a higher price for fancy hamsters because their short hair makes them a little easier to care for.
Habitat
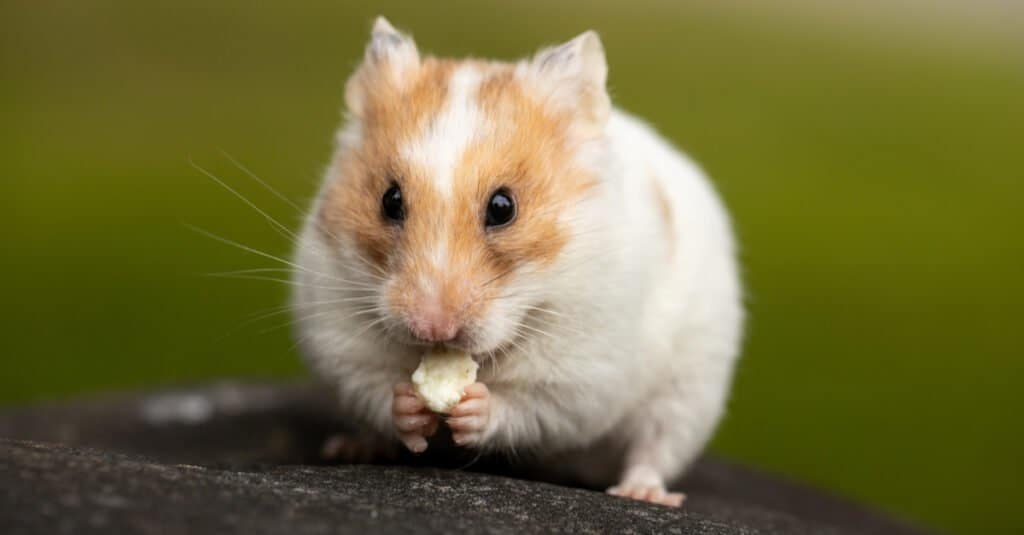

Teddy bear hamsters can still be found in the wild at present
©Sharon Snider/Shutterstock.com
Teddy bear hamsters are originally from Syria. They thrive in an arid climate. In the wild, they live underground in burrows to keep cool and safe from predators during the day. They come out at night to look for food. There are still some Syrian hamsters living in the wild today, but their population is decreasing.
A teddy bear hamster kept as a pet can live in an aquarium or wire cage. These pets need a layer of shredded paper or aspen shavings to serve as bedding. They like to burrow down into the bedding or build up a heap of it in one corner. These creatures are comfortable in a warm room in an area free of cold drafts.
Predators and Threats
All Syrian hamsters are herbivores. They use their sharp teeth to mash up or cut through plants and grains of many types.
What does a teddy bear hamster eat?

Wild and domesticated Syrian hamsters eat plants, grains, vegetables, and fruits. A hamster living in the wild is limited to eating whatever plant life is in its environment. Alternatively, a pet teddy bear hamster gets to eat a variety of fruits, veggies, treats, etc. brought to it by its owner.
Some things are not good for a hamster to eat such as almonds and peanuts. These foods are too high in calories to be healthy for a hamster to consume.
What eats a teddy bear hamster?
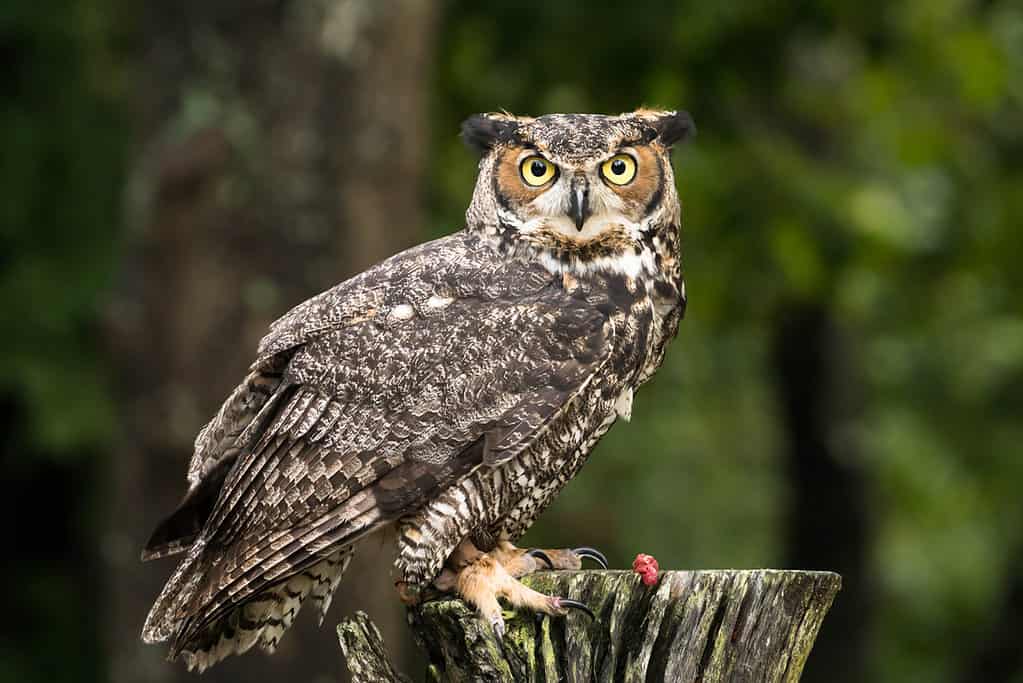

Owls are one of Syrian hamsters’ many predators
©iStock.com/makasana
Some of the predators of wild hamsters include owls, foxes, and snakes. All of these animals have access to wild Syrian hamsters or share the same type of habitat. For instance, a snake can follow a hamster into its burrow to capture it, and owls, as well as foxes, are active at night just like these hamsters.
The wild Syrian hamster has a dwindling population. They’re losing their habitat and sometimes they’re killed as pests by farmers. Their conservation status is Vulnerable.
Reproduction and Lifecycle
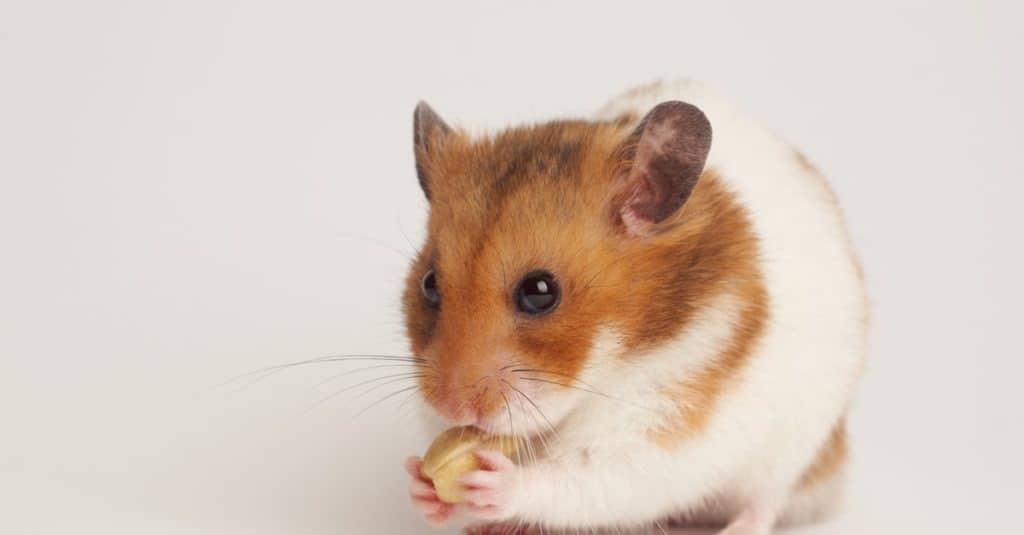

Syrian hamsters are prolific producers and can give birth to as many as 20 pups
©Johannes Menge/Shutterstock.com
Teddy bear hamsters reach sexual maturity at 6 weeks old. But they should not be bred until they are about 6 months old. A female teddy bear hamster won’t mate with a male unless she is in heat. Being in heat means she’s at a point in her menstrual cycle when she can become pregnant. Teddy bear hamsters are not social so even a male and female shouldn’t be kept together for more than a few hours. These animals can have multiple partners throughout their life. The gestation period of this hamster is about 16 days. This is similar to the gestation period of a pet mouse which is 19 to 21 days.
A female hamster usually has 6 to 12 babies, or pups, in a litter. Some females give live birth to 20 pups in a single litter! A hamster pup weighs less than an ounce, has no hair, and is born with its eyes closed. At 5 days old their teeth and coat start to grow. The pups’ eyes open at about 2 weeks old. They continue to nurse from their mother until they’re 2 weeks of age. At that point, the pups begin to eat solid food. At the age of 3 or 4 weeks, hamster pups look like smaller versions of adult hamsters. At 4 weeks old a hamster pup can live apart from its mother.
The lifespan of teddy bear hamsters is 2 to 3 years. The oldest hamster on record lived for 7 years.
These hamsters are vulnerable to an illness called wet tail disease. It causes bacteria in the intestines that lead to diarrhea and loss of appetite. A hamster with this illness needs to be taken to a small animal veterinarian for care.
Population
The population of wild Syrian hamsters is unknown. But biologists believe their population is decreasing and they’re listed as vulnerable.
View all 133 animals that start with TTeddy Bear Hamster FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a teddy bear hamster?
A teddy bear hamster is also known as a long-haired Syrian hamster. These small creatures grow to 6 inches long and weigh up to 5.3 ounces. They got their name from their similarity to a teddy bear with large ears, small dark eyes, and a tiny nose. These animals have solid or mixed coat colors.
Though there are some wild hamsters in Syria, many are kept as pets.
Are teddy bear hamsters carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
They are herbivores.
Are teddy bear hamsters friendly?
Yes, teddy bear hamsters that are handled gently and talked to in a soft voice can be friendly. This is why they are such popular pets!
Are teddy bear hamsters aggressive?
No, they don’t have an aggressive nature.
Do teddy bear hamsters bite?
Like other hamsters, teddy bear hamsters can bite. They are especially prone to bite if they feel frightened or caught by surprise. As a note, hamsters have poor eyesight. Consequently, it’s best to talk to a pet hamster to let it know you’re there before trying to touch or handle it.
How long do teddy bear hamsters live?
The lifespan of this hamster is 2 to 3 years. Of course, some live longer.
How to take care of a teddy bear hamster?
When you own a pet hamster you’re responsible for providing it with excellent care. This hamster can live in a 10 or 20-gallon aquarium with a wire lid to keep it safe. You may want to get a lock for the lid so the hamster can’t climb up to push it open. There are also quality wire cages measuring at least 1 foot wide by 2 feet long for this pet. The cage should be filled with shredded paper or aspen bedding that is 3 or 4 inches deep. Remember this animal likes to burrow!
Put fresh food and water in its cage once each day. Hamsters sometimes play with wheels or chew toys in their cage. They are nocturnal so don’t be surprised if you hear lots of digging and movement at night.
A teddy bear hamster’s cage should be thoroughly cleaned with mild soap and hot water once a week to prevent bacteria growth.
Where can I buy a teddy bear hamster?
Teddy bear hamsters are sold in pet shops. Also, sometimes small animals are given to local animal shelters by people who aren’t able to keep them. Teddy bear hamsters are sometimes available for adoption at animal shelters.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Cool Green Science / Accessed September 2, 2021
- Wikipedia / Accessed September 2, 2021
- PetMD / Accessed September 2, 2021
- bechewy / Accessed September 2, 2021
- Hamster Guru / Accessed September 2, 2021