Yellow Perch
Perca flavescens
Female Yellow Perch grom larger than the males.
Advertisement
Yellow Perch Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Perciformes
- Family
- Percidae
- Genus
- Perca flavescens
- Scientific Name
- Perca flavescens
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Yellow Perch Conservation Status
Yellow Perch Facts
- Prey
- crustaceans, invertebrates
- Group Behavior
- School
- Fun Fact
- Female Yellow Perch grom larger than the males.
- Biggest Threat
- over-fishing
- Gestation Period
- 8-10 days
- Average Spawn Size
- 23000
- Habitat
- freshwater
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- School
- Favorite Food
- insecxts, invertebrates, small fish
- Number Of Species
- 200
Yellow Perch Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Yellow
- Gold
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Lifespan
- 9-10 years
- Weight
- 2-3 pounds
- Length
- 4-14 inches
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 3-4 years for females, 2-3 for males
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Low
View all of the Yellow Perch images!
The Yellow Perch is an abundant freshwater fish in the northern areas of North America. It is recognized by its gold or yellow body with dark vertical stripes. It is a popular sport and commercial fish, especially in the Great Lakes region.
The Yellow Perch has many common names, such as Striped Perch, American Perch, Coontail, Lake Perch, Raccoon Perch, Ringed Perch, and Dodd Fish.
3 Yellow Perch Facts
- The world record Yellow Perch was 18 inches long and weighed 4 lbs. 3 oz. It was caught in New Jersey in 1865 and is the longest-standing record for freshwater fish caught in North America.
- Yellow Perch is the most popular game fish caught in Michigan, with no restrictions on areas or time of year that they can be caught. The daily catch limit in 2022 is 25.
- Sexual dimorphism is shown in Yellow Perch. The females grow faster and larger than the males, which can be evident as early as 60 days after hatching.
Yellow Perch Classification and Scientific name
The scientific name for Yellow Perch is Perca flavescens. They are also called striped perch, American perch, and American River Perch, among other names. Yellow Perch are in the order Perciformes, which is the most numerous order of vertebrates and contains ray-finned fish.
This order contains about 41% of all bony fish. Their family is Percidae, which contains more than 200 species of perches and their relatives, such as walleye, sauger, and ruffe.
Yellow Perch Appearance
Yellow Perch have a long, oval body with a long, blunt snout. They are gold or yellow in color with 6-8 dark vertical bars along the side of the body. Like most perch, they have 2 separate dorsal fins. Their eyes are green to yellow.
Adult Yellow Perch typically grow to 4 to 10 inches, while some can reach up to 14 inches. The females grow faster and reach a larger size in general than the males.
The growth rate varies depending on the geography and habitat, even from one body of water to another in the same region. The world record Yellow Perch was 18 inches long and weighed 4 lbs. 3 oz.
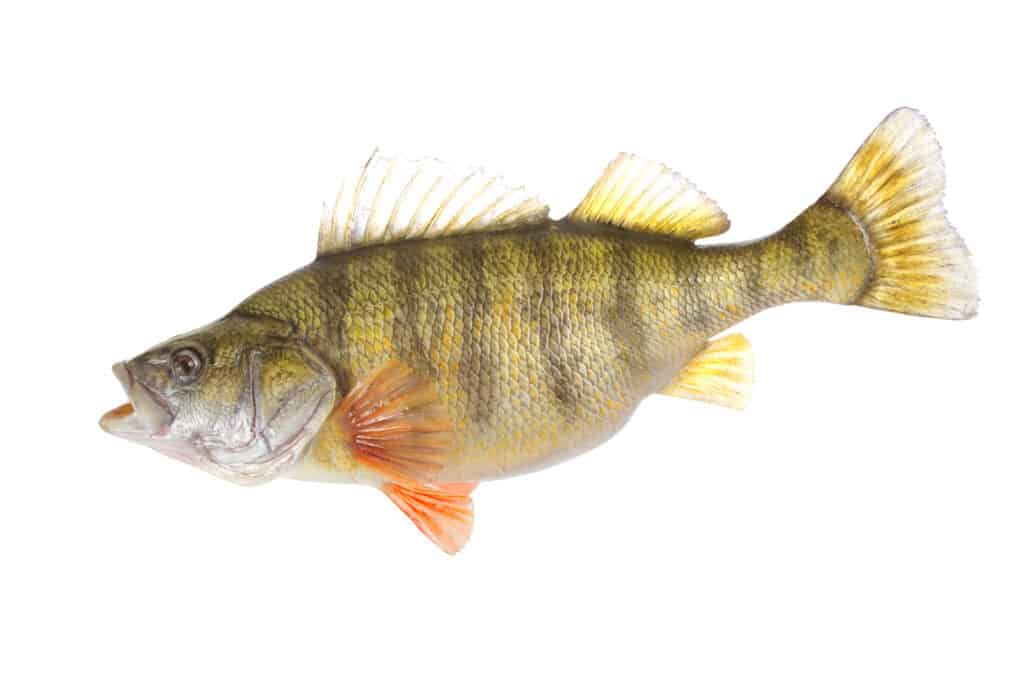

The twin dorsal fins are characteristic of the Yellow Perch and others in the family.
©Keith Publicover/Shutterstock.com
Yellow Perch Distribution, Population, and Habitat
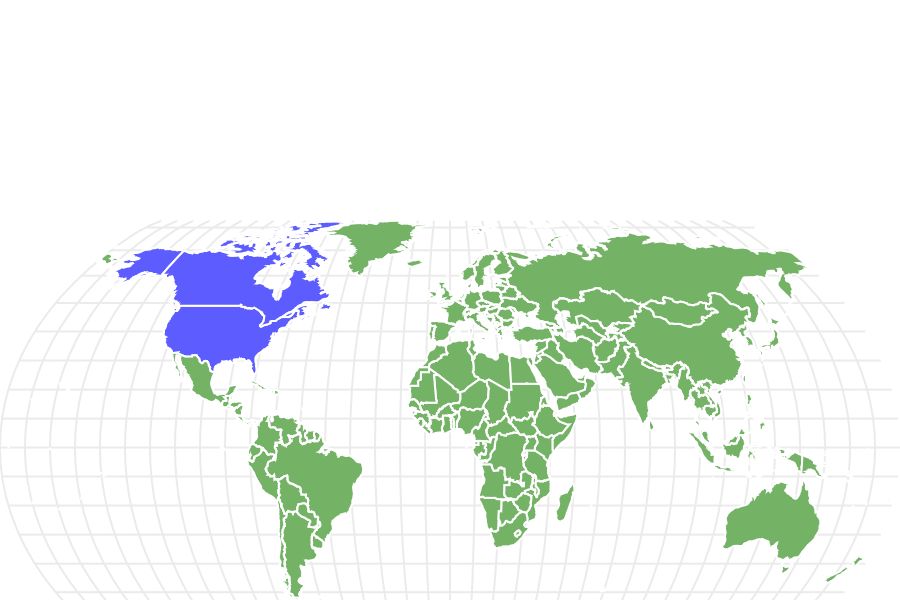
Yellow Perch are only found in North America’s freshwater lakes, rivers, and ponds, mainly around the Great Lakes, the St. Lawrence River, and the Mississippi River basin. They are also found in the eastern ¾ of Canada, and in the Atlantic and Arctic Ocean tributaries.
In the United States, they are found south of Ohio, Illinois, and most Northeastern states. Isolated populations are also found in various northwest and southwest United States areas. These have occurred through unauthorized releases and the use of Yellow Perch as live bait in these areas.
They are a popular sport and commercial fish for food. However, population data is generally not available. Populations have varied in areas over the past century. They were a very popular commercial fish in the 1970s, with harvests in the Great Lakes reaching over 30 million pounds annually.
More recently, that has dropped to under 6 million pounds, with some areas closed to commercial harvesting because of low populations.
Yellow Perch Predators and Prey
The Yellow Perch’s diet depends on body size, which is controlled by age. Plankton is the main food for smaller Perch. By the time they are one year of age, they shift to invertebrates such as worms and insects. Larger adult Perch will eat invertebrates, crayfish, fish eggs, and other smaller fish.
What Eats Yellow Perch?
Common Predators are other larger fish, eagles, herring, gulls, hawks, diving ducks, pelicans, herons, and other large birds. In the eastern US, Yellow Perch are an important food for birds, including the Double-crested Cormorants.
These birds will specifically target young perch as their primary prey. Estimates indicate that Cormorants consume around 29% of the perch population that is less than 3 years old.
What Does Yellow Perch eat?
Yellow Perch eat mainly Plankton under the age of one. Older fish eat insects, invertebrates, and smaller fish.
Yellow Perch Reproduction and Lifespan
These fish spawn once a year and release eggs in the spring. They do not have a specific area for the eggs. Two to five males will congregate first in the shallow areas of a lake or areas of streams and rivers where the current is low.
One female will then arrive and deposit her eggs, followed by the males releasing their milt over the eggs. This entire process only takes about 5 seconds.
The males usually stay with the eggs for a small amount of time, while the females leave immediately. The number of eggs averages 23,000 but can vary between 2,000 to 90,000 depending on the size of the female.
The eggs will drift with the current and attach to vegetation, rocks, and trees. These are thought to contain a substance to protect them, as other fish rarely consume them. The eggs hatch in about 8-10 days. However, it can take up to 21 depending on the temperature and habitat.
Females grow larger and quicker than males and become sexually mature in 3 to 4 years. Males are mature after 2-3 years. The lifespan of the Yellow Perch greatly depends on the geography and water conditions.
Research suggests the typical maximum age to be 9-10 years. However, very few may live past 11 years in good conditions.
Yellow Perch In Fishing And Cooking
Yellow Perch is a popular fish for both commercial and sport fishing. It has a firm, flaky texture and a mild flavor. The meat has less fat than other popular fish and fewer calories per 100-gram serving.
The lower fat content of the meat can result in longer shelf life. It is also high in protein, with 25 grams per 100-gram serving. They have also become fish that is successfully farmed. They can be grown in tank and pond systems and tolerate a wide range of water quality and temperature conditions.
Commercial harvest of yellow perch averaged more than 23 million pounds a year from 1950 to 1970 but decreased to around 6 million per year from 1990 to 2000. Farmed perch has become more popular commercially than catching them in the wild.
Yellow Perch is the most frequently caught game fish for sportfishing in Michigan. Their aggressive feeding behavior makes them fairly easy to catch. They are rarely taken from water more than 30 feet deep and tend to travel in schools toward the shores each morning to feed.
During the spring, they tend to feed all day. Unlike many other fish, they also remain active in the winter and are popular fish for ice fishing.
Yellow Perch can be caught on a variety of live and artificial bait. Live baits include worms, minnows, freshwater clams, and crickets.
Artificial baits can include anything resembling a minnow, such as a Rapala minnow. Jig heads with a soft plastic minnow with a quivering tail also work much of the time.
Cooking Yellow Perch can be done in various ways since it is such a versatile fish. It can be grilled, poached, pan and deep fried, sauteed, baked, and used in chowders. It is normally cooked with the skin on. Because of its mild and distinctive flavor, minimal seasoning is needed.
View all 32 animals that start with YYellow Perch FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the favorite foods of the Yellow Perch?
Yellow Perch under one year rely on zooplankton for their food. Older fish eat insects, invertebrates, and smaller fish.
How big do Yellow Perch get?
The record Yellow Perch, caught in 1865, was 18 inches long and weighed four pounds three ounces.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- US Fish and Wildlife Service / Accessed September 26, 2022
- Washington Dept. of Fish & Wildlife / Accessed September 26, 2022