Monte Iberia Eleuth
Eleutherodactylus iberia
The smallest frog in the Northern Hemisphere!
Advertisement
Monte Iberia Eleuth Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Amphibia
- Order
- Anura
- Family
- Leptodactylidae
- Genus
- Eleutherodactylus
- Scientific Name
- Eleutherodactylus iberia
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Monte Iberia Eleuth Conservation Status
Monte Iberia Eleuth Facts
- Lifestyle
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Insects
- Type
- Amphibian
- Average Clutch Size
- 1
- Slogan
- The smallest frog in the Northern Hemisphere!
View all of the Monte Iberia Eleuth images!

The Monte Iberia eleuth is a dwarf frog (though it is often simply referred to as the Monte Iberia frog), only growing to be less than half an inch in length.
In the entire world, the only frog that is quite as small is the Brazilian Golden frog.
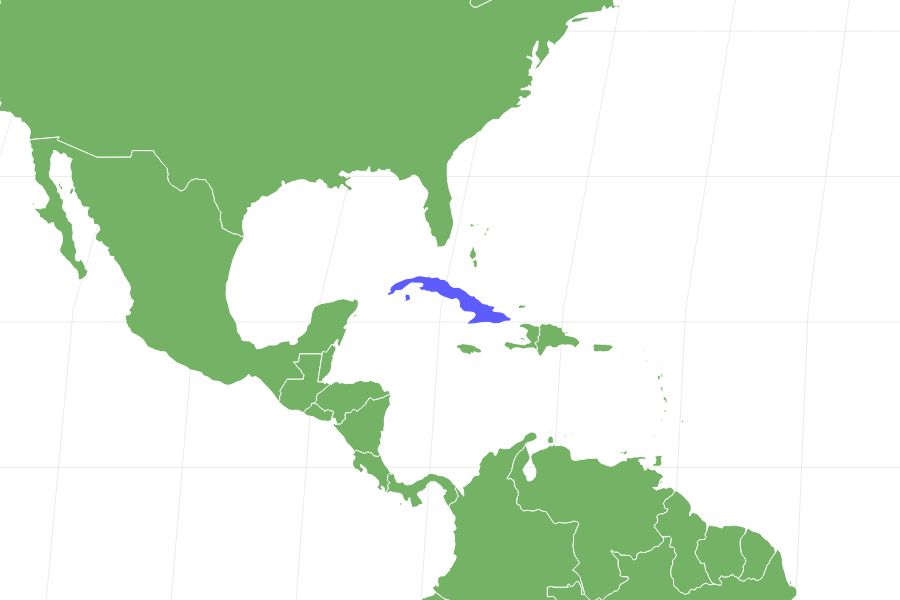
As part of the eleutherodactylid species, the Monte Iberia Eleuth (pronunciation: mon-tee ahy-beer-ee-uh eh-looth) frog can be found in eastern Cuba, though they only live in the rainforest.
Incredible Monte Iberia Eleuth Facts!

In order to protect itself from numerous predators, the Monte Iberia Eleuth employs a defense mechanism by producing a toxin that causes paralysis in muscles.
Here are some of the interesting facts about the Monte Iberia Eleuth
- These frogs are no bigger than the size of a fingertip at 3/8 inch long.
- The head Monte Iberia frog is rather wide, though their thin fingers create quite a contrast.
- These dwarf frogs have a rather bitter odor.
- The Monte Iberia Eleuth produces a muscle-paralyzing toxin to defend itself against its many predators.
- Unlike other frog species, these frogs are never tadpoles. Instead, they are born as a frog when they hatch from their egg.
Scientific Name

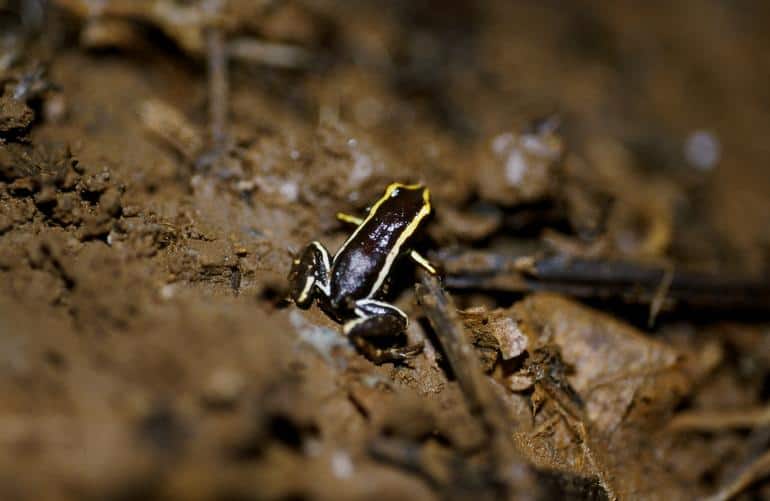
The scientific name given to the Monte Iberia Eleuth is Eleutherodactylus iberia (pronounced: mon-tee ahy-beer-ee-uh eh-looth).
©Haico Stegink/Shutterstock.com
The Monte Iberia Eleuth (pronunciation: mon-tee ahy-beer-ee-uh eh-looth) goes by the scientific name Eleutherodactylus iberia. They come from the kingdom Animalia and phylum Chordata. The class is called Amphibia and the order is Anura. The family that these miniature frogs come from is called Eleutherodactylid and the genus is called Eleutherodactylus.
The word “Eleutherodactylus” from the combination of two Greek words – “eleutheros” (“free” or “unbound”) and “dactylos” (“finger”). The toes of this dwarf hamster are slender and long with various colors.
Evolution and Origins
Discovered in 1993 on Mount Iberia in the Holguin Province, the small creature was named after its place of origin. Despite its initial discovery, there is still much to learn about this fascinating species. The Monte Iberia Eleuth is part of a closely related group found in Cuba, consisting of five other known species.
The dwarf frogs emit a distinctive and somewhat unpleasant odor. To safeguard themselves from numerous predators, the Monte Iberia Eleuth generates a toxin that paralyzes muscles.
Unlike many other frog species, these frogs do not undergo a tadpole stage. Instead, they hatch from their eggs as fully-formed frogs.
Appearance

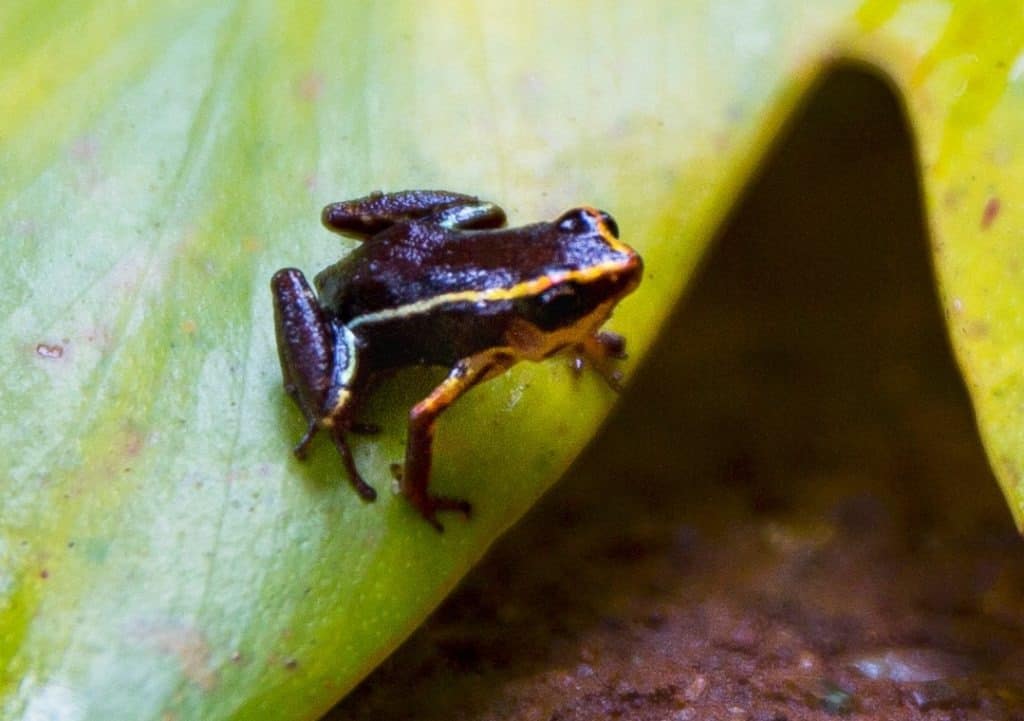
Measuring a mere 3/8 of an inch in length, the Monte Iberia Eleuth ranks among the tiniest dwarf frogs globally, showcasing its remarkably small size.
The Monte Iberia Eleuth is incredibly small at 3/8 of an inch in length, making it one of the smallest dwarf frogs in the world. Learn more about the world’s smallest animals here.
Though the name might have rather difficult pronunciation, their size, and black body make them easy to identify. The only other coloring on their back is a set of parallel yellow stripes that also go down each leg. They have a purple belly as well.
Their body is also quite striking with a wide head and thin fingers, the latter of which gives them their scientific name. Though other frogs may have some degree of teeth, the same is not true of this dwarf frog since they only have a few.
The yellow markings serve a very distinct purpose – warning predators. In nature, the reason for bold colors is to signify a poisonous animal. This rule applies to the Monte Iberia Eleuth as well since they produce pumiliotoxins. These toxins paralyze the muscles of the predator, protecting them from being eaten.
Behavior
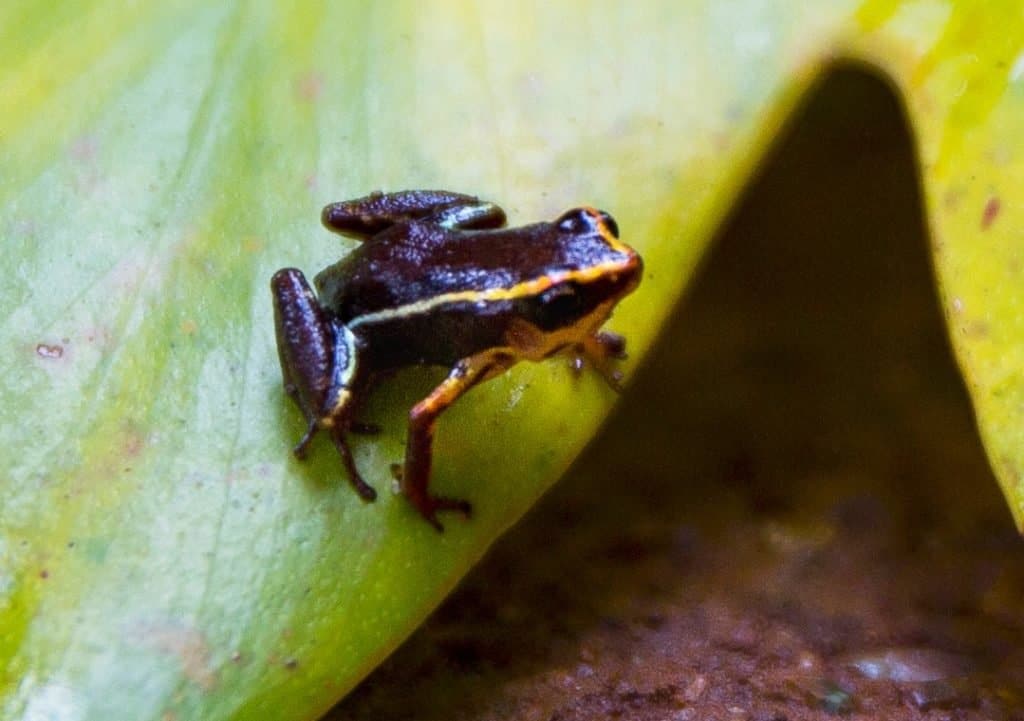

Due to the diminutive size of the Monte Iberia Eleuth, there has been limited research conducted on this particular frog species.
©Haico Stegink/Shutterstock.com
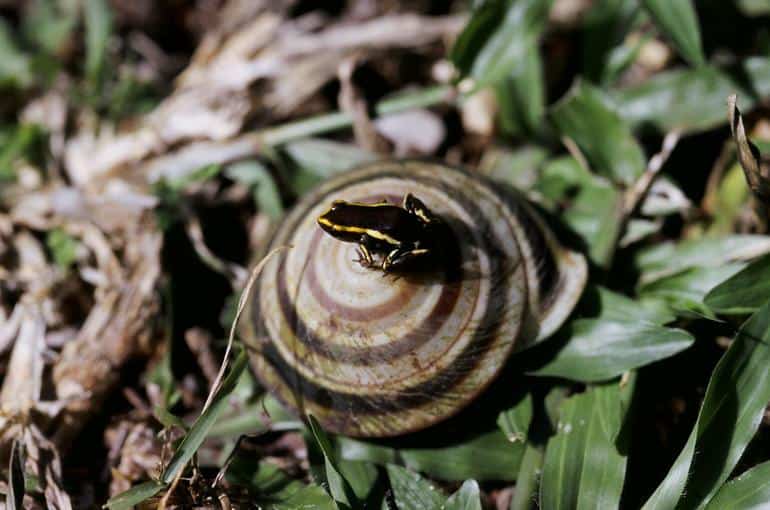
With the small size of the Monte Iberia Eleuth, there has been very little research on the frog. They tend to get around their habitat with little interference or monitoring. However, there are a few typical behaviors that have been witnessed, like their tendency to live diurnally.
The dwarf frog avoids danger to the best of its ability. Whenever a noise as small as a rustle of leaves arises, they jump away and avoid danger. When they wake at night, they keep a solitary lifestyle until they are ready to mate.
The preferred environment of the Monte Iberia Eleuth is in areas with minimal soil drainage, allowing them to hide beneath leaves, ferns, and other plant life. However, they can jump away from potential threats with relative ease.
One of the most unique characteristics of the Monte Iberia Eleuth is their way of communicating with high-pitched noises.
Habitat
Monte Iberis Eleuth prefers the climate of the tropical rainforest, but the population isn’t spread out much. Most of these frogs will find their home in Cuba, using the easternmost part of the area to create their home and source their food. They will live in areas as low as sea level for moisture, though they can survive at mild elevations as well. They need a lot of humidity to thrive.
These dwarf frogs like to stay fairly close to their own kind, which is why the population is condensed into two main groups. Most of them cannot be found more than 600 meters away from each other, even though they prefer to be separate from other frogs in their species until they procreate.
Part of the reason that the dwarf frog gets its name is because it is found on the Monte Iberia tableland. In fact, this is the region in which the Monte Iberia Eleuth was originally discovered.
Diet
The Monte Iberis Eleuth, despite its miniature size, will eat the same insect-rich diet that other frogs eat. Since they are often in moist areas, the diet naturally consists of the invertebrates that are located near these areas. The small carnivores will seek out their prey within the water bodies that they live near, allowing them to get a steady source of nutrients.
The majority of the foods that they will consume include spiders, moths, and other insects. They’ll also go after mites and ants for the protein that they need to keep their energy up.
Predators and Threats
The dwarf frogs, due to being a very tiny size, have a lot of predators and form an essential part of the natural food chain. Most animals that hunt down these dwarf frogs are simply larger than them, allowing the predator to easily overcome them. However, due to the toxic substance that they release, some predators are deterred.
Deforestation by humans has significantly disrupted the natural habitat of the Monte Iberia Eleuth, contributing to their limited population.
What Eats Monte Iberia Eleuth?
The Monte Iberia Eleuth often is hunted by birds, toads, and fish that are local to the area. However, the poisonous chemical that it releases is often the defense it needs to elude danger.
What Does Monte Iberia Eleuth Eat?
Small yet fierce, the Monte Iberia Eleuth is unafraid to go after moths, spiders, insects, and semi-aquatic invertebrates to feed themselves.
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
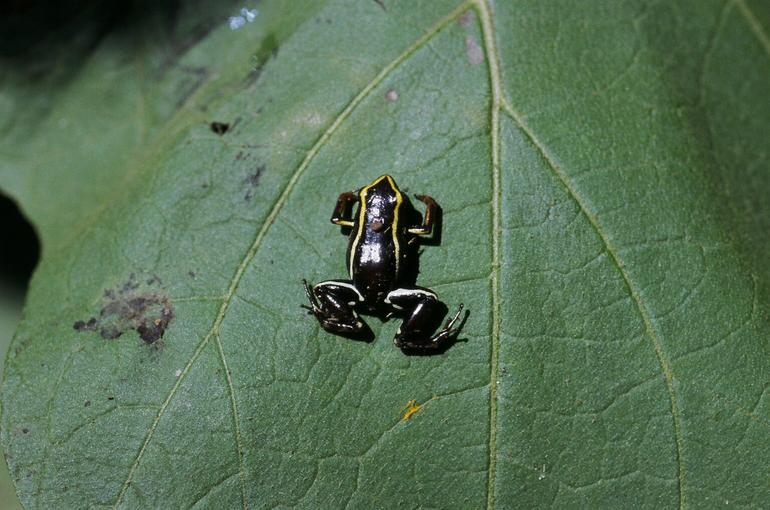

The reproductive process of these frogs remains largely unknown, with limited information available about their breeding and reproductive behaviors.
Little is known about the reproduction process of these frogs. The female releases eggs to hatch the dwarf frogs, but they are unlike other amphibians. They never start as tadpoles like other amphibians, but they are born as small frogs.
Sources suggest that when the first female was found, she was spotted next to a single egg. Researchers surmise that the reproduction process usually results in fewer eggs in this species and they do not lay a lot of eggs at once, which may be part of the reason for the small population.
The clutch size in these frogs is very small, potentially producing as few as one egg at a time. However, during the incubation period, both the male and the female frogs will care for their eggs until they hatch.
Even when they are full-grown, the dwarf frog doesn’t live very long, only reaching about 3 years old in their lifetime. Some of the dwarf frog species only live to be 1 year old.
Population
While the exact population of these frogs is unknown, their preference for living in one specific region in the world leads researchers to believe that the population is rather low. The first time they were discovered was in 1996.
According to the IUCN, this dwarf frog is currently critically endangered. The population is also said to be small around the world because they are tiny and reproduce much slower than the rest of the frogs – leading to a fewer number of eggs. Conservation efforts are not currently being made.
Zoo
Due to the limited population, finding this particular dwarf frog in zoos is rare.
View all 164 animals that start with MMonte Iberia Eleuth FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Monte Iberia Eleuths herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
The dwarf frogs have a carnivorous diet, so they eat a variety of insects (much like all the other frogs). Their diet primarily consists of insects, spiders, and moths.
What Kingdom do Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to?
Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum to Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to?
Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to?
Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to the family Leptodactylidae.
What order do Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to?
Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to the order Anura.
What genus do Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to?
Monte Iberia Eleuths belong to the genus Eleutherodactylus.
What type of covering do Monte Iberia Eleuths have?
Monte Iberia Eleuths are covered in permeable skin.
In what type of habitat do Monte Iberia Eleuths live?
Monte Iberia Eleuths live in waters around Mount Iberia.
What is the main prey for Monte Iberia Eleuths?
Monte Iberia Eleuths prey on insects, moths, and spiders.
What are some predators of Monte Iberia Eleuths?
Predators of Monte Iberia Eleuths include fish, toads, and birds.
What are some distinguishing features of Monte Iberia Eleuths?
Monte Iberia Eleuths have tiny bodies with bright yellow stripes.
How many eggs do Monte Iberia Eleuths lay?
Monte Iberia Eleuths typically lay 1 egg.
What is an interesting fact about Monte Iberia Eleuths?
Monte Iberia Eleuths are the smallest frog in the Northern Hemisphere!
What is the scientific name for the Monte Iberia Eleuth?
The scientific name for the Monte Iberia Eleuth is Eleutherodactylus iberia.
How fast is a Monte Iberia Eleuth?
A Monte Iberia Eleuth can travel at speeds of up to 5 miles per hour.
What is a Monte Iberia Eleuth?
Monte Iberia Eleuth is dwarf frogs, meaning that they are incredibly small. The overall size is about 3/8 of an inch, and they have black bodies with yellow stripes.
Where do Monte Iberia Eleuth live?
Monte Iberia Eleuth frogs can be commonly found in tropical rainforests and are best comfortable in wet atmospheres. They thrive in places with a lot of humidity. These tiny dwarf frogs are commonly found in easternmost Cuba.
What do Monte Iberia Eleuth eat?
Despite their tiny miniature size, these frogs eat much the same things as normal frogs. They hunt down a variety of invertebrates and their diet commonly consists of moths, spiders, and several insects.
How big are Monte Iberia Eleuths?
These frogs are small at just 3/8 inches.
What is the lifespan of the Monte Iberia Eleuth?
Monte Iberia Eleuth do not live for long and their lifespan is just about 1 to 3 years.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Soft Schools, Available here: https://www.softschools.com/facts/animals/monte_iberia_eleuth_facts/2708/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monte_Iberia_eleuth
- Planet Fauna, Available here: http://planetfauna.xyz/13-interesting-things-you-should-know-about-monte-iberia-eleuth
- Animals Around The World, Available here: https://shawnadamsweb.wordpress.com/