Guppy
Poecilia reticulata
Guppies give live birth to their young
Advertisement
Guppy Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Cyprinodontiformes
- Family
- Poeciliidae
- Genus
- Poecilia
- Scientific Name
- Poecilia reticulata
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Guppy Conservation Status
Guppy Facts
- Prey
- Algae, plant particles, mosquito larvae
- Group Behavior
- School
- Fun Fact
- Guppies give live birth to their young
- Biggest Threat
- Water pollution
- Distinctive Feature
- Brightly coloured body and fins and give birth to live young
- Other Name(s)
- Rainbow fish, millionfish
- Gestation Period
- 3-4 weeks
- Optimum pH Level
- 5.0 - 7.0
- Habitat
- Streams, shallow pools near bigger bodies of water
- Predators
- Birds, larger fish
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Favorite Food
- Algae
- Type
- Cyprinodontiformes
- Common Name
- Guppy
- Number Of Species
- 276
- Average Clutch Size
- 80
- Slogan
- Also known as the Millionfish!
The Guppy fish, with their colorful designs and feathery tailfins, are favorites with people who keep freshwater aquariums.
Guppies are tiny tropical fish that live throughout the world. They are sometimes called rainbow fish or million fish. 276 species of guppy belong to the Poeciliidae family.
3 Incredible Guppy Facts!
- The million fish: Guppies go by alternate names, including rainbow fish and million fish. They are called rainbow fish because of their colorful scales. The nickname million fish refers to the breeding habits of the fish. A female guppy can have 50 to 100 babies every month!
- Fighting malaria: Guppies are small tropical fish that play a part in the fight against malaria. Mosquitoes are known carriers of this disease. To reduce the mosquito population, these fish have been released into bodies of water around Asia and other areas to eat mosquito larvae.
- Birth announcement: While most fish reproduce by laying eggs, guppies do things another way. The eggs are incubated while still inside the female guppy. The female is pregnant for about a month, then gives live birth to dozens of babies.

Classification and Scientific Name
Poecilia reticulata is the scientific name for these fish. Poecilia is a Greek word meaning speckled, and reticulata is Latin, meaning a net-like pattern. These wild fish are also called rainbow fish and million fish.
They belong to the Poeciliidae family and are in the class Actinopterygii.
There are 276 species of guppy fish. A few examples include the following:
- Endler guppy
- Swamp guppy
- Cobra guppy
- Glass guppy
- Leopard guppy
Origins and History
In 1866, geologist Robert John Lechmere Guppy sent a small fish from streams in Trinidad to London, where it was given the scientific name Giradinus Guppyi in honor of Mr. Guppy.
Guppy is commonly recognized as the discoverer of the wild Guppy, even though a Spaniard named De Filippi stumbled upon the species on the island of Barbados in 1862 and classified it as a new genus and species, giving it the name Lebistes poeciliodes.
Prior to De Filippi, a German biologist named Julius Gollmer found Guppies in the Rio Guayre near Caracas, Venezuela, in 1857 and 1858. He sent the preserved fish to the Imperial Prussian Academy of Science in Berlin. However, they were not very enthusiastic about them and gave Gollmer only a small reward and nominal recognition. The specimens were put in a storeroom due to a filing mistake.
In 1859, Wilhelm Karl Hartwig Peters wrote the first scientific description of what was in the jars. Sadly, the jars were not properly labeled or stored, so only the female specimens were recognized as a new species named Poecilia reticulata.
Following 1866, the male specimens that Julius Gollmer had sent to Berlin were located and officially called Giradinus Guppyi. The females, which had previously been called Poecilia, were given the same name as the males, as was traditional during this period. Many collectors delivered Guppies to museums, and they were assigned no fewer than 11 distinct scientific names. It was eventually revealed that these were merely different strains and not new species.
The scientific name of Guppies has undergone a number of revisions in the past 100+ years, finally settling on the name of Poecilia reticulata. You may still, however, see the Guppy described under the scientific name of Lebistes reticulata in some scientific publications.
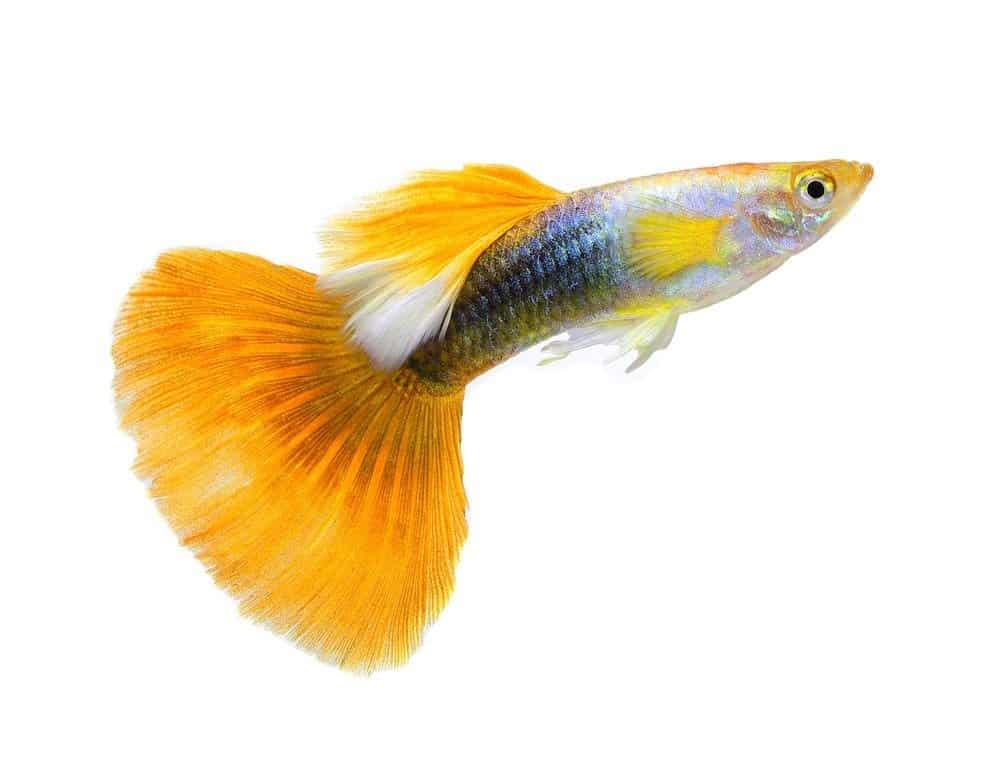

©SOMMAI/Shutterstock.com
Species
Guppy fish are categorized in many ways, including by their scale colors, scale patterns, and even the shape of their tail. Three of the most well-known types include:
- Fancy guppy: They are known for their especially bright colors and elaborate tailfins. They can have fan tailfins, triangle tailfins, and veil tailfins, to name a few.
- Endler’s guppy: These fish are less colorful than fancy guppies and have a simple round or spade tailfin. Someone who wanted a colorful addition to their aquarium would likely choose a fancy over an Endler’s guppy.
- Swamp guppy: This type is rarer than those in the above two groups. They are found in streams around Trinidad and prefer a habitat with brackish water.
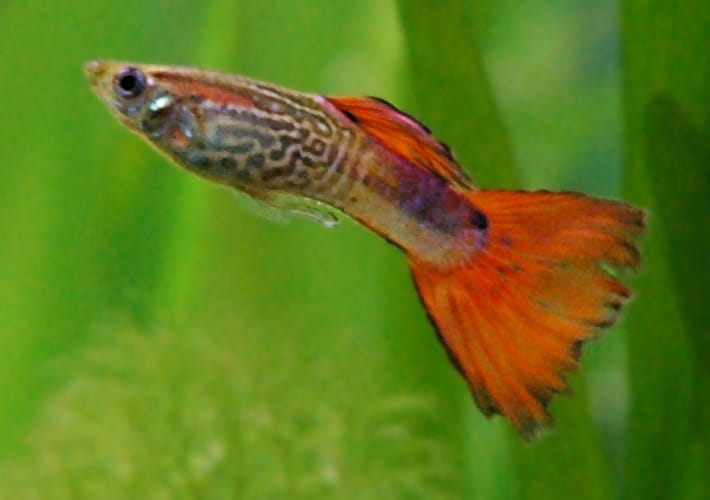

Guppy
©Jdiemer / Creative Commons – Original
Appearance
Guppy fish can be yellow, red, blue, green, black, white, or orange, depending on their species. For instance, a blue cobra guppy has a dark blue body with a vertical black striped pattern that looks like a cobra snake’s back. It has a triangle tailfin of bright blue with a yellow and black pattern mixed in. Alternatively, a red guppy has scales that feature a mixture of bright red and gold. Its fan tailfin is bright red with light gold at its tip. From leopard to cobra guppies to the Dumbo ear dragon guppy, there are unique colors and scale patterns throughout this group.
These fish have a number of different tailfin shapes as well. Fan tail, flag tail, lyre tail, sword tail, round tail, and veil tail are a few examples. The longest a guppy can get is 2.4 inches.
The bright coloration of guppy fish makes them a clear target for many predators. However, they do have a unique defensive feature. When a predator approaches, the fish’s irises turn from silver to black. This allows the fish to dart out of the path of danger while the predator focuses on what it thinks is the fish’s head.
In addition, wild guppies swim in large schools containing sometimes hundreds of fish. This means if a predator attacks, there’s a good chance that most of the fish in the school will be able to get away.
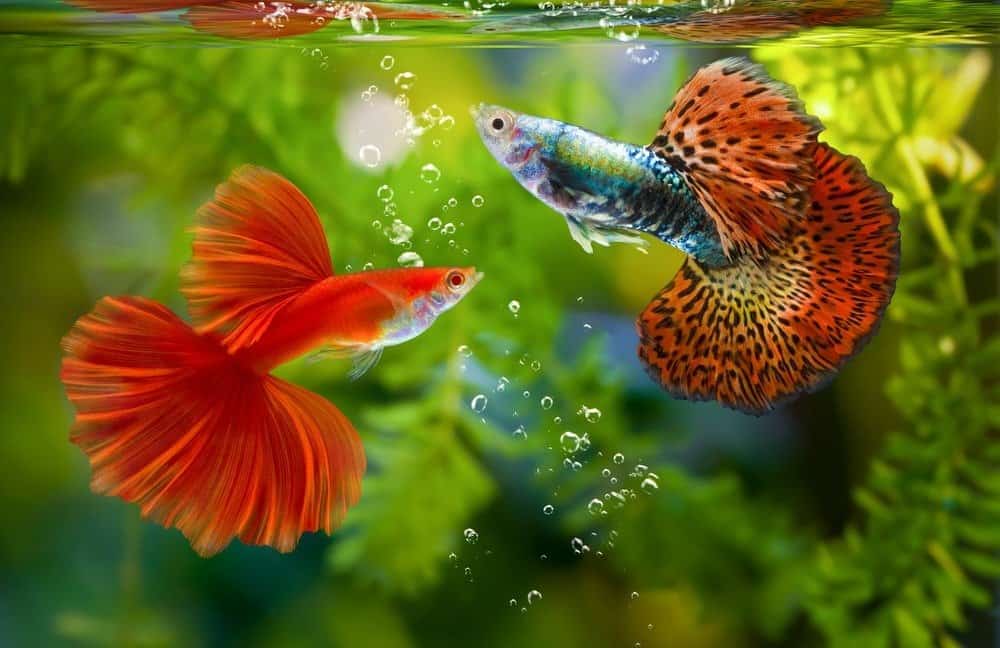

©panpilai paipa/Shutterstock.com
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Brazil, Jamaica, Antigua, Barbados, Venezuela, and the U.S. Virgin Islands are just a few of the places where wild guppy fish are found. In fact, they are now found everywhere in the world except Antarctica. They are able to live in freshwater or brackish water. Their habitat includes streams and shallow pools near larger bodies of water.
The exact population of this tropical fish is unknown. However, the conservation status of the fish is Least Concern. These wild fish reproduce in large numbers, which helps their population remain stable.
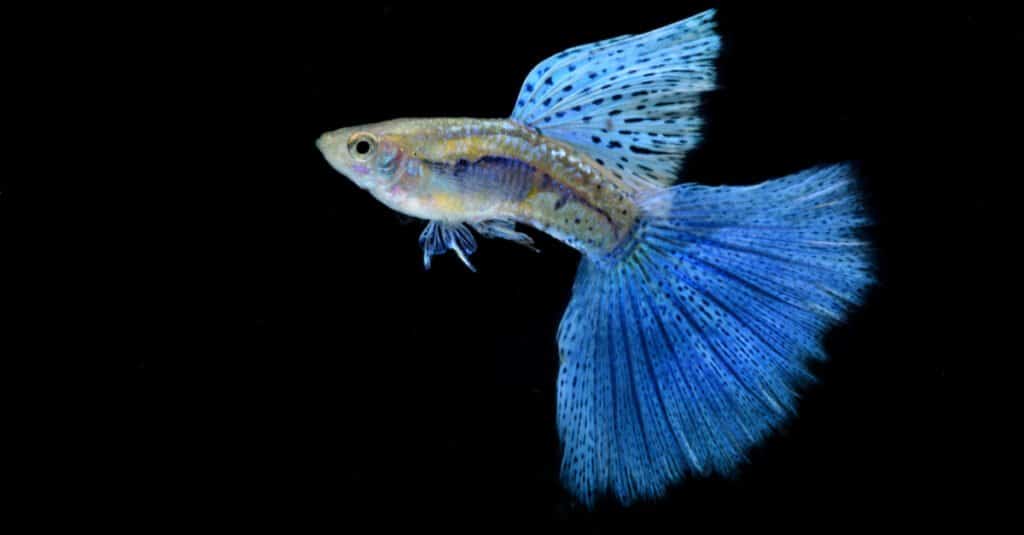

©Nantawat Chotsuwan/Shutterstock.com
Predators and Prey
Most of these fish grow to be about one inch in length, so it’s no surprise they have many predators. Wild guppies swim in schools of hundreds of fish, so a predator is able to grab several at one time.
What eats guppies?
Larger fish, such as the blue acara and pike cichlid are predators of guppy fish. Sea birds such as kingfishers are predators of this tiny tropical fish.
What do guppies eat?
These fish are omnivores. They eat algae, plant particles, and mosquito larvae.
They live in large schools and participate in foraging behavior. This means they search for food while in these large groups. So, when a supply of algae is found, more of them are able to share the nourishment.
The official conservation status of these fish is Least Concern.
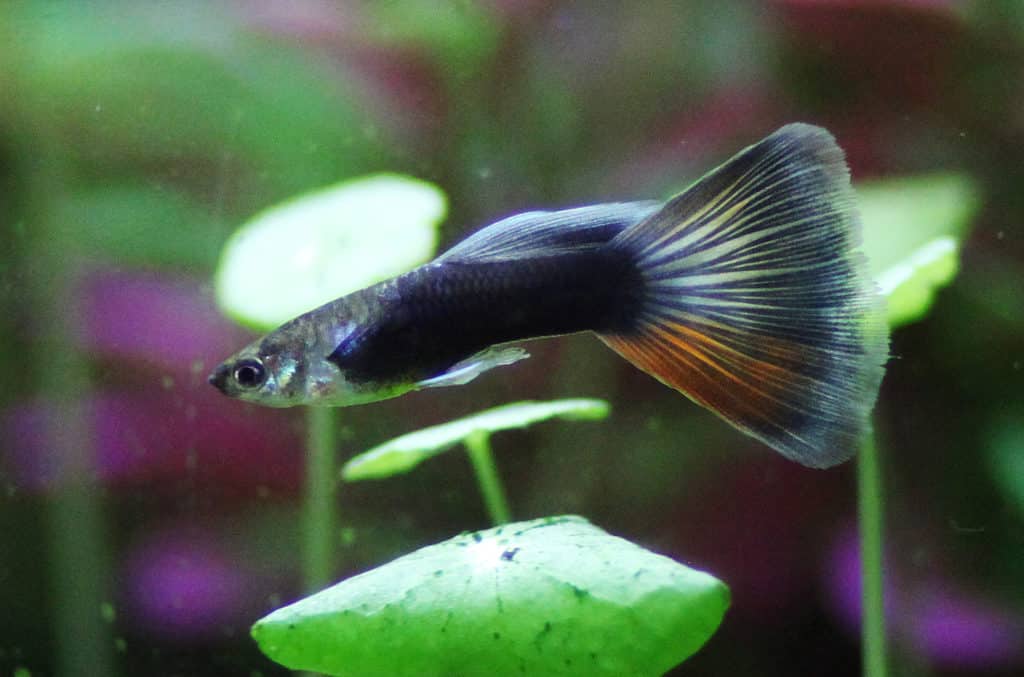

Guppy male moscow
Reproduction and Lifespan
Breeding takes place year-round for these fish. A female mates with multiple males. She is pregnant with fertilized eggs for about one month. They are different from many other types of fish in that they give live birth to their young. A female can have from 50 to 100 babies, also called fry. Due to this breeding activity, a female can have from 2 to 3 generations of fry each year. Fry begin living independently right at birth.
Males are sexually mature at seven weeks old, while females reach sexual maturity at 10 to 20 weeks old. Normally, these fish live to be two years old.
These fish are carriers of many parasites which is another factor affecting their lifespan. Gyrodactylus turnbulli is one of the most common parasites inhabiting the gills and fins of guppies. They spread these parasites to other guppies and even other species of fish.
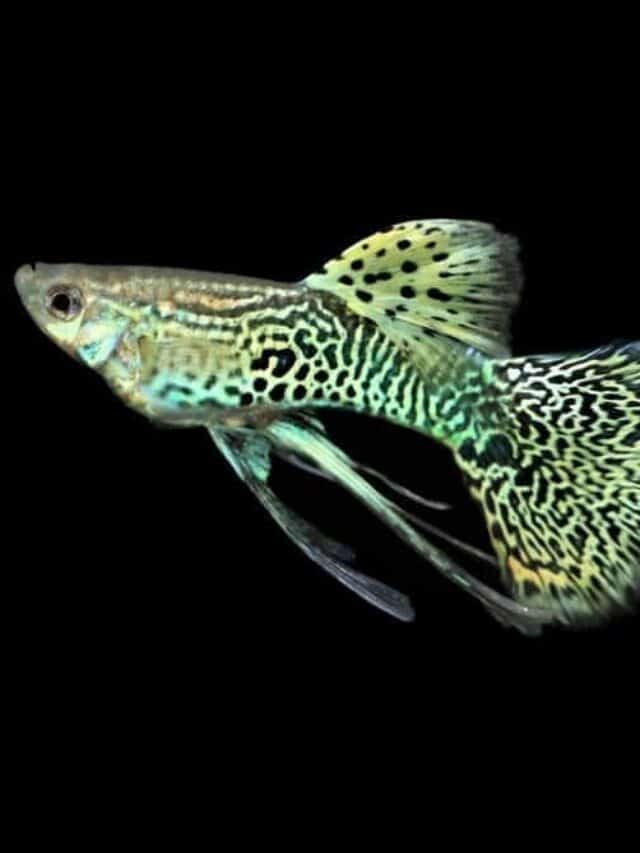

©Arunee Rodloy/Shutterstock.com
Fishing and Cooking
These are very small fish measuring no more than 2.4 inches in length. So, they are not targets of commercial fisheries.
Some recreational fishermen may try to capture rare specimens in small nets to sell to guppy hobbyists or pet shops.
Guppy fish are not cooked and eaten because of their size.
View all 170 animals that start with GGuppy FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are guppies?
The scientific name of the guppy is Poecilia reticulata. Guppies are small tropical fish known for their feathery tailfins and colorful scales. In fact, they are a favorite of people who keep aquariums due to their beautiful coloration and fins.
Where are guppies found?
Guppies are found everywhere around the world except for Antarctica. Brazil, Jamaica, Antigua, Barbados, Venezuela, and the U.S. Virgin Islands are all places where wild guppies are found. They can live in freshwater as well as brackish water.
Where do guppies come from?
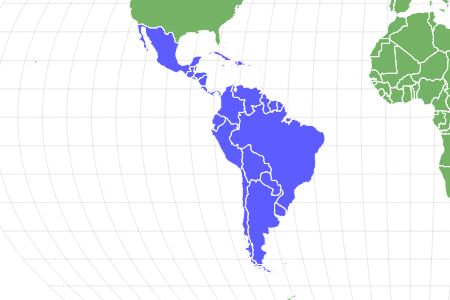
Guppies are native to the warm, tropical waters around South America.
How can you tell if a guppy is pregnant?
A pregnant guppy is hard to miss! She develops a large bulge in her underside. Also, a dark spot develops near her tailfin. This spot is called the ‘gravid spot.’ This spot develops because the female’s body is stretching in preparation for the live birth.
What do guppies eat?
Guppies eat algae, plant particles, and mosquito larvae.
Do guppies die easily?
Unfortunately, the answer is yes. Though the lifespan of these fish usually reaches two years, there are a lot of factors that can cause their death. For one, they can die when their own waste is not filtered out of the water. They can also die when the water in their habitat is too cold or too warm. A high level of ammonia in the water can also kill a guppy.
So, if you want to own a few guppies as pets, it’s important to set up and maintain the proper aquarium habitat to keep them happy and healthy!
What Kingdom do Guppies belong to?
Guppies belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Guppies belong to?
Guppies belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Guppies belong to?
Guppies belong to the class Actinopterygii.
What family do Guppies belong to?
Guppies belong to the family Poeciliidae.
What order do Guppies belong to?
Guppies belong to the order Cyprinodontiformes.
What genus do Guppies belong to?
Guppies belong to the genus Poecilia.
What type of covering do Guppies have?
Guppies are covered in Scales.
What are some predators of Guppies?
Predators of Guppies include birds and larger fish.
What are some distinguishing features of Guppies?
Guppies have brightly colored bodies and fins and give birth to live young.
What is the average clutch size of a Guppy?
Guppies typically lay 80 eggs.
What is an interesting fact about Guppies?
Guppies are also known as the Millionfish!
What is the scientific name for the Guppy?
The scientific name for the Guppy is Poecilia reticulata.
What is the lifespan of a Guppy?
Guppies can live for 2 years.
How many species of Guppy are there?
There are 276 species of Guppy.
What is the biggest threat to the Guppy?
The biggest threat to the Guppy is water pollution.
What is the optimal pH for a Guppy?
The optimal pH for a Guppy is between 5.0 and 7.0.
What is another name for the Guppy?
The Guppy is also called the rainbow fish or millionfish.
How are male guppies different from female guppies?
The differences between male and female guppies are their size, shape, color, tail length, dorsal fin shape anal fin shape, and presence of gravid spot.
What are the key differences between Endlers and guppies?
The key differences between Endlers and guppies include size, body shape, color, reproduction, origin, and gravid spot.
What are the key differences between mosquitofish and guppies?
The major differences between a mosquitofish and a guppy are origin, tail, size, reproduction, appearance, and lifespan.
What are the differences between a guppy and a betta fish?
The key differences between betta fish and guppy include size, reproduction, respiration, behavior, origin, and appearance.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Pet MD / Accessed December 16, 2020
- Wikipedia / Accessed December 16, 2020
- Guppy Expert / Accessed December 16, 2020