Archaeopteryx
Archaeopteryx lithographica
Advertisement
Archaeopteryx Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Family
- Archaeopterygidae
- Genus
- Archaeopteryx
- Scientific Name
- Archaeopteryx lithographica
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Archaeopteryx Conservation Status
Archaeopteryx Facts
- Prey
- Small mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and insects (possibly fruit, seeds, and nuts)
- Biggest Threat
- Drowning
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Small, sharp teeth unlike modern birds
- Habitat
- Islands in the Sea of Tethys
View all of the Archaeopteryx images!
Archaeopteryx is the genus and common name for a dinosaur with features like a bird.

4 Amazing Facts:
- The archaeopteryx was about the size of a raven, just 20 inches long and around 2 pounds.
- It had many small conical (cone-like) teeth in the upper jaw and a bony tail.
- There are certain anatomical structures that the archaeopteryx had in common with modern birds like a wishbone and a partially reversed first toe.
- This dinosaur also had a similar feather structure to modern birds, including flight feathers.
Scientific Name and History
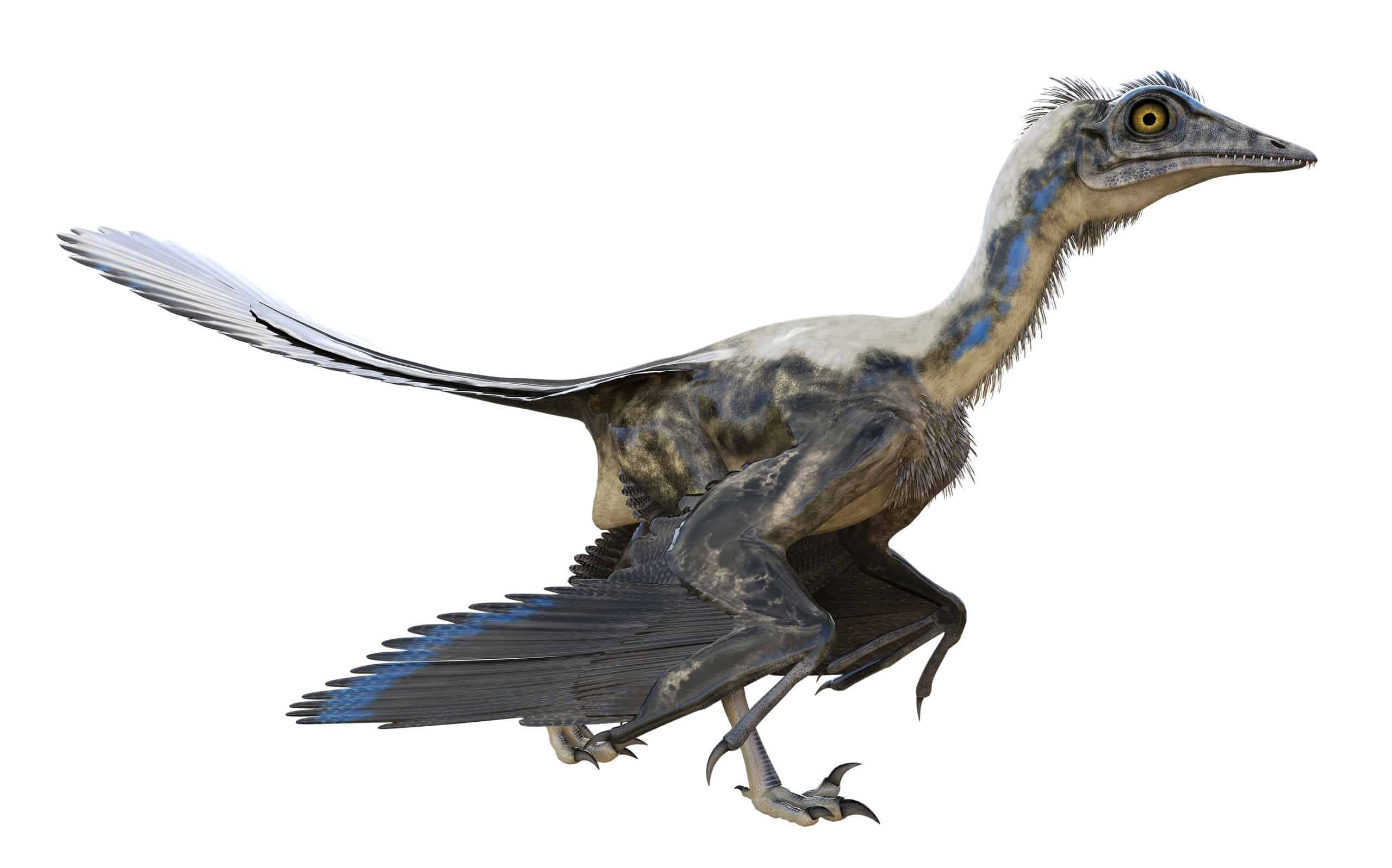

The Archaeopteryx name means ancient wing, which is very appropriate if it is an ancestor of the modern bird.
©Herschel Hoffmeyer/Shutterstock.com
Archaeopteryx gets its name from two Greek words: archaīos and ptéryx. Translated literally, its name means “ancient wing.” Some refer to this ancient bird by its German name, Urvogel, which means “first bird” or “original bird.”
There are arguably two species within the Archeopteryx genus: A. lithographica and A. siemensii. However, there is some disagreement within the scientific community about whether there are actually two unique species or just some variances within A. lithographica.
There are several fossil specimens of the Archaeopteryx, which lived about 150 million years ago in an area that is now southern Germany. Much of Europe was underwater at that time so the area was actually part of island chains in the Tethys Sea. True birds appeared about 70 million years later.
The Archaeopteryx is a theropod, a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods could be as small as the Archaeopteryx or as large as Tyrannosaurus Rex, but all were bipeds with two strong back legs to stand on and two short forelimbs that served as arms with hands.
While it has long been thought that it was the ancestor of the modern bird, increasing fossil evidence suggests other possible candidates as well. Since it has characteristics of both reptiles and avians, it could be a transitional animal, evolving from one type to another.
Description
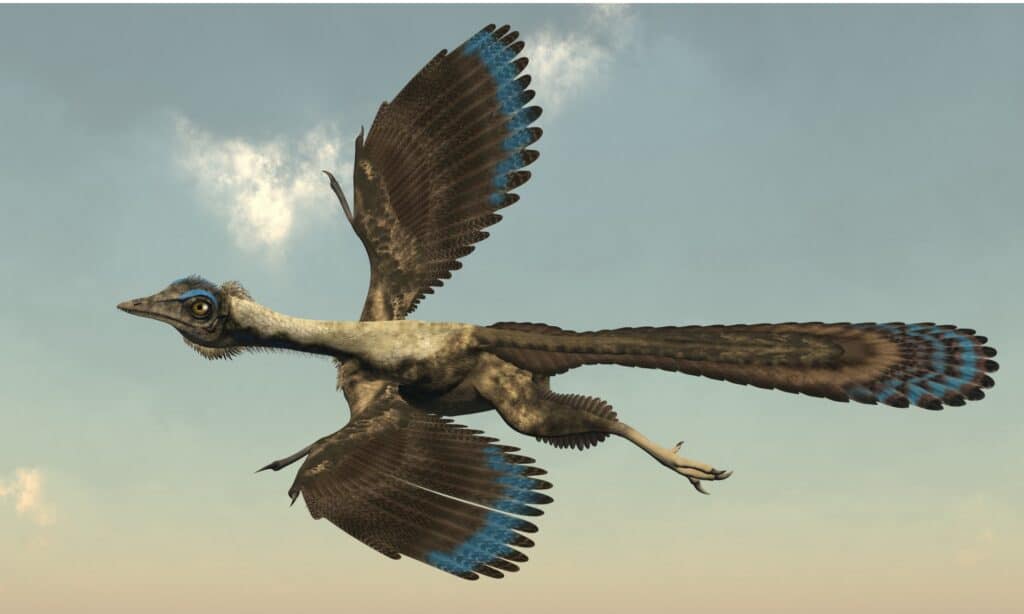

The
Archaeopteryx has features of both reptiles and modern birds, but it is unknown if it could actually fly.
©iStock.com/Elenarts108
Most of these extinct birds would have been around the size of a typical raven or chicken. They measured approximately 20 inches in body length and weighed about 2 pounds.
Don’t let the small size of Archaeopteryx fool you. It was a formidable bird. A couple of its unique features are a mouth full of teeth and a long, bony tail. It also had three claws on each of its wings that it likely used to grasp prey or possibly climb trees.
By using advanced technology, like scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, researchers have been able to analyze feather specimens and conclude that Archaeopteryx was most likely black with some slight variations throughout its plumage.
The presence of flight feathers tells us that this ancient bird was most likely able to fly to a certain degree. However, when we look at its smaller breastbone and how its shoulder joint is shaped, it’s unlikely it was a strong flier because it couldn’t lift its wings above its back. So, it is likely that the presence of feathers was simply for temperature regulation, and the bird hadn’t evolved to use flight. Thus we are left wondering whether this bird was a flapping flier, a glider, or just regulated its temperature with the feathers.
Other than these few differences, Archaeopteryx had much in common with modern birds. For example, their feather structure was very similar, according to fossil records. They also had flight feathers, a wishbone, and a partially reversed first toe. No wonder early researchers believed that Archaeopteryx was the oldest bird and the link between dinosaurs and modern birds. Even if that lineage changes with new studies, the Archaeopteryx has been an immensely important dinosaur discovery
Diet
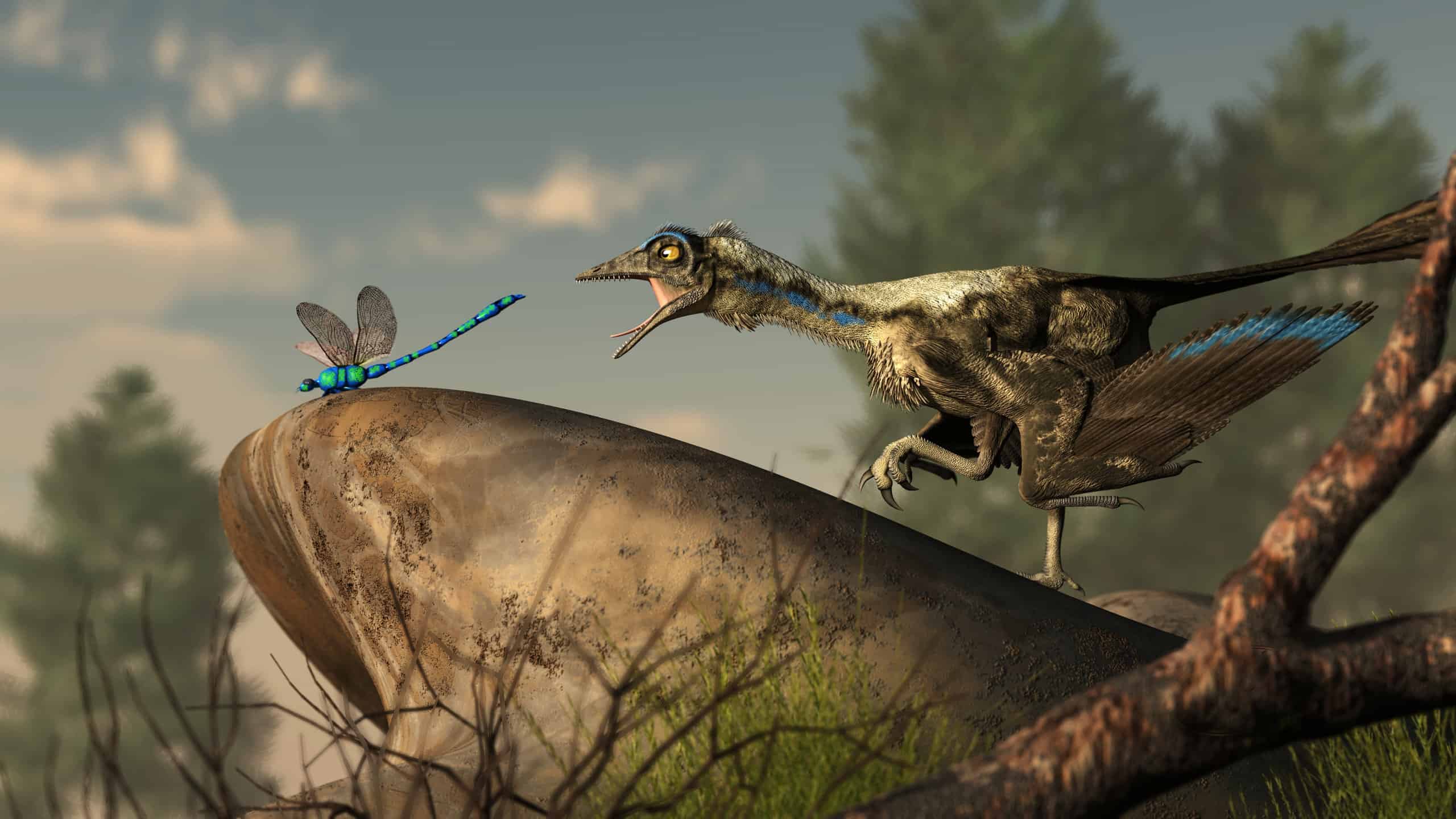

An archaeopteryx, a Jurassic era theropod dinosaur that looked much like a bird, lunges at a
dragonfly
, which may have been on its menu.
©Daniel Eskridge/Shutterstock.com
Although there are several well-preserved specimens, we know little about what Archaeopteryx ate. judging from its small, sharp teeth, it was most likely a carnivore. So, it probably fed on small reptiles, mammals, and insects.
It’s also possible that Archaeopteryx was an omnivore like many modern birds. So, it may have also included seeds, fruit, or berries in its diet.
Habitat
Researchers have found most fossil specimens of the Archaeopteryx in areas with no evidence of large trees. So, even if it was a bird, it was most likely a flightless bird that spent most of its life on the ground or possibly in small shrubs. Judging by its skeleton, Archaeopteryx was well-adapted to life on the ground.
Threats And Predators
At the end of the Triassic Period, a mass extinction event led to almost all animal and plant life being wiped from the Earth. So, when Archaeopteryx showed up towards the end of the Jurassic Period, there likely wouldn’t have been many predators to hunt them.
Small animals for the Archaeopteryx would also have been plentiful, so there wouldn’t have been the threat of starvation. The problem is that the specimens we’ve recovered haven’t told us much about this ancient bird’s daily life.
One possible threat these bird-like dinosaurs likely faced was drowning. Because they were not strong fliers, they may have crashed into the sea surrounding their islands. They would probably have drowned quickly once their feathers became soaked.
Discoveries and Fossils
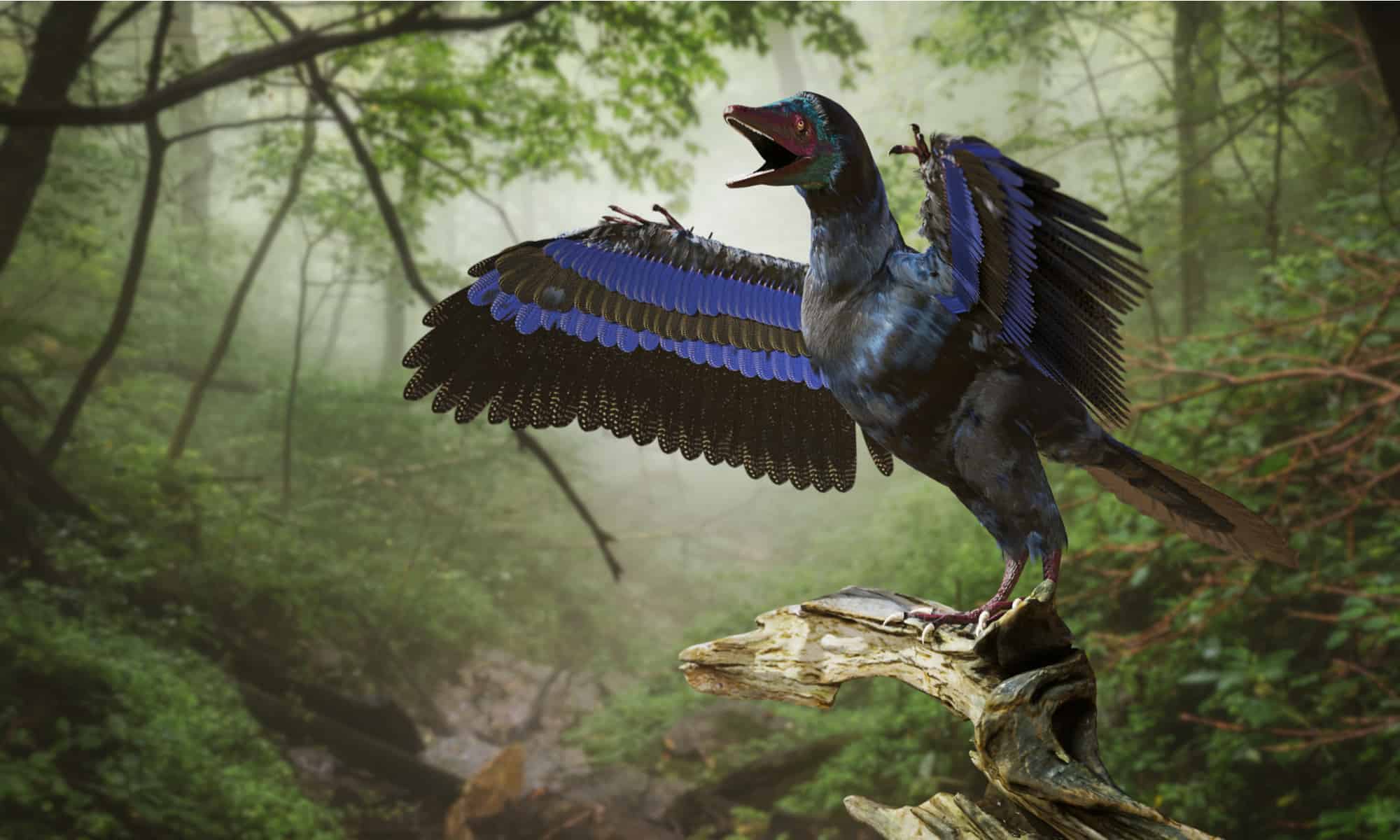

Fossils of the Archaeopteryx, a bird-like dinosaur from the Late Jurassic period around 150 million years ago, have been found in Germany.
©Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
In 1860, the first suspected Archaeopteryx specimen was found near Solnhofen, Germany. However, it was only a feather imprint, and there’s no confirmation that it was indeed from the bird in question.
However, an Archaeopteryx skeleton was found one year later near Langenaltheim, Germany. Even though it was missing most of the head and neck, it was clear this was a new genus. The main reason that this find was such a big deal is that it seemed to confirm Darwin’s origin of species theory. At the time, this skeleton was evidence of the oldest bird that was the link between dinosaurs and birds.
Throughout the years, several more Archaeopteryx specimens have been discovered in Germany, with the latest uncovered in 2010. Unfortunately, new discoveries have disproved the theory that this bird is the link we’ve been searching for.
Xiaotingia zhengi was discovered in the Liaoning deposits in China, and the specimens predate Archaeopteryx by around 5 million years. This other dinosaur shares many of the bird-like characteristics of Archaeopteryx and confirms that birds did not come from the latter, but rather it was just another species in the line, leading up to modern birds.
Extinction
We don’t know why Archaeopteryx went extinct. There was a minor extinction event at the end of the Jurassic period. However, to our knowledge, the larger stegosaurid and enormous sauropod dinosaurs were the main dinosaurs affected by this event. Our best estimate is that Archaeopteryx lived its life for many years and was eventually replaced as true birds evolved.
Similar Animals
- Xiaotingia: This is another genus of bird-like dinosaurs with one species: Xiaotingia zhengi. It shared many similarities like teeth and a hard, bony tail. However, it lived 5 to 10 million years before Archaeopteryx in China.
- Microraptor: The Microraptor was found throughout Asia. It lived approximately 125 to 120 million years ago. Its standout characteristics were that it actually had four wings. However, it did not have flight feathers like Archaeopteryx. It likely glided and had minimal flight capabilities.
- Chicken: The modern dinosaur-bird: the chicken. A large Archaeopteryx would have been about the same size. While there are some striking differences between the two, it’s not a huge stretch to imagine chickens coming from these ancient bird-like dinosaurs.
Archaeopteryx FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When was the Archaeopteryx Alive?
According to fossil dating, researchers believe that Archaeopteryx lived approximately 150 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period in what’s now Germany. Germany (and much of Europe) was underwater during this time.
How Big was Archaeopteryx?
The average Archaeopteryx was around 20 inches long and weighed around 2 pounds. In some cases, they would have been about the same size as a crow or a large chicken.
Could Archaeopteryx fly?
Researchers are undecided. We don’t know whether Archaeopteryx was an active flyer or a glider. Evidence suggests that if it could fly, it was for short distances. One theory is that its feathers were more for temperature regulation than anything.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- UC Museum of Palentology / Accessed June 22, 2022
- Britannica / Accessed June 22, 2022
- National Museum Wales / Accessed June 22, 2022