Tire Track Eel
Mastacembelus armatus
They like to burrow into aquarium sand.
Advertisement
Tire Track Eel Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Synbranchiformes
- Family
- Mastacembelidae
- Genus
- Mastacembelus
- Scientific Name
- Mastacembelus armatus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Tire Track Eel Conservation Status
Tire Track Eel Facts
- Prey
- Worms, krill, plankton
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- They like to burrow into aquarium sand.
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss and being captured for the pet trade
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Design of splotches on its skin resembles tire tracks
- Other Name(s)
- Zig-zag eel, tire-track spiny eel, or marbled spiny eel
- Gestation Period
- 3 - 4 days
- Optimum PH Level
- 6.8 - 7.2
- Habitat
- Rivers, marshes, inland areas
- Diet for this Fish
- Carnivore
- Lifestyle
- Solitary
- Type
- Synbranchiformes
- Common Name
- Eel
- Number Of Species
- 93
View all of the Tire Track Eel images!
The tire track eel gets its name from the dark splotchy pattern on its long back that looks a lot like a tire tread.
This eel lives in rivers and marshes in Southeast Asia. It’s a popular pet for people who own large freshwater aquariums. This carnivorous eel can be as long as 2.4 feet full grown.
3 Tire Track Eel Facts
- Sneaky eels: These eels are fast swimmers that sometimes steal food out of the mouths of other fish in an aquarium.
- Spiny eel: This type of eel is also referred to as spiny eels because of the collection of spines near their dorsal fin.
- Poor vision: These eels are known for their poor vision. But, they have a sense of smell that helps them find food at night.
Classification and Scientific Name
The scientific name for these eels is Mastacembelus favus. They are also known as spiny eels. They are in the Actinopterygii class and the Mastacembelidae family. When broken down, the Latin word Mastacembelidae loosely translates to the phrase: Throws itself forward to bite.
There are 93 species in the Mastacembelidae family. Some of them include:
- Macrognathus siamensis
- Mastacembelus armatus
- Mastacembelus erythrotaenia
- Mastacembelus dayi
Tire Track Eel Types: The Different Species
These eels belong to the Mastacembelidae family containing 93 species of eel. These eels are also known as spiny eels.
Other spiny eels include:
- Fire eel: It’s found in the same area of the world as the tire track eel. At almost four feet long full-grown, these eels are much longer than tire track eels.
- Peacock eel: This is another spiny eel found in southeast Asia. It’s nocturnal like the tire track eel, but only reaches a length of one foot full grown.
- Half-banded eel: The half-banded eel is eight inches in length when fully grown. It has a pointed snout like a tire track eel with a pattern of dark bands curving over its back.
- Black-spotted eel: This spiny eel gets its name from the small black spots along the length of its body. Like tire track eels, they remain near the bottom of rivers so they can burrow into the sand.
Appearance
The first notable thing about these eels is the pattern of color on their skin. The lines of splotches bring to mind tire tread marks. Their skin is a combination of tan with dark brown markings.
These eels have pointed snouts so they can easily poke its head into narrow spaces. Their size ranges from 0.5 to 2.4 feet and they weigh from three to five pounds.
Tire track eels have spines that can deter larger fish from trying to attack. Also, this eel is able to slip into narrow spaces between rocks to escape predators. The dark color of these eels serves as camouflage in their habitat.
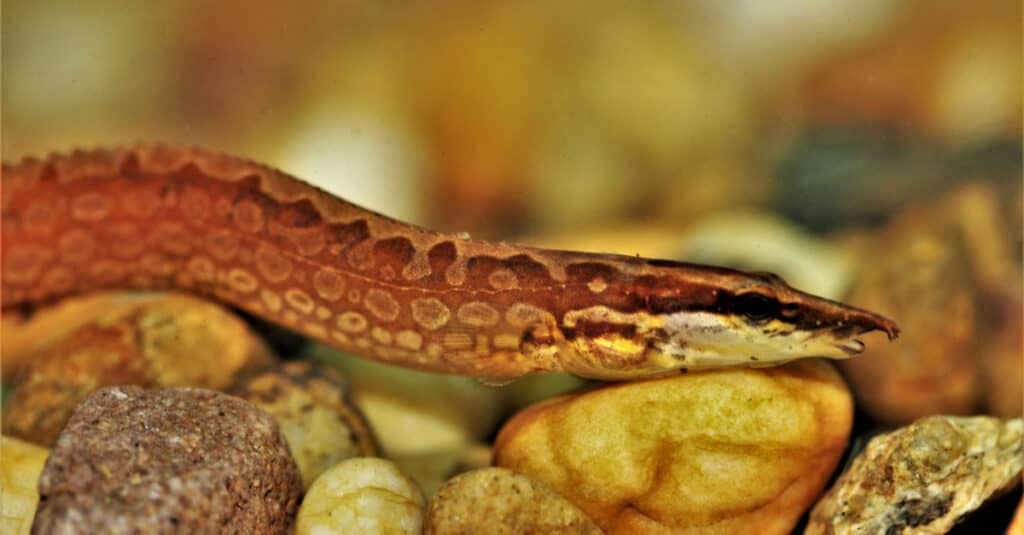

Tire Track Eels have pointed snouts that let them poke into tight crevasses.
©Arunee Rodloy/Shutterstock.com
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
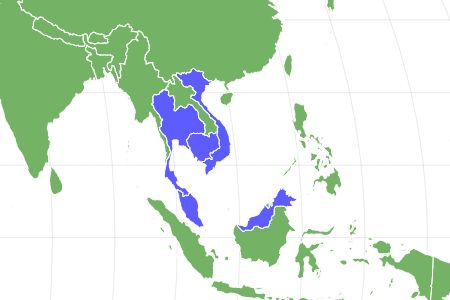
Tire track eels live in Southeast Asia specifically Cambodia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam. They live in inland freshwater streams, rivers, and marshes. This eel hides under the sand or rocky bottom of its habitat by day and comes out to hunt at night.
The total number of tire track eel is unknown, but its population is stable. It has a conservation listing of Least Concern.
Predators and Prey
Tire track eel eels are mainly carnivores though some eat vegetation. They use their strong jaws to latch onto their prey.
What eats tire track eels?
Sea birds such as bitterns and herons as well as larger eels eat these eels. Large fish like the Kelah may eat eel eggs.
Humans are predators of this eel as well. They’re captured in order to be sold as pets. They’re usually sold by fish stores at a price of around $25. Despite being sold as pets, these eels are categorized as Least Concern.
What do tire track eels eat?
These eels eat worms, krill, shrimp, and plankton.
Reproduction and Lifespan
In the wild, a male tire track eel chases a female for hours before mating. They may continually circle around each other during the breeding period. After mating, the female releases her eggs into clumps of floating vegetation. These eels can lay from 700 to 1000 eggs. She doesn’t provide any protection or care for the eggs. They hatch in three to four days.
Breeding these eels in captivity is very difficult. For one thing, in the wild, the beginning of flood season serves as the signal for these eels to breed. Secondly, the lack of space in a tank makes it challenging to mimic this eel’s natural habitat. Another issue with breeding is there’s not an easy way for an owner to determine the sex of this eel.
Tire track eel have a lifespan of eight to eighteen years.
Tire Track Eel in Fishing and Cooking
These eels are caught in order to be sold to people who own large aquariums. They are captured in traps placed in their habitat. Then, they’re shipped to various fish stores to sell to aquarium enthusiasts.
Many people like to keep this variety of eels in large home aquariums because of their attractive patterns. Also, though these eels like to hide, they can be interesting to watch.
Tire Track Eel FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are tire track eels found?
These eels are found in Southeast Asia. Specifically, they live in rivers, streams, and marshes in Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Cambodia.
Are tire track eels aggressive?
Yes and no. They can be aggressive toward other tire track eels. However, they aren’t known to be aggressive toward tank mates such as larger fish.
What fish are compatible with tire track eels?
Blood parrot cichlids, clown loaches, tinfoil barbs, and silver dollar fish are all compatible tank mates. All of these fish are available for a reasonable price at online fish stores.
As an important note on care, avoid any tank mates that are small enough for this eel to eat!
Habitat loss and being captured for the pet trade
They live in freshwater, but their proper care requires sea salt sprinkled into the tank. Put two teaspoons of sea salt in for every three gallons of tank water. This gives the aquarium a brackish quality. Containers of sea salt can be purchased for a low price.
How often do tire track eels eat?
They usually eat once per day, however some eat once every few days.
How big does a tire track eel get?
It can grow to a size of 2.4 feet.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Quality Marine / Accessed April 8, 2022
- Ecology Asia / Accessed April 8, 2022
- Fish Tank Advisor / Accessed April 8, 2022
- Nayturr / Accessed April 8, 2022
- Aqua Fish / Accessed April 8, 2022
- Wikipedia / Accessed April 8, 2022