Longnose Gar
Lepisosteus osseus
The longnose gar species of the gar family has potentially existed for 100 million years.
Advertisement
Longnose Gar Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Lepisosteiformes
- Family
- Lepisosteidae
- Genus
- Lepisosteus
- Scientific Name
- Lepisosteus osseus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Longnose Gar Conservation Status
Longnose Gar Facts
- Main Prey
- Menhaden, sunfish, and perch
- Fun Fact
- The longnose gar species of the gar family has potentially existed for 100 million years.
- Estimated Population Size
- Not known
- Biggest Threat
- Birds that prey on fish
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Long body with a beak-like mouth
- Other Name(s)
- The needle nose gar or the Billy gar
- Gestation Period
- 7-9 days
- Optimum pH Level
- 4.8 to 6.4
- Habitat
- Brackish waters, fresh waters, saline waters (Not salty waters). Found in Texas, Mexico, Florida, Michigan, and Wisconsin
- Predators
- Birds that prey on fish
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Type
- Fish
- Common Name
- Longnose gar
View all of the Longnose Gar images!
The longnose gar, which sometimes goes by the name needle nose gar instead, is a fish species that belongs to the gar family. This fish is also called the Billy gar.
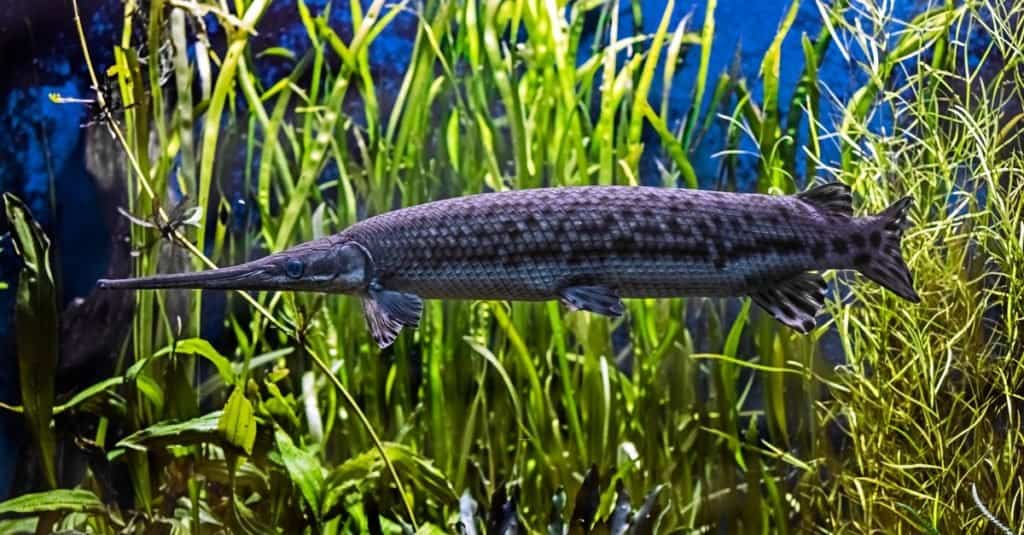
They are greyish to olive in color. The color, however, fades into white along the sides of the longnose gar’s body. They can be as short as 2.5 feet or as long as 4 feet, but their size will primarily depend on where they live.
Just as the name describes it, the longnose fish has a long and narrow snout and mouth, which are paired with extremely teeth.
5 Incredible Longnose Gar Facts!
- Female longnose gars are usually longer than male longnose gars.
- All the longnose gars continue to grow in size throughout their life.
- While female longnose gars sexually mature at six years of age, males usually sexually mature at three to four years of age. Overall, the species can live to be approximately 20 years old.
- One of their dorsal fins is located near the end of their backs.
- Longnose gars have been around for about 100 million years.
Longnose Gar Classification and Scientific Name
Longnose gars go by the scientific name Lepisosteus osseus. Their kingdom is called Animalia while the Phylum is called Chordata. The class is called Actinopterygii and the order is called Lepisosteiforme.
Lepisosteus is a combination of two Greek words – lepis (“scale”) and -osteus (“bone”). The word osseus may come Medieval Latin’s word for “bony” or “made of bones.”
Originally, the longnose gar’s scientific name was Esox osseus. Esox is also Greek, coming from the Celtic root “eog,” which means “salmon.”
Longnose Gar Species
Longnose gars do not have any further species beneath them, but they are a species of the gar family. The longnose gar specifically has already been around for 100 million years now. The largest longnose gar in the world was 60 inches long, weighing almost 50 lbs. when it was caught in Mississippi.
The longnose gar fishes are known to share the gar family with several other species like short nose gar, spotted gar, alligator gar, Florida gar, tropical gar, and Cuban gar. The largest member of the gar family is the alligator gar, which grows to be 8 feet long.
Longnose Gar Appearance
The longnose gar, as the name suggests, has a long, cylindrical body. Though they can have a greyish hue, they sometimes are olive green. Some variations can be brown or black, but the size and color primarily depend on where they live.
These fish has hard scales in a diamond shape all over their body. They have dark spots on their backs, fins, and also on the sides of their bodies. True to its name, longnose gars also have a slender, long snout, making their mouth look fairly similar to a beak.
On average, these fish will grow to about four feet, but the habitat of these fish will determine how long they grow. Some of them can reach lengths of 6.5 feet or more.

©Mikhail Blajenov/Shutterstock.com
Longnose Gar Distribution, Population, and Habitat
These fish are found in different parts of the world of North America. They can be found in the Gulf of Mexico, the Rio Grande, and even in permanent waters towards the northern region of the United States. River basins in Texas, Michigan, and Wisconsin are all prime habitats for these fish.
They’ll also enter the brackish waters of the Perdido Bay (Florida and Alabama), Mobile Bay (Alabama), and Mississippi River. When they are in these regions, they’ll reside in saltier water, though it is not their preferred climate. Most often, the longnose gar thrives in freshwater areas.
Though there is some longnose gar in Wisconsin, the fish is not ordinarily found in large numbers. Still, due to the nutrient-rich composition of the Great Lakes, long nose and short nose gar alike are found in Lake Michigan (which borders Wisconsin).
Longnose Gar Predators and Prey
These fish doesn’t fall victim to any of the typical animals that are found in the lakes and other bodies of water that they inhabit. They have an incredible defense against other fish, thanks to the thick scales that cover their entire body. However, they are sometimes hunted by birds.
Humans also have an influence over the population of these fish, catching them to keep as food.
What Do Longnose Gar Eat?
The diet of these fish consists of small fishes and crustaceans. Since they are carnivores, these fish also likes eating menhaden, sunfish, and perch. However, they don’t have to do much at all to capture their prey. They simply lay motionless until their prey passes by, grabbing it without warning.
What Eats Longnose Gar?
Reports suggest that these fish have no major predators. However, this lack of water-based predators doesn’t mean that they are entirely safe. Osprey, for example, is a type of bird that feeds on fish, catching the fish from above the water.
Longnose Gar Reproduction and Lifespan
The mating and reproduction season of these fish lasts from May and June, overlapping the end of spring and the beginning of summer. They mate in shallow and weedy freshwaters, traveling to areas that have faster movement in the streams.
Before the mating process starts, the male approaches the female. However, there are sometimes 15 males and just one female. Once the female settles on their mate, they will go to open waters to reproduce.
Females lay sticky, green eggs, protected by a poison that can kill animals and humans alike. Each year, the female lays about 30,000 eggs. Though the parents will choose a nursery area, they don’t take care of their eggs after they are laid.
The sexual maturity in the female fish comes at 6 years of age. Males, however, don’t reach sexual maturity until they are 3 or 4 years old.
Longnose Gar in Fishing and Cooking
Catching these fish is not difficult, and there are many types of baits and lures that can be used to do so. Fishermen who seek out these animals often will focus on areas with a lot of brush and shallow waters. One hook has the potential to collect several gars at a time.
When cooked properly, the meat may be gritty but will offer plentiful protein. They are easy to prepare with Cajun flavors, though you can pair it with whatever flavors. Most people relate the texture to that of chicken with a taste like an alligator.
View all 98 animals that start with LLongnose Gar FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are longnose gar found?
The longnose gars are found in different parts of the world. Their range extends from the rivers that run along the Gulf of Mexico from Florida to the Rio Grande, which is located in Texas. They are also found in northern Mexico, Michigan, Wisconsin, and other states that connect to the Great Lakes.
What is a longnose gar?
Longnose gars are fishes that belong to the gar family. They are one of the species of the gar family and have a beak-like mouth.
How do you catch a longnose gar?
Some people use live fish baits to catch Longnose gars. While some others used four to six inches long shinners to catch these fishes.
What does longnose gar eat?
Found in black, brown, and green hues, longnose gars love eating small fishes and crustaceans. They can usually be found eating menhaden, sunfish, and perch as well.
How big do longnose gar get?
Longnose gars can grow to a maximum of 6.5 feet, but the typical range is only 2.5 to 4 feet. In their first year, they grow to about 20 inches in length.
Is longnose gar dangerous?
Due to their very sharp teeth, they pose some danger. Anyone that fishes for longnose gar need to be careful when they handle them.
What are the differences between longnose gars and alligator gars?
The key differences between a longnose gar and an alligator gar are size, snout, teeth, diet, and taxonomy. The longnose gar is not only a different species from the alligator gar, but it is also in a different genus – although both are still in the gar family. Found in a wider range of habitats across the midwest and the eastern United States, the longnose gar is half the size of the alligator gar in both size and weight. In fact, in terms of size, the longnose gar can be as much as a third of the alligator gar’s length.
What was the longest longnose gar ever caught in Florida?
The largest longnose gar ever captured in Florida weighed 41 pounds. It was captured on Lake Panasoffkee on April 4, 1985.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Chesapeake Bay Program, Available here: https://www.chesapeakebay.net/S=0/fieldguide/critter/longnose_gar
- Florida Museum, Available here: https://www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu/discover-fish/species-profiles/lepisosteus-osseus/
- Ranked Boost, Available here: https://rankedboost.com/red-dead-redemption-2/longnose-gar/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longnose_gar