Madora Moth
Gonimbrasia belina
Mopane worms (larva) only live for 3 - 4 days after evolving into an adult (madora), during which they mate and lay eggss
Advertisement
Madora Moth Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Insecta
- Order
- Lepidoptera
- Family
- Saturniidae
- Genus
- Gonimbrasia
- Scientific Name
- Gonimbrasia belina
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Madora Moth Conservation Status
Madora Moth Facts
- Name Of Young
- larva
- Fun Fact
- Mopane worms (larva) only live for 3 - 4 days after evolving into an adult (madora), during which they mate and lay eggss
- Biggest Threat
- Harvesting by humans
- Other Name(s)
- Emperor moth, mopane worm, amacimbi, masontja
- Wingspan
- 120mm (4.7inches)
- Habitat
- Mopane tree, mango tree, tress close to the mopane tree
- Predators
- Birds, humans, insects
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Type
- Insect
- Common Name
- madora moth
- Location
- Zimbabwe, Botswana, Mozambique, Malawi, South-Africa
View all of the Madora Moth images!
The adult madora moth does not feed and only lives for 3 – 4 days
Summary
The adult madora moth is scientifically named Gonimbrasa belina. They are large, robust moths that do not feed and only mate before they die in 3- 4 days. The moth’s larva, referred to as “mopane worm”, feeds primarily on mopane tree leaves. Essentially, they could also feed on other certain host plants around the mopane tree.
The mopane tree is found in the semi-arid areas of South African countries. A mopane worm infestation can destroy the host plant by causing total defoliation. Mopane worm’s major predators are humans and birds. Flies and wasp parasitoids also attack a large aggregation of the larvae.
Mopane worms are edible and are harvested for consumption due to their highly nutritious nature.
Madora Moth Species, Types, and Scientific Name
Madora moth (G. belina) belongs to a group of moths classified as big and robust. The species is a saturniid and belongs to the order Lepidoptera. Members of the Saturniidae family host the largest species of moths in the world. Other members include the luna moth, comet moth, and Io moth.
The immature madora moth larvae (caterpillar) are edible and a major protein source for certain sub-Saharan Africans. John .O. Westwood described this insect in 1849, and since then, the larva has been given common names like mopane worm, emperor worm and emperor moth. The speckled emperor, Gynanisa maja, is another saturniid species that feed almost exclusively on mopane tree.
Appearance: How to Identify Madora Moth
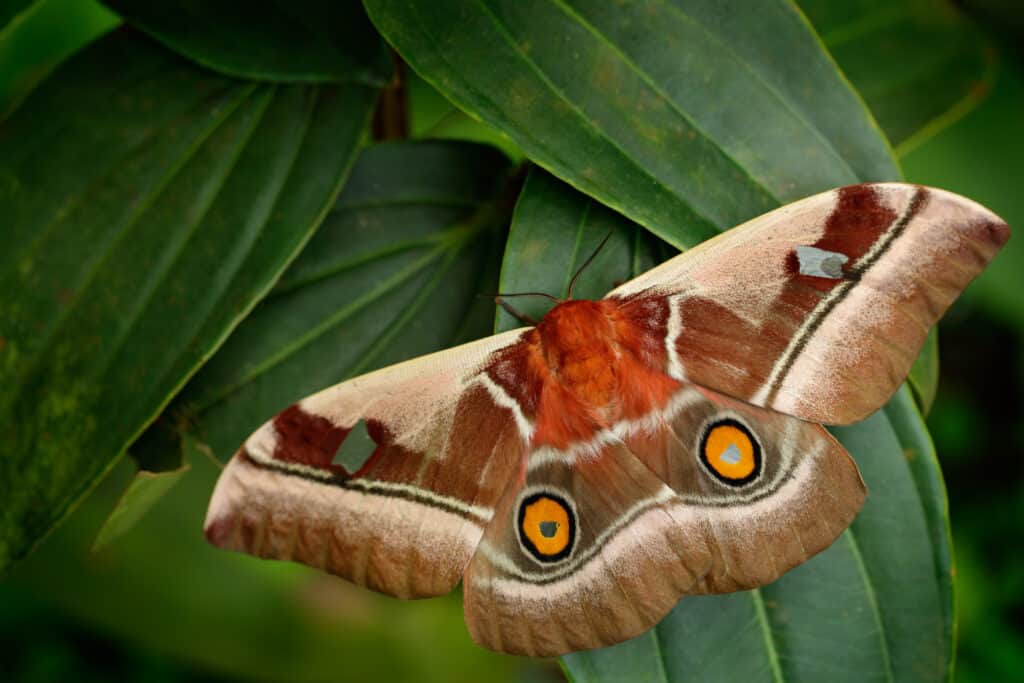

Madora moths are only found in South African countries.
©Ondrej Prosicky/Shutterstock.com
The madora moth has some unique identifying features. Like most saturniids, they are distinctly large, with a wingspan of approximately 12 mm. Generally, the wing could be fawn, green (various shades), brown or red. Madora moth possesses eyespots on both the forewings and hindwings isolated by a white and black band. The eyespots on the hindwings differ from the ones on the forewings. They have an orange coloration that is visibly larger than the ones on the fore wings.
As part of the mating behavior of madora moths, the males possess large feathery antennae to detect the female moth’s presence. Comet moths, another species in the family Saturniidae, have this feature too. The butterfly, however, possesses clubbed antennae.
The caterpillar is visibly long, reaching about 100 mm and 10 mm wide. They are black, peppered with round scales in not too obvious alternating reddish, yellowish and whitish bands. As part of their defense mechanism, the larvae have short reddish or black spines covered in fine white hair. They use this to protect their bodies, sense predators and avoid being devoured.
Since the eggs are favorably hatched during the summer, the caterpillar adopts the habit of burrowing underground to pupate (undergo a complete transformation to become madora moth). This protects them from threats and also allows the caterpillar to overwinter
Habitat: Where to Find Madora Moth
Madora moths are only found in South African countries. They are widely distributed in the eastern half of South Africa and further north into eastern and central Africa. This includes the extreme north of the Limpopo province in South Africa, north-eastern Botswana, northern Nambia, and parts of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. They naturally live in semi-desert, bushveld, and grassland environments, where there’s an abundance of mopane trees.
The young caterpillars live on the tree where they are hatched but migrate to another tree once there is a short supply of nourishment. This can result in mass migrations, and columns can stretch over 5 km.
It is important to note that animals with great values always face overutilization. The mopane worm is not different. Increased commercial exploitation, deforestation (of mopane woodlands), climate change resulting in drought, and predation contribute to the declination of the abundance of this species in their natural habitat.
Diet: What Do Madora Moths Eat?
The adult madora moth lives for about 3 days, and they do not feed. Feeding only occurs in the larval phase of the moth. Amazingly, the moth completes its reproductive cycle within this short period, and the female lays a single cluster of 50 to 200 eggs on the host tree. It takes 10 days before the eggs hatch into larvae (caterpillars). At this stage, the caterpillars are voracious pests as they will continue to eat for about 6 weeks in preparation for the other stages of their life cycle. The food consumed in this phase is used to complete the entire cycle of the moth.
What Does Madora Moth Eat?
The caterpillar feeds on the foliage of a host plant, Colophospermum mopane. This is the most preferred host for mopane worms. However, the worms aren’t fussy eaters. They can also feed on many other plants indigenous to the same region, including the leaves of the Mango tree. Other species like Diospyros spp, Carissa spp, Ficus spp, Sclerocarya caffra, Terminalia spp, Trema spp, and Searsia spp serve as alternatives. The young caterpillars feed voraciously on the foliage of the leaves until they grow into pupa form.
What Eats Madora Moth?
Different predators eat the madora moth at its different stages of growth. Birds and insects like jackals, warthogs, and antbears all eat the pupae of the moth. They do this by digging them out from the ground. The eggs are also preyed upon by different parasitic wasp species.
Humans are the major eaters of the caterpillar of madora (mopane worms). The worms are part of the diet in rural areas of Shangaan and more like a delicacy in urban areas of such countries as Namibia, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Zambia, and the Limpopo province of South Africa. The women and children harvest the worms during the rainy season. People in local areas also trade them actively for consumption. Experts have researched that the worms are highly nutritional and contain about 60% protein (about three times the protein content of beef) and significant amounts of phosphorus, iron, and calcium.
Related Animals:
View all 164 animals that start with MMadora Moth FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How long does a madora moth live?
The adult madora moth only lives for 3 – 4 days after its successful evolution. The male madora mates during this time, while the female lays eggs
How do you identify a madora moth?
Adult Madora moths, also known as Emperor moths, are large and robust moths with two pairs of wings that can have shades of green, dull brown or red coloration. The wingspan is usually about 120mm (4.7inches), and there’s an eyespot on each pair of wings. The eyespot on the hindwings, which is usually orange, is visibly larger than the eyespot on the forewings. The immature m adora (caterpillar) is black and armed with spines that are covered with fine hair.
Is madora moth safe for human consumption?;
Mopane worms are safe. They are usually harvested and consumed because of their high nutritional content. Some of the nutrients include protein, calcium, and iron.
What do madora moths Eat?
Adult madora do not eat, but the caterpillar loves to eat the leaves of the mopane tree. However, the larva doesn’t feed exclusively on this tree and can feast on other trees surrounding it.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- South African National Biodiversity Institute / Zwannda Nethavhani and Ruan Veldtman, Available here: https://www.sanbi.org/animal-of-the-week/mopani-worm/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonimbrasia_belina
- Kidadl, Available here: https://kidadl.com/facts/animals/mopane-worm-facts