Eel catfish
Channallabes apus
Eel catfish breathe air and reach up on land to catch beetles. Scientists think they may be a missing link between fish and lizards.
Advertisement
Eel catfish Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Siluriformes
- Family
- Clariidae
- Genus
- Channallabes
- Scientific Name
- Channallabes apus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Eel catfish Conservation Status
Eel catfish Facts
- Main Prey
- Beetles
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- Eel catfish breathe air and reach up on land to catch beetles. Scientists think they may be a missing link between fish and lizards.
- Biggest Threat
- Parasites, environmental degradation.
- Temperament
- Harmless
- Optimum pH Level
- 6.5-7.8
- Habitat
- Muddy freshwater wetlands.
- Predators
- Humans
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Favorite Food
- Beetles
- Common Name
- Eel catfish
- Special Features
- Lifts itself out of water to eat beetles from land.
- Location
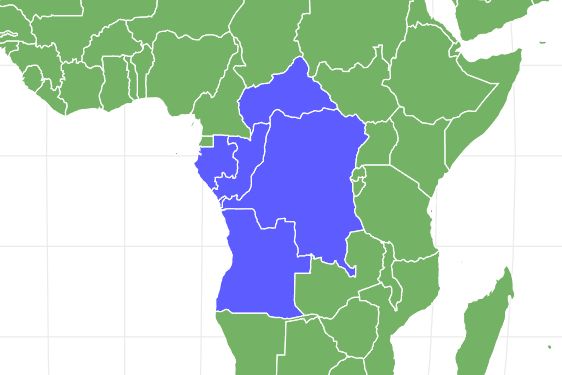
- Congo river basin, central Africa
View all of the Eel catfish images!
“Eel catfish breathes air and reaches out of the water to eat beetles on land!”
Eel Catfish Summary
The eel catfish is an air-breathing fish with a long, snake-like body. It is native to the swampy tropical wetlands of the Congo River basin in south-central Africa. Local people catch and eat them and institutions and private collectors around the world keep them in aquariums. What’s most intriguing about these fish is that they breathe air and they reach out of the water to catch beetles on land! Scientists think they may be an evolutionary link between fish and lizards.
Eel Catfish Facts
- This fish is related to catfish. It is called an “eel” catfish because of its similar appearance to eels.
- Beetles are its favorite food. It reaches out of the water to snatch them from land.
- It breathes air. Scientists think it may be an evolutionary link between fish and lizards.
- Eel catfish are not dangerous. People eat them and keep them in aquariums.
- Although not endangered, they are vulnerable to parasites and polluted water.
Eel Catfish Scientific name
The scientific name of the Eel Catfish is Channallabes apus. It is one of 6 species in the Channallabes family.
Channallabes comes from the Greek words, “channe,” meaning “anchovy” and “allabes,” the name of a variety of Nile lamprey with a similar appearance.
Apus is from the Greek prefix “a-” meaning “without” and “pous” or “foot. This is because the Eel catfish does not have pelvic fins.
Eel Catfish Appearance
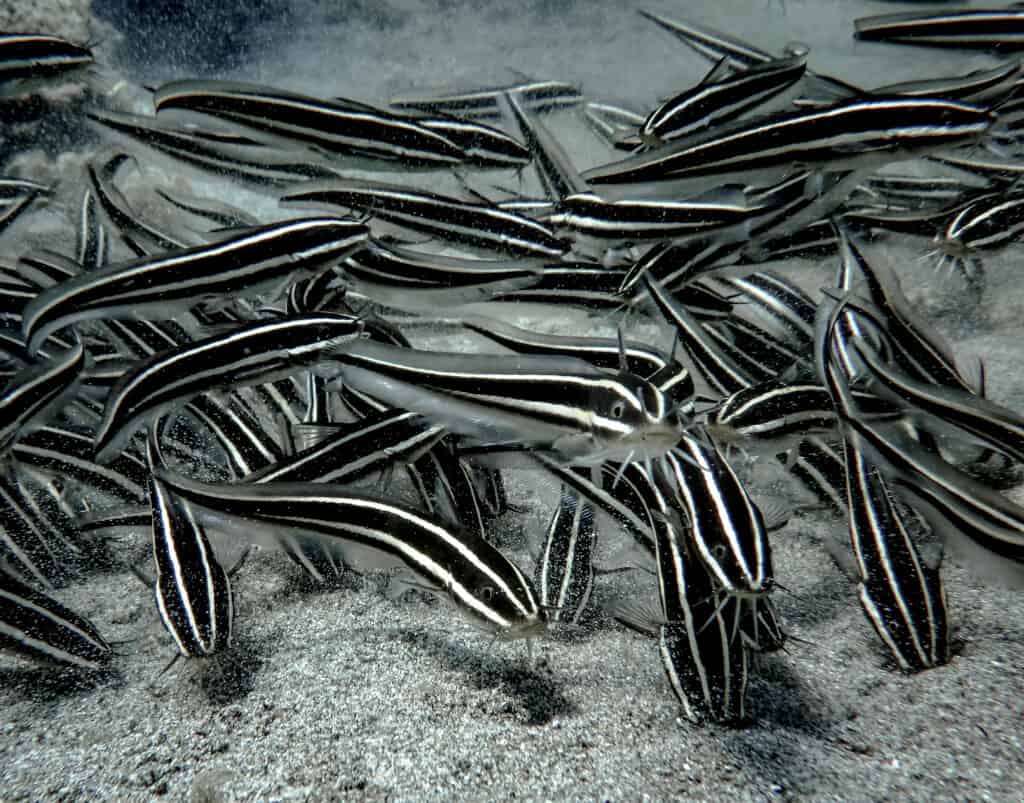

The eel catfish are named for their snakelike body, which resembles an eel. These fish can breathe air for short periods.
©iStock.com/norman lopez
The eel catfish is a species of ray-finned fish. They are black or dark brown, but some unusual red specimens have been found in caves in the Congo. Because they live in dimly lit, muddy conditions, they have small hidden eyes.
This species is part of the family of labyrinth catfishes. Although it is not scientifically classified as an eel its snakelike body resembles one. They have long, slender bodies with widely spaced spines. They have no pectoral fins, but their dorsal fins (the fins on their backs) go around their entire body and make a single fin that includes caudal and anal fins.
Their jaw muscles are hypertrophic — enlarged at the cellular level — an adaptation that gives it an especially powerful bite.
The eel catfish has special tree-like organs growing from its second and fourth gill arches, which allows it to breathe oxygen directly from the air for short time periods.
They can grow up to 16 inches long, which is about the same as the height of a bowling pin. Females are broader in the body than males. They are one of the smallest kinds of catfish regularly hunted by anglers.
Eel Catfish Behavior
The eel catfish is nocturnal and enjoys dim light conditions. It likes to hide in submerged branches, burrow into sand and gravel, and make nests in tangled exposed tree roots on river banks and swampy areas. They congregate with their own kind. In an aquarium it is best to keep three or four of them together.
One of its most interesting behaviors is that it has two different ways of eating. In the water, it sucks water into its mouth to capture pieces of vegetation, worms, or small fish. But it can also hunt on land! It watches from the water until a juicy beetle walks by and then propels itself out of the water. Using its specially adapted, flexible spine, it stabilizes its body in the water while reaching out and bending its head and down and using its jaws to snatch up a beetle.
It’s interesting to compare this method with another fish that feeds on land — the mudskipper. Unlike the eel catfish, the mudskipper actually uses its pectoral fins to pull its whole body onto land and drag itself short distances.
Scientists think these types of behaviors represent an evolutionary transitional step between fish and lizards. The eel catfish appears similar to fossils from the Devonian Period, 400 million years ago, when scientist believe sea creatures first evolved into terrestrial creatures.
Eel Catfish Habitat
Eel catfish are native to the warm tropical wetlands of the Congo River basin in Angola, Congo, The Democratic Republic of Congo, Gabon, and the Central African Republic. They live in muddy swamps and around tree roots in shallow water. Their appearance and coloration give them good camouflage, as they can look like just another tree root. They also like to burrow into boggy soil near rivers. Some people catch them by digging a waterlogged hole next to a river or swamp and fishing in it.
If you decide to keep one as a pet, give it a lot of driftwood for hiding places. Make sure to keep it in a covered tank with a weight on top to keep it from climbing out. The ideal temperature range for this type of fish is 71.6-80.6°F. The ideal pH range for their water is 6.5-7.8.
The best buddies for it in the tank would be more of the same species. But they can be combined with other West African species, such as medium-sized African barbs, tetras, and cichlids that keep to the upper layers of the water while the eel catfish burrow in the sand.
Eel Catfish Diet
They are omnivores. Their favorite foods are Coleoptera (beetles), worms, and shrimp. It’s not a picky eater. In captivity it will eat any kind of pelleted or frozen fish food such as bloodworms and shrimp, or live earthworms.
Eel Catfish Predators and Threats
In its natural environment, Eel catfish are hunted by larger fish and jungle carnivores, but human beings are one of their main predators.
The full size of their population is unknown but they are widely distributed throughout the Congo and are not considered an endangered species. They are listed as a species of “least concern” by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
This species is vulnerable to environmental degradation, including water pollution from human activities and bacterial or parasitic infections.
Eel Catfish Reproduction and Life Cycle
Eel catfish make nests in tangles of exposed tree roots near river banks. Females are larger than males. They reproduce sexually, but not much is known about their breeding habits. Researchers have found egg-filled individuals but this species has not been successfully bred in captivity.
Eel catfish are slow growing. Their average lifespan can range from 5-18 years. As they get older they tend to become more territorial and solitary. They may even eat smaller specimens of their own species.
Eel catfish Population
Their population is unknown but they are not considered endangered.
Related Animals
View all 117 animals that start with EEel catfish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is the catfish a type of eel?
No. It is a type of catfish. It is called an “eel catfish” because it has a long, slender body that looks similar to an eel.
What do eel catfish eat?
They are omnivores, eating vegetation, smaller fish, and insects. Their favorite meals though, are land-based beetles, which they lunge out of the water to grab in their jaws.
Do eel catfish taste good?
Many people in the Congo river basin catch and eat eel catfish, and they are also raised in fisheries. So they must taste pretty good!
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Planet Catfish / Published September 19, 2020 / Accessed September 9, 2022
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species / Published May 1, 2009 / Accessed September 9, 2022
- FishBase / Accessed September 9, 2022
- BBC News / Published April 12, 2006 / Accessed September 9, 2022
- Encyclopedia of Life / Accessed September 9, 2022
- Scotcat.com / Published January 1, 2010 / Accessed September 9, 2022
- The Website of Everything / Published January 1, 2010 / Accessed September 9, 2022
- Planet Catfish / Published July 15, 2010 / Accessed September 9, 2022