The largest feline on the American continent!
Advertisement
Jaguar Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Carnivora
- Family
- Felidae
- Genus
- Panthera
- Scientific Name
- Panthera onca
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Jaguar Conservation Status
Jaguar Facts
- Prey
- Deer, Capybara, Tapir
- Name Of Young
- Cub
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- The largest feline on the American continent!
- Estimated Population Size
- 15,000
- Biggest Threat
- Hunting and habitat loss
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Beautiful rosetted fur pattern
- Gestation Period
- 90 - 105 days
- Habitat
- Rainforest, swamp and floodplains
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 3
- Lifestyle
- Crepuscular
- Common Name
- Jaguar
- Number Of Species
- 1
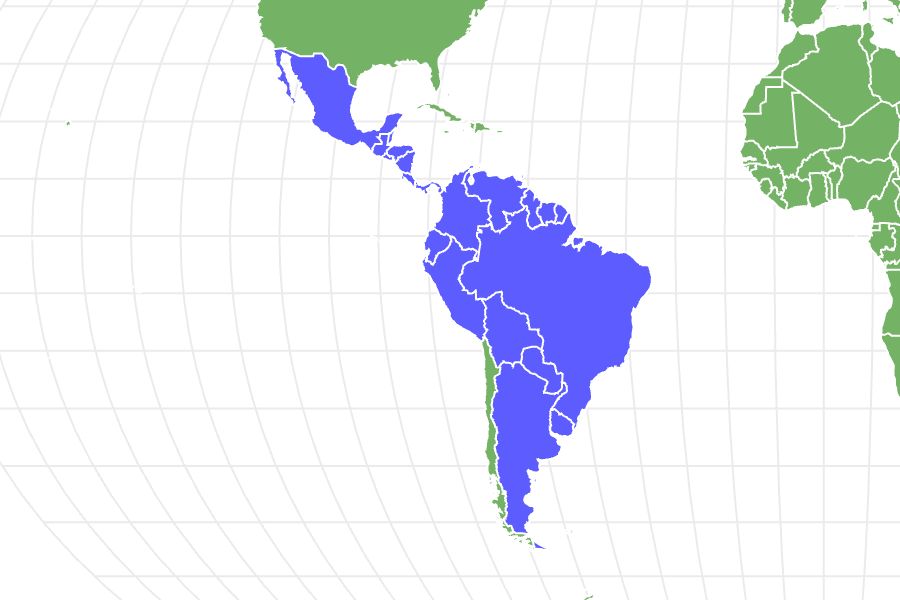
- Location
- Central and South America
- Slogan
- The largest feline on the American continent!
- Group
- Mammal
Jaguar Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Yellow
- Black
- White
- Tan
- Skin Type
- Fur
- Top Speed
- 50 mph
- Lifespan
- 12 - 15 years
- Weight
- 36kg - 160kg (79lbs - 350lbs)
- Length
- 1.1m - 1.9m (43in - 75in)
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 3 - 4 years
- Age of Weaning
- 3 months
View all of the Jaguar images!
Classification
The Jaguar is the largest feline on the American continent, and is the only one of the world’s ‘big’ cats to be found in the New World. Jaguars are close relatives to Leopards and have a number of similar characteristics including the distinctive spotted pattern on their fur. The Jaguar is the third largest cat in the world, only superseded by the Tiger and the Lion. This beautiful cat possesses great power and agility. In fact, the name Jaguar is derived from the Native American word yaguar, defined as “he who kills with one leap”. Despite their incredible power however, Jaguars have been hunted through the ages, mainly for their gorgeous fur. Although hunting for Jaguar fur is now prohibited, population numbers have declined throughout much of their natural range, with Jaguars having completely disappeared from a number of areas.

Types Of Jaguar Animals
While the official taxonomic species of the Jaguar is: Panthera onca, there are many different types of jaguar animals, from the Arizona Jaguar to the Northeastern Jaguar. A complete list of different jaguar types is found below:
- Panthera onca arizonensis (Arizona jaguar)
- Panthera onca centralis (Central American jaguar)
- Panthera onca onca (East Brazilian jaguar)
- Panthera onca palustris (South American Jaguar)
- Panthera onca veraecrucis (Northeastern jaguar)
- Panthera onca paraguensis (Paraguay jaguar)
- Panthera onca peruviana (Peruvian jaguar)
- Panthera onca goldmani (Yucatan Peninsula jaguar)
- Panthera onca hernandesii (West Mexican jaguar)
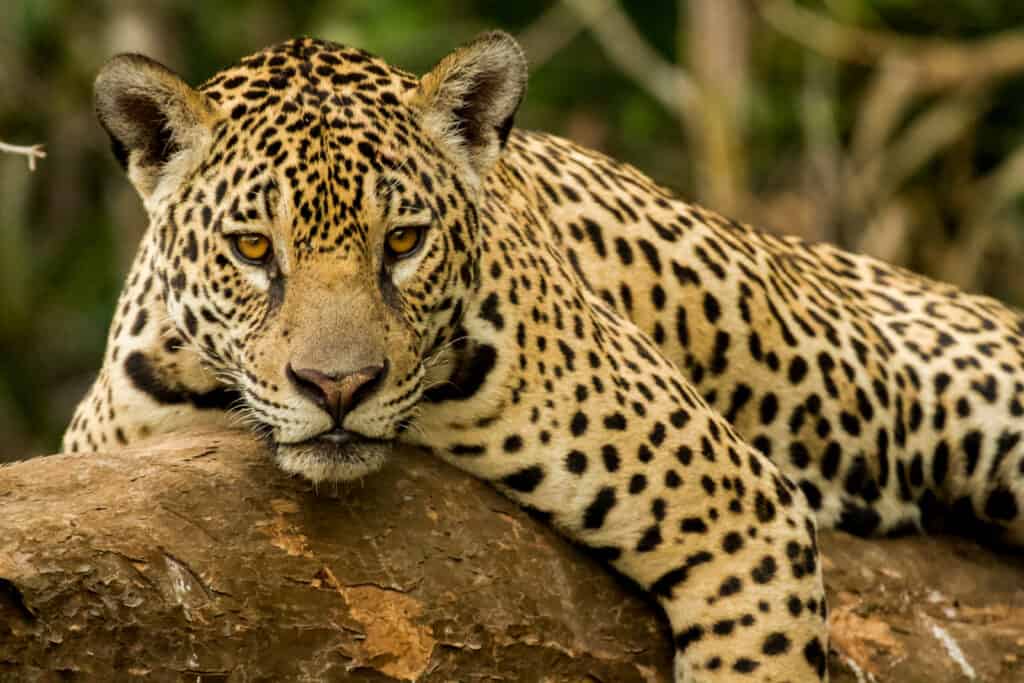

Closely relate to leopards, jaguars have multiple similar characteristics including the distinctive spotted pattern on their fur.
©Pedro Helder Pinheiro/Shutterstock.com
Evolution and History
Jaguars originated in Eurasia around 3 million years ago and slowly spread eastward and westward during the Ice Age, eventually covering areas from southern England to Nebraska to South America. Compared to their predecessors, modern jaguars are 15% smaller in size.
Both jaguars and lions share DNA from the genus Panthera, which dates back further from 6-10 million years ago. Ancestors like the European jaguar suggest it’s most closely related to the leopard.
While equally old cats like sabercats and American lions became extinct, it’s thought that Jaguars survived because of their diet. 16-21% of their diet came from hunting caimans, collared peccary, giant anteaters, wild pigs, nine-banded armadillos, and white-nosed coati. As they migrated, they came to Central America where food was abundant. These ancient, larger jaguars ate the animals aforementioned, as well as many other prey like birds, and somehow survived the Ice Age.
Anatomy and Appearance
The Jaguar is a large and muscular animal, and while very similar to the Leopard in appearance, its body is more heavy and robust. The jaguar has a large, broad head and its strong jaws earned it the title of “strongest bite” among all the large cats in the world. Jaguars tend to have a cover of either tan or dark yellow fur, dotted with darker rose-like patterns with dark spots in the middles–similar to those of a Leopard. Known as rosetting, the pattern on the Jaguar’s fur is unique to each animal. Despite its beauty, the pattern camouflages this animal in the surrounding jungle. This camouflage is vital to its survival, and Jaguars found in the rainforest are often darker in color and smaller than those found in more open areas.
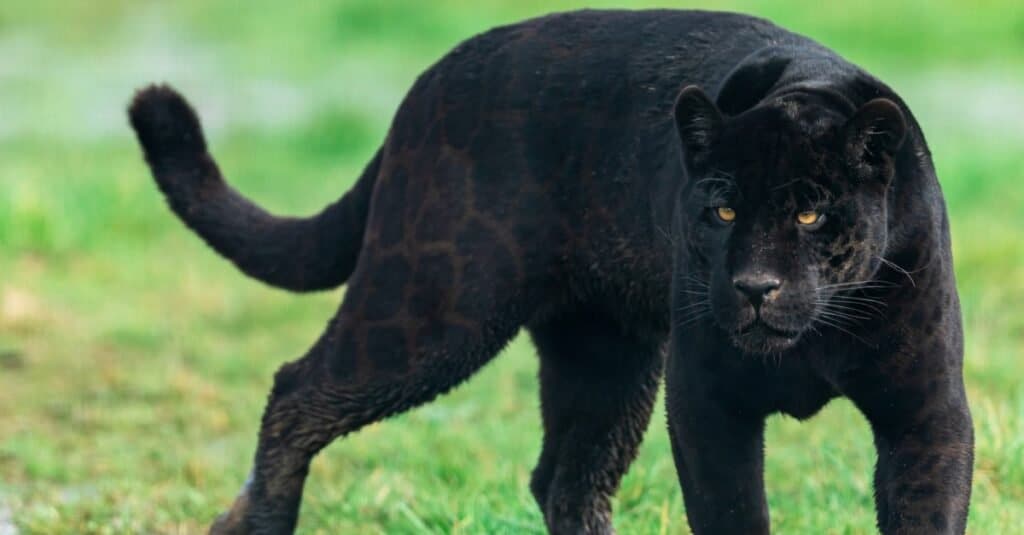

A black panther is a type of jaguar with a melanism condition.
©AB Photographie/Shutterstock.com
Distribution and Habitat
The Jaguar is indigenous to the Western Hemisphere, where it primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of Central and South America. In its history, Jaguars could be found on the entire continent, as well as some of the southern states in North America. Today they stick to remote pockets of rainforest, especially in the Amazon Basin. Jaguars prefer a moist, dense, thick, jungle habitat with plenty of cover in order to successfully hunt and ambush prey. They are nearly always found close to water and prefer either permanent swampland or seasonally flooded forests. The Jaguar has been severely affected by habitat loss throughout much of its natural range along with poachers who shoot them when they get too close to the growing Cattle ranches.
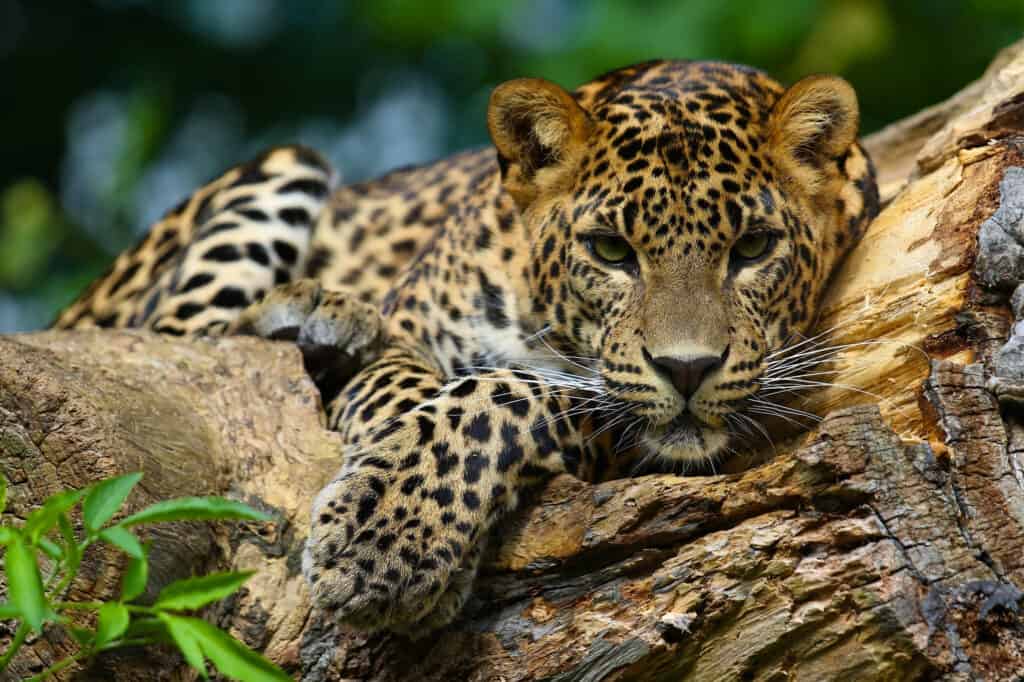

Jaguars inhabit the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, preferring thick, moist, dense jungles.
©L-N/Shutterstock.com
Behavior and Lifestyle
The Jaguar is an elusive creature, spending the majority of its time either resting in the safety of trees or hunting in dense undergrowth. It loves to be near water like floodplains or slow-moving rivers–a behavior that is rare to most members of the cat family. It’s also rare to find a jaguar in dry, desert-like places. This cat is an excellent swimmer and can reach high speeds when maneuvering through the water in pursuit of prey. The Jaguar, like many other cat species, is a solitary animal, save the first couple of years that it spends with its mother. Males are particularly territorial and although their home range will overlap those of a number of females, they will defend their patch fiercely from other males. Jaguars mark their territories with urine by scratching marks onto trees, and asserting themselves with growling vocal calls.
You can check out incredible facts about jaguars.
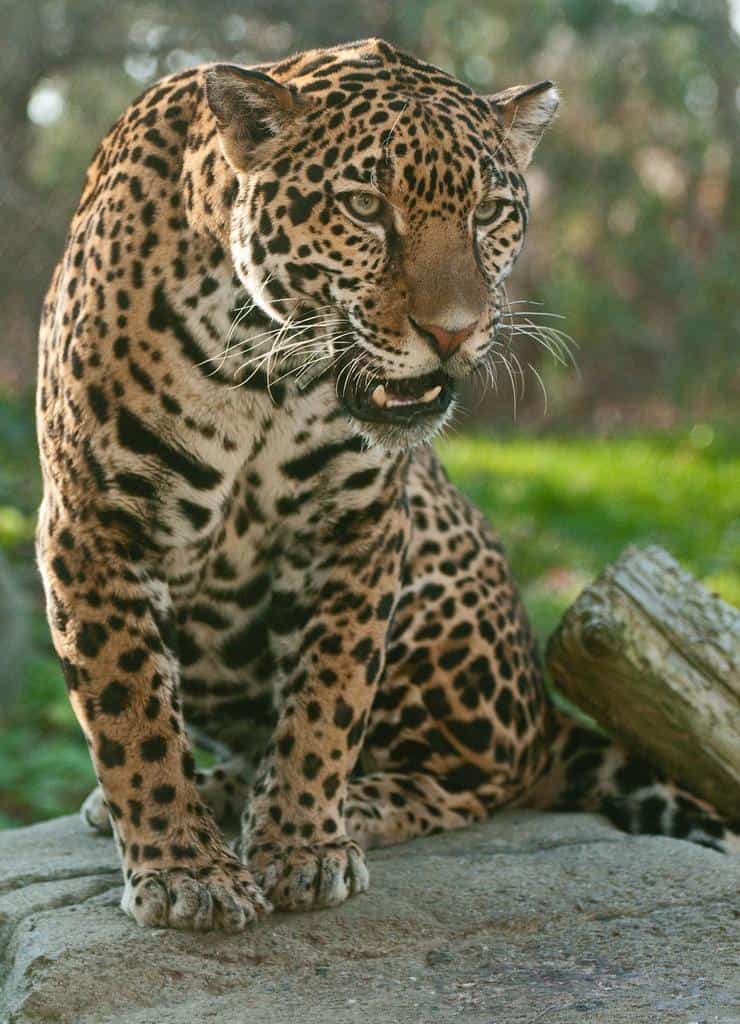

Males jaguars are particularly territorial and will defend their patch of territory fiercely from other males.
©Eric Kilby / CC BY-SA 2.0, Flickr – License
Reproduction and Life Cycles
Jaguar cubs are usually born between the months of December and March, but it’s not unusual for some litters to be born at other times of the year. When mating season occurs, the female Jaguar will make loud vocalized cries to attract a male into her territory. Female Jaguars usually give birth to two or three cubs. Once the cubs are born, the female Jaguar becomes highly protective of her young, and expels the male Jaguar from her territory. Jaguar cubs are born blind and gain their sight after about two weeks. They are weaned by their mother at around 3 months old, and will rely on their mother to hunt and provide for them until about 6 months old. At that point, the Jaguar cubs will accompany their mother on hunts, and will eventually hunt alone at and establish their own territories at 1-2 years of age.
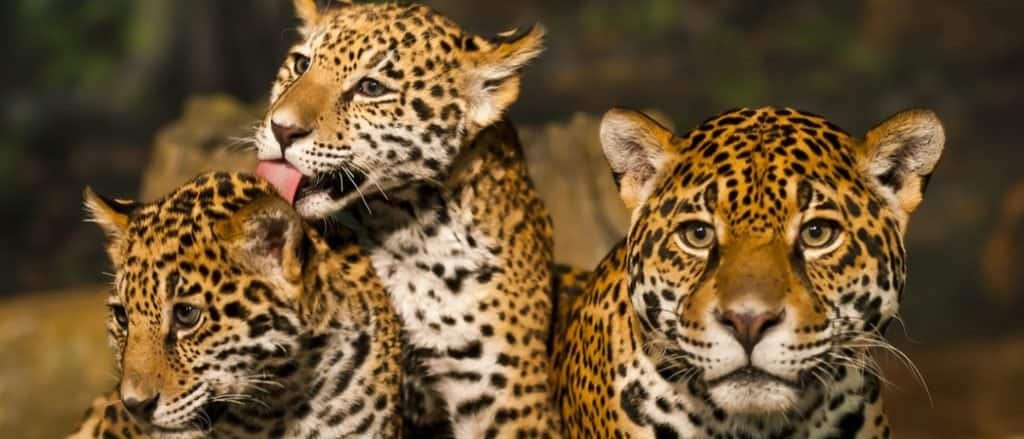

Baby jaguars are weaned by their mother around 3 months of age, and will rely on their mother to provide for them until 6 months old.
©iStock.com/kwiktor
Diet and Prey
The majority of a Jaguar’s hunting is done down on the ground but they are also known to hunt for prey both in the water and from the trees, from where the Jaguar can easily ambush its prey often killing it with one powerful bite. Learn more about the toughest animals in the world here. Medium sized mammals make up the majority of the Jaguar’s diet including Deer, Capybara, Peccaries and Tapirs, which they stalk in silence through the dense jungle. When in the water, Jaguars hunt Turtles, Fish and even small Caiman when the opportunity presents itself. The Jaguar is known to be a formidable and aggressive hunter and is thought to eat more than 80 different animal species in order to supplement its diet. With growing Human settlements, the Jaguar has also been blamed by ranch owners for stealing their livestock, particularly in areas that encroach on the Jaguar’s territory.

Predators and Threats
Due to the large size and dominant nature of the Jaguar, there are no other wild animals that are known to actually consider it as prey. Once found throughout the South American continent, they have been hunted by Humans mainly for their fur which has led to drastic declines in Jaguar population numbers everywhere. Despite now having legal protection and a reduction in the hunting of them for their fur, the Jaguar is at increasing risk from loss of habitat mainly in the form of deforestation to make way for agriculture or growing Human settlements, which means these large and majestic animals are being pushed into more remote regions of their native range.
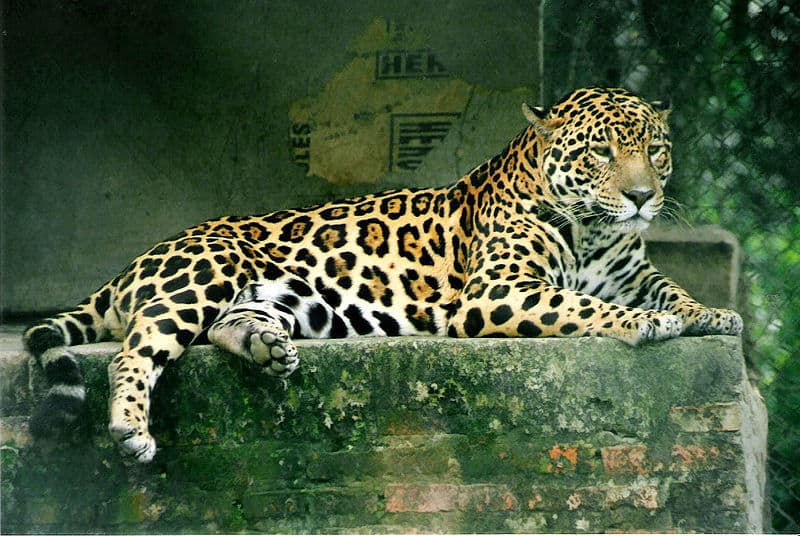

The biggest threat to the jaguar is mankind.
©Lea Maimone, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Interesting Facts and Features
Jaguars have the strongest bite force of all Cats (learn about the strongest animals in the world here) and like other ‘big’ Cats they can roar (other Cats cannot). The Jaguar is undoubtedly a strikingly beautiful animal and has naturally caught the attention of both scientists and hunters alike, with many individuals sadly having been poached for their distinctively patterned fur. Although Jaguars usually have yellowish coloured fur, other colours are also known including black and white. As with black Leopards, they are not completely black as you can still see the spotting (although faint) in strong sunlight. Jaguars are said to be able to cross-breed with both Leopards and Lions. A Lepjag was produced by the film industry to produce a Cat that had the appearance of a Jaguar but was easier to handle with the temperament of a Leopard. He lives in retirement now in a Big Cat sanctuary, and like other ‘big’ cat hybrids he is sterile.
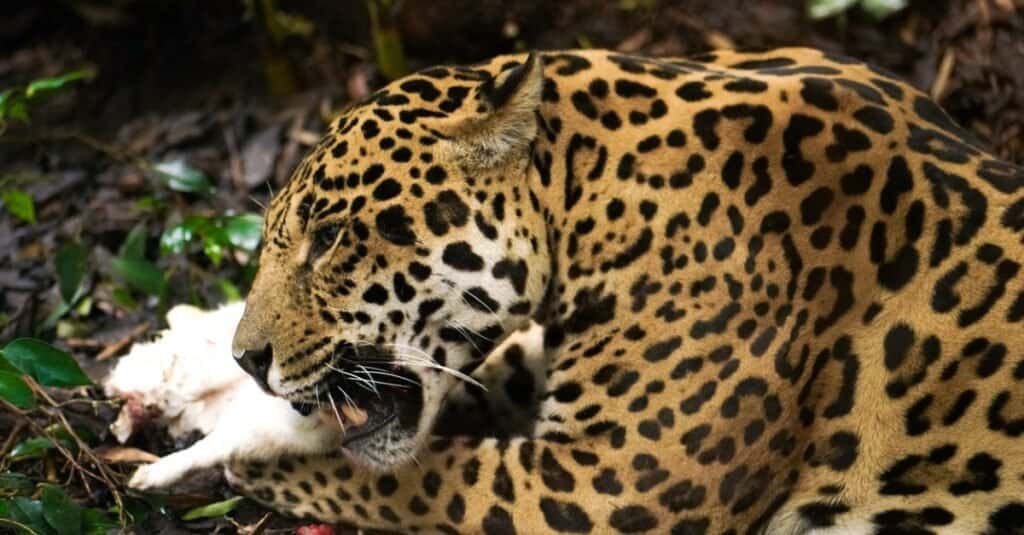

An innumerable amount of jaguars have been poached for their beautiful, distinctive coats.
©iStock.com/Steven Anderton
Relationship with Humans
Historically, Jaguars have featured throughout Native American culture, as these people were well aware of the power of this dominant predator with some believing that the Jaguar was the lord of the underworld. They are feared by Humans who inhabit areas close to the jungle and are also often blamed by ranch owners for their missing livestock. Although Jaguars hold the reputation for being very aggressive, unprovoked attacks on Humans are rare. Jaguars have been severely affected by deforestation throughout much of Central and South America, primarily for agriculture with the highest numbers now found in the Amazon Basin.
Conservation Status and Life Today
The Jaguar was once found from the tip of South America right up to and beyond, the Mexico-USA border but hunting for their fur and habitat loss has led to drastic declines in population numbers. They are today very, very rarely seen in the USA and are considered endangered throughout much of their natural range, although the Jaguar is listed by the IUCN Red List as an animal that is Threatened in its surrounding environment. Although the exact population number is unknown, there are an estimated 15,000 Jaguar individuals left roaming the rainforest today.
View all 36 animals that start with JJaguar FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Jaguars herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Jaguars are Carnivores, meaning they eat other animals.
What Kingdom do Jaguars belong to?
Jaguars belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Jaguars belong to?
Jaguars belong to the class Mammalia.
What phylum to Jaguars belong to?
Jaguars belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Jaguars belong to?
Jaguars belong to the family Felidae.
What order do Jaguars belong to?
Jaguars belong to the order Carnivora.
What type of covering do Jaguars have?
Jaguars are covered in Fur.
What genus do Jaguars belong to?
Jaguars belong to the genus Panthera.
Where do Jaguars live?
Jaguars live in Central and South America.
In what type of habitat do Jaguars live?
Jaguars live in rainforests, swamps, and floodplains.
What are some predators of Jaguars?
Predators of Jaguars include humans.
How many babies do Jaguars have?
The average number of babies a Jaguar has is 3.
What is an interesting fact about Jaguars?
Jaguars are the largest feline on the American continent!
What is the scientific name for the Jaguar?
The scientific name for the Jaguar is Panthera onca.
What is the lifespan of a Jaguar?
Jaguars can live for 12 to 15 years.
What is a baby Jaguar called?
A baby Jaguar is called a cub.
How many species of Jaguar are there?
There is 1 species of Jaguar.
What is the biggest threat to the Jaguar?
The biggest threats to the Jaguar are hunting and habitat loss.
How many Jaguars are left in the world?
There are 15,000 Jaguars left in the world.
How fast is a Jaguar?
A Jaguar can travel at speeds of up to 50 miles per hour.
Would a jaguar or crocodile win in a fight?
Jaguars often come face-to-face with caimans, which are crocodilians that live in South America. In these battles, the jaguar usually comes out on top as many caiman species are smaller than other crocodiles found across the world. If a jaguar were to face-off against crocodiles outside its habitat (such as saltwater crocodiles or Nile crocodiles), it would be unable to hunt these giant beasts.
What's the difference between a jaguar and a mountain lion?
When it comes to mountain lion vs jaguar, the differences go beyond the spots. Mountain lions are spotless, while the jaguar has characteristic markings, but these felines also enjoy unique habitats and display distinct behaviors.
Who would win a fight between a jaguar and a mountain lion?
A jaguar would win a fight against a mountain lion.
This fight is going to end with one big cat wrapping its mouth around the other’s neck. Jaguars are larger and more powerful on average, have a speed advantage, know how to attack from cover, and have a far more powerful bite.
How to say Jaguar in ...
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals
- Jaguar History, Available here: http://animals.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/jaguar/
- Jaguar Information, Available here: http://www.defenders.org/wildlife_and_habitat/wildlife/jaguar.php
- Jaguar Facts, Available here: http://www.tropical-rainforest-animals.com/Jaguar-Information.html