Sinosauropteryx
Sinosauropteryx prima
Sinosauropteryx were prominent in the Cretaceous and Jurassic periods.
Advertisement
Sinosauropteryx Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Family
- Compsognathidae
- Genus
- Sinosauropteryx
- Scientific Name
- Sinosauropteryx prima
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Sinosauropteryx Conservation Status
Sinosauropteryx Facts
- Location
- China
View all of the Sinosauropteryx images!
Sinosauropteryx prima is a compsognathid dinosaur. The compsognathidae consists of a family of colelurosaurian theropod creatures. The creatures are small, carnivorous and conservative in form.
The animals were prominent in the Cretaceous and Jurassic periods. They’re bird-like and the theory is they are a link between dinosaur reptiles and modern avians. It’s described as the first dinosaur taxon to likely have had feathers.
Sinosauropteryx is the first non-avialian dinosaur where coloration has been established. Studies have found evidence of a light banded tail and reddish color.
Description & Size
Here is general information about Sinosauropteryx.
- Sinosauropteryx was a small theropod.
- They have short arms and long tails.
- The longest recorded specimen reached up to less than four feet and weighed only a mere 1.2 pounds.
- Sinosauropteryx unique characteristics included 64 vertebrae in the tail.
- That number makes the Sinosauropteryx tail the longest compared to any other theropod’s body length.
- The hands were actually long in comparison to the arms.
- The creature’s thigh bone was 15 percent shorter than its skull.
- The Sinosauropteryx legs were over 30 percent the size of its arms.
- The avian aspect of Sinosauropteryx comes from the dino having feathers.
- Feathers were up to one inch long and were believed to help keep the animal warm.
Similar anatomically to Compsognathus, Sinosauropteryx differed from its European cousins in its proportions. And while the creature had feathers the animal wasn’t exactly bird-like. The feathers tended to be more thick filaments overlapping each other.
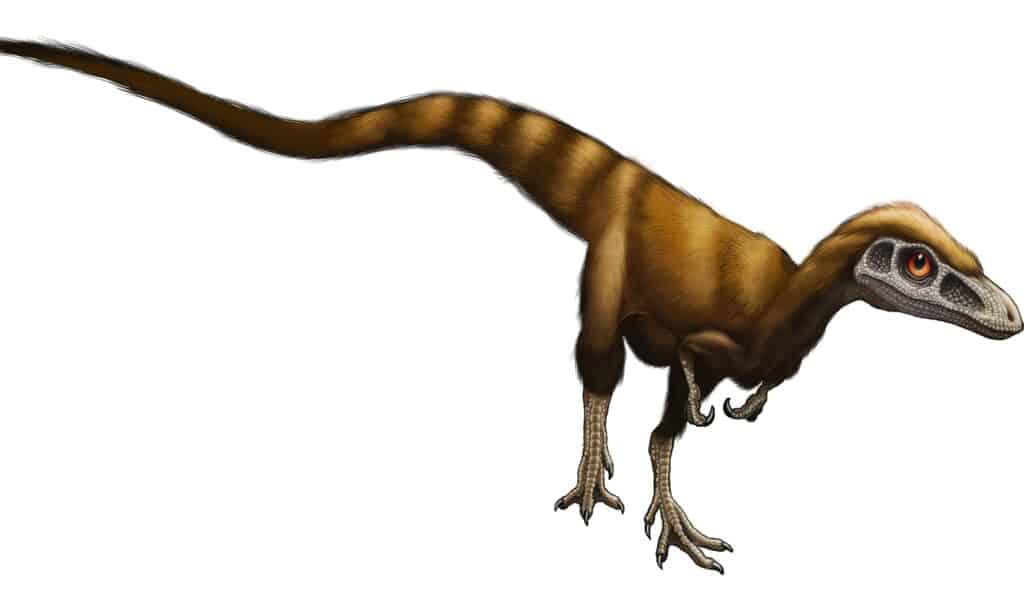
The Sinosauropteryx was a feathered theropod known for its short arms and long tail.
©Bee_acg/Shutterstock.com
Origin of Sinosauropteryx Name
The name “Sinosauropteryx prima” translates into “first Chinese dragon feather.” A framer discovered the first fossil near Liaoning Province’s Sihetun village in the mid-1990s.
The find was the first of non-avian dinosaurs with a feature-like structure. In a 2010 paper, scientists from the UK and China theorized that Sinosauropteryx likely had ginger-colored feathers and a striped tail.
Diet – What Did Sinosauropteryx Eat?
Over 125 million years ago, Sinosauropteryx prima was a meat-eater. Science theorizes the small dinosaur likely chowed on insects, lizards and smaller mammals. That’s evidenced by the finding of animals fossilized in the stomach of Sinosauropteryx.
Habitat – When and Where Sinosauropteryx Lived
Sinosauropteryx lived in the early Cretaceous period in northeastern China. The dinosaur was one of the first discovered in Liaoning Province’s Yixian Formation. The fossils were dug up by a farmer. The fossils, well-preserved, gave paleontologists a lot of information about the creature.
Threats and Predators
There are no records of the kind of lifestyle Sinosauropteryx experienced in its time. So, it’s almost all speculation.
Considering its smaller size, it’s likely Sinosauropteryx was prey for any of the larger carnivorous animals running around China during the early Cretaceous period. That includes Alectrosaurus. There’s a likely chance Sinosauropteryx was a potential diet for other small theropods like Gasosaurus.
The Cretaceous is the Phanerozoic Eon’s longest period, spanning 79 million years. That represents more elapses time than the time since the extinction of dinosaurs, which took place at the end of the Phanerozoic.
During the late Early Cretaceous era, China’s environment was arid-semi-arid with warmer climates in the stratum area in the northeast.
Scientists compiled info about the region via the diversity of known plant life, including a range of growth rings and petrified wood. There was the presence of flora dominated by conifers, cycads, ferns and horsetails. These signs indicate a humid climate.
Yet, evidence of growth rings in petrified wood showed humidity and water levels dropped on the regular. That indicates the humid, wet conditions divided their time with dry seasons. Studies of oxygen isotopes imply the average yearly temps at the time was 50 degrees Fahrenheit. That said there were cold winters, possibly a result of northern China’s high latitude at the time.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where Sinosauropteryx was Found
The Sinosauropteryx prima species was uncovered rather recently, considering how long the world has followed the dinosaur with such fascination.
A farmer in China came across the ancient animal in 1996. Li Yumin was also a part-time fossil hunter. He prospected in the Liaoning Province, acquiring fossils to see. After finding two slabs that had a noticeable quality, he sold the pieces to separate Chinese museums.
One of the museums was the National Geological Museum in Beijing. The director of that museum saw how important the discovery was. So did a pair of visitors to the museum, a Canadian paleontologist and an artist, Phil Currie and Michael Skrepnick, respectively.
Extinction – When Did Sinosauropteryx Die Out?
The truth is, we have no real idea of the precise geological period when Sinosauropteryx died out. But science has guesstimated Sinosauropteryx died out 125 million years ago, along with all other species of dinosaurs.
Similar Animals to Sinosauropteryx
There are a variety of avian-like dinosaurs similar to Sinosauropteryx. Here are several.
- Archaeopteryx: We only have an Archaeopteryx skeleton, cast from a fossil uncovered in a limestone matrix. But the slab itself and later investigation indicated this dinosaur was a feathered animal.
- Confuciusornis sanctus: Confuciusornis was a genus of crow-sized birds that probably lived around 150 million years ago during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods.
- Microraptor: This was a four-winged creature, though we have no evidence as to whether it could fly or glide.
- Dilong: A cousin of the Tyrannosaur, the Dilong distinguished itself by being a feathered creature (though there is an argument it was more likely hair than feathers.)
- Yutyrannus: The largest of known feathered dinos had filamentous feathers covering its entire body.
Sinosauropteryx FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When Was Sinosauropteryx Alive?
Based on studies of fossils, it’s believed the Sinosauropteryx period dates back to the early Cretaceous era. That’s 125 million years ago.
How Big Was Sinosauropteryx?
Sinosauropteryx was a small theropod. They were typically around the size of a medium- to large-sized dog. But unlike those canines, Sinosauropteryx weighed only a little over one pound.
Are Feathered Dinosaurs Normal?
There is strong evidence a large majority of theropod dinosaurs had feathers. These creatures are considered predecessors of the bird, a species categorized as dinosaur even today.
Could Sinosauropteryx Communicate?
It’s believed all dinosaurs may have had forms of communication. They used visual displays and vocalizations that included cracking, bellowing and hooting.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.