Discus
The discus can change its colors slightly based on personal and environmental factors
Advertisement
Discus Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
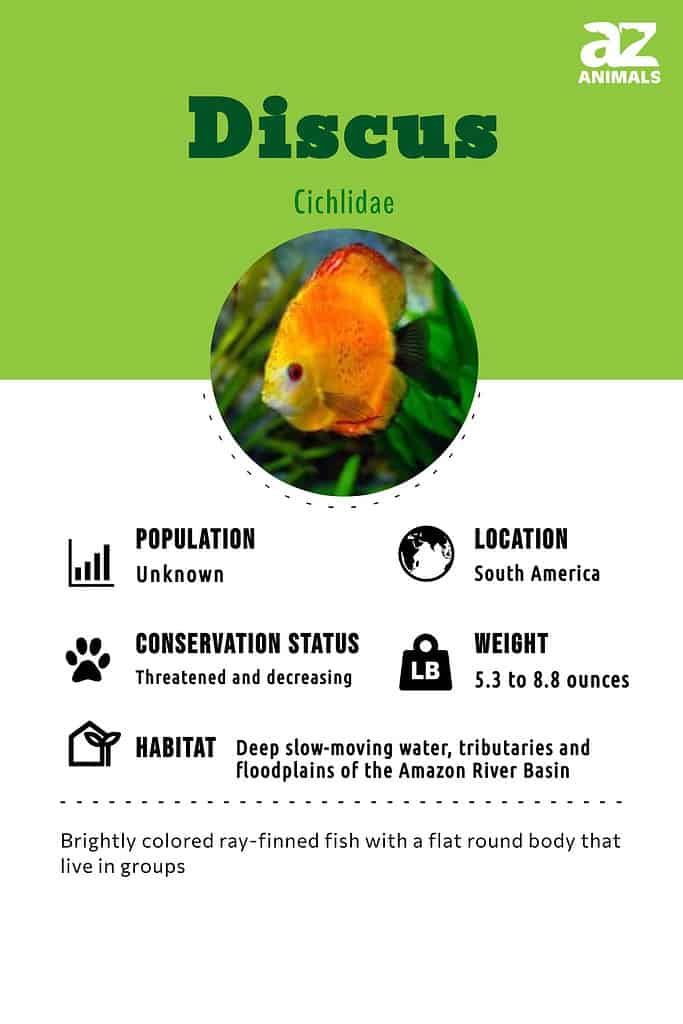
Discus Conservation Status
Discus Facts
- Prey
- Small invertebrates and plant matter
- Name Of Young
- Fry
- Group Behavior
- School
- Fun Fact
- The discus can change its colors slightly based on personal and environmental factors
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat change
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Bright colors
- Other Name(s)
- Pompadour fish
- Gestation Period
- 3 to 4 days
- Optimum pH Level
- 6 - 7
- Incubation Period
- 10 days
- Age Of Independence
- 2 - 3 weeks
- Average Spawn Size
- 150
- Habitat
- Deep, slow-moving waters
- Predators
- Turtles, birds, and other fish
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- Diurnal
- Type
- Ray-finned fish
- Common Name
- Discus
- Number Of Species
- 3
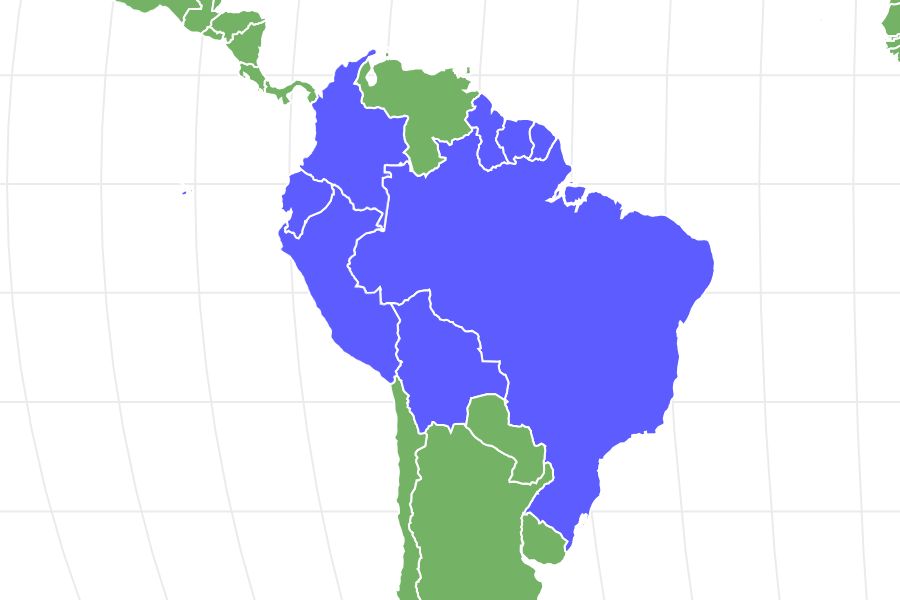
- Location
- Brazil, Columbia and Peru
- Slogan
- One of the only schooling Cichlids!
- Group
- Fish
View all of the Discus images!
The discus fish can change its colors slightly based on personal and environmental factors.
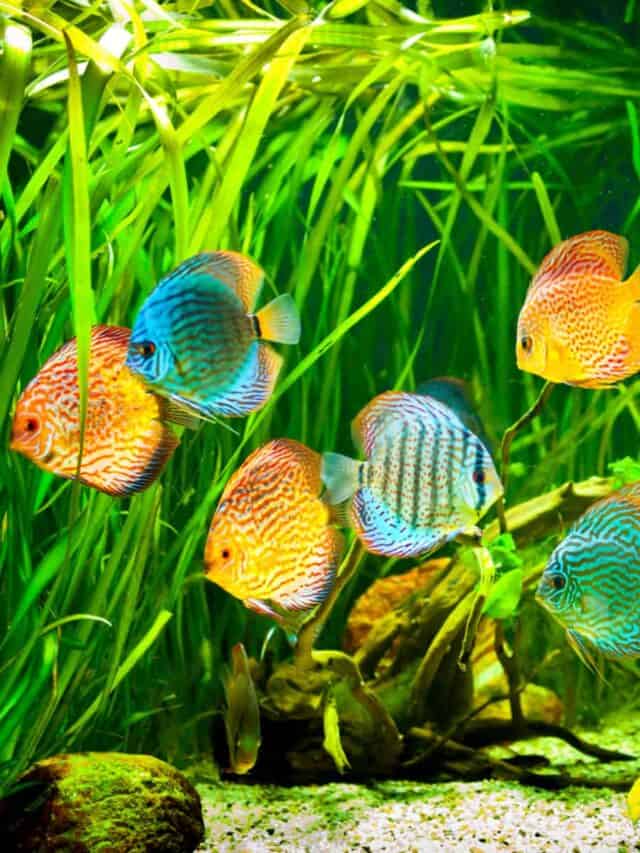
Symphysodon, also known as discus, is a genus of brightly colored tropical fish (and a member of the cichlid family). These fish mainly reside in the long, sinewy waterways of the Amazon Basin. Because of their vivid colors and intricate markings, the discus is one of the most popular tropical aquarium fish in the world. They have undergone selective breeding in captivity for unique types of exotic markings and patterns, many of which don’t exist in the wild.
Incredible Facts!
- Discus fish prefer to congregate in large groups with dozens of members for protection and feeding.
- They appear to derive their bright colors from combinations of pigments within skin cells.
- An alternate name for discus is the “pompadour fish.” Named after Madame de Pompadour, a mistress of King Louis XV of France, the pompadour was a popular hairstyle in which a large volume of hair sweeps over the forehead.
- Because of its bright colors, the discus has also earned the title “King of the Aquarium”
Classification and Scientific Name
While “Symphysodon” and “discus” are used interchangeably, discus is more commonly used to describe the genus. “Symphysodon” may be a combination of the Greek words “symphysis,” meaning “grown together,” and “odous,” meaning “teeth.” Discus belongs to the family of cichlids, one of the most diverse vertebrate families in the world.
3 Species
A genetic study of discus confirms that there are three distinct species under the genus. The blue discus and the red discus, mentioned below, seem to be the most closely related and are able to produce viable hybrids together. However, several other types of discus exist through selective breeding in captivity.
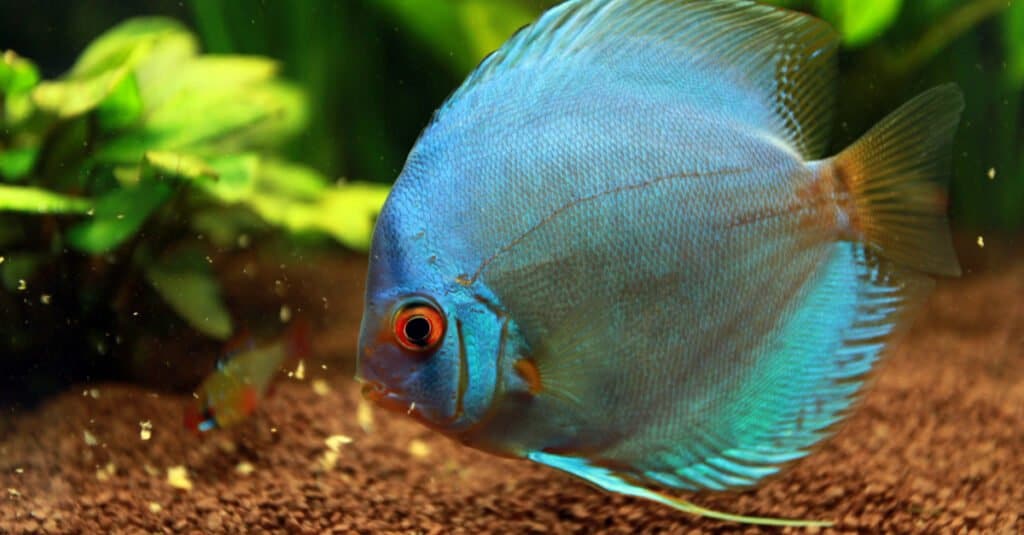
- Blue Discus: Living downriver of the Rio Purus in the Eastern Amazon Basin, the blue (or alternatively, the brown discus) has some combination of blue and brown colors all around its body.
- Green Discus: Also native to the downriver Purus area in the Western Amazon Basin, the green discus sports a yellow-green body with some blue highlights around the fringes and some black stripes over its body.
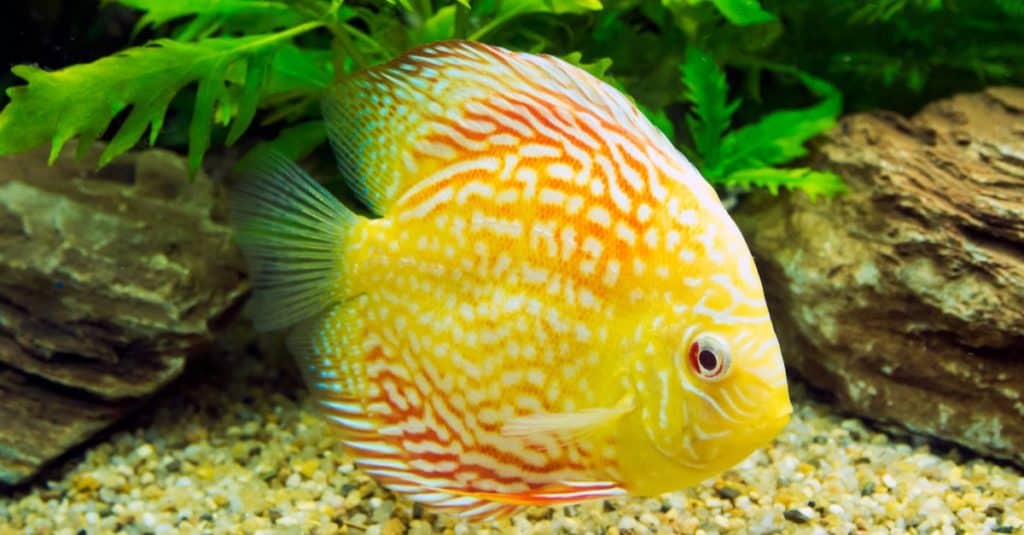
- Red Discuss: Native to the Rio Negro and surrounding areas, the red discus has a bright red-orange body, sometimes complemented with blue-green patterns and black stripes. This species is also known as the Heckel discus.
Evolution
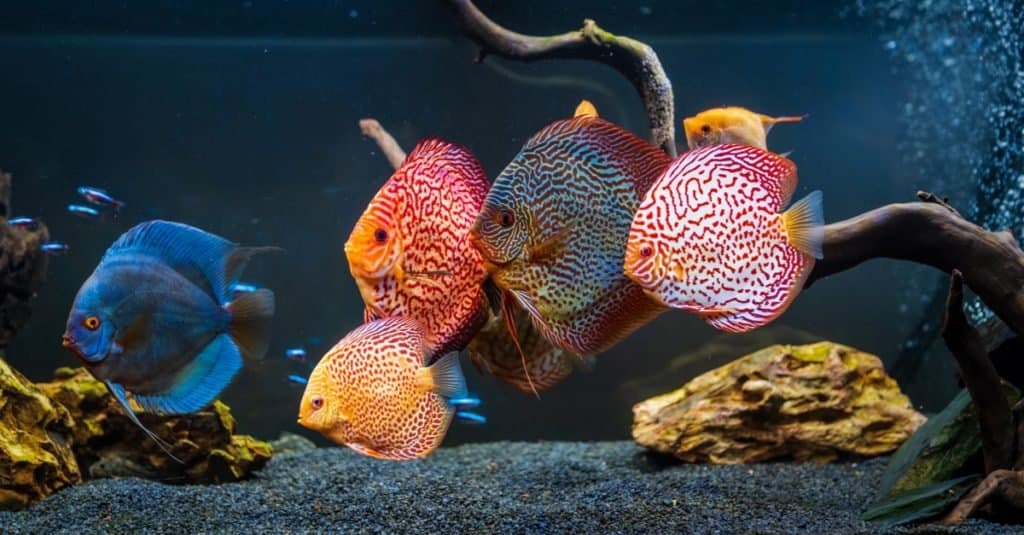

Discus fish have a mysterious evolutionary history.
©Przemek Iciak/Shutterstock.com
The discus fish, also known as the Symphysodon aequifasciatus, is an ancient species of cichlid that has remained unchanged for millions of years. It is thought to have originated in the Amazon River basin and was first discovered by Europeans during their exploration of South America in the 16th century. Since then, discus fish have been selectively bred to develop different varieties with unique morphological features such as vibrant colors and longer fins. However, much about its evolutionary history still remains unknown. Scientists believe that this species may be closely related to other types of cichlids from Africa and Asia but are unsure how they are connected or when they diverged from each other. Further research is needed to understand more about the evolution of this fascinating species.
Appearance
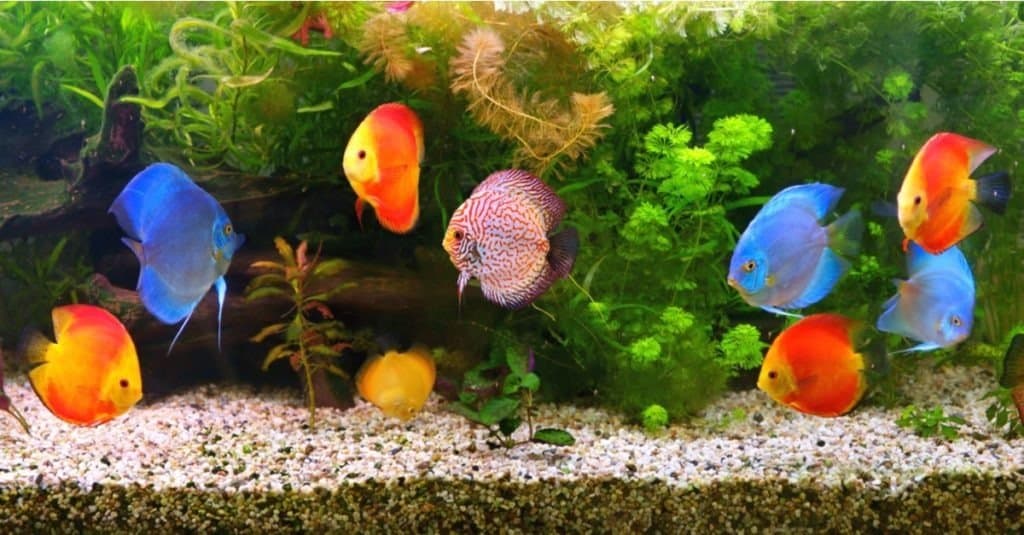

©Mirek Kijewski/Shutterstock.com
For good reason, this fish has earned the name of discus with its relatively flat, rounded body. Large, prominent fins protrude dorsally and on the rear of the fish. As mentioned previously, the discus is classified according to coloration: blue, red, or green. However, there are multitudes of unique patterns. The fish also have remarkable Color-changing abilities based on age, mood, environmental conditions, and stress levels.
Discus usually grow no larger than 6 inches and about half a pound in the wild. Reports indicate growth of around 8 or 9 inches in captivity. Except for breeding season, when the female’s abdomen is enlarged, it is very difficult to tell the sexes apart.
Behavior
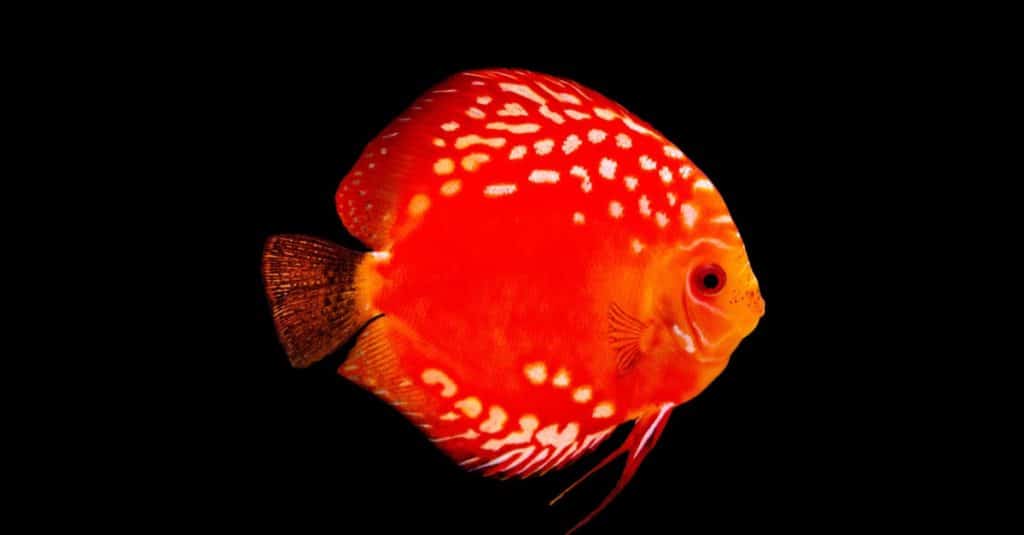

Discus fish prefer to hang out in groups and are friendly with other fish.
©Andrej Jakubik/Shutterstock.com
Discus fish display several unique behaviors, including swimming in circles, displaying “courtship” behavior during mating season, and forming small groups with other discus fish known as “schools.” During courtship season, male discus will chase female discus around the water until they mate. This is often accompanied by vibrant colors and fin displays. In addition to these behaviors, discus also likes to interact with other fish. Discus are generally peaceful toward other species of water inhabitants but may become aggressive if they feel threatened or territorial. Discus fish are shy creatures who will often hide among plants or driftwood when startled by predators. Discus fish also communicate using sounds like grunts and clicks as well as visual cues such as flashing colors or movements of their fins.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
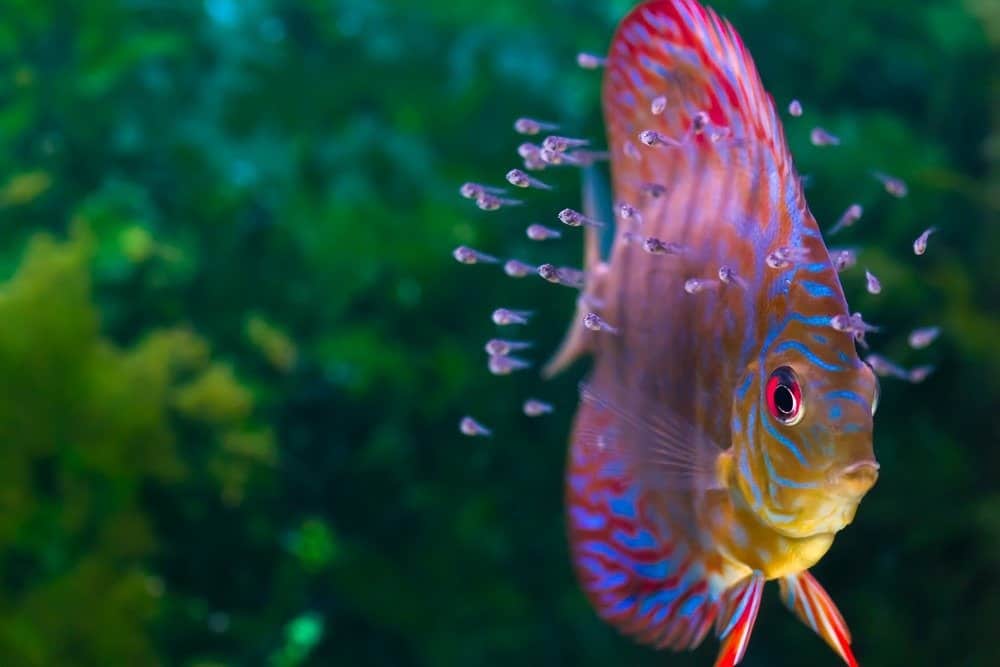

Baby Discus fish swim with their parents.
©Studio 37/Shutterstock.com
In the wild, discus fish are exclusively endemic to the tributaries and floodplains of the Amazon River Basin. They are especially prolific in slow-moving blackwater channels. Discus will often congregate around fallen trees near the shore because of the constant flooding occurring annually.
Discus are not currently classified as threatened by the IUCN Red List. They are presumed to have stable and healthy populations. However, the threats to their natural habitat are probably the greatest potential problems discus populations face.
Predators and Prey

Symphysodon discus eat algae and other plant material.
©Andrey Armyagov/Shutterstock.com
Discus are an intermediate part of the food chain, serving as an important link between nutritious plants and animals at the bottom and the predators above it.
What does the discus fish eat?
The majority of discus’ diet consists of algae and other small plant material supplemented with small invertebrates such as worms and crustaceans.
What eats the discus fish?
The main predators of these fish include turtles, birds, and larger species of fish. Discus are also known to act as cannibals to unrelated larvae of their own species.
Reproduction and Lifespan

Discus fish mate by spawning.
©Ivan Roth/Shutterstock.com
Based on scientific observations, it appears that the timing of discus mating season is highly influenced by changes in the flood levels of their local environment. They tend to spawn right as the water levels begin to rise as a way to take advantage of the abundant food and lower predator density. When ready to mate, a pair moves away from the rest of the group, perhaps to reduce the incidence of cannibalism. After copulating, the eggs usually hatch in about three or four days.
As with many other cichlid species, discus parents invest some time and care into the development of their offspring, guarding and cleaning the eggs. However, unlike many other cichlids, the discus has a unique adaptation: they secrete a mucus-like substance through their skin for the larvae to feed on for the first few weeks of their lives. When one parent begins to tire of this process, the larvae will switch to another parent. At the end of this period, the larvae will have grown large enough to fend for themselves.
The young discus will start to reproduce on their own after a year of age. The typical lifespan is some 10 to 15 years. But life is rough for young fish, and many of them fall prey to other animals before they can reach full size.
Fishing and Cooking
The discus is rarely caught in the wild for its meat. It’s isolated, difficult to reach, and simply undesirable. However, the discus is often raised in artificial environments for the purpose of selling it on the pet market, where it has proven to be incredibly valuable.
Population and Conservation

Discus fish are threatened by habitat loss.
©MemoPlus/Shutterstock.com
Discus fish are native to the Amazon River Basin. Their natural habitats have been greatly reduced due to deforestation and water pollution caused by human activities. As a result, their population has significantly declined over recent years. To help protect this species from extinction, conservation efforts have been taken in some countries, including Brazil and Peru. These include regulations on fishing and hunting as well as habitat protection measures. In addition to these efforts, captive breeding programs are being used to increase the population of discus fish in certain areas where they are threatened with extinction. Captive breeding involves raising wild-caught specimens in controlled environments until they can be reintroduced into their natural habitats. This helps ensure that healthy populations of discus fish will remain for future generations to enjoy.
View all 110 animals that start with DDiscus FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Discuses herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Discuses are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Discuses belong to?
Discuses belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What is the best food for discus fish?
Even in an artificial environment, it is a good idea to replicate its natural diet as closely as possible. Tropical flakes, algae rounds, and shrimp pellets are some of the best foods you can give it. Try to make sure that you have a good balance between plant food and meat.
Is discus fish aggressive?
The discus has a reputation for its peaceable and docile nature, but the male will sometimes display dominant behavior toward nearby discus fish, especially in the breeding season. If you notice constant fights, then it may be a good idea to remove one of them from the aquarium. Outside of its own species, the discus works best with other tropical fish that thrive in similar conditions such as the neon tetra and dwarf cichlids.
How many discus should be kept together?
Since the discus is a rather social fish, it is a good idea to keep at least six of them in your tank with at least 10 gallons of water per fish.
Are discus fish hard to keep?
The discus has specific water requirements that make it somewhat difficult to keep and care for. It is a good idea to purchase a tall tank with gentle water movement and vertically arranged plants and driftwood to simulate its natural environment. The pH should be around 6.0 or 7.0. You will want to add a water heater to keep the temperature a balmy 82 to 86 degrees Fahrenheit. The Heckel discus prefers a water temperature of 90 degrees.
How long do discus live?
If it receives the proper care and maintenance, the discus can survive at least 10 to 15 years in captivity. You should always be on the lookout for early signs of disease such as discoloration, lethargy, and swelling.
What phylum to Discuses belong to?
Discuses belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Discuses belong to?
Discuses belong to the family Cichlidae.
What order do Discuses belong to?
Discuses belong to the order Perciformes.
What type of covering do Discuses have?
Discuses are covered in Scales.
What genus do Discuses belong to?
Discuses belong to the genus Symphysodon.
Where do Discuses live?
Discuses live in Brazil, Columbia, and Peru.
In what type of habitat do Discuses live?
Discuses live in deep, slow-moving waters.
What are some predators of Discuses?
Predators of Discuses include turtles, birds, and other fish.
What is an interesting fact about Discuses?
Discuses are one of the only schooling Cichlids!
What is a distinguishing feature of the Discus?
Discuses are brightly colored.
How many species of Discus are there?
There are 3 species of Discus.
What is the biggest threat to the Discus?
The biggest threat to the Discus is habitat change.
What is the optimal pH for a Discus?
The optimal pH for a Discus is between 6.0 and 7.0.
What is another name for the Discus?
The Discus is also called the pompadour fish.
How many Discuses are left in the world?
The population size of the Discus is unknown.
How do Discuses have babies?
Discuses lay eggs.
How to say Discus in ...
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Britannica / Accessed December 27, 2020
- Aqueon / Accessed December 27, 2020
- The Spruce Pets / Accessed December 27, 2020