Stargazer Fish
Uranoscopus scaber
Uses an electric shock to stun its prey!
Advertisement
Stargazer Fish Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Trachiniformes
- Family
- Uranoscopidae
- Genus
- Uranoscopus
- Scientific Name
- Uranoscopus scaber
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Stargazer Fish Conservation Status
Stargazer Fish Facts
- Prey
- Crustaceans, crabs, small fish
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- Uses an electric shock to stun its prey!
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Diseases and parasites
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Eyes on top of its head
- Distinctive Feature
- These fish suck prey in like a vacuum or use a tentacle-like appendage
- Other Name(s)
- Monkfish
- Gestation Period
- 2 months
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Type
- Perciformes
- Common Name
- Stargazer fish
- Special Features
- An organ on their heads helps these fish deter predators and disable prey with shocks
- Number Of Species
- 4
Stargazer Fish Physical Characteristics
- Color
- White
- Green
- Dark Brown
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Lifespan
- Diseases and parasites
- Weight
- Eyes on top of its head
- Height
- These fish suck prey in like a vacuum or use a tentacle-like appendage
- Length
- Monkfish
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 2 months
- Age of Weaning
- Aggressive
- Venomous
- Yes
- Aggression
- High
View all of the Stargazer Fish images!

The Stargazer Fish, also inaccurately known as the Monkfish, has Northern and Southern varieties in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
This unusual fish features eyes positioned on top of its head and awaits prey on ocean bottoms. These fish are venomous and may also deliver minor electric shocks.
5 Fish Facts
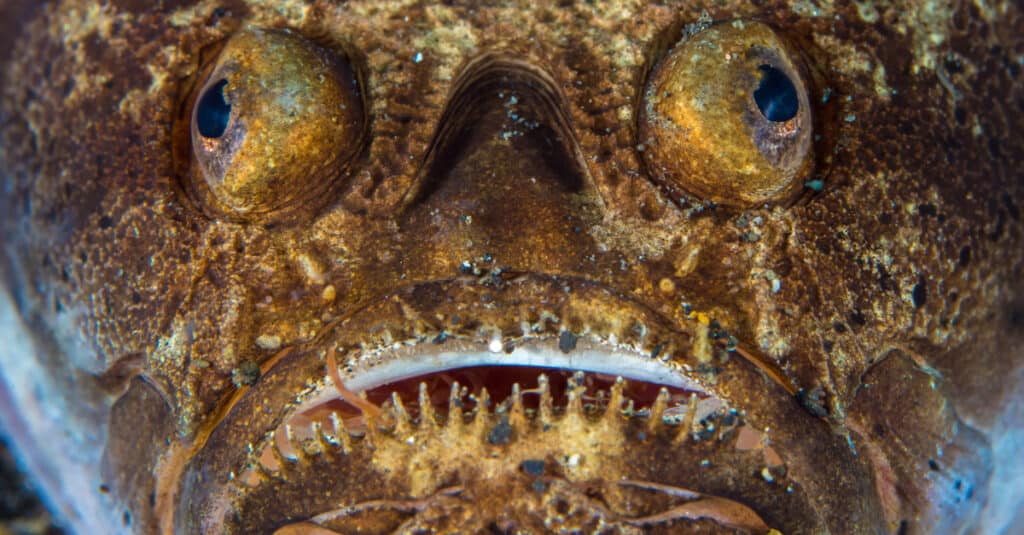

The Stargazer Fish possesses the ability to conceal itself within the ocean floor, patiently awaiting its prey.
©Mike Workman/Shutterstock.com
- Stargazer Fish can bury themselves in ocean bottoms to wait for prey
- These fish suck prey in like a vacuum or use a tentacle-like appendage
- Females lay their eggs on ocean bottoms, but the eggs rise to the surface before hatching
- The side fins can act as shovels to allow the fish to bury themselves in ocean bottoms
- An organ on their heads helps these fish deter predators and disable prey with shocks
Classification and Scientific Name
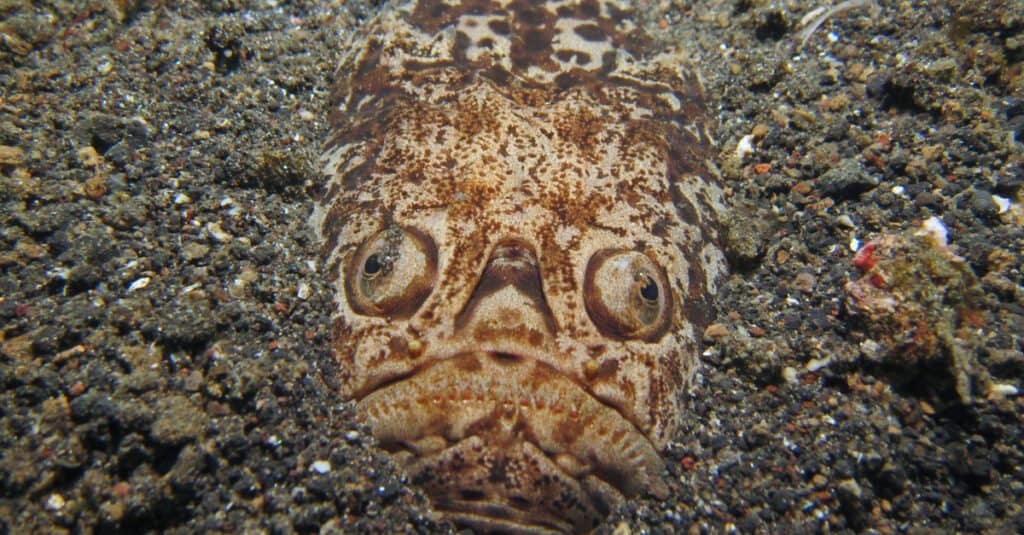

A stargazer preparing to ambush prey at the bottom of the ocean
©Luke Suen/Shutterstock.com
The scientific name for the most common type of Stargazer fish is the Uranoscopus scaber. Despite being a separate species, these fish are also called Monkfish in some regions. Stargazer Fish is part of the Trachiniformes order, including the Uranoscopidae family. There are 50 species of fish within this family, with Northern, Southern, and being among the most typical subspecies.
Evolution and Origins
This particular species is found in temperate marine waters stretching from southern Queensland to southwestern Western Australia, encompassing Tasmania as well. Northern stargazers have a diet consisting of small fish, crabs, and various crustaceans.
This remarkable and robust fish has fully adapted to a lifestyle of residing buried in sand, patiently preparing to ambush and engulf its prey. Remarkably, its eyes, gill slits, nostrils, and the majority of its mouth are positioned on the upper part of its body. Additionally, its pectoral fins possess exceptional digging and burying abilities, further enhancing its specialized adaptation.
They employ a hunting technique wherein they bury themselves in the sand, leaving only their eyes and mouth exposed. With this strategic positioning, they are able to scan for prey.
When a desirable meal comes within range, the stargazer utilizes its spacious mouth to generate a vacuum, swiftly drawing the prey in.
Species
Northern Stargazer
The Northern Stargazer (Astroscopus guttatus) has a range that stretches from North Carolina to New York, with a population of considerable size in the Chesapeake Bay area. Depending on ocean conditions, including temperatures, these fish sometimes appear in the Mediterranean. This type of Stargazer may shock its prey but won’t go out of its way to shock divers unless disturbed.
Common Stargazer
The Common Stargazer (Kathetostoma leave) is known as the Southern Stargazer. Like the Northern Stargazers that inhabit the Atlantic, these fish also live in ocean bottoms and are a biting risk to divers. These fish live primarily off the Australian coast, near Queensland and Tasmania.
Appearance
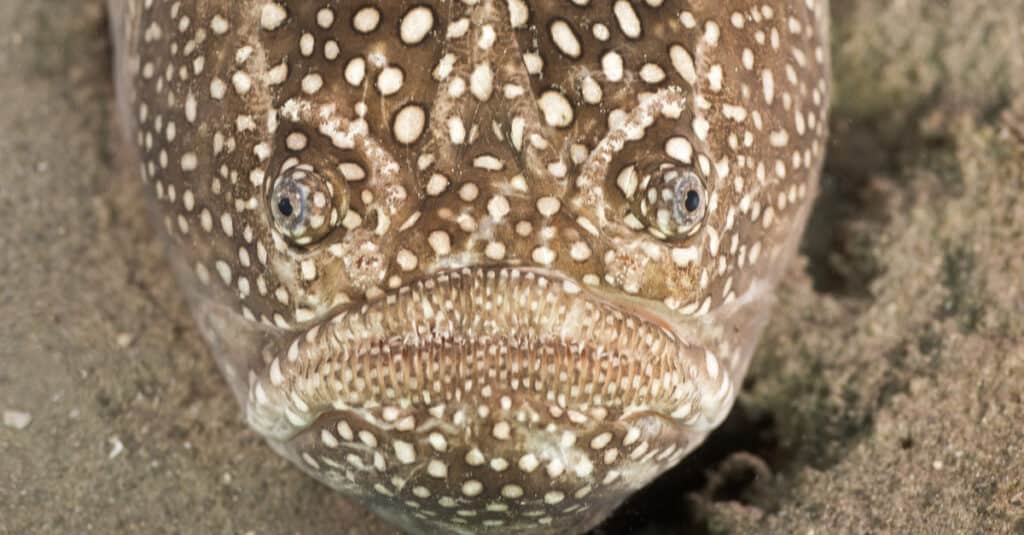

Stargazer Fish are dark brown with white speckles
©Peter Leahy/Shutterstock.com
Most Stargazer Fish measure 8-22 inches long. These fish are reasonably large, with some easily reaching 20 pounds. These are not common recreational fish but are capable of putting up a substantial fight if hooked.
Stargazers are a dark brown color allowing them to blend in when on the seafloor, and their scales also have white speckles. These fish’ bodies offer a stark contrast, with large, flat heads and tapered bodies.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
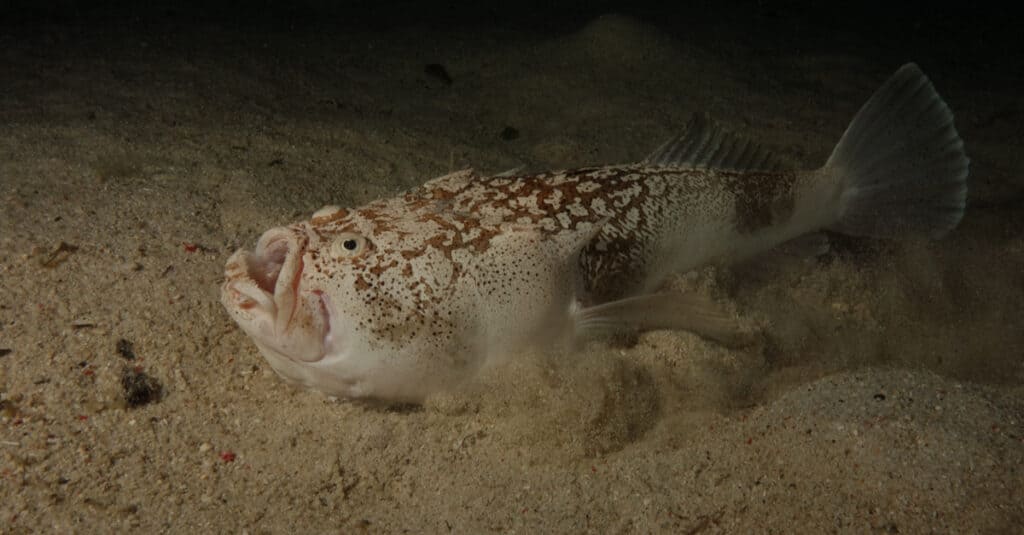

Stargazer Fish use their side fins like shovels to burrow in the sand
©Dirk van der Heide/Shutterstock.com
Stargazer Fish live in areas of the western Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean, and the Pacific Ocean off Australia‘s coast. These fish are the most populous in the Atlantic between North Carolina and New Jersey. The populations in the Pacific are at their highest south of Australia. Depths of about 120 feet are common for these fish.
These are saltwater fish usually considered a species of Least Concern, although the population size is unknown. However, most fish populations are stable, and some of these fish help make up aquarium populations. Researchers have not observed substantial population losses, with the average lifespan remaining stable.
Where to find: Stargazer Fish and How to Catch Them
The greatest chances of catching a Stargazer Fish for eating are in locations close to the shore. Lures resembling worms are likely to get this fish’s attention. However, live bait like shrimp or minnows will also do the job.
Predators and Prey
Stargazer Fish are carnivorous, hunting their prey from holes dug into the seafloor. These fish will suck them into their open mouths when the prey approaches. Some subspecies also have a type of tentacle that they use to grab their prey.
What eats Stargazer Fish?
These fish have few predators except humans. Because all these species are venomous and several have an organ that creates shocks, few predators are willing to take on one of these fish. Venom effects and electric shocks are primary reasons for people catching these fish to use caution.
What does Stargazer Fish eat?
The Stargazer Fish eats small crustaceans, crabs, and fish. This fish’s prey includes species small enough to easily get sucked into its mouth.
Reproduction and Lifespan
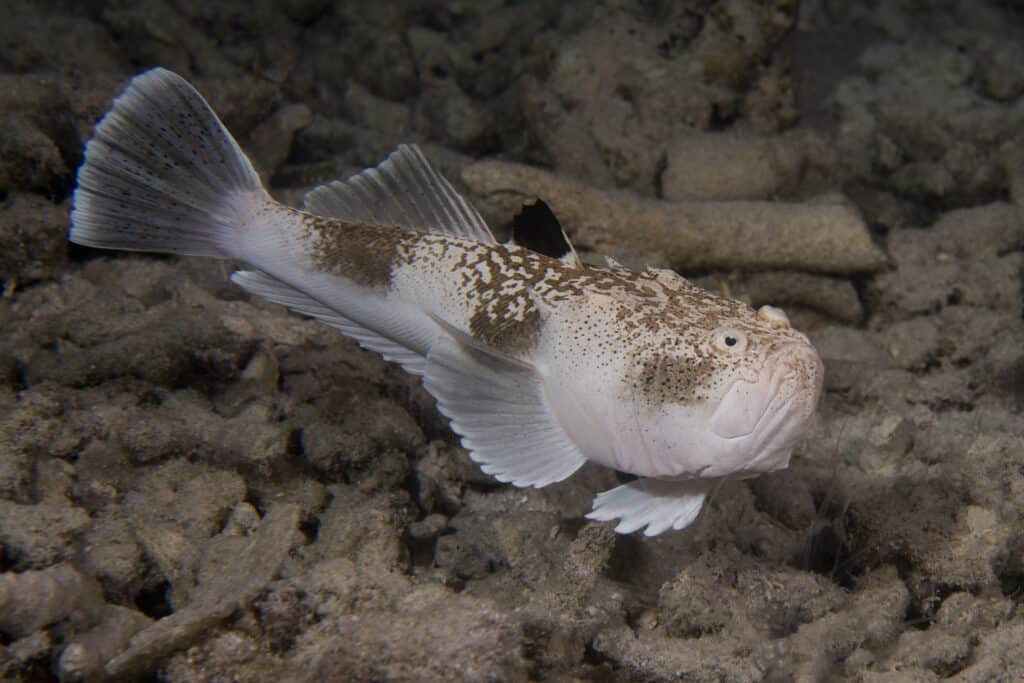

Stargazer Fish’s eyes are on top of their heads, so they appear to be staring up at the stars
©Andrea Izzotti/Shutterstock.com
Stargazer Fish usually spawn between May and June, laying eggs in the mud at the ocean bottom that later floats to the surface. These fish reach sexual maturity quickly, being ready to spawn four to eight months after hatching. Stargazers live five to six years, with females likely to have a slightly longer lifespan due to less aggressive behavior.
Fishing and Cooking
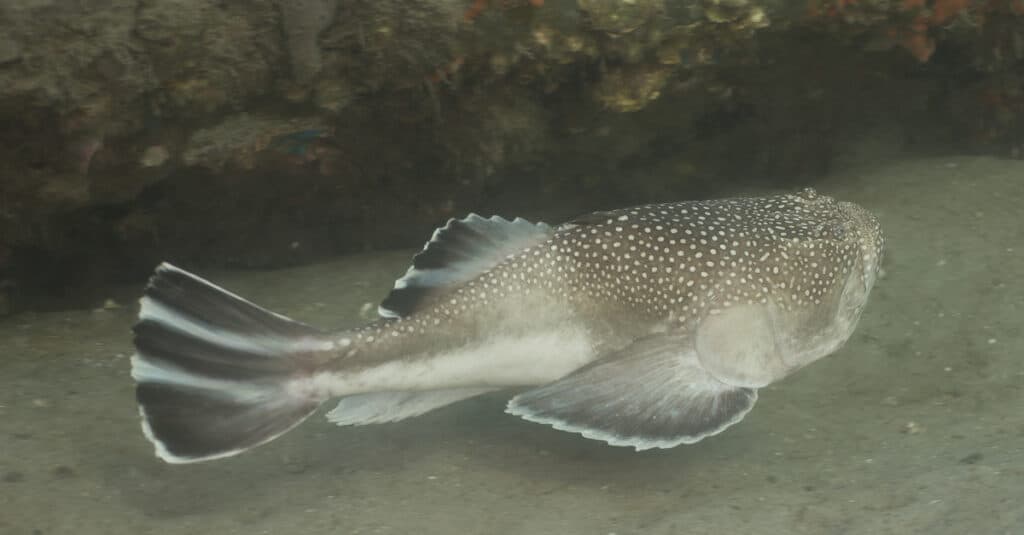

Northern Stargazer Fish can grow up to 22 inches long
©Peter Leahy/Shutterstock.com
Stargazer Fish is a little challenging to catch because of their stinger with venom effects and their ability to shock anglers who aren’t careful. Although these fish are more likely to be captured for aquarium exhibitions than for food, the fish offer an exciting challenge when an angler gets a bite.
Catching these fish is a somewhat rare event. For example, between 1991 and 1995, only five of these fish were caught off the New Jersey coast. The summer months are the best time to catch one of these fish.
Stargazers have a firm texture and a lobster-like taste. This fish has 93 calories and 17g of protein and is a popular casserole, stew, and soup ingredient. If you want an excellent choice for cooking and eating, Stargazer Fish is ideal.
View all 293 animals that start with SStargazer Fish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is a stargazer fish poisonous?
Stargazer Fish are a venomous species, with sharp spines injecting a similar amount of venom as a bite. The venom effects from these fish are unlikely to kill a person. However, the stings are as painful as bites, resulting in swelling. In rare cases, these stings can cause shock.
Is the stargazer fish good to eat?
Stargazer Fish can be good to eat because of a flavor similar to lobster. One of the things that enthusiasts enjoy about this fish is the range of recipes possible. These fish taste great in everything from basic soups and stews to ethnic dishes.
Is stargazer fish the same as monkfish?
Although some use the terms interchangeably, the Stargazer and the Monkfish are different species. In the Northern Hemisphere, the Monkfish refers to a fish of a different Genus.
Why are they called stargazer fish?
Stargazers get their name from the position of their eyes. The fish has eyes on top of its head, giving the impression of looking at the sky.
What do stargazer fish eat?
Stargazer Fish eat smaller crustaceans and crabs, along with small fish. The species these fish consume as prey are small enough to suck in.
Where do stargazer fish live?
Stargazer Fish live in the Atlantic off the United States coast from North Carolina to New Jersey and in the Mediterranean. Pacific ocean populations live off Australia’s southern coast. Some aquarium locations may also have these fish among their exhibits.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Nature World News / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Chesapeake Bay Program / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Florida Museum / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Australia Museum / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Britannica / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Sea-Ex / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Seafish Blog / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Guidesly / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Britannica / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Chesapeake Bay Program / Accessed April 18, 2022
- NJ Department of Environmental Protection / Accessed April 18, 2022
- Life of Fish (1970) Up to 20 pounds / Accessed April 18, 2022