Guinea Pig
Cavia porcellus
Communicate using chirps, squeaks and burbles!
Advertisement
Guinea Pig Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Rodentia
- Family
- Caviidae
- Genus
- Cavia
- Scientific Name
- Cavia porcellus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Guinea Pig Conservation Status
Guinea Pig Facts
- Prey
- Grass, Seeds, Flowers
- Name Of Young
- Pup
- Group Behavior
- Herd
- Fun Fact
- Communicate using chirps, squeaks and burbles!
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss and hunting
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Four large front teeth
- Other Name(s)
- Cavy, Little Pig
- Gestation Period
- 58 - 72 days
- Habitat
- Grassland and mountain slopes
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Average Litter Size
- 4
- Lifestyle
- Diurnal
- Common Name
- Guinea Pig
- Number Of Species
- 5
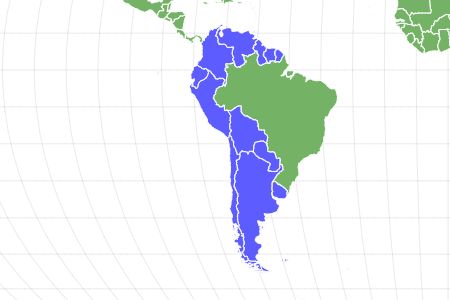
- Location
- South America
- Slogan
- Natively found in the Andes Mountain range!
- Group
- Mammal
Guinea Pig Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Grey
- Black
- White
- Orange
- Skin Type
- Fur
- Top Speed
- 5.5 mph
- Lifespan
- 3 - 8 years
- Weight
- 0.5kg - 1.5kg (1lbs - 3.5lbs)
- Length
- 20cm - 40cm (8in - 16in)
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 3 months
- Age of Weaning
- 3 weeks
View all of the Guinea Pig images!

Classification and Evolution
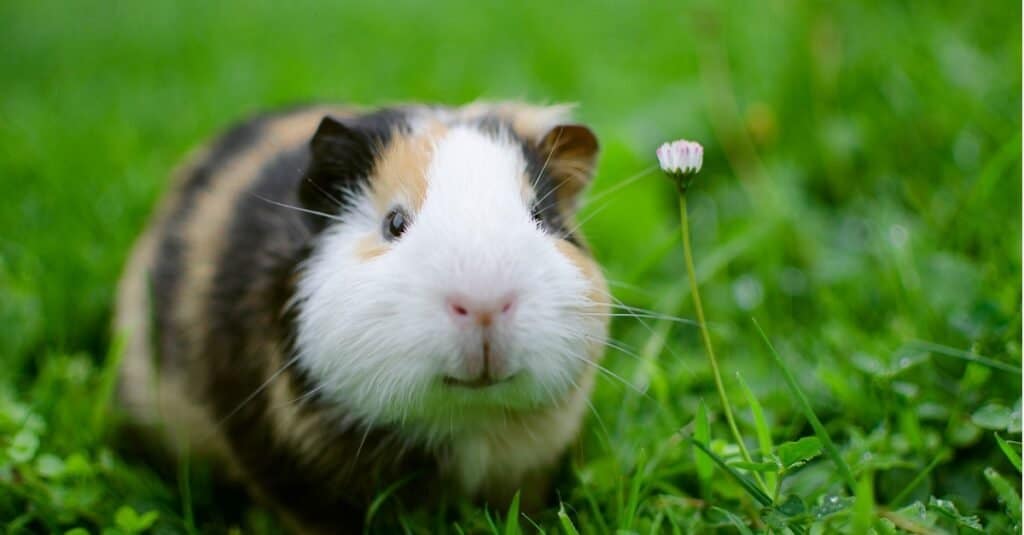

The Guinea Pig is a small species of rodent that is found inhabiting the Central Andes Mountains in South America.
©iStock.com/Galyna0404
See all of our expert product reviews.
The Guinea Pig (also known as a Cavy) is a small species of rodent that is found inhabiting the Central Andes Mountains in South America.
Named after Guyana where they are found in the wild and “pig” resembling their short and stout bodies, Guinea Pigs have been domesticated by people for over 3,000 years as they were originally kept and farmed as a source of food throughout much of their natural range in South America.
With the arrival of the Spanish to the continent in the 1500s, Guinea Pigs were then more selectively bred to be kept as pets and today are one of the most common domestic household pets, loved and kept by people all around the world due to their calm and docile nature, coupled with their small size.
Today there are five species of Guinea Pig found in the wild and fourteen different breeds of domestic Guinea Pig bred all around the world.
Different Types of Guinea Pig
- Peruvian guinea pig
- Skinny pig
- Abyssinian guinea pig
- American Guinea Pig
- Teddy guinea pig
- Sheltie guinea pig
- American Crested
- English Crested Guinea Pig
- Rex guinea pig
- Cuy
- Texel guinea pig
- Himalayan guinea pig
- Satin
Anatomy and Appearance
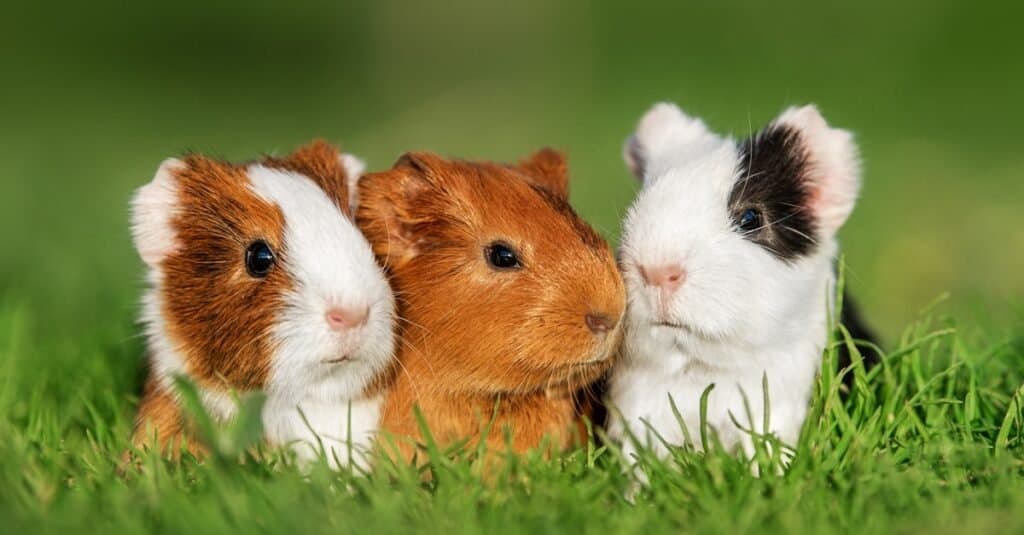

Guinea Pigs have a very distinctive appearance with small, stout bodies with no tail and a large head with large and alert eyes.
Health and Entertainment for your Guinea Pig
See all of our expert product reviews.
©Rita_Kochmarjova/Shutterstock.com
Guinea Pigs have a very distinctive appearance with small, stout bodies with no tail and a large head with large and alert eyes.
They have strong, short legs with four toes on their front feet and three on the back, all with sharp claws that help them when they are burrowing and scrabbling around in the wild. Like other species of rodents, Guinea Pigs have an exceptional sense of smell and hearing that coupled with their long whiskers, gives them a heightened awareness of changes in their surroundings so they are able to detect predators more effectively.
Guinea Pigs have long, coarse fur that in the wild is grey, brown, or black in color. Domestic Guinea Pigs, however, can be found in a variety of different colors with different hair lengths and smoothness. One of the most characteristic features of Guinea Pigs (and indeed all rodents compared to other mammal species) is the four large incisors at the front of their mouths.
These teeth are long and curved and grow continuously, but only the fronts are protected by a hard enamel coating. The backs of their teeth are made of a softer material that corrodes easily with constant gnawing which allows Guinea Pigs to keep their teeth as sharp as possible at all times.
Distribution and Habitat

Guinea Pigs are also found inhabiting regions of varying altitudes from 300 meters to 3,000 meters above sea level provided they are able to have good access to food and in areas that are suitable for burrowing.
©Miroslav Hlavko/Shutterstock.com
Guinea Pigs are found in a variety of habitats throughout the Central Andes Mountain Range in South America, from Colombia in the North to Southern Argentina with the exception of the more tropical regions of the Amazon Basin. They prefer grasslands, swamps, and rocky hillsides in areas with plenty of vegetation but that is predominantly open so they are more easily able to locate the threat of approaching predators.
Guinea Pigs are also found inhabiting regions of varying altitudes from 300 meters to 3,000 meters above sea level provided they are able to have good access to food and in areas that are suitable for burrowing.
Although they are capable of digging their own burrows, Guinea Pigs often prefer to move into abandoned burrows created by other small mammals or reside in rocky crevices on the hillside.
Behavior and Lifestyle
Guinea Pigs are diurnal animals that are most active during dawn and dusk. This is thought to be due to lower levels of activity from predatory species that struggle during these hours with the drastic changes in light. They are highly sociable living together in small groups of up to 10 individuals. Guinea Pig groups have a well-established hierarchy that is ruled by a single male and female, competition for which can often lead to fatalities.
Guinea Pigs are highly vocal, communicating with each other using an extensive range of vocalizations including chirps, squeaks, or burbles to show excitement or to warn others of approaching danger. They are also known to communicate by smell, excreting odors through scent glands on their bodies.
Guinea Pigs settle in burrows close to good sources of food with their little groups but often have their own individual nests where they sleep and hide.
Pets
Guinea Pigs make excellent pets due to their playful, social nature. They also live for several years, longer than most other rodents, so you can enjoy them longer than other pet rodents.
As noted above; Guinea Pigs are highly vocal and use their voice to express their personality. They make an excellent first pet for a child as they are fun to play with and require minimal maintenance.
If you’re considering a Guinea Pig for a pet, or already have one be sure to check out our guide to keeping guinea pigs as pets!
Reproduction and Life Cycles
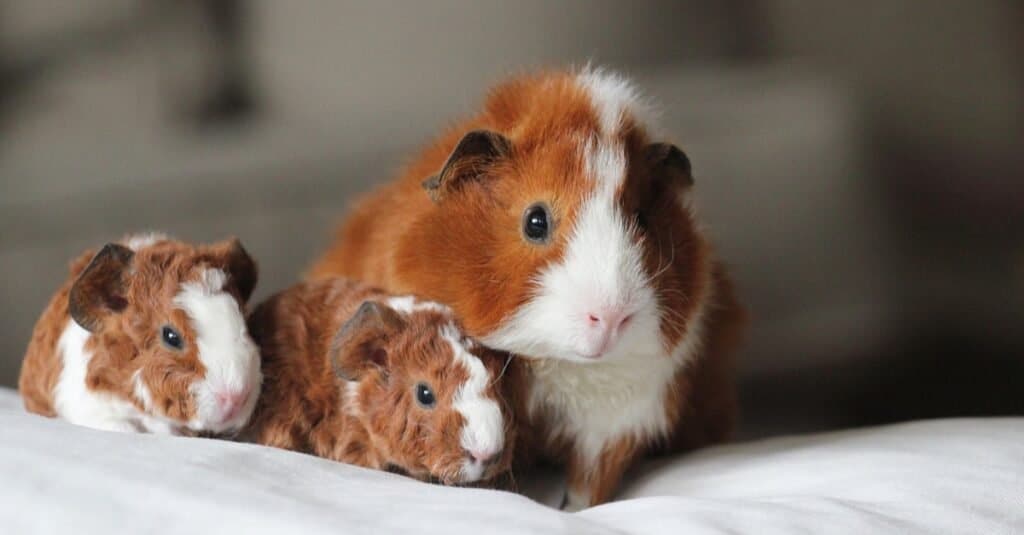

Pregnant Guinea Pigs
©Naomi Marcin/Shutterstock.com
Guinea Pigs are able to breed when they are around three months old. In the wild, there is no distinct breeding season as they are known to produce litters of young all year round but there are fewer born in the colder winter months. After a relatively long gestation period of between 58 and 72 days, the female Guinea Pig (known as a sow), gives birth to as many as 13 young although the average in the wild is closer to three or four.
Guinea Pig pups are very well developed at birth and unlike a number of other rodent species, are born with their long fur. They suckle on their mother’s milk for the first 21 days but are able to begin grazing independently within the group on solid foods by the end of their first week. During the course of a year, a female Guinea Pig may give birth to up to five litters that have a lifespan in the wild of three or four years.
Domestic Guinea Pigs are known to live a great deal longer than their wild counterparts, normally reaching the age of 6 although some have been known to live for even longer with the oldest recorded Guinea Pig being 15 years old.
Diet and Prey

Guinea Pigs are herbivorous animals which means that they only eat plant material in order to gain all of the nutrients that they need to survive. Grasses, leaves, seeds, bark, and flowers make up the majority of their diets on the mountain slopes in South America. Guinea Pigs are constantly grazing rather than eating large amounts of food in one go, which they primarily do during the twilight hours when there are fewer predators around.
They have well-trodden paths that they use to get between their food sources and their burrows and can often be seen in a mass gathering when a number of Guinea Pig groups are in the same area where food is in abundance. The natural diet of Guinea Pigs is very high in vitamin C so it is essential that domesticated pet Guinea Pigs are provided with a diet that contains plenty of it.
Along with grasses, hay, and vegetables, domestic Guinea Pigs are often supplemented with special nuggets that contain plenty of the nutrients that they need in order to effectively and healthily survive.
Predators and Threats

Due to their small size and natural instincts to freeze before attempting to quickly escape back to their burrows
©Lucie3/Shutterstock.com
Due to their small size and natural instincts to freeze before attempting to quickly escape back to their burrows, Guinea Pigs are preyed upon by a number of other animal species throughout their mountain habitats. Mammals including weasels and birds of prey are the main predators for wild Guinea Pigs along with domesticated dogs and cats in regions where they reside close to human populations.
Although some populations are heavily affected by habitat degradation, Guinea Pigs are fairly adaptable animals that are able to inhabit areas where other species may not thrive. They are also still captured and farmed for food by people throughout much of their natural range in South America.
Some populations have also been known to be severely affected by diseases from other animals in places where they are coming into regular and close contact with other domestic species.
Interesting Facts and Features
Guinea Pigs are known to exhibit a behavior known as “popcorning” when they become excited. Mostly displayed by young Guinea Pigs, they are able to jump into the air whilst running and quickly turn around in order to jump again in excitement.
Oddly enough, Guinea Pigs are known to very rarely close their eyes even while they are sleeping. Most commonly observed with domestic animals, it is thought to be a protective trait that enables them to stay as alert as possible at all times.
Interestingly enough, it has been reported that Guinea Pigs have been used by doctors to help to find illnesses in people. By placing the Guinea Pig on the person, they will give a little squeak when they have detected the location of the problem.
Click here to read more interesting Guinea pig facts.
Relationship with Humans
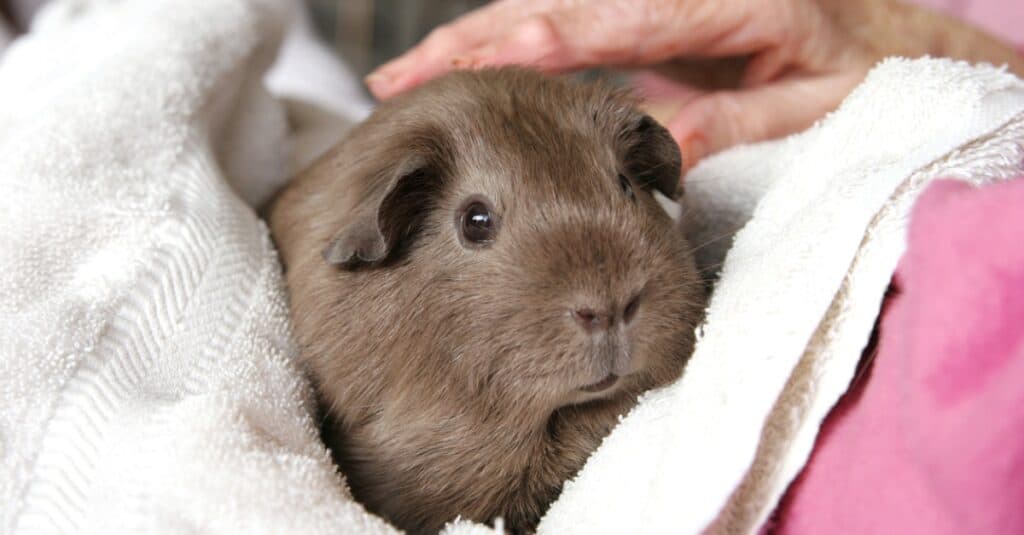

Guinea pigs are social companion animals.
©iStock.com/suemack
Due to their small size and ease of keeping, Guinea Pigs have been farmed by local people for food for thousands of years. Their calm and docile nature has led to them becoming one of the most commonly kept household pets all around the world, and they are now found in a wide variety of sizes and colors due to selective breeding.
The sweet and chatty temperament of Guinea Pigs has led to them becoming a favorite amongst pets for children, who are able to look after them with relative ease (providing they are overseen by a responsible adult). Their placid nature however has also sadly led to them being widely used in laboratory experiments for many years.
Conservation Status and Life Today
Today, four of the five Guinea Pig species found throughout South America are listed by the IUCN as animals that are of Least Concern of becoming extinct in the wild in the near future.
Despite declining population numbers in specific regions, their ability to breed so effectively and in a wide variety of changing habitats has allowed Guinea Pig population numbers to remain relatively stable.
The exception to this is the Santa Catarina’s Guinea Pig which is found in one area of Brazil. With only 42 individuals thought to remain in the wild and only in one small area, they have been listed as Critically Endangered in their natural environment.
Even More Guinea Pig Information
If you would like to learn even more about Guinea pigs, check out the following articles:
- Discover the Largest Guinea Pig Ever
- The World’s Oldest Guinea Pig
- Guinea Pig Names: Boy and Girl Names for Your Guinea Pig
- Guinea Pig as a Pet: How to Care for Your Guinea Pig
- Guinea Pig Types: The Ultimate Guide to Guinea Pig Breeds
- Guinea Pig Nail Clipping: How to Trim Guinea Pig Nails
- Discover Hairless Guinea Pigs: Skinny Pigs & Baldwin Guinea
- Bladder Stones in Guinea Pigs: Everything You Need to Know
- Do Female Guinea Pigs Have Periods?
- Guinea Pig Lifespan: How Long Do Guinea Pigs Live?
- What Temperature is Too Hot for Guinea Pigs?
- 7 Best Places to Adopt Guinea Pigs
- Do Guinea Pigs Bite? Everything to Know About Guinea Pig & Human Interaction
- Pregnant Guinea Pigs: How to Tell if Your Guinea Pig is Pregnant
- Are Guinea Pigs Nocturnal?
- Where Do Guinea Pigs Come From Originally?
- Why Do Guinea Pigs Squeak?
- Do Guinea Pigs Sleep?
- Male Guinea Pigs vs Female Guinea Pigs: What’s the Difference?
- How Long Are Guinea Pigs Pregnant?
- How Much Does a Guinea Pig Cost Per Year?
Guinea Pig FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What's the difference between guinea pigs and hamsters?
Guinea pigs and hamsters are often compared as they’re two of the most popular pet rodents. The primary difference between the two is that guinea pigs are several times larger. In addition, guinea pigs live longer than hamsters and are less nocturnal as well.
Are Guinea Pigs herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Guinea Pigs are Herbivores, meaning they eat plants.
What Kingdom do Guinea Pigs belong to?
Guinea Pigs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Guinea Pigs belong to?
Guinea Pigs belong to the class Mammalia.
What phylum to Guinea Pigs belong to?
Guinea Pigs belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Guinea Pigs belong to?
Guinea Pigs belong to the family Caviidae.
What order do Guinea Pigs belong to?
Guinea Pigs belong to the order Rodentia.
What type of covering do Guinea Pigs have?
Guinea Pigs are covered in Fur.
What genus do Guinea Pigs belong to?
Guinea Pigs belong to the genus Cavia.
Where do Guinea Pigs live?
Guinea Pigs live in South America.
In what type of habitat do Guinea Pigs live?
Guinea Pigs live in Grasslands and mountain slopes.
What are some predators of Guinea Pigs?
Predators of Guinea Pigs include weasels, raptors, and dogs.
How many babies do Guinea Pigs have?
The average number of babies a Guinea Pig has is 4.
What is an interesting fact about Guinea Pigs?
Guinea Pigs are natively found in the Andes Mountain range!
What is the scientific name for the Guinea Pig?
The scientific name for the Guinea Pig is Cavia porcellus.
What is the lifespan of a Guinea Pig?
A baby Guinea Pig is called a pup.
How many species of Guinea Pig are there?
There are 5 species of Guinea Pig.
What is the biggest threat to the Guinea Pig?
The biggest threats to the Guinea Pig are habitat loss and hunting.
What is another name for the Guinea Pig?
The Guinea Pig is also called the cavy or little pig.
How many Guinea Pigs are left in the world?
The population size of the Guinea Pig is unknown.
How fast is a Guinea Pig?
A Guinea Pig can travel at speeds of up to 5.5 miles per hour.
What are the differences between Guinea pigs and Gerbils?
The major differences between Guinea pigs and gerbils are size, diet, behavior, and temperament.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals