Anchovies
November 12th is celebrated as National Pizza with the Works Except Anchovies Day
Advertisement
Anchovies Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Anchovies Conservation Status
Anchovies Facts
- Prey
- Recently hatched fish and planktons
- Group Behavior
- School
- Fun Fact
- November 12th is celebrated as National Pizza with the Works Except Anchovies Day
- Estimated Population Size
- 20,700 metric tons
- Biggest Threat
- Halibut, salmon, sharks, bluefish, striped bass, weakfish, and other fishes
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Protruding upper jaw that extends to behind their eyes
- Habitat
- Salt waters and brackish waters, as well as in temperate waters
- Predators
- Humans, halibut, salmon, sharks, bluefish, striped bass, weakfish, and other fishes
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Favorite Food
- Recently hatched fish and planktons
- Type
- Fish
- Number Of Species
- 144
View all of the Anchovies images!
Anchovies are small green forage fishes. These fishes are very common and high in nutrition and belong to the family Engraulidae.
There are more than 100 species of anchovies – most of which are found in marine waters. However, some of these small fishes are also found in brackish waters. While some others can also exist in the fresh waters of South America.
Anchovies are fish that are mostly distinguished by their large mouths. Their upper jaw extends behind their eyes. Besides that, a long, pig-like snout extends beyond the tips of their lower jaws.

Incredible Facts!
- These fishes are easier to catch on a full moon night since their bodies glisten under the moonlight. They are canned and salted right after and sometimes dried for eating purposes.
- Anchovies are fish that can concentrate an acid, making them poisonous for humans to consume as a whole.
- Crab paste is known to be the best bait for catching these fishes.
- November 12th is celebrated as National Pizza with the Works Except Anchovies Day.
- The freshest anchovies have black irises instead of reddish ones. They are also often confused with Sardines that have white flesh.
Classification and Scientific Name
Anchovies are fish that belong to the kingdom Animalia and phylum Chordata. Their class is Actinopterygii, and they come from the order of Clupeiformes. These small fishes belong to the family Engraulidae. They also go by the scientific name Engraulidae. However, different anchovy species have different scientific names to go by.
Engraulidae comes from the Greek word Engraulis, which means anchovy. However, the name possibly comes from the word γρυλίζω, meaning “to grumble.”
Species
As per sources, there are 144 different species around the world. These different species are distributed into 17 genres. The majority of these species differentiate as the result of the location that they are found in, though there are a few ways that they distinguish themselves.
Some of the common species include:
- European anchovy: These anchovies are one of the most common species to consume, and they are predominantly located in the Mediterranean Sea and the North Sea. They often have a silver underbelly, spawning through the spring and summer months.
- Peruvian anchoveta: This species is often found in the southeast Pacific Ocean, and it is harvested by the ton.
- Indian anchovy: The Indian anchovy also goes by the name Hardenberg’s anchovy. It can be used as either live bait or as dead bait.
- Northern anchovy: Not to be mistaken for the European anchovy, this species is typically found in two separate parts of the United States, spanning across Oregon, Washington, and California.
Evolution
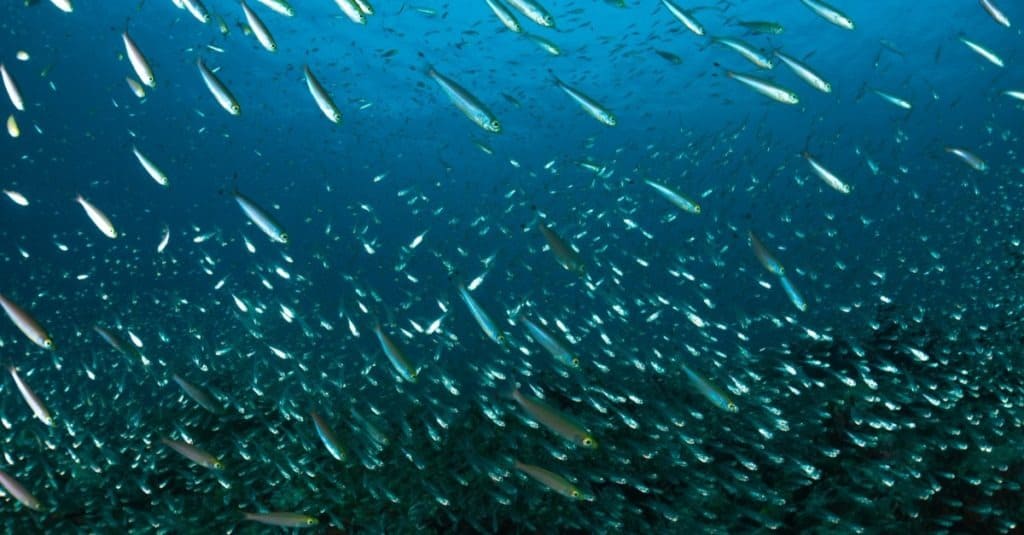

Anchovies have been on earth for millions of years.
©Divefriday/Shutterstock.com
Anchovies have been around for millions of years, and their evolution is believed to be closely linked to the evolution of other species in the same family, such as herrings and sardines. It is thought that anchovies evolved from a common ancestor that lived during the Miocene epoch, some 15 million years ago. Since then, they have adapted to inhabit many different environments across the world’s oceans and seas.
Anchovies are now considered one of the most abundant fish species. Anchovy populations tend to fluctuate due to changes in ocean temperatures caused by climate change, making them vulnerable if not managed properly. Despite this vulnerability, anchovies remain one of our planet’s most important food sources due to their high nutritional value, which includes essential omega-3 fatty acids and protein content – meaning they are here to stay for generations more yet!
Anchovies vs. Sardines
Anchovies, as a result of curing, often have dark, reddish-grey flesh, while Sardines have white flesh. Sardines have a slightly protruding lower jaw, while the upper jaw of Anchovies extends till behind their eyes.
Comparatively, sardines are about two inches longer than anchovies, though they are still incredibly similar.
The main way that these two types of fish differ is in their taste. While anchovies tend to make any dish saltier. However, for individuals that want a meatier taste that is a little more mellow and subdued, then sardines may be the right choice.
Sardines belong to the Clupeidae family, while anchovies belong to the Engraulidae family.
Appearance
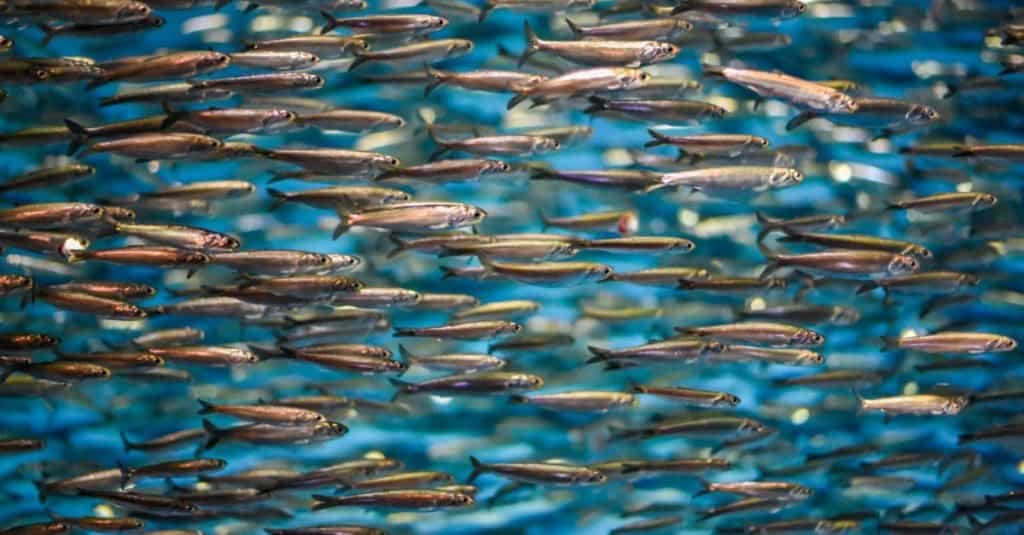

Anchovies are small green fish with longitudinal stripes of blue and silver.
©David A Litman/Shutterstock.com
These are small green fishes. They are slender and streamlined and resemble herrings a lot. Usually, they are categorized by large mouths.
Their upper jaws extend behind their eyes, and a pointed pig-like snout extends beyond the lower jaw. They have a straight lateral line.
These fishes have large scales that can be easily detached. An adult fish is about 5 to 6 inches in size. Even the heaviest of these fishes do not weigh more than a few ounces.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
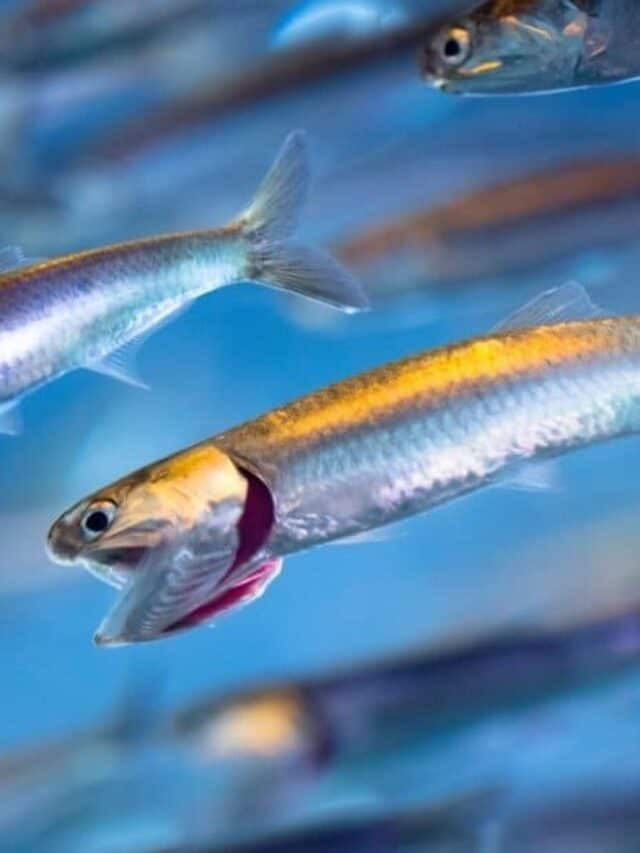

Anchovies are found in temperature waters in oceans around the world.
©iStock.com/EvanTravels
These fish are found in several oceans around the world. They live in scattered spots throughout these oceans. However, they are mostly concentrated in temperate waters.
They are very rare or are completely absent in areas with extreme temperatures. That is why it is difficult to find them in very cold or very warm waters. The European species is especially abundant in the Black Sea, Alboran Sea, and the Aegean Sea.
These fish are usually found in saltwater. However, some of them can also exist in brackish waters. They are pelagic, meaning that they thrive best in open oceans. In brackish waters, they exist in estuaries and bays.
According to a study, as of 2015, the estimated population is 20,700 metric tons.
Predators and Prey
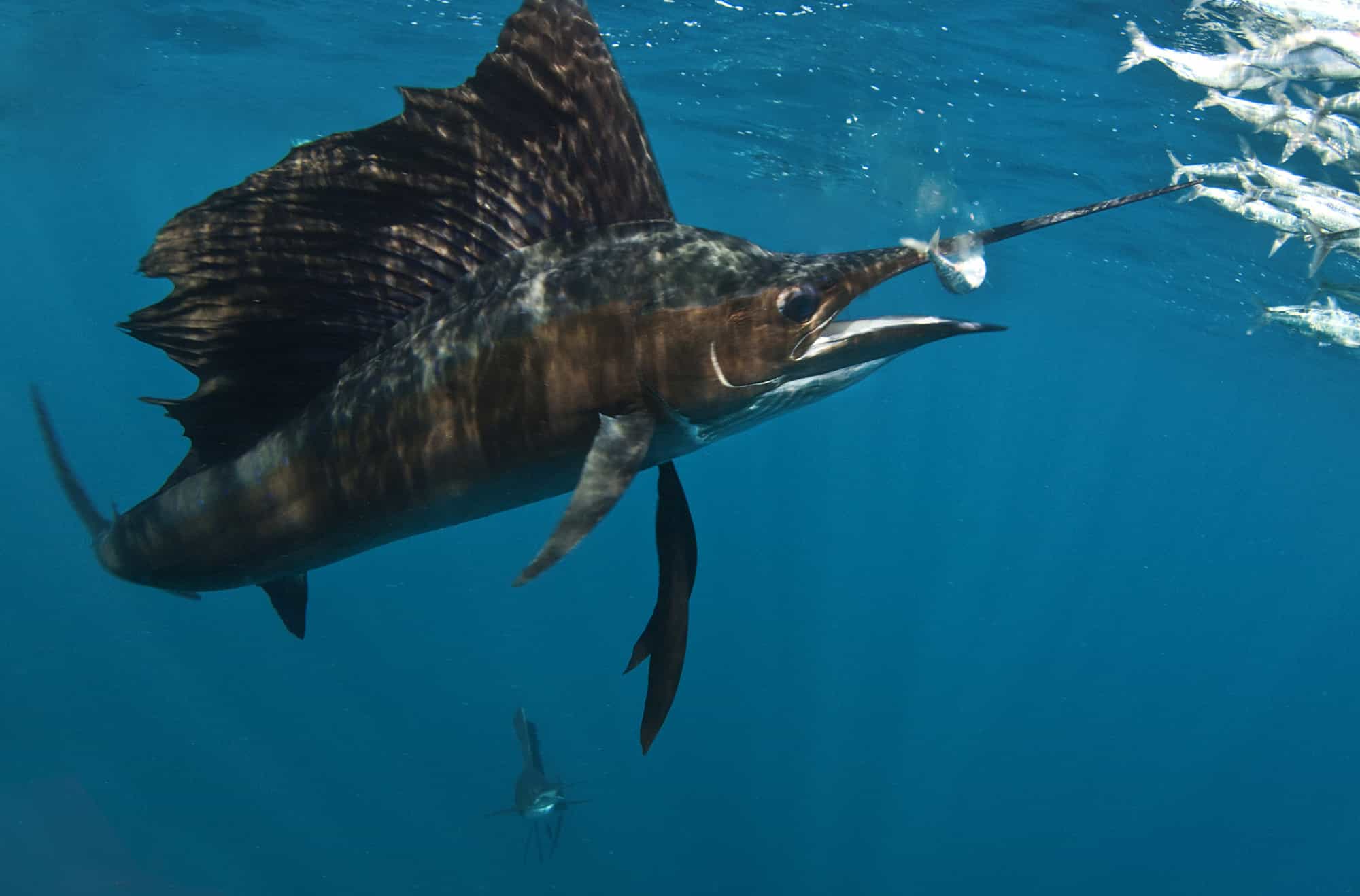

Sailfish rely on anchovies and sardines for food.
©A Cotton Photo/Shutterstock.com
These fish, especially the bay anchovies, have bluefish, striped bass, and weakfish as predators. Apart from that, seabirds also feed on them, including the bay anchovy. Other predators of these fish include sharks, salmon, halibut, and other fishes. They, in turn, eat recently hatched fish as well as plankton.
What Eats Anchovies?
Anchovies are an important food source for many animals, including birds such as seagulls, penguins, and pelicans. Many marine mammals, such as dolphins, seals, and whales, rely on anchovies for food. Large predatory fish like tuna and mackerel and other smaller fish like sardines and herring all eat anchovies. Several types of reptiles, like sea turtles and crustaceans such as crabs and lobsters, also eat anchovies. Anchovies provide essential nutrients to all these creatures since they contain high levels of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, sodium chloride (salt), iodine, trace elements/minerals needed for metabolism activities. Thus anchovies play a key role in maintaining the balance of life in oceans around the world.
What Do Anchovies Eat?
These fish feed majorly on plankton as well as recently hatched fish.
Reproduction and Lifespan

Anchovies reproduce by spawning.
©Stografi/Shutterstock.com
Much like herring, the fish reproduce by spawning. Males and females gather in large groups and release their eggs and sperm into the water.
The sperms are known to fertilize the eggs outside the bodies of the fish. The eggs, once fertilized, float in water columns until they hatch.
The gestation period and the time that it usually takes for the babies to reach sexual maturity varies from species to species. They rarely live after four years of age.
Fishing and Cooking
Most of these fish are caught by Deepwater trawlers. Once caught, most of these fishes are canned and salted. After, they are turned into a paste which is later used to make sauces. Crab paste is a common bait used to bring anchovies to the surface.
Further, they are considered to be a magic ingredient in dishes. They have a savory and briny flavor. Usually, they are stir-fried in tomato sauce or shallow-fried in olive oil.
People also love these small fishes as toppings on their pizza or butter them up in their toast as an easy snack idea. They are sometimes dried for eating purposes. Dried fish also make great snacks.
Population and Conservation
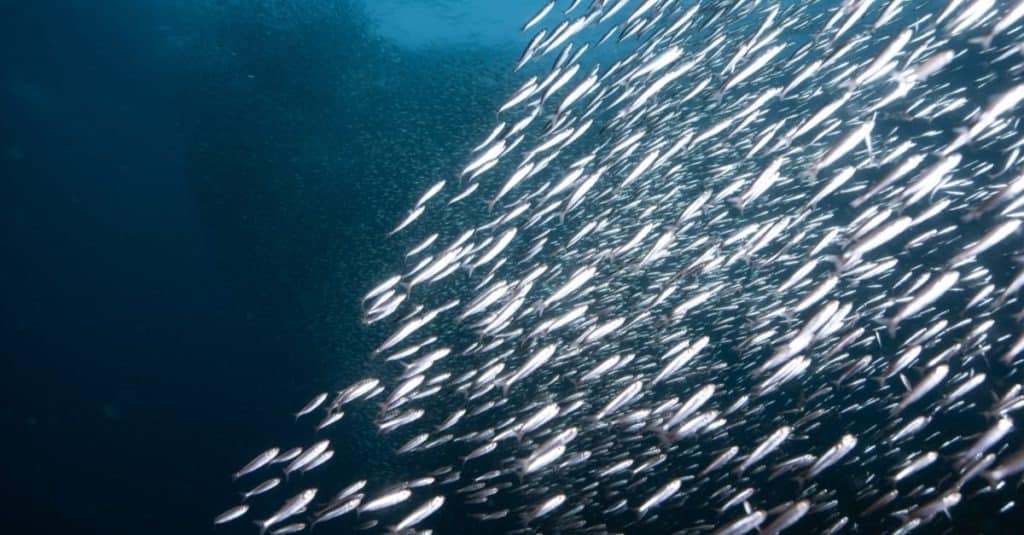

Overfishing is an issue for the declining andhovy populations.
©Divefriday/Shutterstock.com
The most recent population study of anchovies puts their population around 20,000 metric tons.
Anchovies are classified as a ‘Least Concern’ species on the IUCN Red List, meaning they have healthy populations and their conservation status is considered low risk. However, there are still several threats to anchovy populations around the world. Overfishing of anchovies has been an issue for centuries, with some stocks becoming depleted due to unsustainable fishing practices. Anchovies can also be threatened by water pollution from agricultural runoff or oil spills, which contaminate their habitats and food sources. Additionally, climate change is causing ocean temperatures to rise in many areas, which affects fish reproduction cycles and migratory patterns. It is important that we continue to monitor anchovy populations so we can ensure sustainable fisheries management and protect these important fish from further harm or a decline in numbers.
42 Types of Anchovies
There are 144 species of anchovies spanning 17 genera.
- Rio Negro pygmy anchovy – Amazonsprattus scintilla
- Zabeleta achovy – Anchovia clupeoides
- Big-scale anchovy -Anchovia macrolepidota
- Suriname anchovy – Anchovia surinamensis
- Atlantic anchovy – Cetengraulis edentulus
- Pacific anchovy – Cetengraulis mysticetus
- Buccaneer anchovy – Encrasicholina punctifer
- Hawaiin anchovy – Encrasicholina purpurea
- Jurua anchovy – Jurengraulis juruensis
- Sabretooth anchovy – Lycothrissa crocodilus
- Chinese anchovy – Pseudosetipinna haizhouensis
- Scaly hair fin anchovy – Septipinna taty
- New Jersey anchovy – Thryssa encrasicholoides
- Guatama anchovy – Thryyssa guatamiensis
- Hamilton’s anchovy – Thryssa hamiltonii
- Malbar anchovy – Thryssa malabarica
- Gangetic anchovy – Thryssa mystax
- Freshwater anchovy – Thryssa scratchleyi
- Borad-striped anchovy Anchoa hepsetus
- Shortfinger anchovy – Anchoa lyolepis
- Bay anchovy – Anchoa mitchilli
- Allen’s anchovy – Anchoviella alleni
- Carriker’s anchovy – Anchoviella carrikeri
- Manamo anchovy – Anchoviella manamensis
- Goldspotted grenadier anchovy – Coilia dussumieri
- Japanese grenadier anchovy – Coilia nanus
- Argentine anchovy – Engraulis anchoita
- Australian anchovy – Angraulis australis
- South African anchovy – Engraulis capensis
- European anchovy – Engraulis encrasicolus
- Japanese anchovy – Engraulis japonicus
- Californian anchovy – Engraulis mordax
- Peruvian anchovy – Engraulis ringens
- Bates’ sabretooth anchovy Lycengraulis batesii
- Atlantic sabretooth anchovy – Lycengraulis grossidens
- Schultz’s sabretooth anchovy – Lycengraulis limnichthys
- Pacific sabretooth anchovy – Lycengraulis poeyi
- Littlefin anchovy – Papuengraulis micropinna
- Wingfin anchovy – Pterengraulis atherinoides
- Commerson’s anchovy – Stolephorus commersonnii
- Indian anchovy – Stolephorus indicus
- Hardenberg’s anchovy – Stolephorus insularis
Anchovies FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are anchovies found?
Anchovies are found in different oceans around the world. They live in scattered spots throughout these oceans. However, they are mostly concentrated in temperate waters.
What are anchovies?
Anchovies are small forage fishes. These fishes are very common and belong to the family Engraulidae. There are 144 different species of anchovies.
What's the difference between anchovies and sardines?
Anchovies have dark, reddish-grey flesh while Sardines have white flesh. Sardines have a slightly protruding lower jaw while the upper jaw of Anchovies extends till behind their eyes.
What do anchovies taste like?
These small fishes have a rich, savory, and briny flavor and are savored in several parts of the world.
Can you eat anchovies raw?
If the quality is right, yes you can eat them right from the canned condition that they are usually put in. These small fishes are high in nutrition.
Are anchovies good for you?
Yes, anchovies offer immense nutrition to lower levels of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood. It is also a very good source of protein.
Are Anchovies herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Anchovies are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and animals.
What Kingdom do Anchovies belong to?
Anchovies belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
How do Anchovies have babies?
Anchovies lay eggs.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- New World Encyclopedia / Accessed December 24, 2020
- Wikipedia / Accessed December 24, 2020
- Mobile cuisine / Accessed December 24, 2020
- Food and Wine / Accessed December 24, 2020
- Nature Gate / Accessed December 24, 2020
- Animals / Accessed December 24, 2020
- The Spruce Eats / Accessed December 24, 2020