Compsognathus
†Compsognathus longipes
Advertisement
Compsognathus Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Order
- Theropoda
- Family
- †Compsognathidae
- Genus
- †Compsognathus
- Scientific Name
- †Compsognathus longipes
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Compsognathus Conservation Status
Compsognathus Facts
- Diet
- Carnivore
Compsognathus Physical Characteristics
View all of the Compsognathus images!

It’s not every day we think of a dinosaur as cute, but the Compsognathus may be the exception.
This carnivore was small, around the size of a large chicken or small turkey, walked on two legs, and had a slender body with a long tail. The Compsognathus was a Theropod that lived during the Jurassic Period. Learn more about this small but mighty dinosaur that lived during the period when some of the most fearsome dinosaurs roamed the earth.
Species, Types, and Scientific Names
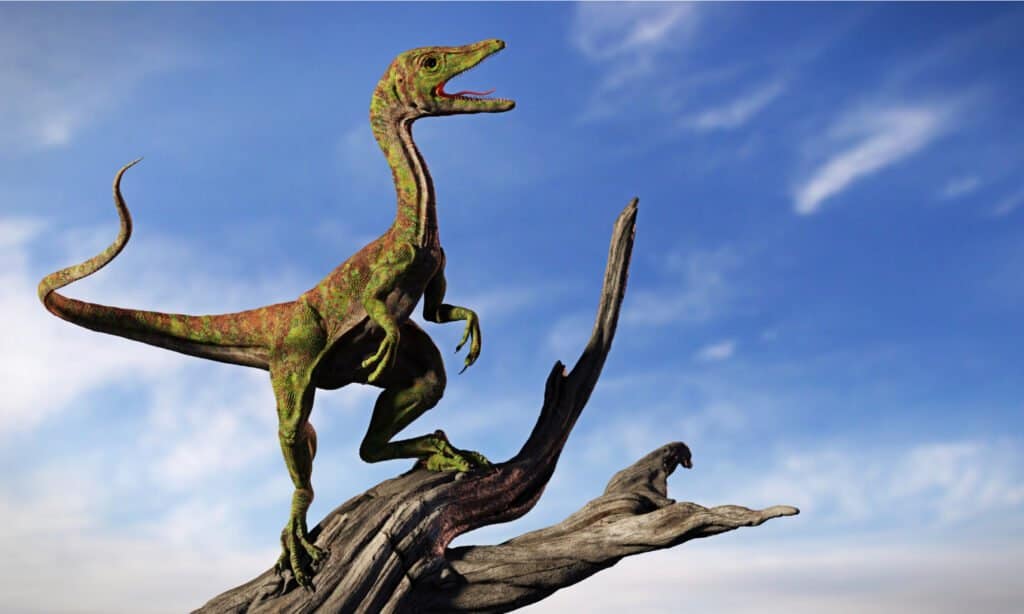

Compsognathus longipes, a small dinosaur, was only between 28 and 49 inches long.
©Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
There is only one known species of Compsognathus, although there are two specimens that show how the range of size that these dinosaurs could be. The Compsognathus longipes is part of the Compsognathidae family, which includes four genera of dinosaurs that display some bird-like features that hint at the link between dinosaurs and modern birds.
They belong to the Theropoda clade. Therapod dinosaurs had three toes on each foot and hollow bones. Tyrannosaurus rex and Velociraptors are two well-known examples of Therapods. Compsognathus was part of the Chordata phylum and Animalia kingdom.
Evolution and Origins
Roughly 150 million years in the past, during the Tithonian epoch of the late Jurassic period, they inhabited the region that is presently Europe. Two excellently preserved fossils have been discovered by paleontologists: the first in Germany during the 1850s, and the second more than a hundred years later in France.
Compsognathus inhabited the Late Jurassic Period, existing in the regions that are present-day Germany and France. This diminutive dinosaur likely subsisted on a diet of lizards, small mammals, young dinosaurs, and insects. Additionally, it likely scavenged leftover bits of flesh from deceased animals’ remains.
Description and Size
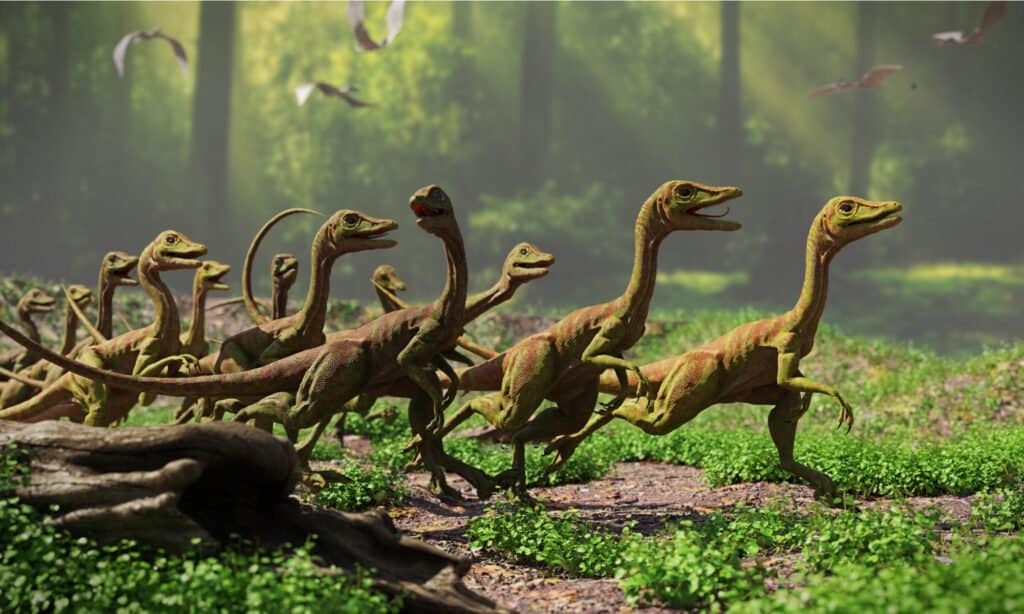

Compsognathus had slender bodies and their back legs were longer and more powerful than their front arms.
©Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
These dinosaurs were quite small. In fact, their size is one of their most notable features. They were between 28 and 49 inches long. There is some difference in size between the two specimens of Compsognathus discovered. One was on the lower end of this estimate, around 28 to 30 inches long. The other larger specimen was just over 4 feet long.
They probably weighed between 1 and 5 pounds. Again, the smaller, shorter specimen was also the lighter of the two. They had slender bodies and their back legs were longer and more powerful than their front arms. They also had long tails that helped them balance as they walked on two legs.
These dinosaurs had small but powerful jaws with sharp teeth. Due to their size, it’s likely that they ate smaller animals and insects. Some of their teeth were serrated, like a knife that can cut through meat. They probably used these teeth for chewing.
Some researchers believe that Compsognathus may have had feathers, although they were likely small if they were present at all. Evidence of feathers has not been found near any of the Compsognathus specimens, even though other dinosaurs preserved from the same time in similar conditions did have their feathers remain intact. So why do researchers think feathers were a possibility? Other related dinosaurs had feathers and there is some evidence on fossilized skin of similar dinosaurs that they had something like feathers or scales on at least part of their bodies.
Diet — What Did They Eat?
Even though they were small, these dinosaurs were carnivores. They likely ate small animals or other dinosaurs, as well as insects. Analysis of their preserved tooth fossils and jaws show that they could tear into the meat as well as efficiently chew it.
A lizard‘s remains were found inside the fossilized skeleton of one Compsognathus. This is some of the best evidence to show what a dinosaur ate while it was alive. The lizard was actually intact, showing that the dinosaurs swallowed it whole. Because the specific species of lizard was small and fast, scientists realized that the Compsognathus was an agile hunter and could outrun even quick, elusive prey.
Habitat — When and Where It Lived
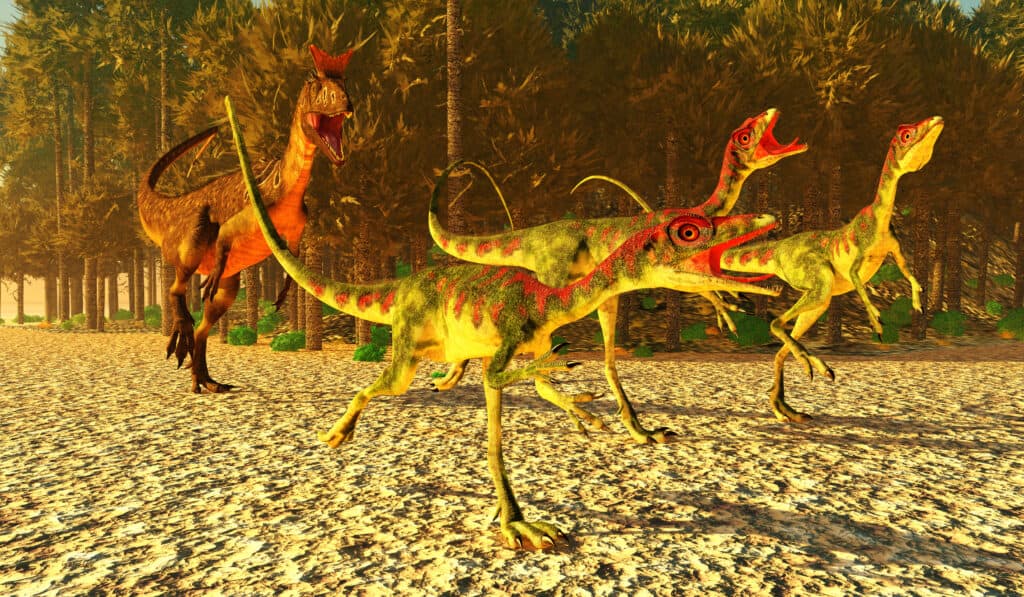

Compsognathus dinosaurs run for their lives as a Cryolophosaurus predator tries to catch them during the Jurassic Age.
©iStock.com/CoreyFord
This dinosaur lived during the Jurassic Period, around 150 million years ago. Their specimens were discovered in Germany and France. During the Jurassic, these regions were actually island chains in the Tethys Sea. Now, the Tethys Sea has become part of the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. The islands that the Compognathus called home are now parts of Europe.
The only two specimens of Compsognathus that have been discovered were in Germany and France. So while scientists can say without a doubt that they lived in these areas and when they were alive, they do not know how, where, or when they may have migrated or evolved elsewhere. It is possible that they were confined just to these regions.
Threats And Predators
Compsognathus was a small dinosaur and vulnerable to the hungry urges of larger carnivores. Allosaurus lived during the same time period, although their remains have been found in the western United States. Similar carnivores likely ate Compognathus dinosaurs. Birds also evolved during this time.
Because they were small, Compognathus could have been prey for larger bird-like creatures as well. Archaeopteryx was one example of a bird-like dinosaur that lived alongside the Compsognathus. Scientists can trace the origins of modern birds to these dinosaurs.
Young Compsognathus
Compsognathus was probably the most vulnerable as eggs or juveniles. These dinosaurs laid eggs to reproduce. Other dinosaurs could have easily stolen them from the nest. While adult Compognathus were small, juveniles were even smaller. Many scientists believe that the smaller of the two known specimens was a young Compsognathus. They would have had a harder time fighting off or running from potential predators.
Discoveries and Fossils — Where It was Found
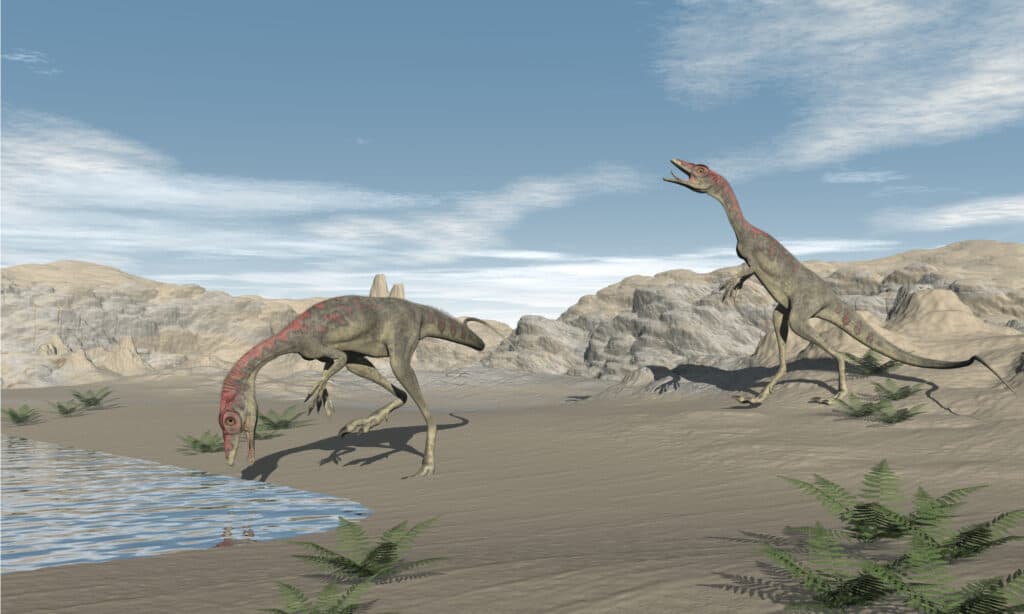

Compsognathus dinosaurs were carnivores. They likely ate small animals or other dinosaurs, as well as insects.
©Elenarts/Shutterstock.com
There are only two fossil specimens of Compsognathus. They were both discovered in Europe, one in Germany and the other in France. Amazingly, both were almost completely intact. This helped scientists learn a lot about what they looked like and how they lived. They even found the remains of their last meal, a lizard, inside the fossils.
The German fossil was initially thought to be a lizard when it was first mentioned in 1859. As interest in the specimen increased, researchers realized that it was actually a new species of dinosaur. The fossilized skeleton from France was discovered in 1971 near Nice. It was the larger of the two, at over 4 feet long. This led scientists to conclude that the smaller German specimen was a younger version of the same species.
Because they bear so much resemblance to the first prehistoric birds, scientists have studied Compognathus as a possible link between dinosaurs and birds. They are helped by the fact that they have not one, but two complete specimens to study. In 1998, paleontologists discovered teeth in Portugal that they believe belong to a relative of the Compsognathus, although they do not have enough of a specimen to know more than that.
Extinction — When Did It Die Out?
Scientists do not know exactly when the Compsognathus went extinct because the only two specimens they have do not correspond with any known extinction event. It is possible that they lived further into prehistoric times and we have not discovered evidence yet. It is also possible that they went extinct during the Jurassic Period due to competition for resources, predators, or even the rise and evolution of other species.
Similar Animals
- Archaeopteryx: While they may have been one of Compsognathus’ predators of the time, this bird-like dinosaur shared many of the same features. They were slightly larger and probably had feathers, however.
- Procompsognathus: This dinosaur lived during the Triassic Period but was very similar in size and overall structure to the Compsognathus. It may not be scientifically related to the Compsognathus, however. But because they share so many features, they share similar names.
Compsognathus FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When did Compsognathus live?
Compsognathus lived during the Jurassic Period, around 150 million years ago. Scientists do not know exactly when it went extinct, although both known specimens date to this time period.
How big was a Compsognathus?
These carnivorous dinosaurs were quite small, around the size of a modern chicken. They grew to be around 4 feet long and up to 5 pounds. As expected, the juvenile Compsognathus was considerably smaller.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Encylopedia Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/Compsognathus
- NPS: Jurassic Period, Available here: https://www.nps.gov/articles/000/jurassic-period.htm#:~:text=The%20Sauropoda%20were%20long%2Dnecked,Birds%20descended%20from%20Theropoda.
- Natural History Museum, London, Available here: https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/dino-directory/compsognathus.html