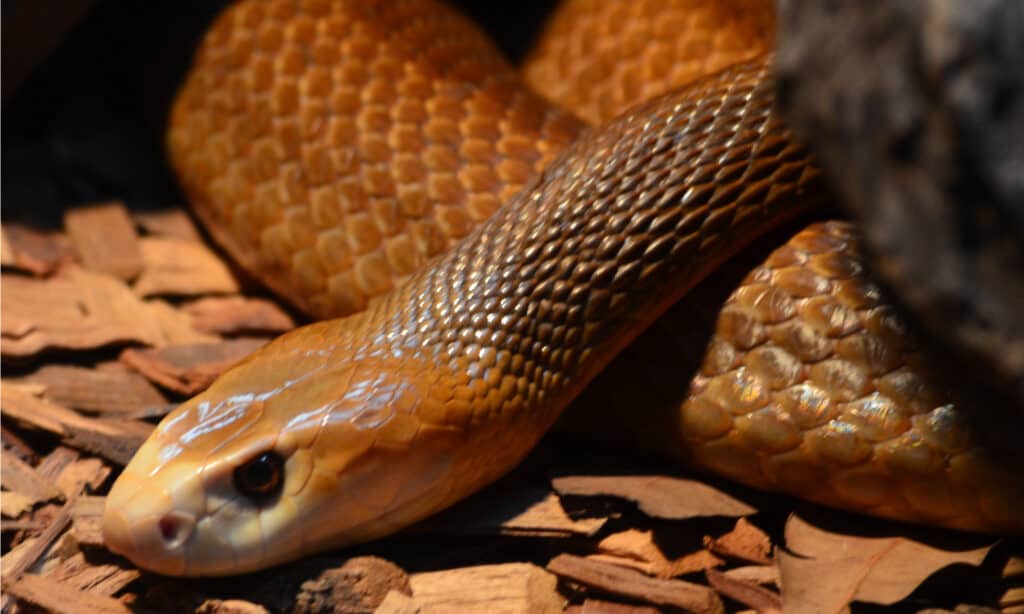
Coastal Taipan
Oxyuranus scutellatus
The venom in its bite starts to have adverse effects on a human within 30 minutes
Advertisement
Coastal Taipan Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Squamata
- Family
- Elapidae
- Genus
- Oxyuranus
- Scientific Name
- Oxyuranus scutellatus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Coastal Taipan Conservation Status
Coastal Taipan Facts
- Prey
- Mice, bandicoots, rats, birds
- Name Of Young
- hatchlings or snakelets
- Fun Fact
- The venom in its bite starts to have adverse effects on a human within 30 minutes
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Keeled (ridged) scales
- Distinctive Feature
- White belly with orange spots
- Habitat
- Dry woodlands, rainforests, and grassy slopes
- Diet
- Omnivore
Coastal Taipan Physical Characteristics
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Length
- 6 - 9.5 feet
- Venomous
- Yes
- Aggression
- Medium
View all of the Coastal Taipan images!
It’s known as the third most venomous snake in the world.
The coastal taipan is an Australian snake known for its potent venom. It lives on a diet of rats, mice, bandicoots, and birds. Dry woodlands, rainforests, and grassy slopes are all habitats of this snake. The average length of a coastal taipan is around six feet, but they can grow as long as nine and a half feet. Though an adult coastal taipan is not threatened by predators, a baby is vulnerable to goannas and hawks.

4 Amazing Facts About the Coastal Taipan
- A female lays 3 to 20 eggs in a hollow log or a hole
- A baby coastal taipan measures 12 to 13 inches in length and has strong venom
- The venom in its bite starts to have adverse effects on a human within 30 minutes
- Its scales turn darker in the wintertime in order to absorb more sunlight so the snake can stay warm
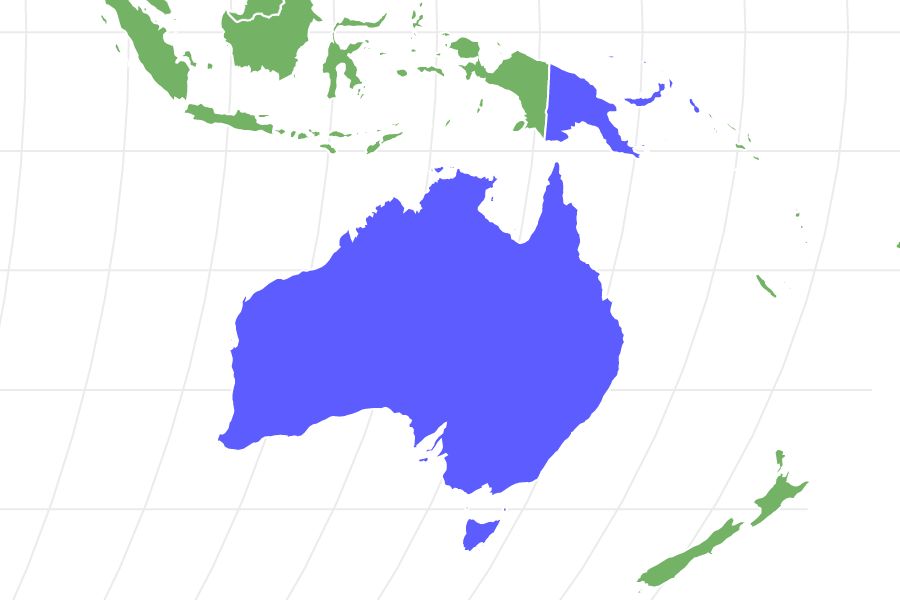
Where to Find Coastal Taipan
This is an Australian snake. Look at a map and you’ll see its territory covers a large area of the Australian coastline. It extends across the coastlines of Western Australia, Queensland, Victoria, the Northern Territory, and New South Wales. They also live on the southern coast of Papua New Guinea.
These snakes dwell in dry woodland areas, rainforests, and on grassy slopes in temperate to tropical regions.
Coastal taipan snakes are active during the breeding season extending from August to December.

Coastal taipans are native to Australia and New Guinea.
©stefan seiden/Shutterstock.com
Scientific Name
Oxyuranus scutellatus is the scientific name of a coastal taipan. It’s also known as the common taipan. Its scientific name is Latin meaning sharp-tailed serpent with shield-like scales. The word Taipan means, “boss.” This boss can strike very quickly with potent venom!
It’s in the Elapidae family and the Reptilia class.
Species
The coastal taipan has two subspecies:
• Oxyuranus scutellatus , or coastal taipan, found along the northeastern coast of Queensland, Australia.
• Oxyuranus scutellatus canni, also known as the Papuan taipan, is found on the southern coast of New Guinea.
Evolution
Fossil records show that snakes first appeared during the Cretaceous period – although they often retained their hind limbs. The earliest true snake fossils come from the marine simoliophiids, the oldest being Hassiophis tereasanctus, dated between 112 and 94 million years ago.
Scientists believe that snakes descended from lizards. Pythons and boas, the most primitive snakes, have vestigial hind limbs and some remnants of a pelvic girdle, appearing as horny projections.
Many modern snakes originated during the Paleocene, alongside the radiation of mammals that occurred after the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs. The expansion of grasslands in North America led to a major radiation of snakes. During the Miocene, the number of snake species increased with the first vipers and elapids and the diversification of Columbridae.
Population and Conservation
Conservationists at the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species report this snake’s population as stable. In fact, it’s described as common in some regions. Its conservation designation is Least Concern.
Appearance and Description
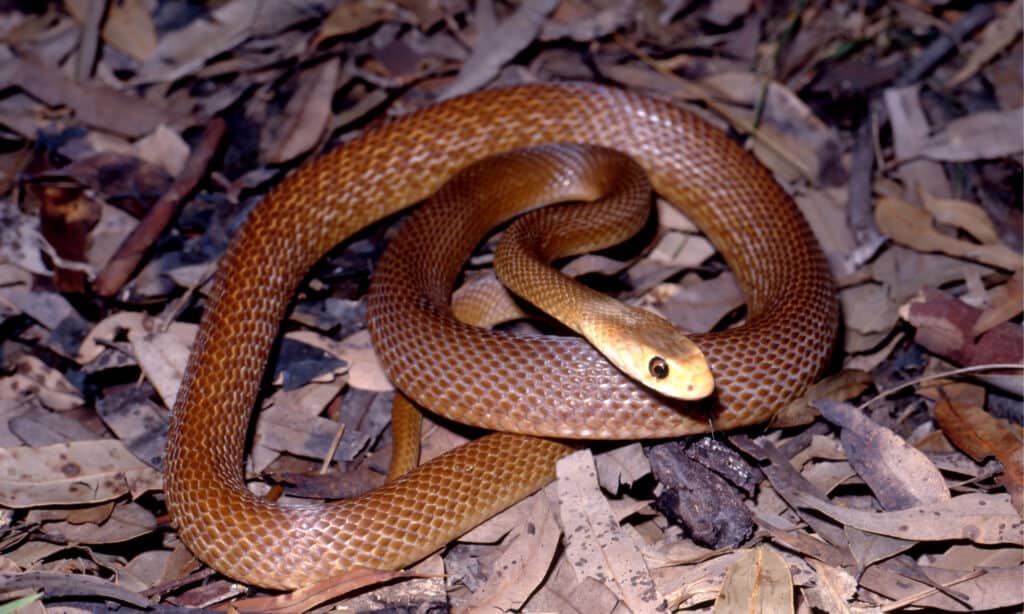

The scales of the coastal taipan are keeled (ridged).
©iStock.com/Ken Griffiths
The scales of the coastal taipan are keeled or ridged. Its color can be brownish-red, tan, or yellow in tone. Its belly is white with orange spots. This snake’s color changes with the seasons. In the winter, its scales become darker, and they fade in the summertime. Darker scales absorb more sunlight and warmth in the winter whereas lighter-colored scales reflect sunlight and heat to keep the snake cooler.
This Australian reptile has a very long slender body with a whip-like, narrow tail. Its average length is six feet but can grow as long as nine and a half feet. Males are usually larger than females.
The coastal taipan snake’s head is wider than the rest of its body. It has a narrow, somewhat angular snout. Its eyes are brownish orange with round pupils. This snake is known to have excellent vision.
How to identify a coastal taipan:
- Keeled scales
- Brownish red, tan, or yellowish in color
- White belly with orange spots
- Narrow snout
- Brown eyes with round pupils
Reproduction and Lifespan
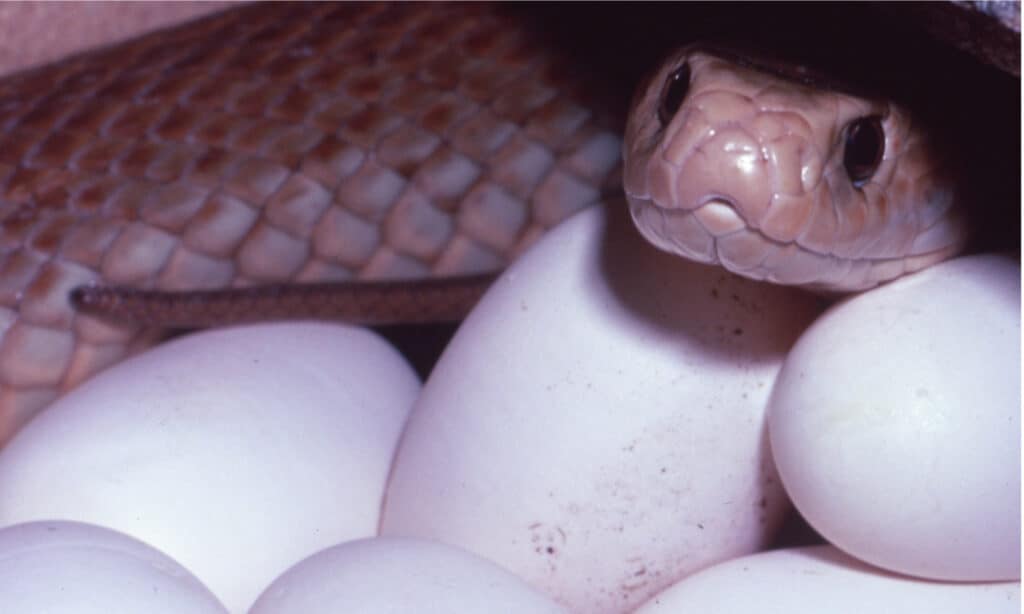

Coastal taipan lay 3 to 20 eggs in a hollow log or a hole.
©iStock.com/Ken Griffiths
After a breeding season that occurs between August and December, the female coastal taipan lays a clutch of 3 to 20 eggs. Newly hatched snakes emerge after 60 to 80 days – already 12 inches in length. The young snakes grow quickly – reaching a length of over 3 feet by their first birthdays. Males reach sexual maturity at around 16 months of age – while females are not able to breed until around 28 months. Coastal taipans tend to live 10 – 15 years in the wild or in captivity.
Coastal Taipan vs. Black Mamba
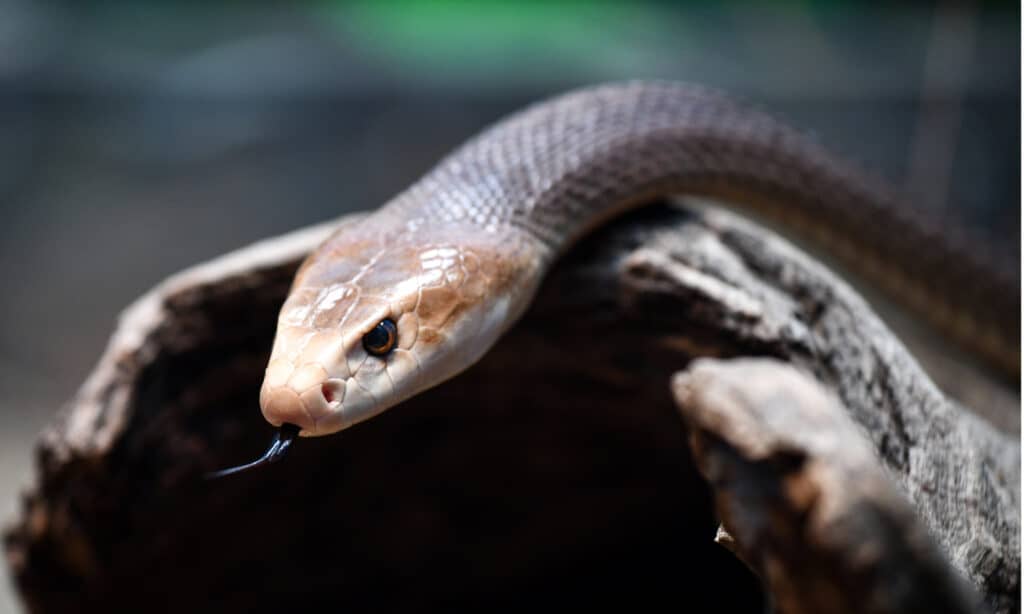

The coastal taipan snake’s head is wider than the rest of its body.
©iStock.com/ROBERT STYPPA
The coastal taipan and the black mamba snake are often compared and have several things in common. One of the first similarities between them is they both have potent venom and they both eat large quantities of rodents. One difference in the black mamba’s diet is that it includes bats.
Another similarity between these snakes is they are active during the day. In addition, conservationists list both snakes as Least Concern with stable populations.
With all of those similarities, there are some notable differences between these two snakes. One difference relates to where they live. While coastal taipan snakes live in Australia and Papua New Guinea, black mambas live in Africa.
Coastal taipan snakes can be as long as 9.5 feet but are usually around six feet. Alternatively, the typical size of a black mamba is around seven feet long. So, when you look at the average size, the black mamba is the winner in that category.
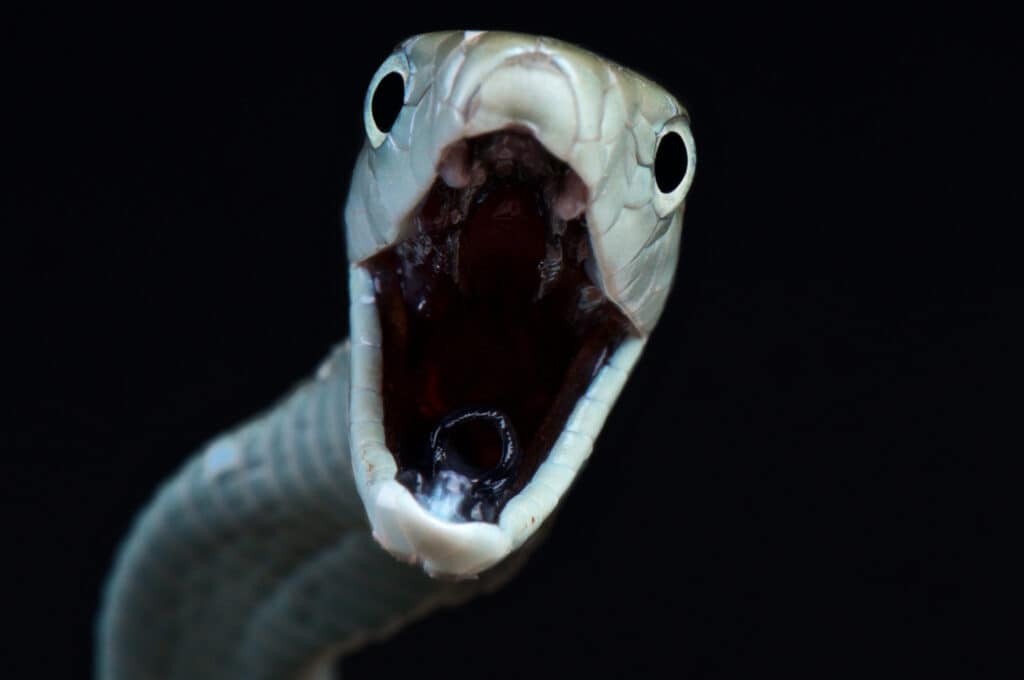

The interior of a black mamba’s mouth is an inky black void seen by its prey during their last moments.
©reptiles4all/Shutterstock.com
One of the most intriguing facts about a black mamba has to do with the interior of its mouth. It’s black which is unusual for a snake. So, the inside of this snake’s dark mouth is only seen by prey or a human who has an unfortunate encounter with this reptile!
Biologists report the venom of a black mamba is so dangerous it results in death 100 percent of the time if the bite goes untreated. This is the same for coastal taipan snakes. However, deaths as a result of a coastal taipan’s bite are rare due to an effective, readily available antivenom.
Doctors suggest there are more deaths from a black mamba’s bite because of the difficulty of getting the injured person to the hospital in a timely way. Though there is an antivenom for the black mamba’s bite, not all hospitals in Africa have it available to patients.
Diet

Coastal taipans possess superior eyesight and can often be seen slithering with its head up – looking for prey. When prey is found, the snake freezes in place for a second before darting forward while delivering several quick bites. Prey is allowed to stagger away until they are immobile to prevent injuries to the snake.
How Dangerous is the Coastal Taipan?
The bite of a coastal taipan is extremely venomous. Keep in mind these snakes want to avoid encounters with humans but will strike if they feel trapped or are stepped on.
A person who is bitten must be taken to the hospital for antivenom immediately. Dizziness, convulsions, nausea, and other symptoms start quickly after a bite.
While waiting for an ambulance, put a pressure bandage on the bite wound and make a splint to keep the limb immobile. Try to keep the person as still and calm as possible.
Behavior and Humans
Despite having potent venom, coastal taipan snakes are known to retreat from potential encounters with humans. People are bitten usually because they accidentally step on this snake or reach into an area without noticing its presence.
View all 235 animals that start with CCoastal Taipan FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are coastal taipan snakes venomous?
Yes. One of the most amazing facts about this snake is it’s the third most venomous in the world. Even a newly hatched, baby coastal taipan snake has potent venom!
How do coastal taipan snakes hunt?
They use their excellent sense of smell and sight to track down prey. When this reptile sees a mouse or bandicoot, it freezes for a moment, then strikes. This snake is known for its ability to dart forward and bite its prey several times within seconds. Furthermore, it can release a large amount of venom within a short duration of time.
It allows its prey to start moving away, but the small animal doesn’t get far due to the powerful venom in its system. After the prey dies, the coastal taipan swallows it.
The snake allows it to move away because some of its prey such as rats and large birds can still scratch, bite, or otherwise injure the snake though they are close to death. Despite being very dangerous, this snake takes care to avoid injury from even the smallest types of prey.
Are coast taipan snakes aggressive?
No, they avoid confrontations with humans.
Where do coastal taipan snakes live?
Looking at a map of Australia you’ll see these snakes are found in Western Australia, Queensland, Victoria, the Northern Territory and New South Wales. They’re in Papua New Guinea as well.
What do coastal taipan snakes eat?
They eat rats, mice, bandicoots, and birds.
6 - 9.5 feet
They are an average of around six feet but can be as long as 9.5 feet.
Is the coastal taipan deadly?
Yes, this snake’s bite can be deadly if not treated right away with antivenom.
Is the coastal taipan poisonous?
Yes, they are poisonous.
Where can the coastal taipan be found?
The habitat of this snake includes dry woodlands, rainforests, and grassy hillsides. They are sometimes found hiding in piles of leaf debris or beneath logs.
What is the difference between the inland taipan and coastal taipan?
The main difference between these snakes is their location on a map of Australia. The coastal taipan lives on the coast of Australia whereas the inland taipan lives in the central and eastern parts of Australia.
Is the coastal taipan the most venomous snake?
No. It’s the third most venomous snake worldwide. Still in the top three!
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Australian Museum, Available here: https://australian.museum/learn/animals/reptiles/coastal-taipan/
- Monaco Nature Encyclopedia, Available here: https://www.monaconatureencyclopedia.com/oxyuranus-scutellatus/?lang=en
- The Animal Facts, Available here: https://www.theanimalfacts.com/reptiles/coastal-taipan/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coastal_taipan
- Reptile Database, Available here: http://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/species?genus=Oxyuranus&species=scutellatus&search_param=%28%28search%3D%27coastal+taipan%27%29%29
- IUCN Red List, Available here: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/42493166/42493177
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mamba
- St. John SW, Available here: https://www.stjohnnsw.com.au/secure/downloadfile.asp?fileid=1004638