Eastern Lowland Gorilla
Gorilla Berengei Graueri
Less than 5,000 in the wild!
Advertisement
Eastern Lowland Gorilla Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Primates
- Family
- Hominidae
- Genus
- Gorilla
- Scientific Name
- Gorilla Berengei Graueri
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Eastern Lowland Gorilla Conservation Status
Eastern Lowland Gorilla Facts
- Main Prey
- Leaves, Seeds, Herbs
- Habitat
- Tropical forest and jungles in mountainous regions
- Predators
- Human, Leopard
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 1
View all of the Eastern Lowland Gorilla images!
“The largest primates in the world.”
One of the largest subspecies of the Great Apes, the Eastern lowland gorilla is one of two species of a gorilla living in Africa. They are an endangered species, with recent estimates placing the count at about 5,000 individuals left in the wild. These gorillas are vulnerable to poaching, and they fall victim to the results of civil unrest in their territory.
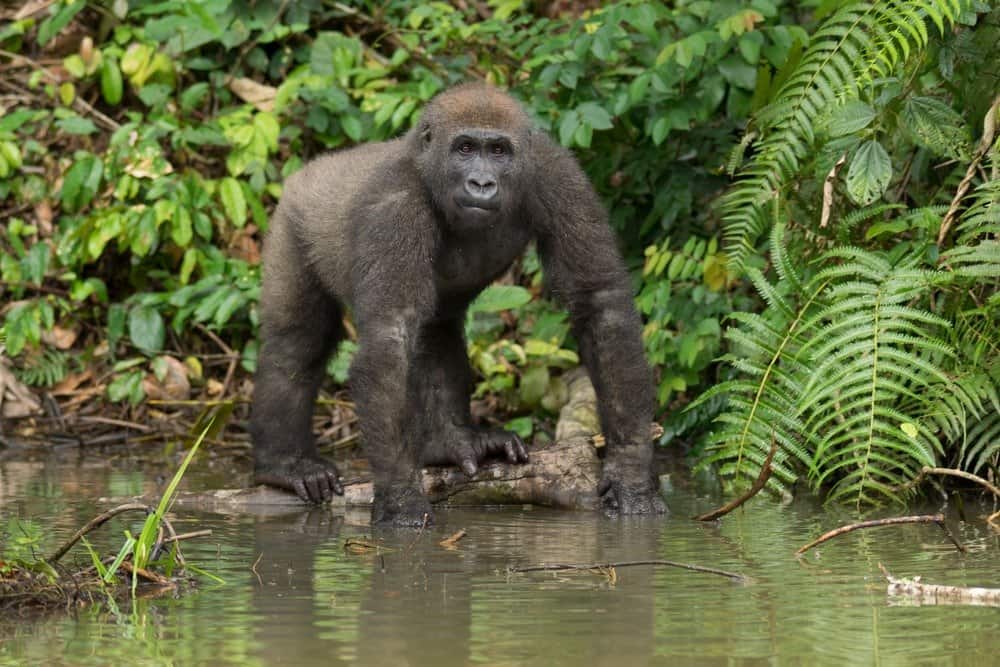


Eastern lowland gorillas are one of the most intelligent species of primates.
©Vaclav Sebek/Shutterstock.com
Facts About Eastern Lowland Gorillas
- Eastern lowland gorillas are the largest primates in the world.
- They are also known as Grauer’s gorilla after the scientist who discovered them.
- They are one of the most intelligent species of primates.
- They are the second most endangered subspecies of gorillas.
- A group of Eastern lowland gorillas is called a troop, and they are led by a large adult male known as a silverback gorilla.
Scientific Name
Eastern lowland gorillas are also known as Grauer’s gorilla, after the Austrian scientist Rudolph Grauer who discovered them in the early 1900s. Grauer is where the second half of this subspecies’ scientific name, Gorilla Berengei Graueri, comes from. Berengei means Kivu highlands, so their scientific name means “Grauer’s gorilla of the Kivu highlands.” They are in the phylum Chordata and are also considered primates. Members of the Chordata phylum are called chordates, and this Phylum includes all vertebrates.
Evolution
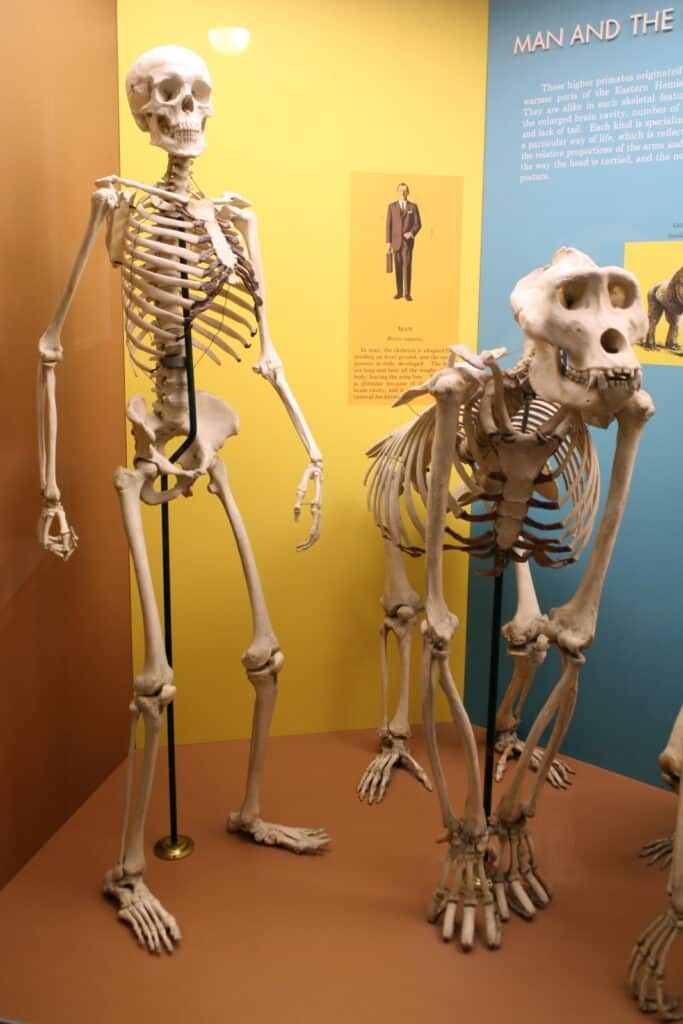

Human gene sequences differ from gorilla sequences by only 1.6%
©Cliff from Arlington, Virginia, USA, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons – Original / License
Although not much is known about the evolution of gorillas, they are closely related to humans and chimpanzees. They all diverged from a common ancestor about 7 million years ago. Human gene sequences differ from gorilla sequences by only 1.6% on average.
Gorillas were previously thought to be a single species with three subspecies (western lowland, eastern lowland, and mountain gorillas), but it is now agreed that there are two main species, the western gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) and the eastern gorilla (Gorilla beringei), and they each have two subspecies. Western and eastern gorillas split into two groups around 77,700 years ago.
Appearance
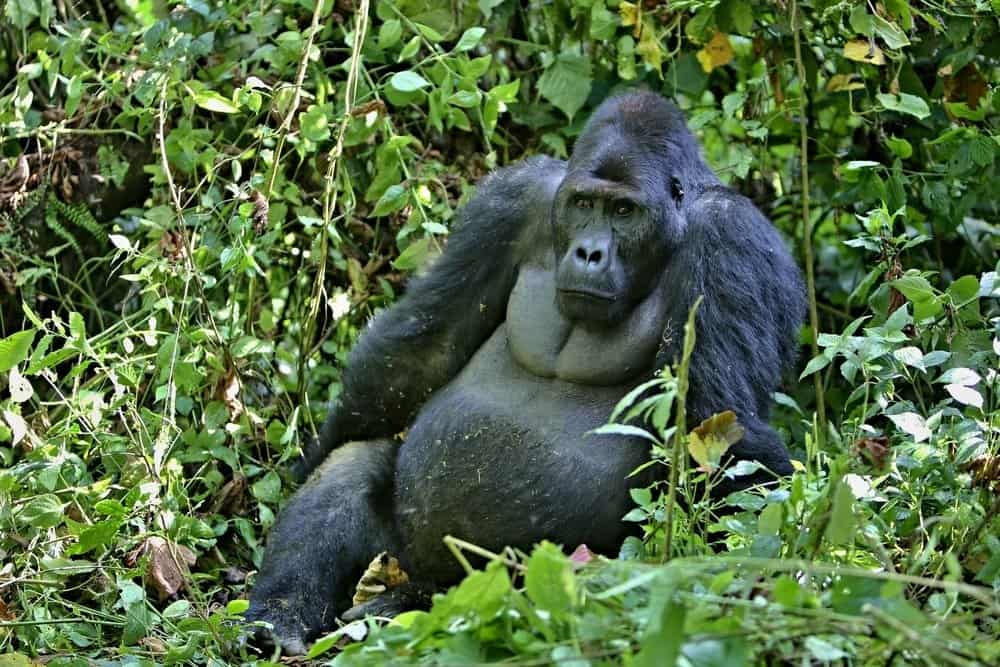

Eastern lowland gorillas are the largest species of primate on earth.
©PhotocechCZ/Shutterstock.com
These gorillas are massive, as they are the largest species of primate on earth. Males are typically larger than females, and the species weighs in at about 450-500 lbs. That means that the Eastern lowland gorillas weigh a little less than a vending machine. These gorillas can be 5-6 feet tall. They have large heads in comparison to the rest of their bodies, as well as strong jaws and teeth. Like other gorillas, they have a thick coat of dark fur save for their faces and hands. They prefer to walk around on their knuckles.
For added protection and warmth, gorillas have a thick layer of dermis and epidermis or inner and outer layers of skin. They also have a significant amount of fat on their bodies.
Behavior
Gorillas are social animals, and the Eastern lowland gorilla is no exception. The distribution of gorillas is in tight-knit family groups called troops or bands. These troops travel, feed, and raise their young together. The troops are led by a large male gorilla, called a silverback. They also contain two or three female gorillas and their young, and can also include a few subordinate male gorillas. Though the troops are usually small, researchers have recorded groups as large as 30 individuals. Rarely, there are two silverback leaders in a group.
Gorillas spend most of their days eating and, contrary to popular belief, are not aggressive or territorial creatures. Though the silverbacks do have a dominant leadership position, which includes mating with females and being alert to threats, they are also in charge of practical decisions. These include deciding where the group feeds, travels and sleeps.
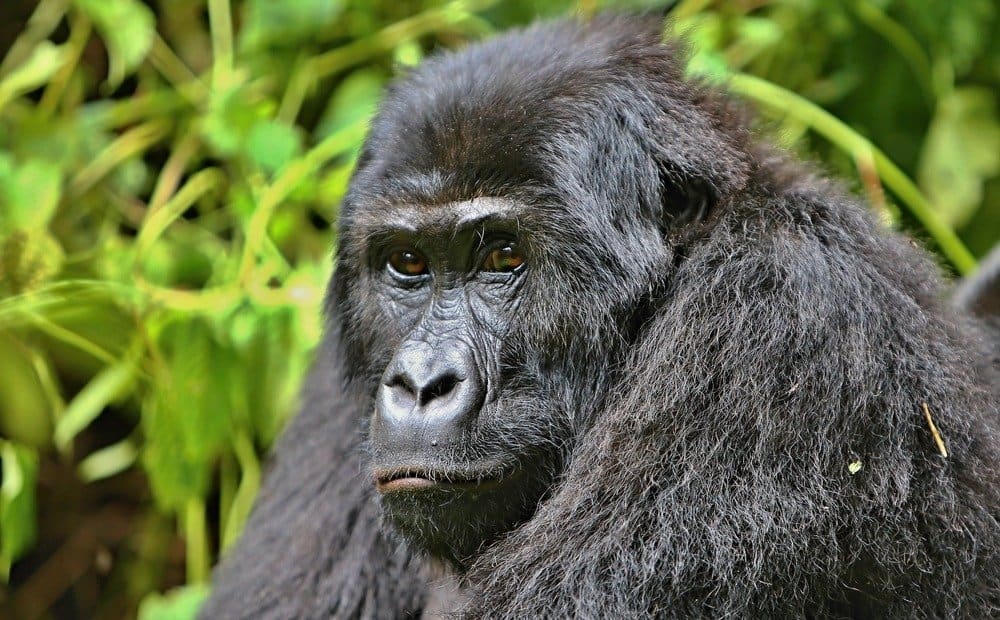

Gorillas live in family groups called troops or bands.
©PhotocechCZ/Shutterstock.com
These apes are usually quiet, but they are capable of vocalizing in many different ways. Over 25 various vocalizations have been recorded. Eastern lowland gorillas communicate using hoots, growls, barks, screams and laughs. Each of these has a distinct meaning. Gorillas are one of the most intelligent species of primates — they can even be taught sign language and have been known to use tools to better access food.
Habitat
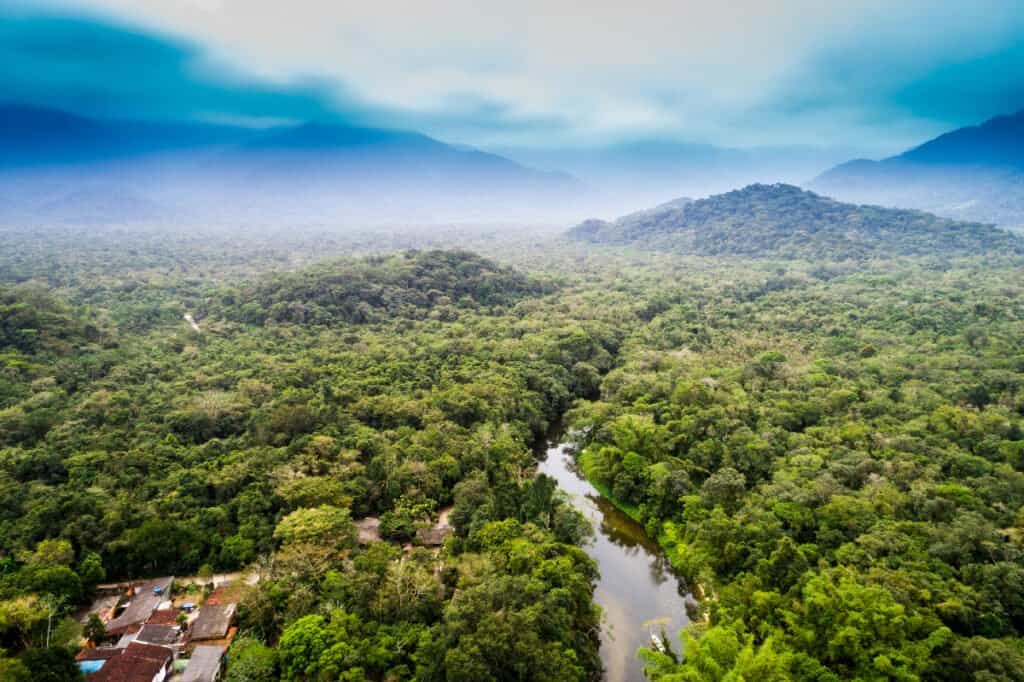

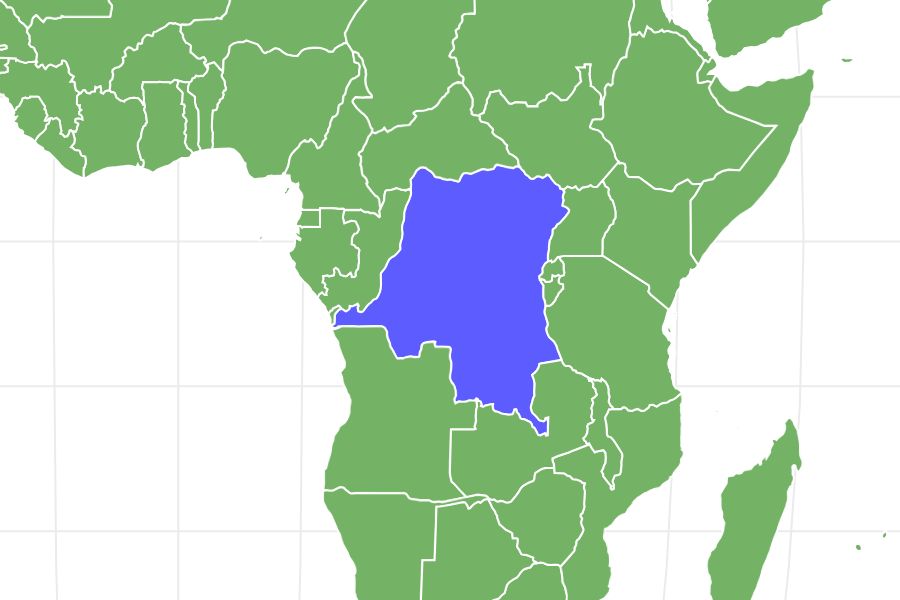
Eastern lowland gorillas live in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
©iStock.com/gustavofrazao
This species of gorilla lives in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). They thrive in tropical lowlands and rainforests which have decreased drastically in the last few decades. The distribution of gorillas is also much more sparse because of habitat fragmentation. They used to inhabit a range of about 8,100 square miles, the size of the state of Massachusetts. They now inhabit around 4,600 square miles. Many national parks cover Eastern lowland gorilla habitats, such as the Kahuzi-Biega National Park and the Maiko National Park. There are also a few wildlife reserves dedicated to preserving gorilla habitats.
Diet

Eastern lowland gorillas are omnivores, enjoying both a plant-based and an insect-based diet. They mostly eat fruits but also consume berries, leaves, and nuts. As for insects, the Eastern lowland gorilla prefers termites and ants. Occasionally, these gorillas go after small rodents or lizards. They have been known to travel great distances in search of food.
Their powerful jaws allow them to eat fibrous and tough vegetation. They also rarely drink water directly, as most of the water they consume comes from the plants they eat. Adult gorillas need to eat about 18kg, or about 40 lbs, of food per day.
Predators and Threats
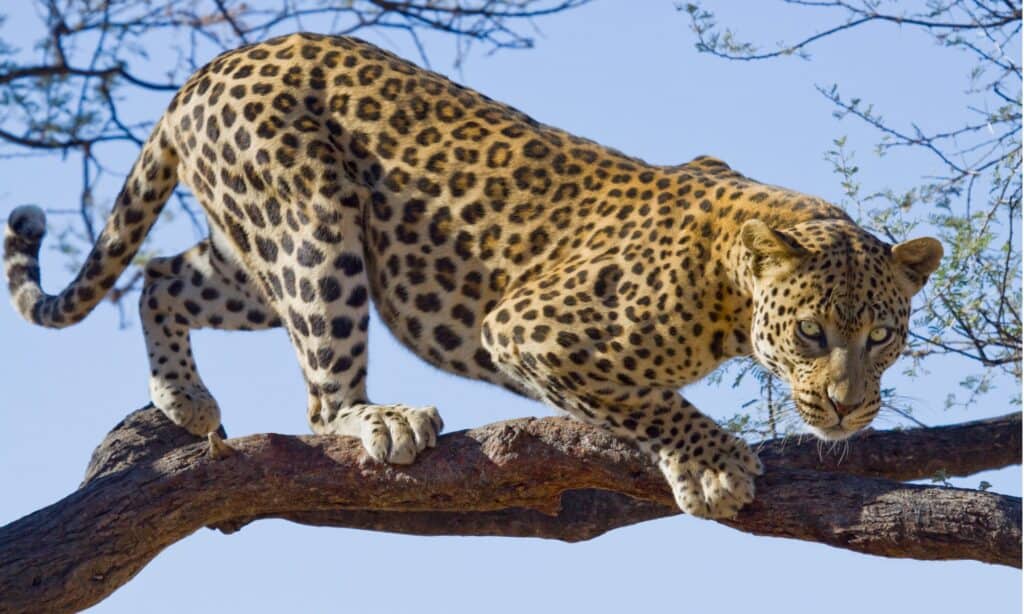

Leopards sometimes prey on gorillas but humans are their biggest threat.
©lightstock/Shutterstock.com
A fully grown adult gorilla faces few threats from predators. Only larger animals, such as leopards and crocodiles, pose a threat to adult Eastern lowland gorillas.
Humans are by far the biggest threat to this animal. Habitat loss due to mining and civil unrest in the DRC has impacted this species. They also fall victim to poaching, even in national parks meant to protect them. Rebels and poachers invade these areas to hunt gorillas. Organizations like the World Wildlife Fund have intervened to help the park regain control of the land, but continued civil unrest in the area makes conservation difficult. The eastern lowland gorilla is considered an endangered species according to the Red List of the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
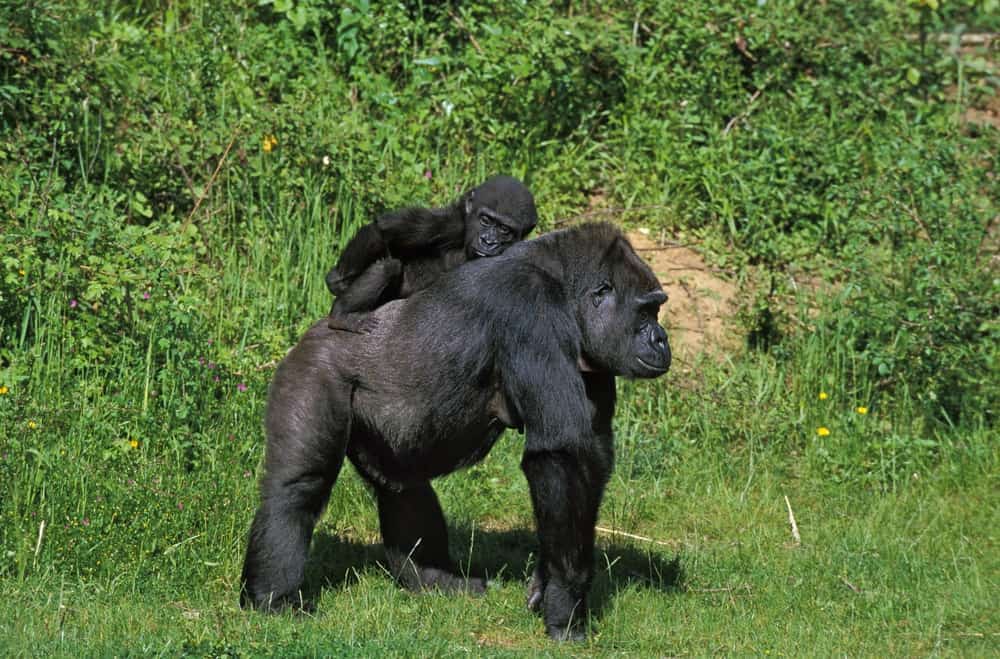

Female gorillas usually give birth to one baby at a time.
©slowmotiongli/Shutterstock.com
Once they are old enough, about half of all male gorillas will leave their birth group when they reach sexual maturity, around 15 to 20 years of age. They travel with other male gorillas or sometimes travel alone until they establish a harem of females. Like other gorilla species, the male silverback Eastern lowland gorilla routinely mates with the females in the troop and is the only male allowed to do so. They form strong bonds with the female members so that the females are less likely to leave. Silverback males usually stay with the same group of females for life, unless they are overtaken by a competing male. Fights between male gorillas for rule over the harem are intense and may end in death. Eastern and Western varieties of lowland gorillas cannot mate with one another.
Young gorillas are called babies. Females have a gestation period of around 8.5 months. Babies will sleep in the same nest as their mother for the first three years of their life, and continue to stay with the group until they reach sexual maturity. Sons of the male silverback can sometimes take over the group later in their lives. Females often only give birth to one young at a time, and infant mortality rates among young gorillas are very high. Babies can crawl around on their own when they reach 9 weeks old, and walk when they are 35 weeks old.
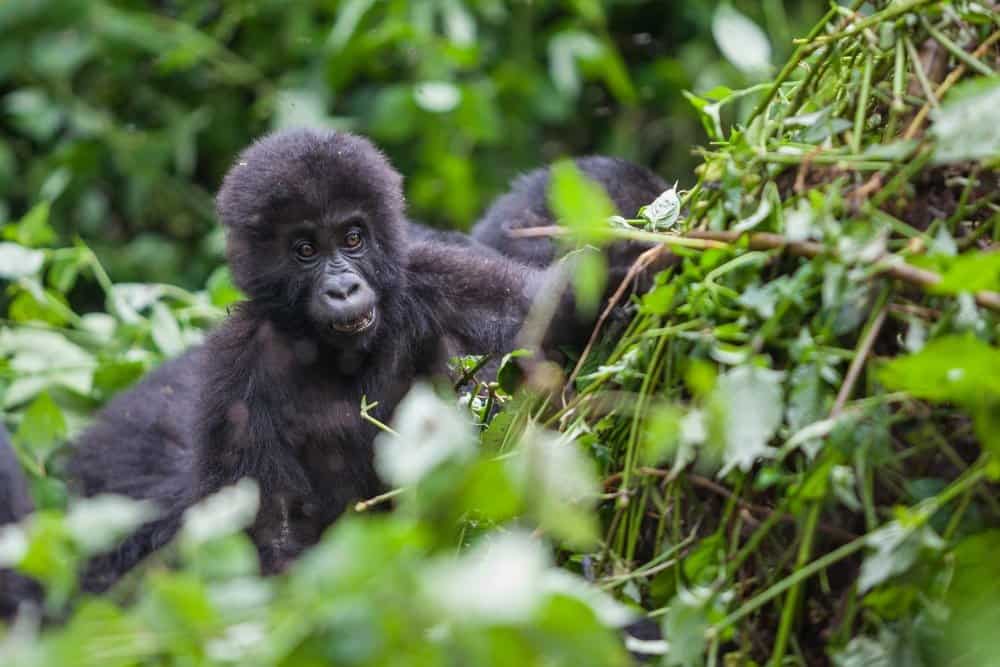

Baby gorillas sleep in the nest with their mothers until they are three years old.
©Katja Tsvetkova/Shutterstock.com
In the wild, eastern lowland gorillas can reach 30-40 years of age. In captivity, gorillas can live to be as old as 60.
Population
Over the last 30 years, the population of Eastern lowland gorillas has gone down by over 50%. It is estimated that only around 5,000 individuals remain in the wild. Accurate population counts are hard to achieve due to the ongoing civil war in the DRC.
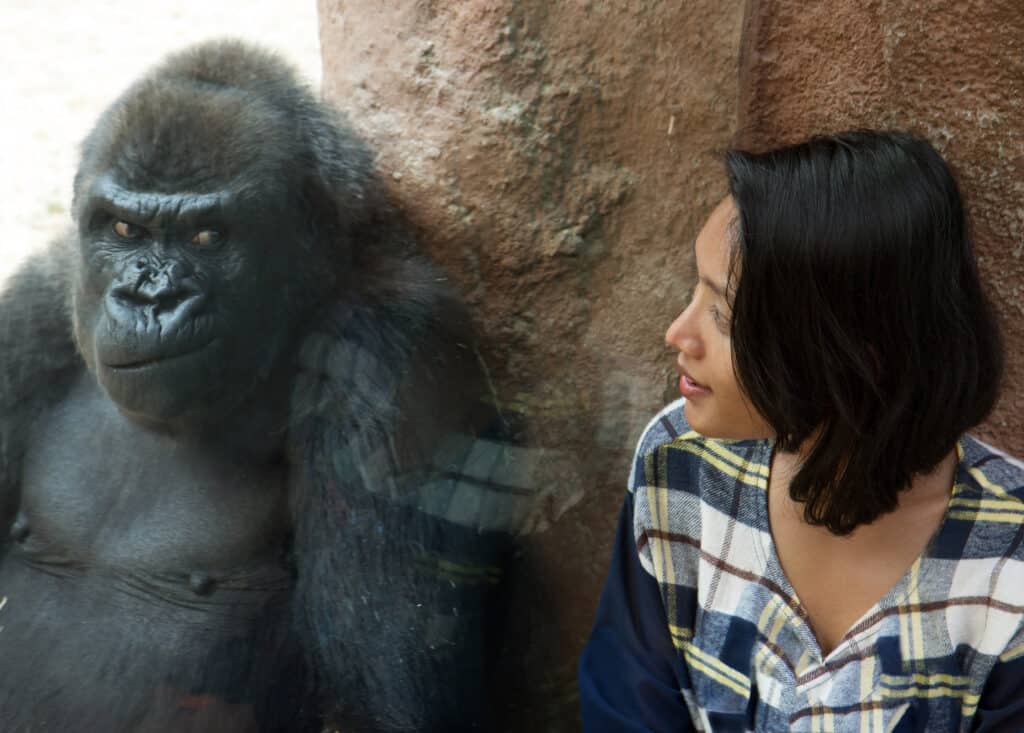

Most gorillas in zoos are the less endangered western lowland gorillas.
©Milkovasa/Shutterstock.com
In the Zoo
Most gorillas found in zoos are western lowland gorillas, which are not as endangered as their eastern cousins. Some zoos, such as the San Diego Zoo, have conservation programs in central Africa that aid in protecting all species of gorillas. The San Diego Zoo also runs a recycling program for cell phones, which contain metals that are mined for in Eastern lowland gorilla territory. This program helps prevent new metals from being mined, which reduces habitat loss and the hunting of the species.
There are only two Eastern lowland gorillas in captivity, both of which are females. They live at the Antwerp Zoo in Belgium and are named Victoria and Amahoro.
View all 120 animals that start with EEastern Lowland Gorilla FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why is the Eastern lowland gorilla endangered?
Eastern lowland gorillas are threatened by habitat loss due to civil war, as well as the mining of metals to produce cell phones and other electronics. They also fall victim to poaching, as well as illegal animal trafficking. Like most forest animals, deforestation also presents a threat to the eastern lowland gorilla habitat.
Why conservation efforts are being made to save the Eastern lowland gorilla?
Many zoos, such as the San Diego Zoo, have conservation efforts in gorilla territories in central Africa. Organizations like the World Wildlife Fund have also aided national parks in gaining better control over their land to protect gorillas from poachers.
How many Eastern lowland gorillas are left?
The distribution of eastern lowland gorillas is very small, with recent counts placing them at less than 5000 individuals left in the wild. However, accurate population counts are difficult to obtain due to civil unrest in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Are Eastern lowland gorillas carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
Though eastern lowland gorillas mostly eat fruit and leaves, they are considered omnivores as they also eat termites, ants, and other insects.
Why are gorillas so strong?
Gorillas are strong because they have a high ratio of muscle mass to the rest of their bodies. This large muscle mass aids them in finding mates. Their teeth and jaws are powerful so that they can easily rip through the tough leaves and vegetation of their diet.
What is the Eastern lowland gorilla's scientific classification?
Eastern lowland gorillas are in the kingdom Animalia, the phylum Chordata, the class Mammalia, the order Primates, the family Hominidae, and the genus Gorilla. Their scientific name is Gorilla Berengei Graueri.
What Kingdom do Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum to Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to the family Hominidae.
What order do Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to the order Primates.
What genus do Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas belong to the genus Gorilla.
What type of covering do Eastern Lowland Gorillas have?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas are covered in Hair.
In what type of habitat do Eastern Lowland Gorillas live?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas live in tropical forests and jungles in mountainous regions.
What is the main prey for Eastern Lowland Gorillas?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas eat leaves, seeds, and herbs.
What are some predators of Eastern Lowland Gorillas?
Predators of Eastern Lowland Gorillas include humans and leopards.
How many babies do Eastern Lowland Gorillas have?
The average number of babies a Eastern Lowland Gorilla has is 1.
What is an interesting fact about Eastern Lowland Gorillas?
There are less than 5,000 Eastern Lowland Gorillas in the wild!
What is the lifespan of an Eastern Lowland Gorilla?
Eastern Lowland Gorillas can live for 35 to 50 years.
How fast is an Eastern Lowland Gorilla?
An Eastern Lowland Gorilla can travel at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.