Warthog
Phacochoerus africanus
Has two sets of tusks on it's face!
Advertisement
Warthog Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Artiodactyla
- Family
- Suidae
- Genus
- Phacochoerus
- Scientific Name
- Phacochoerus africanus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Warthog Conservation Status
Warthog Facts
- Main Prey
- Grass, Roots, Bulbs
- Habitat
- Arid savannas and grass plains
- Predators
- Lion, Hyena, Crocodile
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 4
View all of the Warthog images!
“Warthogs are herbivores by choice, omnivores by necessity.”

A large member of the swine family, the warthog is an animal species that is best known for its four sharp tusks and padded bumps, or warts, on its face. The females of the species are quite social and live out their lives in family groups called sounders. Although they may look vicious, these animals prefer to run from predators rather than fight and are not aggressive unless backed into a corner. Warthogs have a conservation status of “Least Concern” at this time, but humans have become a severe threat to these animals due to overhunting in certain areas.
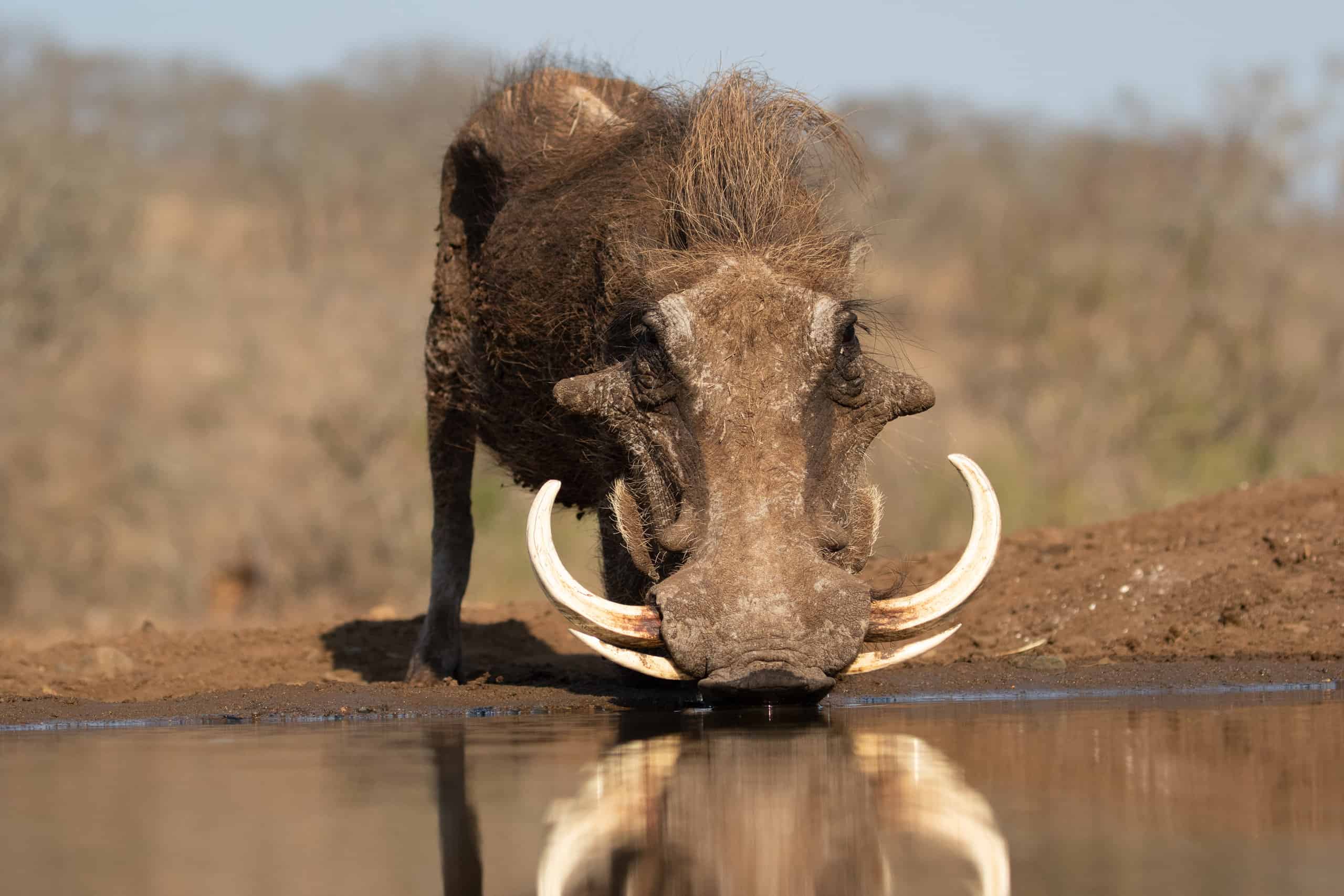

Warthog drinking by the water’s edge and looking like it just wallowed in the mud to cool off.
©Peter van Dam/Shutterstock.com
Incredible Warthog facts!
- The thick bumps on a warthogs face help to protect the males when they fight during mating season.
- Warthogs are animals that don’t make their own homes. Instead, they move into abandoned aardvark dens.
- Female warthogs are social animals and live in groups called soundings, while the males are more territorial and prefer to live alone.
- Like other pigs, they don’t have sweat glands and must roll around in the mud to cool off.
- Females who lose their own babies will foster other nursing piglets.
Scientific name
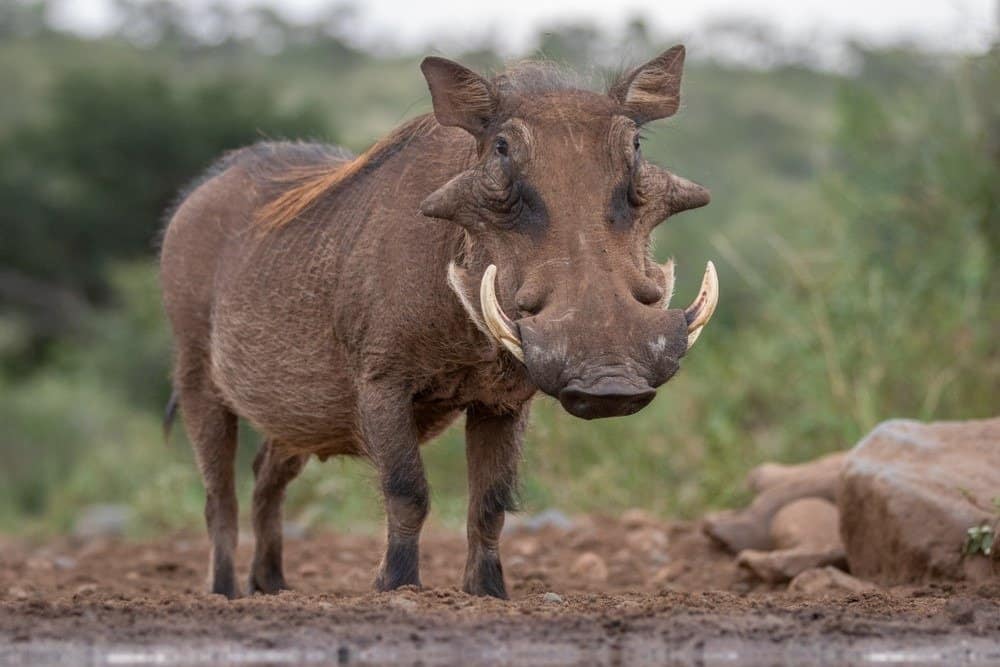

Common Warthog in the wild
©Wim Hoek/Shutterstock.com
The warthog is a mammal, which means it is warm-blooded and its young are suckled by the females. The common warthog’s scientific name, Phacochoerus africanus, comes from the Greek words “phakos,” which means “a mole or wart,” and khoiros, which means “a pig or hog.” As you can see, that translates directly to its common name, warthog. The last part, Africanus, refers to its location in Africa.
Types
There are two species of warthog:
- Common warthog (Phacochoerus africanus), which has four subspecies
- Nolan warthog (P. a. africanus)
- Eritrean warthog (P. a. aeliani)
- Central African warthog (P. a. massaicus)
- Southern warthog (P. a. sundevallii)
- Desert warthog (Phacochoerus aethiopicus), once thought extinct but recently discoverd in East Africa, has different facial features. For example, the ends of the ears have curled back tips; the incisors are missing, and the snout is larger. There were two subspecies, but the Cape Warthog (Phacochoerus aethiopicus aethiopicus) went extinct in the 1870s. The remaining subspecies is the Somali warthog (P. a. delamerei).
Evolution
These two species of warthog may have diverged already 4.4 million years ago. Research is revealing a long history of interbreeding, adaptation to diseases, and expansion of range.
Appearance
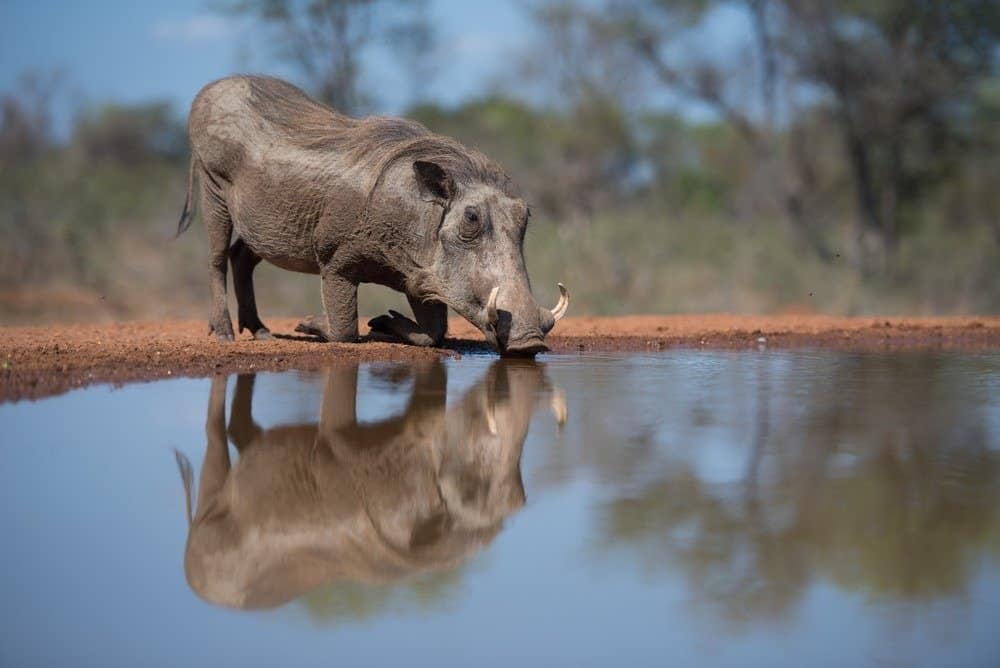

A warthog, with its large head and four tusks, will kneel on its forelegs’ calloused pads to drink from a pool of water.
©Villiers Steyn/Shutterstock.com
Warthogs are animals with big heads with padded bumps on each side and four sharp tusks. They are dark brown in color and mostly bald, but they do have a thick mane that runs from their head to the middle of their back. They also have tiny, tufted tails that stand straight up in the air when they run. Warthogs are unusual in that they will kneel to drink from a pool of water or to graze which has given them calloused pads on their forelegs.
The average size is between 120 and 250 pounds and about 30 inches tall at the shoulder. The males of this species tend to be larger than the females. Learn about the ugliest animals on earth here.
Behavior
Because of the warthog’s size and appearance, many people think they are aggressive. On the contrary, they generally prefer to run away from predators rather than fight. Reaching speeds of up to 30 miles an hour, they are quite adept at outrunning danger. When fleeing danger, they will back into their dens with their massive tusks facing forward so they can defend themselves if necessary.
This species of the pig family likes to wallow in the mud like its domesticated cousins. They submerge themselves both to cool down and to avoid insects. Warthogs also enjoy a symbiotic relationship with oxpeckers to aid them with insect relief. These tiny birds ride on the animal’s back and eat the bugs that are bothering them.
Habitat

Warthogs like to live in savannahs where there are watering holes for wallowing. Shown is the extinct Cape Warthog.
©Avrand6 / CC BY-SA 4.0 – License
Warthogs are native to the sub-Saharan region of Africa (East and Southern Africa). They prefer to live in cooler, open areas like savannahs and rainforest. While they avoid severe deserts, they will sometimes live in a semi-desert area. Though warthogs are excellent diggers, they don’t make their own dens. Instead, they move into abandoned aardvark dens.
Diet
Warthogs are omnivores that eat grass and tubers almost exclusively. They have thick, calloused pads on their forelegs that protect their limbs while they bend to graze. If food is scarce, they will scavenge carcasses or eat insects to fulfill their caloric needs, but they never hunt for their food. They can also live for a few months without any water during dry seasons.
Predators and Threats
The most common predators of the warthog are lions, leopards, cheetahs, hyenas, and crocodiles. Eagles can also pose a threat to babies. Since many of these animals are nocturnal hunters, these animals go out to forage during the day and return to the safety of their burrows at night.
Humans also threaten the warthog population due to overcrowding and overhunting. In areas where humans are the most common predators, these animals will adjust their schedules to forage at night and hunker down in their dens during the day.
Warthog Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
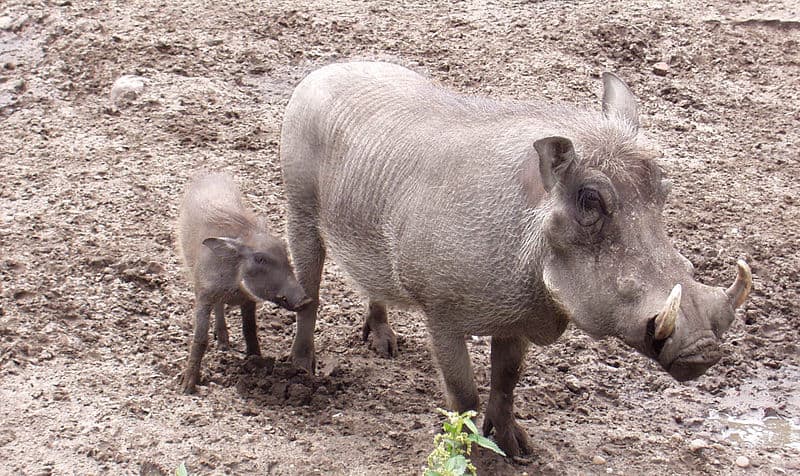

An adult warthog with a piglet. The gestation period is around 175 days.
©Herrick with Olympus C-220 Zoom, CC BY-SA 2.0 DE, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Males are known as boars, while female warthogs are known as sows. Both boars and sows have many mates throughout their lifetime. Unlike many other animals, the males rarely become aggressive during the mating season. Fights do occur from time to time, but these fights rarely ever cause significant injuries as they usually only strike with their heads and upper tusks.
Warthogs have the longest gestation period of any species of the pig family. Sows are pregnant for about 175 days and generally give birth during the dry season. Litters contain an average of three babies, called piglets. The piglets live exclusively in the den with their mothers for about six or seven weeks, and the females can live in the same sounding as their mothers for their entire lives.
On average, these animals can live for about 15 years in the wild and can live for up to 20 years in captivity.
Warthog Population
At this time, warthogs are at “Least Concern” on the conservation list. Their numbers have begun to dwindle in some areas because there are no regulations on how many of these animals may be killed by one hunter. This lack of regulation has led to overhunting. A recent count showed about 22,250 warthogs in the country of South Africa, but they live in other African countries as well.
Warthogs are still thriving in wildlife reserves, but many zoos have had little to no success at breeding them in captivity.
View all 108 animals that start with WWarthog FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a warthog?
A warthog is a large member of the pig family and a close cousin of the wild boar. They are dark brown in color and mostly hairless, aside from a mane that runs from their head to the middle of their back. Their most distinctive features are their four sharp tusks and the thick, bumpy pads or “warts” on their faces.
Are warthogs dangerous to humans?
Warthogs are not aggressive animals and, therefore, usually pose no threat to humans. They are still wild animals, however, and humans should respect them as such. A warthog that feels threatened or cornered may attack to defend itself.
What do warthogs eat?
Warthogs prefer to eat grass and tubers but will scavenge carcasses and eat insects when food is scarce.
What do warthogs eat at the zoo?
Although they are technically omnivores, warthogs prefer to keep an herbivore diet; they only eat meat when food is scarce. As such, the diet of warthogs in captivity typically consists of grain pellets and alfalfa hay and is supplemented by tasty vegetables like broccoli, squash, and carrots.
Where do warthogs live?
The common warthog is found all across the sub-Saharan region of Africa, while the desert warthog lives in northern Kenya and the Horn of Africa. While they both prefer wide-open spaces where it’s difficult for them to become cornered, the desert warthog favors a drier climate than the common warthog.
What is the difference between a common warthog and a desert warthog?
Desert warthogs have shorter, broader heads than common warthogs, and they have puffy areas around their eyes that extend to their warts. They are also lighter in color, and the tips of their ears are bent backward.
How fast can a warthog run?
When fleeing predators, a warthog can reach speeds of up to 30 miles per hour.
How big is a warthog?
The average warthog weighs between 120 and 250 pounds and stands about 30 inches at the shoulder. The males of this species tend to be slightly larger than the females.
What Kingdom do Warthogs belong to?
Warthogs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Warthogs belong to?
Warthogs belong to the class Mammalia.
What phylum to Warthogs belong to?
Warthogs belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Warthogs belong to?
Warthogs belong to the family Suidae.
What order do Warthogs belong to?
Warthogs belong to the order Artiodactyla.
What type of covering do Warthogs have?
Warthogs are covered in Hair.
What genus do Warthogs belong to?
Warthogs belong to the genus Phacochoerus.
What are some predators of Warthogs?
Predators of Warthogs include lions, hyenas, and crocodiles.
How many babies do Warthogs have?
The average number of babies a Warthog has is 4.
What is an interesting fact about Warthogs?
Warthogs have two sets of tusks on their faces!
What is the scientific name for the Warthog?
The scientific name for the Warthog is Phacochoerus africanus.
What is the lifespan of a Warthog?
Warthogs can live for 12 to 18 years.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/w/warthog/
- Safari Bookings, Available here: https://www.safaribookings.com/blog/warthog-facts